The Human Brain | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction of the Human Brain |

|
| (i) Forebrain |

|
| (ii) Midbrain |

|
| (iii) Hindbrain |

|
Introduction of the Human Brain
The brain is the body's main organ for processing information, acting as the central 'command and control system.' It manages a wide range of functions, including:
- Voluntary Movements: The brain controls all voluntary actions, such as walking, talking, and any other activities we choose to do.
- Balance: It helps maintain the body's balance, ensuring we can stand and move steadily.
- Vital Organs: The brain regulates the functions of essential organs like the lungs, heart, and kidneys, which work involuntarily.
- Thermoregulation: It controls body temperature, keeping it within a safe and stable range.
- Hunger and Thirst: The brain monitors and regulates our feelings of hunger and thirst, prompting us to eat and drink when necessary.
- Circadian Rhythms: It governs the body’s natural 24-hour cycles, affecting sleep and wakefulness.
- Endocrine Glands: The brain manages the activities of several endocrine glands, which release hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
- Human Behaviour: It influences and controls human behaviour, including emotions and social interactions.
- Processing Senses: The brain is responsible for processing sensory information such as vision, hearing, and speech.
- Memory and Intelligence: It plays a crucial role in memory storage and recall, as well as in reasoning and problem-solving.
- Emotions and Thoughts: The brain is where emotions and thoughts are generated and processed, influencing our reactions and decisions.
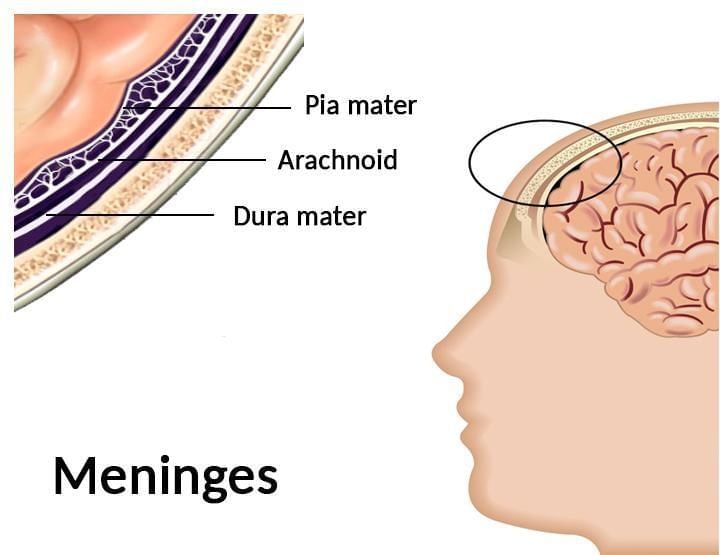
Protection of the Brain
The human brain is well-protected by the skull, which acts as a hard case to shield it from injury. Inside the skull, the brain is further protected by the cranial meninges, a three-layered covering:
- Dura Mater: The outer layer, which is tough and durable.
- Arachnoid: The thin middle layer, which helps cushion the brain.
- Pia Mater: The inner layer, which is in direct contact with the brain tissue and provides additional protection.
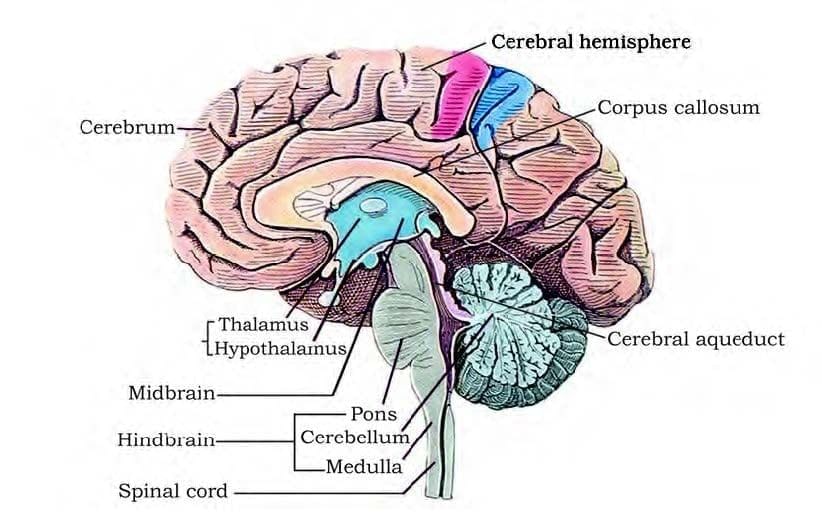
Parts of the Brain
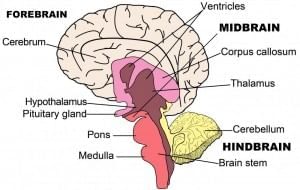
The brain can be divided into three main parts:
(i) Forebrain
(ii) Midbrain
(iii) Hindbrain
(i) Forebrain
The forebrain is made up of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
Cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain, divided into two halves called the left and right cerebral hemispheres by a deep cleft.
- These hemispheres are connected by a bundle of nerve fibres known as the corpus callosum.
- The outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres is called the cerebral cortex, which is known for its prominent folds and greyish appearance; hence, it is referred to as the grey matter.
- The grey matter contains a high concentration of neuron cell bodies, which give it its colour.
- The cerebral cortex is crucial for various functions:
- Motor Areas: Control voluntary movements.
- Sensory Areas: Process sensory information.
- Association Areas: Responsible for complex functions like memory, communication, and intersensory associations.
- Beneath the cerebral cortex lies the white matter, which consists of nerve fibres covered with a myelin sheath, giving it an opaque white appearance.
- The cerebrum encases the thalamus, a key coordinating centre for sensory and motor signals.
Thalamus
- The thalamus is a crucial part of the forebrain, acting as a major hub for coordinating sensory and motor signals.
- It plays a vital role in processing and relaying information from the senses to the appropriate areas of the brain for further processing.
- By doing so, the thalamus helps ensure that the brain receives and responds to sensory information efficiently, making it an essential component of the brain's information processing system.
Hypothalamus
- The hypothalamus is a small but vital part of the brain located below the thalamus.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's internal balance (homeostasis) by regulating various essential functions, including:
- Body Temperature: The hypothalamus helps control and regulate body temperature, ensuring it stays within a narrow, healthy range.
- Hunger and Thirst: It monitors the body's energy needs and fluid levels, triggering feelings of hunger and thirst when necessary.
- Hormone Production: The hypothalamus contains specialised cells that produce hormones, known as hypothalamic hormones.
- These hormones play a key role in regulating various bodily functions, including the activity of the pituitary gland, which in turn influences many other endocrine glands throughout the body.
Limbic System
- The inner parts of the cerebral hemispheres, along with a group of associated deep structures such as the amygdala and hippocampus, form the limbic lobe or limbic system.
- The limbic system, together with the hypothalamus, plays a crucial role in regulating various important functions, including:
- Sexual Behaviour: It is involved in regulating sexual behaviour and reproductive functions.
- Emotional Reactions: The limbic system is responsible for the expression of emotional reactions such as excitement, pleasure, rage, and fear.
- Motivation: It plays a key role in motivation, influencing behaviour and emotional responses.
(ii) Midbrain
- The midbrain is situated between the forebrain (thalamus and hypothalamus) and the hindbrain (pons).
- A canal called the cerebral aqueduct runs through the midbrain.
- The dorsal (upper) part of the midbrain consists of four round swellings known as the corpora quadrigemina, which are involved in processing visual and auditory information.
(iii) Hindbrain
The hindbrain is made up of the pons, cerebellum, and medulla (also called the medulla oblongata).
- Pons: The pons consists of fibre tracts that interconnect different regions of the brain, facilitating communication between various parts.
- Cerebellum: The cerebellum has a highly convoluted surface, which allows for additional space for a greater number of neurons. This structure is important for coordinating voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
- Medulla: The medulla is an extension of the spinal cord and contains vital centres that control essential functions such as respiration, cardiovascular reflexes, and gastric secretions.
Brain Stem
- The brain stem is composed of three major regions: the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- It serves as a critical connection between the brain and spinal cord, facilitating communication and coordination between these two essential parts of the central nervous system.
|
169 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on The Human Brain - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the average weight of the human brain? |  |
| 2. How many neurons are present in the human brain? |  |
| 3. Can the human brain regenerate or grow new neurons? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the frontal lobe in the human brain? |  |
| 5. Can the human brain multitask effectively? |  |
















