The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 8th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

India, Pakistan and modifying the Indus Waters Treaty
Why in News?
India’s move to serve formal notice on August 30, 2024, in line with Article XII (3) of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), underlines its concerns about meeting ever-increasing domestic water needs in a sustainable manner. The notice is to review and modify the treaty to address India’s specific concerns relating to altered population demographics, along with agricultural and other uses apart from the need to accelerate the development of clean energy to meet India’s emission rights. India has also mentioned in the notice that the impact of persistent cross-border terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir is impeding smooth operations of the Treaty, undermining the full utilisation of its rights in the Indus.
About:
- The Indus Waters Treaty was signed on September 19, 1960, between India and Pakistan.
- This treaty was facilitated by the World Bank.
- It provides a way for both countries to work together and share information.
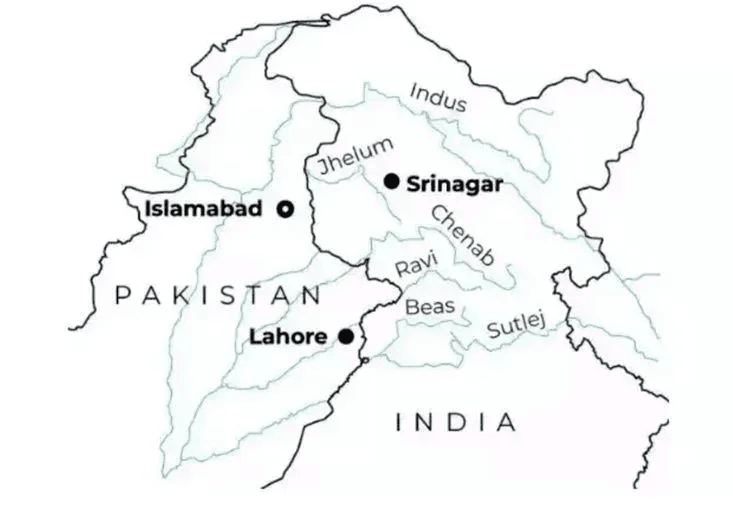
- The focus of the treaty is on the use of water from the Indus Riverand its five tributaries:
- Sutlej
- Beas
- Ravi
- Jhelum
- Chenab
Key Provisions:
Water Sharing:
- It outlines how water from the six rivers of the Indus River System will be divided between India and Pakistan.
- The three rivers in the west—Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum—are allocated to Pakistan for unlimited use. India has some rights for specific non-consumptive purposes, as well as for agriculture and domestic needs.
- The three rivers in the east—Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej—are assigned to India for unrestricted usage.
- This arrangement means that about 80% of the total water supply is available to Pakistan, while India has access to the remaining 20%.
Permanent Indus Commission:
- According to the Indus Waters Treaty, both nations are required to establish a Permanent Indus Commission.
- This commission is expected to meet every year.
Dispute Resolution Mechanism:
- The IWT includes a three-step process for settling disputes.
- Any issues from either side can first be addressed at the Permanent Commission.
- If unresolved, these issues can be escalated to the inter-government level.
- Differences regarding water-sharing that cannot be resolved can be taken to a Neutral Expert appointed by the World Bank.
- Decisions made by the Neutral Expert can be appealed to a Court of Arbitration set up by the World Bank.
Various Projects to be Inspected Under IWT:
- Pakal Dul and Lower Kalnai:
- The Pakal Dul Hydro Electric Project is built on the Marusudar River, which is a tributary of the Chenab River.
- Lower Kalnai is also developed on the Chenab.
- Kishanganga Hydroelectric Project:
- This project is a run-of-the-river type located in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Pakistan raised concerns that this project would impact the flow of the Kishanganga River, which is known as Neelum River in Pakistan.
- In 2013, the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague ruled that India could divert all the water under certain conditions.
- Ratle Hydroelectric Project:
- This is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power station located on the Chenab River in Jammu and Kashmir.
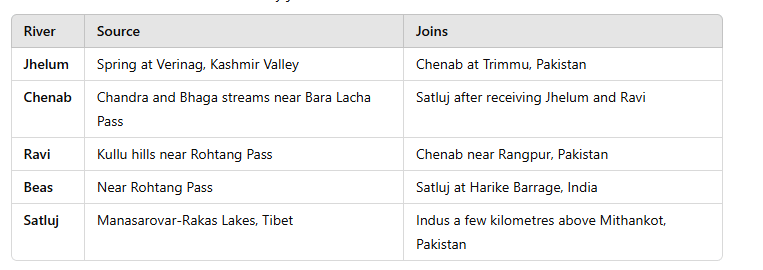
Indus River and Its Tributaries
- Source: The Indus River, known as Sengge Chu or "Lion River" in Tibetan, is an important river in South Asia. It starts in Tibet close to Mansarovar Lake in the Trans-Himalaya region.
- The river travels through Tibet, India, and Pakistan, and around 200 million people live within its drainage basin area.
- Course and Major Tributaries: The Indus enters India in Ladakh and continues through Jammu and Kashmir before reaching the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan.
- Left-bank tributariesof the Indus include:
- Zaskar
- Suru
- Soan
- Jhelum
- Chenab
- Ravi
- Beas
- Satluj
- Panjnad
- Right-bank tributariesinclude:
- Shyok
- Gilgit
- Hunza
- Swat
- Kunnar
- Kurram
- Gomal
- Kabul
- The Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea near the city of Karachi in southern Pakistan.
Way Forward
- Focus on Technical Dispute Resolution: Both parties should aim to use the existing treaty's framework to solve technical disagreements.
- Transparency and Data Sharing: Both countries can exchange water data to tackle shared issues.
- Joint Basin Management: Challenges from climate change and population growth in the Indus basin highlight the need for cooperative efforts in managing water, controlling floods, and ensuring sustainable use.
- Political Commitment and Dialogue: Achieving lasting solutions needs both governments to commit to prioritizing conversation and teamwork instead of conflict.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
















