Theory & Procedure, Boyle's Law | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Objective
To study the variation in volume with pressure for a sample of air at constant temperature by plotting graphs between P and V, and between P and 1/V.
Theory
Properties of gases and Gas laws
Gaseous state is a state of matter in which the substance does not have any specific shape or volume. It adopts the form and size of its container. The fundamental macroscopic properties of gases are pressure, volume, temperature and mass of the gas. These can be explained by kinetic theory by considering their molecular composition and motion. Careful, scientific observation has determined that these variables are related to one another, and the values of these properties determine the state of the gas.
These relationships among pressure, temperature and volume of a gas lead to Gas laws. Boyle's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles' Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases and Avogadro's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the amount of gas increases. The ideal gas law is the combination of the three simple gas laws.
Boyle’s Law
According to Boyle’s Law, the pressure (P) of a given mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume (V), provided that the temperature of the gas remains constant.
For an enclosed gas, at constant temperature (T);
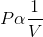
or, 
ie; 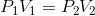
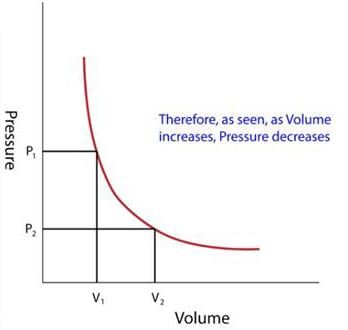
The quill tube is helpful in verifying Boyle’s law.
Since the volume of gas inside the tube(V) = cross sectional area of the tube(a) × length of air column(l),

So, 
Learning outcomes
- Students learn about the properties of gases and their relationships.
- Students understand Boyles law and its applications.
- Students understand the relation between pressure and volume of a given mass of the gas.
Materials Required
- Quill tube
- Stand
- Metre scale
Real Lab Procedure
- Arrange the quill tube horizontally on a stand.
- The length of the air column is measured using a metre scale.
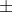
- Vertical heights at the two ends of mercury thread from the table are also measured using a metre scale.
- The difference between them gives the vertical height ‘h’ of the mercury thread. Here h=0. So pressure inside the tube is also H, which is the atmospheric pressure.ie; 76 cm of Hg
- The quill tube is then placed in a slanting position with the open end upwards.
- The length of the air column is measured and the vertical height, h of Mercury is noted. Now the pressure inside the tube, P=H + h.
- Quill tube is then placed in different positions, such as: vertical position with open end upwards and with open end downwards, slanting position with open end downwards and measure its corresponding length of the air column l and vertical height h.
- Now P×l is calculated in each case.
Simulator Procedure – (As performed through the Online labs)
- Use the ‘Mercury column length (cm)’ slider to change the length of the mercury column.
- Use the ‘Air column length (cm)’ slider to change the length of the air column.
- The atmospheric pressure (H) is already shown in the window.
- We can change the position of the quill tube by dragging it in different directions.
- Click on the ‘Show Scale’ button to see the 50 cm scale for taking measurements.
- We can click the arrows on the scale to rotate the scale. Also, click and drag the scale to move it to different positions.
- Now, take the readings and calculations are done as per the observation column.
- Click on the ‘Reset’ button to redo the experiment.
Observations
Sl No. | Position of the tube | Height of Hg thread from table to | Vertical height, h = h2 - h1 (cm) | Pressure, P = H | Length of air column, l (cm) | P×l (cm2) | |
Lower end, h1 (cm) | Upper end, h2 (cm) | ||||||
1 | Vertical (open end up) | ||||||
2 | Slanting (open end up) | ||||||
3 | Horizontal | ||||||
4 | Slanting (open end down) | ||||||
5 | Vertical (open end down) | ||||||
Calculations
- Calculate P × l in each case.
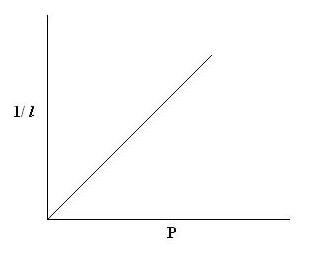
- Plot a graph between Pressure and reciprocal of length, taking pressure (P) along X axis and reciprocal length (1/l) along Y axis.
Result
From the tabular column, it is found that; P × l is a constant.
The graph between reciprocal of length and pressure is a straight line, which shows that pressure of the given mass of gas is inversely proportional to length of air column.
It indicates the inverse proportionality of pressure and volume of a given mass of gas, hence verifies Boyle’s law.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Theory & Procedure, Boyle's Law - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is Boyle's Law? |  |
| 2. What is the procedure to experimentally verify Boyle's Law? |  |
| 3. How does Boyle's Law relate to scuba diving? |  |
| 4. What are the practical applications of Boyle's Law? |  |
| 5. How does Boyle's Law impact the inflation of a balloon? |  |

 h (cm)
h (cm)














