Topic wise Previous Year Questions(Solved): Geomorphology | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Ans: Truncated spurs are prominent geomorphic features in glaciated landscapes, reflecting the erosive power of glaciers. Their study is essential for understanding glacial processes and landform evolution.
- Definition: Truncated spurs are steep, triangular ridges in glaciated valleys with their tips eroded by glacial action, transforming interlocking river valley spurs into flat-faced features.
- Formation Process: Glaciers erode pre-existing river valleys with interlocking spurs through abrasion and plucking. The glacier’s movement truncates spur ends, creating U-shaped valleys with steep ridges. Geologist W.M. Davis emphasized glacial erosion’s role in reshaping landscapes.
- Locations: Found in glaciated regions like the Himalayas (Zanskar Valley), Alps, and Rocky Mountains, where glacial valleys are common.
- Significance: Indicate past glacial activity, aiding in reconstructing glacial histories. Recent studies (2024) on Himalayan glaciers highlight accelerated spur erosion due to climate-driven glacial retreat.
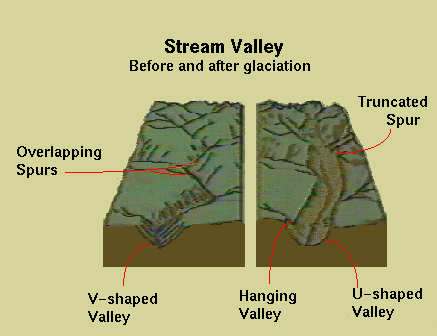
Conclusion: Truncated spurs are key indicators of glacial erosion, shaping rugged landscapes. Their study enhances understanding of glacial dynamics, critical for geomorphic analysis and environmental planning.
Q2: Examine the recent views on mountain building process and divide the world mountains on the basis of their genesis. (2024)
Ans: Mountain building, or orogeny, is a dynamic tectonic process shaping Earth’s crust. Recent research has refined our understanding, emphasizing diverse mechanisms driving mountain formation.
- Modern Perspectives: Geodynamic models highlight lithospheric delamination, where dense lower crust detaches, enabling uplift (e.g., Tibetan Plateau). Seismic studies reveal subduction and collision as primary drivers. Geologist R. Dietz (1961) linked plate tectonics to orogeny, a view now expanded by mantle convection theories.
- Classification by Genesis:
- Collisional Mountains: Formed by continental plate collisions (e.g., Himalayas, Alps).
- Volcanic Mountains: Result from volcanic activity (e.g., Andes, Cascades).
- Fault-Block Mountains: Created by extensional faulting (e.g., Sierra Nevada).
- Fold Mountains: Formed by crustal folding (e.g., Zagros Mountains).
- Recent Insights (2024): Research on the Andes suggests magma buoyancy significantly contributes to uplift, challenging purely tectonic models. This underscores the complexity of orogenic processes.
Conclusion: Advances in orogeny research reveal multifaceted tectonic processes. Classifying mountains by genesis aids in understanding Earth’s dynamic crust, crucial for geological studies and hazard assessment.
Q3: What is a Yazoo stream? Why are Yazoo basins the areas of repeated flooding? Give examples of Yazoo stream/areas from various parts of the world. (2024)
Ans: Yazoo streams are unique fluvial features associated with floodplains, notable for their role in recurrent flooding events, making them critical in geomorphic and disaster management studies.
- Definition and Characteristics: A Yazoo stream is a tributary flowing parallel to a main river within its floodplain for a significant distance before joining, delayed by natural or man-made levees. Geologist Harold Fisk (1944) attributed their formation to sediment deposition creating levees.
- Causes of Flooding:
- Natural Levees: Block water flow, causing backswamp flooding during high river stages.
- Human Interventions: Levee construction and agriculture disrupt drainage, exacerbating floods, as seen in the 1927 Yazoo Basin flood.
- Backwater Effect: High main river levels trap water, as in the 2019 Yazoo Backwater flood lasting 200 days.
- Examples: Yazoo River, USA (parallels Mississippi River for 280 km); Wakarusa River Tributaries, Kansas, USA; Montana and Jordan Creeks, Alaska, USA.
- Recent Events (2024): The Yazoo Pumps project in Mississippi sparked environmental justice debates, highlighting flood control challenges.
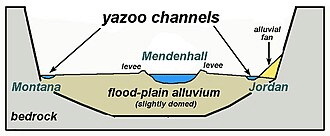
Conclusion: Yazoo streams and their flood-prone basins reflect complex fluvial dynamics. Understanding their formation and flooding mechanisms is vital for effective river management and flood mitigation strategies.
Ans: Palaeomagnetism and sea floor spreading provide compelling evidence for plate tectonics, confirming that continents and ocean basins are in constant motion, reshaping Earth’s surface over millions of years.
- Palaeomagnetism: Rocks record Earth’s magnetic field at formation, revealing past continental positions. Polar wander paths show India’s northward drift, forming the Himalayas. Magnetic reversals, studied by geologist B. Brunhes, indicate plate movements.
- Sea Floor Spreading: Harry Hess (1960) proposed that new oceanic crust forms at mid-ocean ridges and spreads outward. Symmetrical magnetic stripes on either side of ridges (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge) confirm this process, pushing continents apart.
- Supporting Evidence: The jigsaw fit of South America and Africa, coupled with matching magnetic stripes, validates continental drift. Radiometric dating shows younger crust near ridges, supporting continuous spreading.
- Recent Advances (2024): High-resolution magnetic surveys of the Pacific Ocean floor reveal faster spreading rates, refining tectonic models.
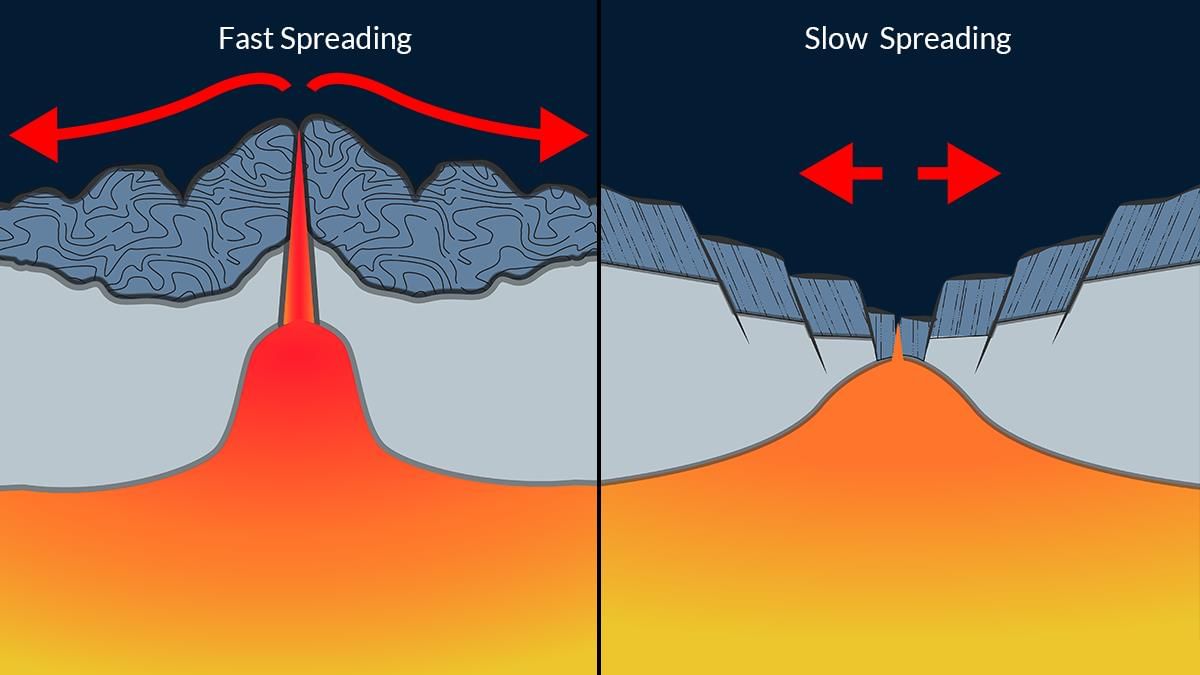
Conclusion: Palaeomagnetism and sea floor spreading conclusively demonstrate Earth’s dynamic nature. These processes underpin plate tectonics, essential for understanding global geomorphic evolution and tectonic hazards.
Q5: Define Peneplains. Describe the landscape features associated with peneplains under different geomorphic cycles. (2023)
Ans: Peneplains are significant geomorphic features representing the final stage of landscape evolution, offering insights into long-term erosional processes across diverse environments.
- Definition: A peneplain is a low-relief, nearly flat surface formed by prolonged erosion, reducing a landscape to minimal elevation, often with isolated residual hills (monadnocks). William Morris Davis formalized this concept in his cycle of erosion.
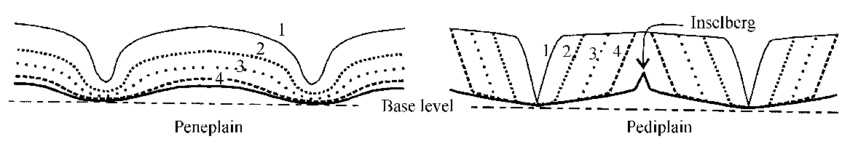 Landscape Features by Geomorphic Cycle:
Landscape Features by Geomorphic Cycle:- Fluvial Cycle (Humid Regions): Characterized by gentle slopes, broad valleys, and meandering rivers. Example: Deccan Plateau remnants in India.
- Arid Cycle: Features pediments, inselbergs, and sparse drainage networks. Example: Australian Shield’s flat landscapes.
- Glacial Cycle: Displays smoothed surfaces, low hills, and glacial deposits. Example: Canadian Shield’s eroded terrain.
- Significance: Peneplains reflect geomorphic stability, disrupted by tectonic uplift, initiating new cycles. Recent studies (2024) on the African Shield highlight peneplain rejuvenation due to rift tectonics.
Conclusion: Peneplains encapsulate the culmination of erosional cycles, varying by environmental conditions. Their study is crucial for understanding landscape evolution and predicting future geomorphic changes.
Q6: What is “Geostrophic Wind”? Explain the relationship between barometric slope and air circulation. (2023)
Ans: Geostrophic wind is a fundamental concept in meteorology, crucial for understanding atmospheric circulation patterns. It arises from the balance of forces influencing air movement, shaping weather systems.
- Definition: Geostrophic wind is a theoretical wind that flows parallel to isobars (lines of equal atmospheric pressure) due to the balance between the pressure gradient force and the Coriolis effect, as described by meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes.
- Relationship with Barometric Slope: The barometric slope, or pressure gradient, drives air from high to low pressure. A steeper slope (closer isobars) results in stronger winds, as the pressure gradient force increases. The Coriolis effect, caused by Earth’s rotation, deflects this flow (right in the Northern Hemisphere, left in the Southern), aligning it parallel to isobars.
- Mechanism: In ideal conditions (straight isobars, no friction), geostrophic wind speed is proportional to the pressure gradient. Friction near the surface reduces speed and alters direction, creating ageostrophic flow.
- Applications (2024): Geostrophic wind models are used in weather forecasting, with recent advancements improving cyclone track predictions in the Indian Ocean.
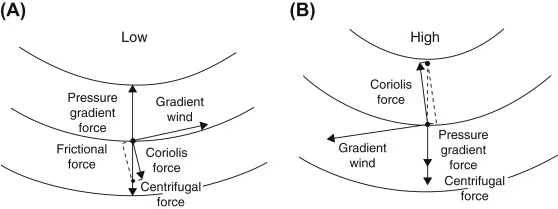
Conclusion: Geostrophic wind, driven by the interplay of pressure gradients and Coriolis forces, is central to air circulation dynamics. Its study enhances weather prediction and climate modeling, vital for disaster preparedness.
Q7: Define Speleothem. Discuss the various forms and features of speleothem. (2022)
Ans: Speleothems are mineral formations in caves, offering insights into geological processes and paleoclimates. Their diversity and formation mechanisms are key in karst geomorphology studies.
- Definition: Speleothems are secondary mineral deposits formed in caves by the precipitation of minerals, primarily calcium carbonate, from water seeping through limestone, as studied by geologist J Harlen Bretz.
- Forms and Features:
- Stalactites: Icicle-shaped formations hanging from cave ceilings, formed by dripping water depositing calcite.
- Stalagmites: Upward-growing mounds on cave floors, formed below stalactites as water drips and deposits minerals.
- Columns: Form when stalactites and stalagmites merge, creating pillars (e.g., Carlsbad Caverns, USA).
- Flowstones: Sheet-like deposits formed by water flowing over cave surfaces.
- Significance: Speleothems record climate data via isotopic analysis. Recent studies (2024) on Indian cave speleothems reveal monsoon variability over millennia.

Conclusion: Speleothems, with their varied forms, are vital for understanding karst processes and past climates. Their study aids in reconstructing environmental histories, crucial for geological and climatic research.
Q8: Explain how various aspects of channel morphology are used in transportation, settlement and land use planning, flood control and flood management. (2022)
Ans: Channel morphology, the study of river channel forms and processes, is integral to planning human activities and managing natural hazards, shaping sustainable development in riverine regions.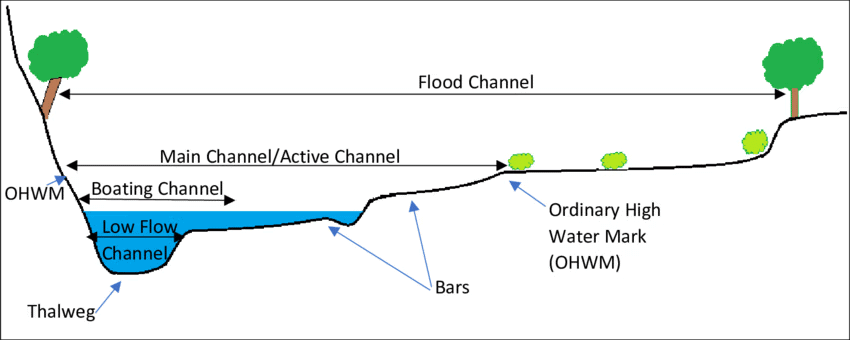
- Transportation: Wide, stable channels with gentle gradients (e.g., Ganga River) support navigation. Morphology studies guide dredging and port placement, ensuring safe waterways.
- Settlement and Land Use: Flat floodplains with meandering channels are ideal for agriculture and urban development (e.g., Nile Valley). Morphology informs zoning to avoid erosion-prone banks.
- Flood Control and Management: Channel characteristics like depth, width, and sinuosity influence flood risk. Narrow, straightened channels (e.g., Mississippi River) require levees, while braided channels need embankments. Geologist Luna Leopold’s work on channel hydraulics aids flood prediction and dam design.
- Recent Advances (2024): Morphological analysis using GIS in Bangladesh improved flood forecasting, enhancing embankment planning along the Brahmaputra.
Conclusion: Channel morphology guides critical decisions in transportation, settlement, and flood management. Its application ensures sustainable land use and effective hazard mitigation, vital for riverine communities.
Q9: Discuss the role of Slope, Altitude, and Relief (SAR) in landscape development. (2022)
Ans: Slope, Altitude, and Relief (SAR) are fundamental geomorphic factors shaping landscapes, influencing erosion, deposition, and ecological patterns across diverse terrains.
- Slope: The angle of inclination drives erosion and sediment transport. Steep slopes (e.g., Himalayas) promote rapid runoff and mass wasting, while gentle slopes (e.g., Indo-Gangetic Plains) favor deposition. Geologist G.K. Gilbert’s slope-erosion models highlight this dynamic.
- Altitude: Elevation affects climate and weathering. High altitudes (e.g., Andes) experience frost action, shaping rugged terrains, while low altitudes support fluvial processes, forming plains.
- Relief: The vertical difference between high and low points influences drainage and landform diversity. High-relief areas (e.g., Alps) feature deep valleys, while low-relief areas (e.g., Australian Shield) are flat.
- Recent Studies (2024): SAR analysis in the Western Ghats revealed accelerated erosion due to monsoon intensification, aiding conservation planning.
Conclusion: SAR profoundly shapes landscape evolution, driving geomorphic processes and ecological patterns. Understanding their roles enhances land management and hazard assessment, critical for sustainable development.
Q10: With the help of suitable sketches describe the mountain genesis and mountain types. Give suitable examples from various mountain systems of the world. (2022)
Ans: Mountain genesis, or orogeny, involves tectonic processes creating diverse mountain types, shaping Earth’s topography. Their classification aids in understanding global geodynamics.
- Mountain Genesis: Orogeny results from plate interactions—collision, subduction, or faulting. Geologist John Tuzo Wilson’s plate tectonics theory (1960s) explains how convergence forms mountains like the Himalayas.
- Mountain Types:
- Collisional Mountains: Formed by continental plate collisions (e.g., Himalayas, Alps).
- Volcanic Mountains: Built by volcanic activity (e.g., Andes, Mount Fuji).
- Fault-Block Mountains: Created by extensional faulting (e.g., Sierra Nevada).
- Fold Mountains: Result from crustal folding (e.g., Zagros Mountains).
- Recent Insights (2024): Studies on the Andes suggest magma buoyancy enhances uplift, complementing tectonic processes.
Conclusion: Mountain genesis reflects complex tectonic interactions, producing varied mountain types. Their study is essential for understanding Earth’s crustal dynamics and managing associated hazards.
|
303 videos|635 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Topic wise Previous Year Questions(Solved): Geomorphology - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the key concepts of geomorphology that are essential for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. How can previous year questions in geomorphology help in preparing for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What are some common geomorphological processes that UPSC aspirants should focus on? |  |
| 4. How does geomorphology relate to environmental studies in the context of the UPSC syllabus? |  |
| 5. What are some important case studies in geomorphology that candidates should be aware of for the UPSC exam? |  |





















