UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 19th August 2024
The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 19th August 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

Migrants toil in Tamil Nadu’s Cauvery delta
Why in News?
Migrant workers from other parts of India are slowly making their presence felt in the agricultural fields in the Cauvery delta, in Tamil Nadu, often referred to as the granary of South India. The development comes amid there being a severe shortage of farmhands.
Cauvery River
- The Cauvery River is known as the 'Ganga of the South' and starts at an elevation of 1,341 meters in Karnataka.
- It stretches for 800 kilometers from its source to where it meets the sea.
- The river flows for 705 kilometers through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, descending the Eastern Ghats in a series of impressive waterfalls.
- Before reaching the Bay of Bengal, the river splits into many branches, creating a broad delta known as the 'garden of southern India.'
- The Cauvery basin covers Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and Puducherry, draining 81 thousand square kilometers.
- Bounded by the Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, and ridges separating it from other basins, the Cauvery basin is a significant geographical area.
- The basin is divided into three parts: the Western Ghats, the Mysore Plateau, and the Delta.
- The delta region is exceptionally fertile, with various soil types supporting agriculture.
- The river's water supply is relatively stable, making it valuable for irrigation and power generation.
- The Sivasamudram Falls, located near Sivasamudram, are a picturesque sight and a source of hydroelectric power.
- The Cauvery River is well-managed, with most of its irrigation and power potential already utilized.
- The river ultimately flows into the Bay of Bengal, with a significant portion of the basin used for agriculture.
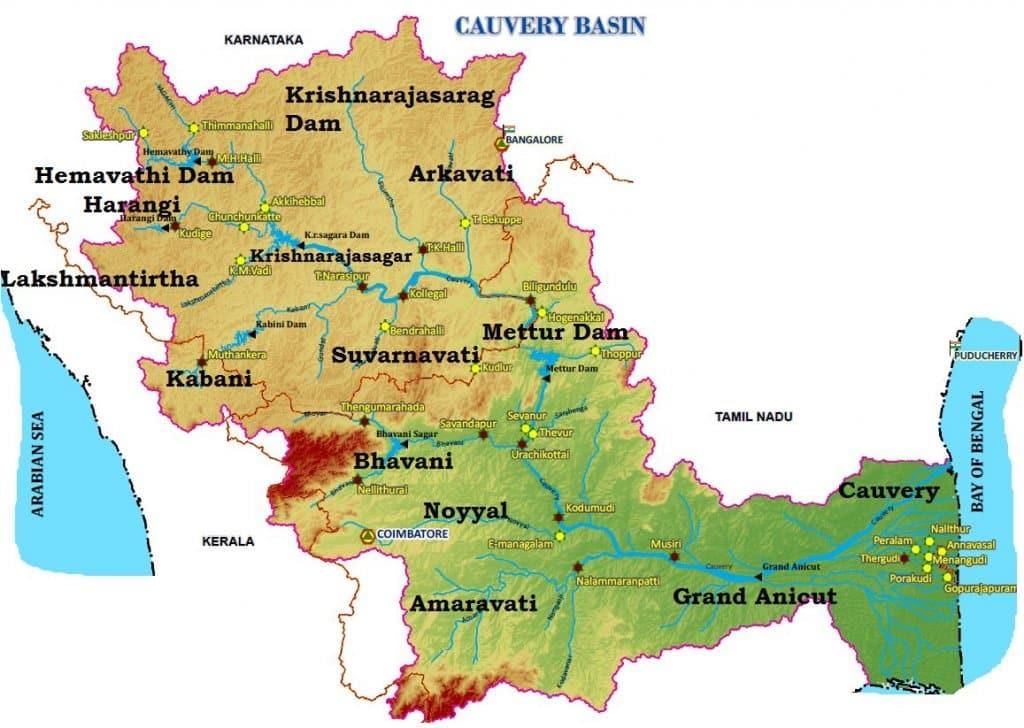
Tributaries of the Cauvery River
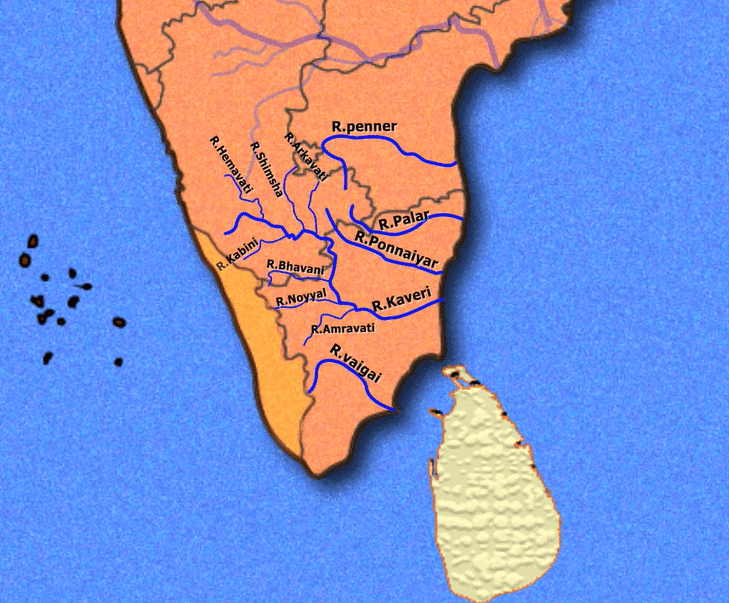
- Left Bank: the Harangi, the Hemavati, the Shimsha, and the Arkavati.
- Right Bank: Lakshmantirtha, the Kabbani, the Suvarnavati, the Bhavani, the Noyil, and the Amaravati joins from the right.
- The river descends from the South Karnataka Plateau to the Tamil Nadu Plains through the Sivasamudram waterfalls (101 m high).
- At Shivanasamudram, the river branches off into two parts and falls through a height of 91 m. in a series of falls and rapids.
- The falls at this point is utilized for power generation by the power station at Shivanasamudram.
- The two branches of the river join after the fall and flow through a wide gorge which is known as ‘Mekedatu’ (Goats leap) and continues its journey to form the boundary between Karnataka and the Tamil Nadu States for a distance of 64 km.
- At Hogennekkal Falls, it takes a Southerly direction and enters the Mettur Reservoir.
- A tributary called Bhavani joins Cauvery on the Right bank about 45 Kms below Mettur Reservoir. Thereafter it enters the plains of Tamil Nadu.
- Two more tributaries Noyil and Amaravathi join on the right bank and here the river widens with a sandy bed and flows as ‘Akhanda Cauvery’.
- Immediately after crossing Tiruchirapalli district, the river divides into two parts, the Northern branch being called ‘The Coleron’ and Southern branch remains as Cauvery and from here the Cauvery Delta begins.
- After flowing for about 16 Kms, the two branches join again to form ‘Srirangam Island’.
- On the Cauvery branch lies the “Grand Anicut” said to have been constructed by a Chola King in 1st Century A.D.
- Below the Grand Anicut, the Cauvery branch splits into two, Cauvery and Vennar.
HEMAVATI
- It is a significant branch of the Kaveri River.
- Originating from the Western Ghats at an elevation of around 1219m near Ballalarayana Durga in the Chikmagalur District of Karnataka, it flows through Chikkamagalooru, Hassan District, and Mysore district before meeting the Kaveri near Krishnarajasagara.
- Approximately 245 km in length, a large reservoir has been constructed on the river at Gorur in the Hassan district.
SHIMSHA
- It begins at a height of 914 meters from the Devarayanadurga hills in the Tumkur District of Karnataka.
- One of the streams that flow into the river Kaveri.
- The town of Maddur is situated along this river.
- Markonahalli Dam is constructed on the Shimsha River in the Kunigal Taluk of Tumkur district.
- Shimsha features a waterfall at Shimshapura in Malavalli Taluk.
- The Shimsha Hydro Electric Project is located in this area.
ARKAVATHY RIVER
- This 161 km long river originates at Nandi Hills of Chikkaballapur district of Karnataka
- It is a tributary of the Kaveri River, which it joins at Kanakapura, called Sangama in Kannada, after flowing through Kolar District and Bangalore Rural district
- The river drains into the Chikkarayappanahalli Lake near Kanivenarayanapura
- The picturesque Chunchi waterfall on the Arkavathi River at Sangama near Kanakapura attracts numerous tourists
- The water is taken from two reservoirs built on the river, the Hesaraghatta (or Hesseraggatta), and the Tippagondanahalli Reservoir (or T G Halli).
LAKSHMANA TIRRTHA
- It originates from the Irupu Falls (also known as Iruppu Falls), situated in the Brahmagiri Range within the Kodagu district of Karnataka. This area borders the Wayanad district of Kerala.
- Subsequently, it flows towards the east and merges with the Kaveri River at the Krishna Raja Sagara Lake.
- Its primary tributary is Ramathirtha.
KABINI
- Kabini, also known as Kabani and Kapila, starts from Pakramthalam hills in Wayanad District of Kerala where the Panamaram River and Mananthavady River meet.
- The Kabini reservoir's backwaters teem with wildlife, especially during summer when the water level drops, creating lush grassy meadows.
- About two kilometers downstream from the Panamaram river junction, Kabini gives rise to Kuruva Island, a 520-acre expanse featuring diverse plants and animals.
SUVARNAVATHY
- River Origin: The river starts from the Nasrur Ghat Range in Karnataka and stretches for 88 kilometers.
- Tributary Information: It is a river that flows into the Kaveri River.
- Catchment Area: This river has a total catchment area of approximately 1787 square kilometers.
- Suvarnavathy Dam: Located close to Attigulipura village in Chamarajanagar Taluk, the Suvarnavathy dam crosses the Suvarnavathy River, situated about 3 kilometers from the Chikkahole Reservoir Project.
NOYYAL RIVER
- Its original name was Kanchinadi but changed later to the name of the place where it drains into the Kaveri River
- It rises from the Vellingiri hills in the Western Ghats in Tamil Nadu and drains into the Kaveri River
- Noyyal joins with river Cauvery at Kodumudi in Erode District. The place is also called Noyyal.
- The 173 km long tributary of the Kaveri River filled 32 tanks
- These interconnecting tanks held the water flowing from the Noyyal.
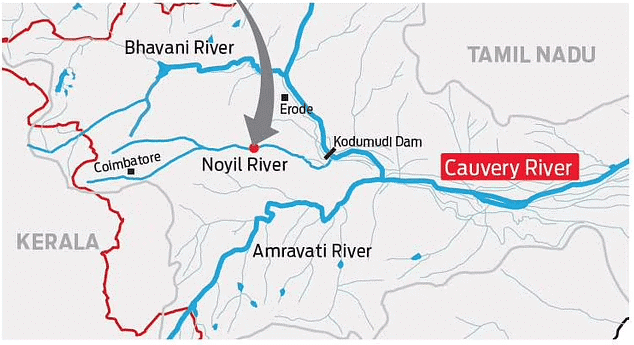
AMARAVATHI
- Also known as Pournami, this 175km long river starts at the border of Kerala and Tamil Nadu, near the bottom of the Manjampatti Valley, nestled between the Annamalai Hills and the Palni Hills in the Indira Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park.
- It flows in a northward direction, passing through the Amaravathi Reservoir and Amaravathi Dam at Amaravathinagar.
- This river supports the farming activities in the Erode District.
- The Amaravathi River and its surrounding area, particularly near Karur, are extensively utilized for industrial water usage and waste disposal. Unfortunately, the region is heavily contaminated due to the presence of a significant number of textile dyeing and bleaching facilities.
Distributaries of the Cauvery River
Kollidam River ( also called Coleroon River)
- The Kollidam river is found in the southeastern part of India.
- It is the upper branch of the Kaveri river as it moves through the delta of Thanjavur.
- Starting at the island of Srirangam, it diverges from the main stream of the Kaveri river and flows eastwards into the Bay of Bengal.
- The distribution system in Kollidam is located at Lower Anaicut, an island within the river.
- The town of Chidambaram is situated on the banks of the river.
Vennar or Vennaaru River
- The Vennar River, also known as Vennaaru, is a river that branches off from the Kaveri River in the Kaveri delta.
- It flows through Thanjavur, Tiruvarur, and Nagapattinam districts in Tamil Nadu.
- Originating at the Grand Anaicut on the eastern side of Srirangam Island, the river moves towards the east after separating from the Kaveri.
- Northwest of Thennankudi, the Vennar River divides into northern and southern branches at the Thenperambur dam. The northern branch becomes the Vettar River, while the southern one continues eastward as the Vennar.
- Further northwest of Needamangalam, the river undergoes another split, forming three branches. The Pamaniyar and Koraiyar Rivers stem from the two southern branches, while the Vennar persists through the northern branch.
Arasalar River
- The river Arasalar flows through Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
- It is a branch of the Kaveri river that splits into five rivers in Thanjavur district.
- Starting from Thiruvaiyaru in Thanjavur, it eventually meets the Bay of Bengal at Karaikal.
- Karaikal used to be a river port until the 19th century, facilitating trade activities.
- The river is contaminated by nitrate and chromium, mainly from sewage and industries.
Floods in Cauvery Basin
- The Cauvery basin is fan shaped in Karnataka and leaf shaped in Tamil Nadu. The run-off does not drain off quickly because of its shape and therefore no fast raising floods occur in the basin.
Projects on Cauvery River
- During the pre-planning phase, several projects were finished in this region, such as the construction of Krishnarajasagar in Karnataka, the Mettur dam, and the Cauvery delta system in Tamil Nadu.
- Important projects completed during this period include Lower Bhavani, Hemavati, Harangi, and Kabini.
Industry in Cauvery Basin
- The city of Bangalore is located just outside this area.
- Key industries in this region involve the cotton textile sector in Coimbatore and Mysore, cement plants in Coimbatore and Trichinapally, and businesses centered on minerals and metals.
- The steel mill in Salem and numerous engineering enterprises in Coimbatore and Trichinapally are also present in this region.
Cauvery River Disputes
- Historically, Tamil Nadu used around 602 TMC of the river's total water in a year.
- By the early 1900s, only about 138 TMC was left for Karnataka.
- In 1924, Tamil Nadu constructed the Mettur dam on the Cauvery river.
- After that, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu made a deal that lasted for 50 years.
- Under this agreement, Tamil Nadu could increase its farming area by 11 lakh acres from 16 lakh acres.
- Karnataka could also expand its irrigation land from 3 lakh acres to 10 lakh acres.
- The Cauvery River mainly met the needs of Tamil Nadu farmers.
- When the 50 years ended in 1974, the agreement expired.
- Karnataka then argued that the pact limited its ability to grow agriculture in the Cauvery basin.
- To compensate, Karnataka tried to boost farming activities in the basin and began constructing reservoirs.
- This led to the emergence of the Cauvery river water sharing conflict.
- Now, it's a significant dispute involving Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Puducherry, and Kerala.
- Tribunal - In response to Tamil Nadu's request, the Union government established the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT) in 1990.
- The dispute was settled by the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT) in 2007.
- Both Tamil Nadu and Karnataka contested the tribunal's decision.
- The court then postponed its judgment in September 2017.
The document The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 19th August 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 19th August 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What are the working conditions like for migrants in Tamil Nadu's Cauvery delta? |  |
Ans. Migrants in Tamil Nadu's Cauvery delta often toil in difficult working conditions, facing challenges such as long hours, low wages, and lack of proper facilities.
| 2. How significant is the migrant population in the Cauvery delta region? |  |
Ans. The migrant population in the Cauvery delta region plays a crucial role in various industries such as agriculture, construction, and manufacturing, contributing significantly to the local economy.
| 3. What are some of the reasons that drive migrants to work in the Cauvery delta? |  |
Ans. Migrants are often driven to work in the Cauvery delta region due to factors such as lack of employment opportunities in their home regions, poverty, and the promise of better wages in Tamil Nadu.
| 4. How do migrant workers in the Cauvery delta region cope with challenges such as language barriers and cultural differences? |  |
Ans. Migrant workers in the Cauvery delta region often rely on support networks within their communities, as well as seek assistance from local organizations and NGOs that provide services to help them overcome language barriers and cultural differences.
| 5. What are some of the initiatives taken to improve the working conditions and well-being of migrants in Tamil Nadu's Cauvery delta? |  |
Ans. Various initiatives have been launched to improve the working conditions and well-being of migrants in the Cauvery delta region, including providing access to healthcare, education, and legal support, as well as advocating for their rights and welfare.
Related Searches
















