UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 10th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Cyclone’s effect on Monsoon Onset
Why in News?
Biparjoy, a very severe cyclonic storm that has developed in the Arabian Sea, is likely to affect the progress of the monsoon season.
What is Monsoon?
- A monsoon is a seasonal change in the direction of the prevailing, or strongest, winds of a region. Monsoons cause wet and dry seasons throughout much of the tropics.
- Monsoons always blow from cold to warm regions. The summer monsoon and the winter monsoon determine the climate for most of India and Southeast Asia.
Factors Affecting the Monsoon
- Mascarene High: The southwest monsoon derives its name from winds which blow from a south-westerly direction in the Indian subcontinent. These come from a powerhouse located more than 4,000 kilometres from India known as the Mascarene High. This high-pressure region is located between 25°S-35°S and 40°E-90°E near the Mascarene Islands in the southern Indian Ocean.
- A stronger high pressure will produce stronger winds or monsoon current. If there is a delay in the formation of Mascarene High, there is also the possibility of a delay in the onset of monsoon in India.
- Coriolis Force: Coriolis Force is a pseudo force which exists only because of the Earth’s rotational effect. Rotational motion observed in a tropical cyclone is also due to this force.
- Hence, these monsoon winds get deflected eastwards and now they blow from south-west to the north-east direction. They split into two branches—the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch.
- Differential Heating: A mechanism is needed to attract the monsoon winds from the Arabian Sea or the Bay of Bengal. Winds flow from high pressure to low pressure areas.
- The Himalayan range plays a vital role in summer heating by restricting the intrusion of cold air from the north and allowing heating to occur.
- It is during this season that the land of India, particularly Rajasthan and surrounding areas (Gujarat and also Pakistan) heat up extensively.
- The seas surrounding the country also see a temperature rise. As a result of the differential heating rates and capacities of air over the sea and the land, we observe a gradient between air pressure over the sea and that over India (especially Rajasthan).
- The air pressure over India is lower than that over the southern part of the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. This acts as an attractor mechanism for the monsoon winds.
- El Nino Southern Oscillation: El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) refers to the oscillatory mode of the sea surface temperatures near the equatorial Pacific Ocean in which a warming (El Nino or cooling (La Nina) or neutrality is observed.
- Due to its mostly unpredictable nature, ENSO has been a big challenge for forecasters for a long time. Even trusted models have failed many times.
- ENSO has been a driver of global weather (particularly in countries surrounding the Pacific Ocean) as it affects atmospheric circulation.
- Indian Ocean Dipole: In 1999, N H Saji of Japan’s University of Aizu and others discovered an ENSO-like phenomenon in the Indian Ocean which they named the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD).
- Like ENSO, IOD also has three phases—positive, negative and neutral. During the positive phase of IOD, sea surface temperatures are warmer in the western Indian Ocean (which gives a boost to monsoon winds) as compared to the eastern Indian Ocean—hence a dipole nature.
- The reverse happens during IOD negative and no gradient is observed during the IOD neutral period.
- It has been observed that during the period of positive IOD, the Indian summer monsoon rainfall is considerably good as compared to the negative IOD period. Despite 1994 and 2006 being El Nino years, India did not witness drough as IOD was significantly positive.
What are Cyclones?
- The word Cyclone is derived from the Greek word Cyclos meaning the coils of a snake. It was coined by Henry Peddington because the tropical storms in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea appear like coiled serpents of the sea.
- Cyclones are caused by atmospheric disturbances around a low-pressure area distinguished by swift and often destructive air circulation. The air circulates inward in an anticlockwise direction in the Northern hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern hemisphere.
- Cyclones are classified as: (i) extra tropical cyclones (also called temperate cyclones); and (ii) tropical cyclones.
- Worldwide terminology: Cyclones are given many names in different regions of the world – They are known as typhoons in the China Sea and Pacific Ocean; hurricanes in the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean; tornados in the Guinea lands of West Africa and southern USA.; willy-willies in north-western Australia and tropical cyclones in the Indian Ocean.
How Does the Formation of Cyclones Effect Monsoon?
Some cyclones in the North Indian Ocean have had both positive and negative impacts on the onset of the monsoon.
- The development of the cyclone has delayed the onset of the Southwest Monsoon, which usually begins in June and ends in September.
- The powerful weather system in the Arabian Sea may spoil the advancement of the monsoon deep inland. Under their influence, the monsoon stream may reach coastal parts but will struggle to penetrate beyond the Western Ghats.
- When the circulation of winds around the cyclones is in the anticlockwise direction, the location of the cyclone is critical as far as the cyclone’s impact on the transition of the monsoon trough is concerned (The monsoon trough is a low-pressure region that is a characteristic feature of the monsoons.).
- For example, if a cyclone lies further north in the Bay of Bengal, the back-winds blowing from the southwest to the northeast can pull the monsoon trough forward, and assist in the monsoon’s onset.
- Earlier this year, the Bay of Bengal had Cyclone Mocha develop in the first half of May and intensify briefly into a ‘super cyclonic storm’, before weakening rapidly upon landfall.
- Mocha dissipated and the back-winds helped the monsoon set in on time over the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Cyclone Biparjoy is not interacting much with the monsoon trough at this time. However, its late birth as well as the late onset of the monsoon are both closely related to typhoons in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
- Westerly winds, which pull the monsoon towards the Indian mainland, are weak now. All the moisture is rotating around the cyclone.
- Winds have been blowing strongly towards the northeast over the Bay, a key reason why the monsoon trough has been struggling to reach Kerala.
- Cyclonic storms in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea have been intensifying rapidly and retaining their intensity for a longer duration due to climate change.
Source: The Hindu
Burial tradition of Homo Naledi

Why in News?
Recent evidence suggests that Homo Naledi buried their dead.
About Homo Naledi:-
- Homo naledi is an extinct human species that lived hundreds of thousands of years ago.
- Homo Nalediis a species of human discovered in the Rising Star cave system, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in South Africa in 2013.
- Homo naledi exhibits a combination of primitive and modern features and is not a direct ancestor of modern humans.
- They are believed to have existed between 300,000 to 200,000 years in Southern Africa.
- They walked upright.
- Their shoulders were built for climbing.
- Their teeth were shaped like that of older primates.
- One of the most interesting things was that their brain size was between 450 to 600 cubic centimetres (Small brain). It was one-third of that of modern humans.
About the Study:
- Homo Naledi buried their dead, which would challenge existing notions about advanced mortuary behavior.
- Modern Humans exhibit a unique behavior among primates by burying their dead, which sets them apart from other animals. This behavior is known as Mortuary behavior, characterized by social acts and a complex understanding of death.
- Previously, the earliest evidence of Mortuary behavior was found among Neanderthals and modern humans, occurring more than 100,000 years after Homo naledi.
- Homo naledi may have created rock art in Rising Star Cave. This is intriguing because rock art has traditionally been associated with Homo sapiens and other large-brained ancestors.
- The report describes engravings in the form of deeply impressed cross-hatchings and geometric shapes such as squares, triangles, crosses and X’s.
- Additionally, a rock-like object found near a Homo naledi body suggests it could be a stone tool.
- Homo naledi used fire strategically for illumination during mortuary and engraving activities in the cave.
Burial tradition in India:-
- It is said that the practice of burying dead people started some 3000 years ago in India.
- Megaliths or large stones were used to indicate the place where the dead were buried.
- We still find this practice in various cultures of India.
- 3000 years ago, people living in southern regions, Kashmir, and the Deccan plateau were involved in such burial practices.
- The people who died were buried with the help of pots known as Red and Black Ware.
Megalith Sites in India
- Nilaskal – Karnataka
- Hire Benkal- Kerala
- Chamber Tomb: Hire Benakal- Karnataka
- Dolmens: Hire Benakal– Karnataka
- Hanamsagar– Karnataka
- Kudakkallu Parambu– Kerala
- Junapani- Maharashtra
Source: Indian Express
Mahua laddoos
Why in News?
Mahua ladoos, prepared by Odisha tribal women have showed huge revenue success in recent times.
About Mahua ladoos:-
- The tribal women in Odisha’s Kandhamal district use mahua flowers to prepare various delicious varieties of food. Mahua flowers are mainly used for brewing local liquor, are popular across India
- Around 120 tribal women members of the state’s Van Dhan Vikas Kendras prepare laddus, cakes, jam, toffees, pickles, squash, pakodas and biscuits using dry mahua flowers, which they supply, in the local market to earn revenues.
- Mahua laddus are in high demand compared to other products.
- The laddu is prepared using ingredients such as cashew, rasi, groundnut, jaggery, and mahua flowers.
Van Dhan Vikas Kendras:
- These are set up under the Pradhan Mantri VanDhan Yojana(PMVDY).
- They aim to promote Minor Forest Products (MFPs) -centric livelihood development of tribal gatherers and artisans.
- Minor forest produce are economic commodities growing naturally in a forest and sold for purposes other than timber and fuel. Examples include bamboo, wild honey, gum, lac, waxes, resins etc.
- These Kendras would act as common facility centres for procurement cum value addition to locally available MFPs.
Pradhan Mantri VanDhan Yojana(PMVDY):-
- It was launched in 2018.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and TRIFED.
- Objective: to improve tribal incomes through the value addition of tribal products.
- It is a Market Linked Tribal Entrepreneurship Development Program for forming clusters of tribal Self-Help-Groups (SHGs) and strengthening them into Tribal Producer Companies.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Time has come for postal voting for NRIs: CEC

Why in News?
While addressing a group of trainee Indian Foreign Service officers,Chief Election Commissioner said the time had come for the Election Commission to facilitate postal voting for Non-Resident Indians.
- The EC’s proposal for introducing Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballots is currently pending with the government.
What is the current process of voting by NRIs/overseas Indian voters?
- Currently, Election Commission of India (ECI) allows NRIs to register as overseas electors as long as they have not acquired the citizenship of another country.
- An NRI can vote in the constituency in which his/her place of residence, as mentioned in the passport, is located.
- He/she can only vote in person and will have to produce the passport in original at the polling station for establishing identity.
- Voting rights for NRIs were introduced only in 2011, through an amendment to the Representation of the People Act 1950.
- As per the government, total number of overseas voters on January 1, 2023 stood at over 1.15 lakh.
- In Lok Sabha elections of 2019, roughly 25,000 of them flew to India to vote.
Origin of the idea of postal ballot
- A 12-member committee was set up after the 2014 Lok Sabha elections to study mainly three options — voting by post, voting at an Indian mission abroad and online voting.
- The committee ruled out online polling as it felt this could compromise “secrecy of voting”.
- It also shot down the proposal to vote at Indian missions abroad as they do not have adequate resources.
- In 2015, the panel recommended that NRIs should be given the additional alternative options of e-postal ballot and proxy voting.
- The EC, in 2020, had written to the Law Ministry proposing NRIs be allowed to vote through postal ballots.
- Following this, the matter has been under consideration by the government.
What has been proposed by the EC?
- To extend voting facility for NRI electors, EC had proposed the extension of Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS) facility to these voters.
- ETPBS enables the voters to cast their vote on an electronically received postal ballot from their preferred location.
- ETPBS facility is so far available only to service voters, including
- members of the armed forces and central armed police forces posted outside their home constituencies and
- members of Indian embassies and diplomatic missions.
- Voters on election duty
- Voter above 80 years of age or person with disabilities (PwD)
- Voter who are under preventive detention
- Media persons (Journalist)
- According to the EC proposal, any NRI interested in voting through the postal ballot in an election will have to inform the Returning Officer (RO).
- RO should be informed in a time period not later than five days after the notification of the election.
- On receiving such information, the RO will dispatch the ballot paper electronically.
- The NRI voters will download the ballot paper, mark their preference on the printout and send it back.
- This ballot is to be sent back along with a declaration attested by an officer appointed by the consular representative of India in the country where the NRI is resident.
News Summary:
Key highlights of the Speech of CEC
- CEC said that time has come when the fifth largest economy of the world invokes technology driven methodology to facilitate its over 1.34 crore overseas Indians to participate in elections by ETPBS.
- The CEC spoke to the trainees about the challenges being faced by election management bodies across the world.
- This includes the rising threat from fake news and deep fakes on social media, derailing the election narratives.
- India’s elections were often regarded as the largest peace-time mobilisation, with over 1 crore polling officials being deployed.
- Linked to India’s impressive economic growth trajectory, the credibility of its electoral domain effectively counters the non-democratic discourse that the electoral process hinders growth.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Financial Inclusion in India
Why in News?
In June 2023, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor launched a Financial Inclusion Dashboard, named Antardrishti.
About Antardrishti:
- The dashboard will provide the required insight to assess and monitor the progress of financial inclusion by capturing relevant parameters.
- The dashboard, presently intended for internal use in the RBI, will further facilitate greater financial inclusion through a multi-stakeholder approach.
About Financial Inclusion:
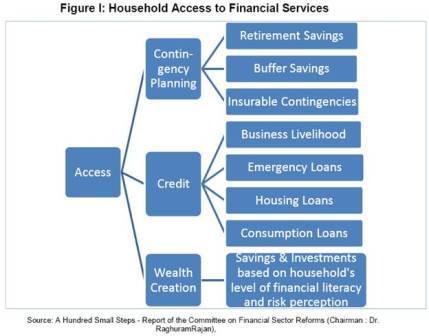
- According to the world bank, financial inclusion means that individuals and businesses have access to affordable financial products and services that meet their needs.
- Accessibility, affordability and availability of financial services are 3 pillars of financial inclusion.
- It is a method of offering banking and financial solutions and services to every individual in the society without any form of discrimination.
- The concept of financial inclusion was first introduced in India officially in 2005 by the Reserve Bank of India.
The objectives of financial inclusion are to provide the following:
- A basic no-frills banking account for making and receiving payments
- Saving products (including investment and pension)
- Simple credit products and overdrafts linked with no-frills accounts
- Remittance, or money transfer facilities
- Micro insurance (life) and non-micro insurance (life and non-life)
- Micro pension and
- Financial Literacy.
Significance of Financial Inclusion:
- Financial inclusion strengthens the availability of economic resources and builds the concept of savings among the poor.
- Financial inclusion is a major step towards inclusive growth. It helps in the overall economic development of the underprivileged population.
- In India, effective financial inclusion is needed for the uplift of the poor and disadvantaged people by providing them with the modified financial products and services.
Challenges to financial inclusion in India:
- Socio-economic factors: Financial exclusion is related to the social conditions of low-income households, who are not able to access the available financial products and services.
- Various constraints such as low income, low savings and generally low levels of awareness hinders financial inclusion.
- Geographical factors: A review by the Rangarajan Committee shows that financial exclusion is highest among households in the Eastern, North -Eastern and Central areas of the country partly due to poor infrastructure.
- This coupled with remoteness and less population in some areas resulting is in problems with access.
- Limited availability of appropriate technology: The key driver of financial inclusion is the proliferation of stable and reliable Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
- The lack of infrastructure and cost effective technology for facilitating transactions at the doorstep is a hindrance to financial inclusion.
- Perception of obligation: The financial institutions are reluctant to serve small value and unprofitable customers with irregular income.
- Banks perceive inclusion as an obligation rather than a business opportunity.
- This discourages banks from providing financial services to low income individuals.
- Lack of documents: Another factor preventing them from accessing formal financial institutions are the requirement of various document proof.
- The poor generally lack documents such as Aadhaar card, income certificate, birth certificate, address proof etc.
- Financial illiteracy: The absence of basic education prevents people from following even simple information related to financial inclusion.
- The rural population as a result, relies mostly on the informal sector for availing finance at high rates, which lead to the vicious circle of poverty and debt repayment.
- Penetration: At present, only about 5% of India’s 6 lakh villages have bank branches. There are 296 under-banked districts in states with below-par banking services.
- Thus, bank reach is poor in rural areas leading to financial exclusion.
Steps taken to achieve Financial Inclusion:
Government of India Initiatives:
- PM Mudra Yojana – for small loans to non-corporate businesses
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana
- Insurance scheme – PM Suraksha Bima Yojana and Jeevan Jyoti Beema Yojana
- Pension Scheme – Atal Pension Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Mann Dhan Yojana (PM-SYM)
- Nandan Nilekani Panel on deepening of Digital Payments
- Kisan Credit Card
Initiatives by the RBI:
- National Strategy for Financial Inclusion (NSFI) 2019-24
- Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF)
- ATM infrastructure
- Project Financial Literacy
Way Forward:
The availability of banking facilities and strong bank branch network are the major facilitators of developmental activities. A strong and sturdy financial system is a pillar of economic growth, development and progress of an economy. The problem of financial exclusion needs to be tackled if we want our country to grow in an equitable and sustainable manner.
Source: Business Standard
NEW EEL DISCOVERED

Why in News?
The scientists of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have discovered a new species of eel from Palur canal in Odisha’s Ganjam district.
Eels
- Eels are elongated ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders and about 800 species.
- Eels live both in salt and fresh water, and some species are catadromous.
New Species of Eels
- Scientific Name: The new species has been named Pisodonophis kalinga after the name of ancient Odisha.
- Common Name: The scientists have proposed kalinga snake eel as the common name of the new species.
- Family: It belongs to the family Ophichthidae and order Anguilliformes.
- Features: It has a snake-like appearance and varies in length from 560 millimetres to 7 metres.
o The dorsal side of the body of new species is dark olive-brown, ventrally pale white and both the colors meet at the lateral side.
- Distribution: The species was found in the Chilika lagoon, Asia’s biggest brackish water lagoon, and the adjoining Palur canal, where water flow is completely tide dependent.
o The Palur canal connects Chilika with River Rushikulya.
Source: DTE
WOLF-DOG HYBRIDISATION / INDIAN WOLF

Why in News?
Researchers have found the first evidence of wolf-dog hybridisation in the country.
- The findings claimed that wolf (Canis lupus)-dog (Canis lupus familiaris) hybridisation may lead to immense reduction of certain adaptations in wolves eventually causing a drop in wolf populations.
Indian wolf
- Scientific name: Canis lupus pallipes.
- Distribution: It is a subspecies of gray wolf that ranges from Southwest Asia to the Indian subcontinent.
- Features: It is intermediate in size between the Himalayan wolf and the Arabian wolf, and lacks the forman er's luxuriant winter coat due to it living in warmer conditions. It has shorter fur with little to no underfur.
- Behaviour: The Indian wolf travels in smaller packs and is less vocal than other variants of the gray wolf.
- IUCN Status: Endangered
- Mahuadanr Wolf Sanctuary in the state of Jharkhand is only wolf sanctuary in the country.
Source: DTE
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|

















