Theory of Evolution (Darwinian) | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
What is Evolution
- Evolution, in the context of biology, refers to the gradual change in species and populations of organisms over time. This concept is often associated with Charles Darwin, a British naturalist who played a significant role in shaping our understanding of evolution.
- During the 1850s, Darwin published a groundbreaking book titled "On the Origin of Species," which put forth the idea that species evolve through a process called "descent with modification." This implies that all living organisms share a common ancestry and have evolved over time to form the diverse range of species we observe today.
- The primary mechanism that Darwin proposed for evolution is natural selection. This process involves the preferential survival and reproduction of organisms possessing heritable traits that enable them to better adapt to their environment. As a result, these advantageous traits become more prevalent in the population over time, leading to evolutionary change.
- Darwin's ideas on evolution were shaped by his extensive travels aboard the HMS Beagle, during which he observed a wide variety of species and ecosystems. These observations helped him develop his theory of evolution by natural selection.
- To better understand how evolution through natural selection works, consider the following example: In a population of birds, some individuals have longer beaks than others. If longer beaks are advantageous for accessing food resources, birds with longer beaks are more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, this selective pressure will lead to an increase in the prevalence of long-beaked birds in the population, resulting in evolutionary change.
- The concept of evolution refers to the gradual change in species and populations over time, primarily driven by the process of natural selection. Charles Darwin's work on the subject has had a lasting impact on our understanding of the natural world and the diverse range of species that inhabit it.
Darwin's Theory of Evolution: Natural Selection
1. Heritability of Traits
- One of the essential components of Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection is the idea that traits are often heritable. In other words, many characteristics in living organisms are inherited from their parents and passed on to their offspring. Although Darwin was unaware of the existence of genes, which carry the information for these inherited traits, his observation still holds true in modern genetics.

2. Overproduction of Offspring
- Another crucial observation made by Darwin was that organisms have the ability to produce more offspring than their environments can support. Due to limited resources such as food, shelter, and mates, not all offspring can survive to adulthood and reproduce. This overproduction of offspring leads to competition within each generation, as individuals strive to secure the necessary resources for their survival and reproduction.
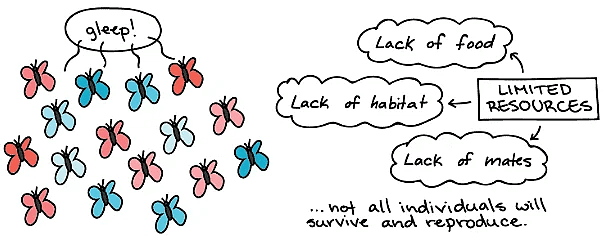
3. Variation in Offspring Traits
- In addition to overproduction of offspring, Darwin also observed that offspring within a generation display variations in their traits, such as size, shape, and color. Many of these variations are heritable, meaning that they can be passed down from parent to offspring. These slight differences in traits can have a significant impact on an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
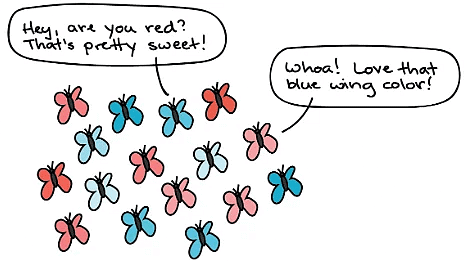
4. Survival and Reproduction of the Fittest
- Based on the above observations, Darwin proposed the concept of natural selection as a mechanism for evolution. In this process, individuals with heritable traits that provide them with a better chance of surviving and reproducing in their environment will be more likely to pass on these advantageous traits to their offspring. Over time, these beneficial traits will become more common in the population, leading to the evolution of a species and its adaptation to its environment.
Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection is based on the key observations of heritability of traits, overproduction of offspring, variation in offspring traits, and the survival and reproduction of the fittest individuals. This elegant and logical theory explains how species can evolve and adapt to their environments over time.
Based on these simple observations, Darwin concluded the following:
- Darwin deduced from his observations that within a population, certain individuals possess inherited traits that enhance their ability to survive and reproduce in their specific environment. These advantageous traits, such as effective predation or food source utilization, enable these individuals to produce more offspring compared to others in their population.
- Since these beneficial traits are inheritable, and organisms with these traits have higher reproductive success, these traits will become more prevalent in the population over successive generations. As a result, the population gradually becomes better adapted to its environment as individuals with favorable traits consistently outperform their peers in terms of survival and reproduction.
- Darwin's concept of evolution through natural selection provided a framework for understanding the patterns he observed during his travels, such as the similarities and differences among Galápagos finch species. For example, if these finch species shared a common ancestor, it would be expected that they would exhibit some resemblance to one another and to mainland finches, who likely also shared that common ancestor. However, if groups of finches had been isolated on various islands for many generations, they would have experienced unique environmental conditions that favored different heritable traits, such as diverse beak sizes and shapes for accessing distinct food sources. This process could have led to the development of separate species on each island.
Conclusion
The concept of evolution refers to the gradual change in species and populations of organisms over time, primarily driven by the process of natural selection. Charles Darwin's work, especially his book "On the Origin of Species," played a significant role in shaping our understanding of evolution. His theory of evolution through natural selection is based on the key observations of heritability of traits, overproduction of offspring, variation in offspring traits, and survival and reproduction of the fittest individuals. Darwin's ideas have had a lasting impact on our understanding of the natural world and the diverse range of species that inhabit it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for Theory of Evolution
Who is Charles Darwin and why is he important in the context of evolution?
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who played a significant role in shaping our understanding of evolution. His groundbreaking book, "On the Origin of Species," introduced the concept of evolution by natural selection, which explains how species change over time and adapt to their environments.
What is natural selection and how does it drive evolution?
Natural selection is the process by which organisms with heritable traits that provide them with a better chance of surviving and reproducing in their environment are more likely to pass on these advantageous traits to their offspring. Over time, these traits become more common in the population, leading to the evolution of a species and its adaptation to its environment.
What are the key components of Darwin's theory of evolution?
Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection is based on four key observations: heritability of traits, overproduction of offspring, variation in offspring traits, and survival and reproduction of the fittest individuals.
How does variation in offspring traits contribute to the process of evolution?
Variation in offspring traits allows for a range of heritable characteristics within a population. These variations can have a significant impact on an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment. As a result, individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to pass on these traits to their offspring, leading to evolutionary change over time.
How has Darwin's work impacted our understanding of the natural world and the diverse range of species that inhabit it?
Darwin's ideas on evolution have provided a framework for understanding the patterns and relationships between species, as well as the mechanisms by which species adapt to their environments. This has led to significant advancements in fields such as biology, ecology, and genetics, as well as a deeper appreciation for the intricate connections between all living organisms on Earth.
|
209 videos|299 docs
|





















