The Root: Types, Regions & Modifications | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Roots? |

|
| Types of Roots |

|
| Regions of Roots |

|
| Modifications of Roots (Only in NEET) |

|
What are Roots?
Roots are the vital underground structures that are present in all vascular plants, typically found underground, that serves several essential functions.
Functions of Root System:
- Absorption of Water and Minerals: Roots are responsible for absorbing water and essential minerals from the soil, which are vital for the growth and development of the plant.
- Anchorage: Roots provide a strong anchorage to the plant parts, holding them firmly in the ground and preventing them from being uprooted.
- Storage of Reserve Food: Roots store reserve food material, which can be used by the plant during times of scarcity or for future growth.
- Synthesis of Plant Growth Regulators: Roots synthesize plant growth regulators, which are hormones that regulate various physiological processes in the plant, promoting its overall growth and development.
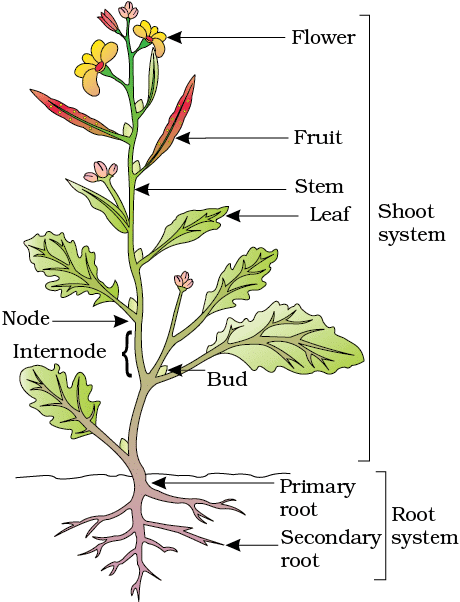
In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral roots of several orders that are referred to as secondary, tertiary, etc. roots.
Types of Roots
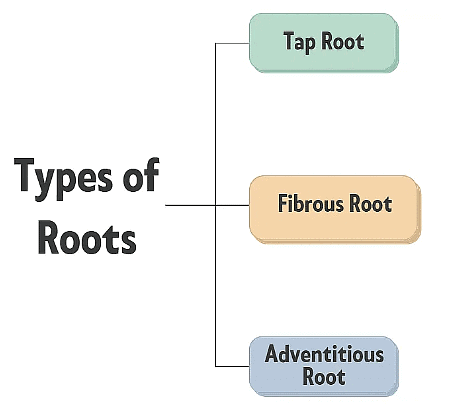
(a) Tap Root System:
In dicotyledonous plants, the root system consists of a main tap root with smaller lateral roots branching out from it. This type of root system is called the tap root system, and it is commonly seen in plants like mustard.
(b) Fibrous Root System:
In monocotyledonous plants, the primary root is short-lived and is replaced by a large number of roots that originate from the base of the stem. This type of root system is called the fibrous root system, and it is commonly seen in plants like wheat.
(c) Adventitious Roots:
In some plants, roots can arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle. These roots are called adventitious roots. Examples of plants with adventitious roots include grass, Monstera, and the banyan tree.
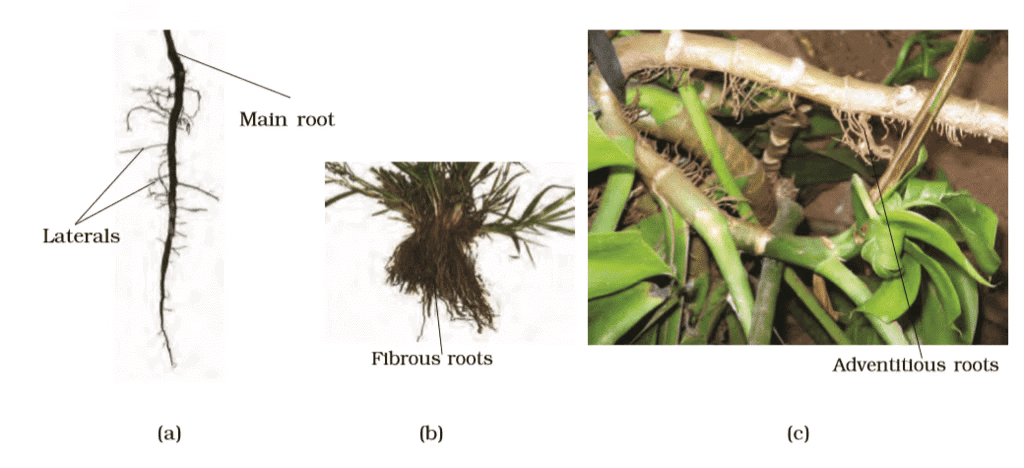 Different types of roots : (a) Tap (b) Fibrous (c) Adventitious
Different types of roots : (a) Tap (b) Fibrous (c) Adventitious
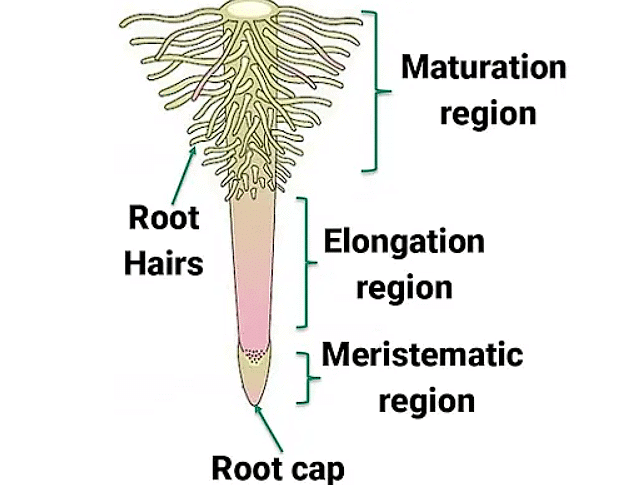
Regions of Roots
The regions of a root refer to the different zones or sections along the length of a root that exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of cell activity, differentiation, and function. These regions include:
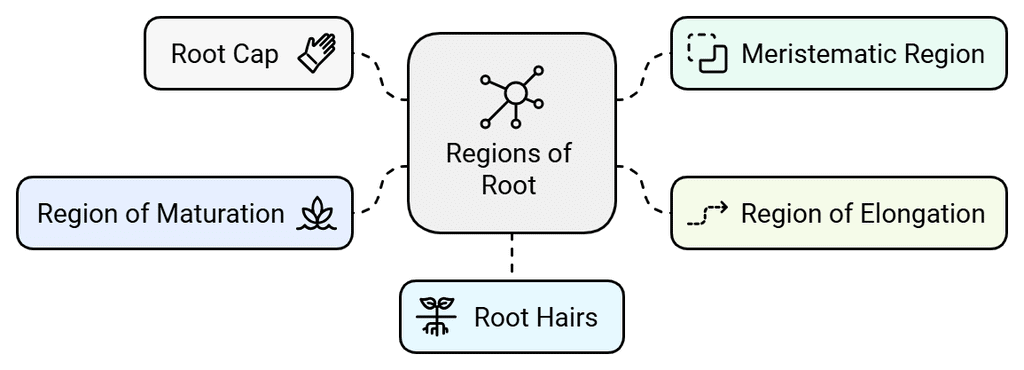 Regions of Root
Regions of Root
- Root Cap: The root cap is a thimble-like structure that covers the apex of the root. It protects the delicate tip of the root as it grows through the soil.
- Meristematic Region: Located a few millimeters above the root cap, the meristematic region is where active cell division takes place. The cells in this region are small, thin-walled, and have dense protoplasm. They continuously divide, contributing to the growth of the root.
- Region of Elongation: The cells proximal to the meristematic region undergo rapid elongation and enlargement, resulting in the elongation of the root in length. This region is called the region of elongation, and it is responsible for the primary growth of the root.
- Region of Maturation: As the cells of the elongation zone continue to differentiate and mature, they form the region of maturation, which is proximal to the region of elongation. In this region, the cells differentiate into different types of root tissues and structures.
- Root Hairs: Some of the epidermal cells in the region of maturation form root hairs, which are delicate, thread-like structures that protrude from the surface of the root. Root hairs have a large surface area and are responsible for absorbing water and minerals from the soil, playing a crucial role in nutrient uptake.
Modifications of Roots (Only in NEET)
Roots are essential for plants as they anchor them to the soil and absorb water and nutrients. However, in some plants, roots modify their shape and structure to perform additional functions such as storage, support, and respiration.
Here are some examples of modified roots:
- Storage Roots: Some plants, like carrots and turnips, have taproots that become swollen to store food. Similarly, the adventitious roots of sweet potatoes store food.
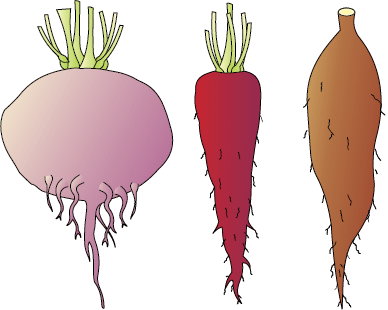 Storage Roots
Storage Roots
- Prop Roots: Banyan trees have prop roots that grow down from their branches and support the tree.
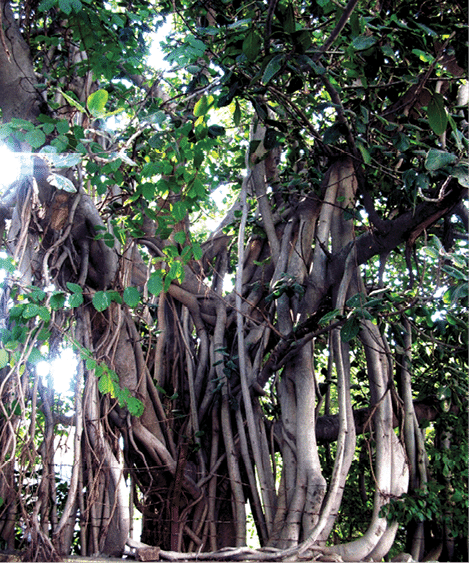 Prop Roots : Banyan Tree
Prop Roots : Banyan Tree
- Stilt Roots: Plants like maize and sugarcane have stilt roots that grow from the lower nodes of their stems and provide additional support.
- Pneumatophores: In swampy areas, plants like Rhizophora develop roots called pneumatophores that grow vertically upwards to obtain oxygen for respiration.
 Pneumatophores
Pneumatophores
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on The Root: Types, Regions & Modifications - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main functions of roots in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of roots found in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the different regions of roots and their significance? |  |
| 4. How do root modifications help plants adapt to their environment? |  |
| 5. What types of root systems can be commonly observed in plants? |  |
















