UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 10th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Indian Society
Costs of Population Decline
Source:The Hindu
Why in news?
The Chief Ministers of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu have recently expressed their concerns regarding the low fertility rates observed in their states. The Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh announced plans to introduce legislation that would encourage families to have more children. This initiative is indicative of the increasing anxiety surrounding demographic challenges, as both states are experiencing declining birth rates that could potentially affect future economic growth and social stability.
Decades of effective family planning policies in India have contributed to slower population growth but have also resulted in a rapidly ageing population, particularly in certain regions. This transition presents challenges as the number of elderly individuals increases, affecting both economic and social structures.
Declining Fertility Rates in Southern and Smaller Northern States
- Fertility rates, which indicate the average number of children born to women during their reproductive years, have significantly decreased in southern states such as Tamil Nadu and West Bengal (1.4 between 2019 and 2021), as well as in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala, Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh (1.5).
- States with lower fertility rates have generally experienced faster development.
Higher Fertility Rates in Northern States
- Conversely, states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh continue to have relatively high fertility rates (3, 2.7, and 2.6, respectively), suggesting a slower demographic transition and a younger population structure.
Projected Growth in India’s Elderly Population
- According to the India Ageing Report (UNFPA), the elderly population in India is expected to rise from 10.1% in 2021 to 15% by 2036.
- Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh are projected to experience a significant demographic shift, with elderly populations expected to represent 22.8%, 20.8%, and 19% of their total populations by 2036. In contrast, Bihar's elderly population is projected to comprise only 11% by the same year.
India’s Ageing Crisis and Socio-Economic Political Challenges
- The demographic transition in India is advancing more swiftly than its socio-economic development.
- A critical measure is the old age dependency ratio, which indicates the number of older dependents per 100 working-age individuals (ages 18-59).
- As noted by Associate Professor Srinivas Goli, an ageing crisis occurs when this ratio exceeds 15%.
States with High Old Age Dependency Ratios
- Several states have already surpassed this threshold, including Kerala (26.1 in 2021), Tamil Nadu (20.5), Himachal Pradesh (19.6), and Andhra Pradesh (18.5).
- This indicates that these states’ demographic dividend—benefits from a younger workforce with low dependency—has largely diminished, resulting in increased pressure on healthcare and social services.
Healthcare Burden of Ageing Populations
- States with ageing populations are facing rising healthcare costs. A study from 2017-18 revealed that southern states, which account for only 20% of India’s total population, represented 32% of the country's out-of-pocket spending on cardiovascular diseases.
- In contrast, eight states in the Hindi belt, which house 50% of the population, contributed only 24% of such spending.
Economic and Gender Implications of Increasing Fertility
- While some state leaders suggest increasing fertility rates as a solution to counteract ageing, this could negatively affect women's workforce participation, potentially impeding economic growth.
- Southern states argue that despite their contributions to the economy and higher tax revenues, they receive a smaller portion of central resources due to their slower population growth, which raises concerns about fiscal equity.
Impact of Uneven Population Growth on Parliamentary Representation
- With the freeze on parliamentary seats ending in 2026, a new delimitation process will adjust Lok Sabha representation according to population changes, affecting the federal structure.
- Research indicates that states with higher population growth, like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Rajasthan, are expected to gain seats (12, 10, and 7 respectively), while states experiencing slower growth, including Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh, are likely to lose seats (9, 6, and 5 respectively) due to their diminishing share of the national population.
Limitations of Pro-Natalist Incentives
- Chief Ministers in southern states are advocating for incentives to promote higher fertility rates. However, analysts caution that such measures have seen limited success globally.
- Educated women are generally unresponsive to enforced fertility incentives that do not address genuine family needs.
Recommended Policy Changes for Sustainable Fertility Rates
- Experts recommend implementing work-family policies that promote gender equity, such as paid maternity and paternity leave, accessible childcare, and employment policies that eliminate the “motherhood penalty.”
- These changes could enable women to maintain economic independence, making them more inclined to have children.
Alternative Solutions: Extending Working Lifespan and Migration Policies
- Extending the working lifespan may help reduce the old age dependency ratio.
- Southern states, which are already economic centers attracting migrants, face challenges as these migrants often depend on the social services of their destination states.
- Additionally, migrants are counted in their home states for political and financial allocations, which can strain resources in southern states.
- A suitable migration policy is essential to address these challenges.
GS3/Defence & Security
Report Reveals 2023 Ransomware Attack on Key Defence Unit
Source:The Hindu
Why in news?
According to the 2023-24 annual report of the Department of Personnel Training (DoPT), a significant defense unit faced a ransomware attack in 2023. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) looked into various cybercrimes that posed risks to national security, which included ransomware incidents, a large Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack on critical infrastructure, and a malware breach within a governmental ministry.
About
A cyber attack refers to a malicious effort by individuals or groups aimed at disrupting, damaging, or gaining unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or data. Such attacks can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and compromised security, affecting individuals, businesses, and national infrastructures alike.
Types of Cyber Attacks
- Phishing:Phishing attacks involve tricking users into disclosing sensitive information, such as login details or financial information, through fraudulent emails or websites. For instance, in a 2020 incident, hackers sent phishing emails mimicking World Health Organization officials, taking advantage of public fears during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Ransomware:Ransomware is a type of malware that locks or encrypts data, demanding payment for its restoration. A notable example is the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017, which impacted organizations globally, including the UK's National Health Service, leading to disruptions in critical healthcare services.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS):DDoS attacks involve overwhelming a server with excessive traffic, causing services to become unavailable. Such an attack disrupted a planned live interview between Elon Musk and Donald Trump on X during the 2024 US Presidential election.
- Malware:Malware encompasses various forms of harmful software, including viruses, worms, and spyware, which can disrupt systems, steal information, or damage files. A prime example is the 2010 Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iran's nuclear facilities, damaging centrifuges and hindering nuclear development.
Challenges
- Evolving Attack Methods:Cyber attackers constantly innovate their techniques, making it challenging for defenses to keep up. Ransomware has notably evolved into a double extortion model, where attackers threaten to leak sensitive data in addition to locking it if the ransom isn't paid.
- Lack of Skilled Cybersecurity Professionals:The demand for qualified cybersecurity experts frequently exceeds the available supply, leaving many organizations vulnerable to attacks.
- Cross-Border Complexity:Many cyber attacks originate from outside national borders, complicating law enforcement efforts and international cooperation.
- Rising Costs and Impact on Critical Infrastructure:Cyber attacks can incur substantial financial costs for those affected and disrupt essential services. For instance, a ransomware attack in 2023 on a vital Indian defense unit highlighted the national security risks associated with such incidents.
Ransomware Attack on Defence Unit and Surge in Cyber Crimes
- A significant defense unit was compromised by a ransomware attack in 2023.
- In October 2023, Resecurity reported a major data breach at the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), which exposed Aadhaar and passport details of 81 crore Indians.
- CERT-In recorded 15,92,917 cybersecurity incidents in 2023, including website intrusions, phishing attacks, and data breaches, marking a dramatic increase from 53,117 incidents in 2017.
- Collaborative remedial measures were implemented with stakeholders to address these issues.
Cross-Border Cyber Fraud Investigations and International Collaboration
- The CBI collaborated with international agencies, such as the FBI, Royal Canadian Mounted Police, and Singapore police, to dismantle fraud networks operating from India.
- Notable cases included cryptocurrency scams, call center fraud targeting U.S. and Canadian citizens, and crypto fraud linked to tax evasion in Australia.
Cyber Crime Impact on Indian Citizens and Financial Fraud Investigations
- The CBI addressed cyber fraud issues affecting Indian citizens, including app-based investment scams originating from neighboring countries.
- An IMPS fraud case initiated by the RBI involved ₹820 crore in reversed transactions across various banks.
Revised Cybersecurity Oversight and Coordination Roles
- In September 2023, the Cabinet Secretariat updated the Allocation of Business Rules.
- The National Security Council Secretariat, under NSA Ajit Doval, was tasked with leading cybersecurity coordination.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology was designated to secure telecom networks, while the Ministry of Home Affairs was assigned to manage cybercrime incidents.
GS1/History & Culture
What is a Menhir?
Source: Deccan Herald

Why in News?
An Iron Age menhir, referred to locally as ‘Niluvu Rayi,’ is a memorial pillar located in Kamasanpalli village of Nagarkurnool district in Telangana, which is currently facing neglect.
About Menhir:
- A menhir is defined as a large upright standing stone.
- Menhirs can be found either as isolated monoliths or as part of groups of similar stones.
- These stones are distributed across various regions, including Europe, Africa, and Asia, with the highest concentration found in Western Europe.
- Menhirs vary significantly in size; their shapes are typically uneven and squared, often narrowing towards the top.
- In many cases, menhirs were arranged together to form circles, semicircles, or extensive ellipses.
- Megalithic menhirs were sometimes positioned in parallel rows, known as alignments.
- The most notable alignment is found in Carnac, France, which comprises 2,935 menhirs.
- Some menhirs feature engravings of abstract designs, including lines and spirals, as well as images of objects like axes.
- The exact purposes of menhirs remain largely speculative; however, it is believed that many were associated with fertility rites and seasonal events.
GS2/Polity
National Company Law Tribunal
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
Recently, the Supreme Court of India underscored the frequent issue of member shortages in the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) and the lack of adequate infrastructure that hampers its operations.
About
- The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) serves as a quasi-judicial body established to address corporate disputes of a civil nature under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It was officially constituted on June 1, 2016, in accordance with the Companies Act, 2013.
- The creation of the NCLT was influenced by recommendations from the Balakrishna Eradi committee, which focused on laws concerning insolvency and the winding up of companies.
Composition
- The Tribunal is composed of a President along with a requisite number of Judicial and Technical Members as needed.
What are the Powers of NCLT?
- The NCLT operates without being restricted by the rules outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure, adhering instead to principles of natural justice, while also complying with relevant statutory provisions and rules set forth by the Central Government.
- It possesses the authority to enforce its orders in a manner akin to that of a court.
- The Tribunal can review and scrutinize its own orders.
- It is empowered to regulate its own procedures.
- The NCLT acts as the adjudicating authority for the insolvency resolution process pertaining to companies and limited liability partnerships, as per the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
GS3/Environment
Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary
Source:Times of India

Why in News?
Environmental activists have raised concerns regarding the increasing dangers faced by elephants in Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary, particularly following the tragic death of a young male elephant due to electrocution.
About Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: The sanctuary is situated in the Shimoga District of Karnataka, encompassing an area of 395.6 square kilometers. It was officially designated as a wildlife sanctuary on November 23, 1974.
- Associated Areas: The sanctuary includes the Mandagadde Natural Bird Sanctuary, which is located on a small island in the River Tunga. Additionally, the Tunga Anicut Dam, found within the sanctuary, serves as a habitat for otters and various water birds.
- Human Settlements: There are numerous human settlements within the Shettihalli Sanctuary, primarily consisting of families displaced during the construction of the Sharavathi Dam in the 1960s.
- Vegetation:The sanctuary predominantly features Dry and Moist Deciduous Forests in its eastern and central regions. Towards the western side, with the increase in rainfall, Semi-evergreen Forests become more prevalent.
- Flora:The sanctuary is home to several significant tree species, including silver oak, teak, Indian Thorny Bamboo, Calcutta Bamboo, Asan, Tectona Grandis, Sweet Indrajao, and Amla.
- Fauna:
- The sanctuary is inhabited by various mammals such as tigers, leopards, wild dogs, jackals, gaurs, elephants, sloth bears, sambars, spotted deer, wild pigs, common langurs, and bonnet macaques.
- Numerous bird species can also be found here, including hornbills, kingfishers, bulbuls, parakeets, doves, pigeons, babblers, flycatchers, munias, swallows, woodpeckers, peafowl, jungle fowl, and partridges.
GS3/Science and Technology
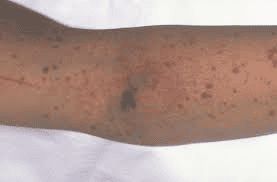
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
Source:The Hindu
Why in News?
A recent study has identified a link between the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech and immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP).
About Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP):
- TTP is a rare but severe blood disorder that can be life-threatening.
- The term “Thrombotic” indicates the formation of blood clots.
- “Thrombocytopenic” refers to a lower-than-normal count of platelets in the blood.
- “Purpura” describes the purple bruises that appear due to bleeding beneath the skin.
- In TTP, blood clots occur in small blood vessels throughout the body.
- These clots can restrict or obstruct blood flow to vital organs, including the brain, kidneys, and heart.
- This blockage can impair organ function and may cause damage.
- The excessive clotting in TTP consumes platelets, which are crucial for forming blood clots.
- With depleted platelets, the body may struggle to form clots when necessary, leading to internal bleeding and bruising.
What causes TTP?
- TTP arises from an insufficient amount of an enzyme known as ADAMTS13, which is essential for regulating blood clotting.
- A deficiency in this enzyme leads to the formation of excessive blood clots.
- TTP can be either inherited or acquired.
- The condition typically presents suddenly and can last from several days to weeks, and in some cases, it may continue for months.
- Additionally, TTP can accelerate the breakdown of red blood cells, resulting in a rare type of anemia called hemolytic anemia.
- Symptoms of TTP:
- Bleeding into the skin or mucous membranes.
- Confusion and altered mental state.
- Fatigue and general weakness.
- Fever and headaches.
- Pale or yellowish skin.
- Shortness of breath.
- Rapid heart rate (over 100 beats per minute).
- If untreated, TTP can lead to severe complications, including brain damage or stroke.
- Treatment:
- Common treatments include plasma therapies and medications specifically targeted at managing TTP.
- If these treatments fail, surgical options may be considered.
GS3/Environment and Ecology
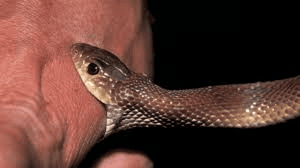
Snakebite Envenoming
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has officially classified snakebite envenomation as a notifiable disease under the Tamil Nadu Public Health Act of 1939.
About Snakebite Envenoming:
- Snakebite envenoming is a serious medical emergency caused by the bite of venomous snakes.
- This condition is a significant health issue, especially in rural areas and regions where snakes are common.
- It mainly threatens vulnerable groups, such as agricultural workers, children, and individuals residing in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Antivenoms are effective treatments that can counteract the harmful effects of snake venom and are recognized as essential medicines by the WHO.
- The World Health Organization has identified snakebite as a pressing global health challenge and has initiated a global strategy aimed at decreasing the number of deaths and disabilities caused by snakebites.
India’s Action Plan:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has introduced the National Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Snakebite Envenoming.
- This plan aims to reduce the number of snakebite fatalities by 50% by the year 2030 through a 'One Health' approach, which combines human health, animal health, and environmental health initiatives.
Advantages of Notifiable Disease Status:
- By designating snakebite as a notifiable disease, the Tamil Nadu government seeks to enhance data collection related to snakebites, bolster clinical infrastructure, and ensure proper distribution of antivenom.
- This initiative is projected to improve prevention strategies, lower mortality rates, and upgrade treatment facilities throughout the state.
- Under this new regulation, both public and private healthcare institutions are now mandated to report snakebite cases and any associated deaths to the government.
- This reporting system will be integrated with the State’s Integrated Health Information Platform, part of the Integrated Disease Surveillance Program.
GS3/Science and Technology
Caterpillar fungus
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
New research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus that has shown promise as a possible cancer treatment has revealed how it interacts with genes to interrupt cell growth signals.
About
- Caterpillar fungus: The scientific name is Ophiocordyceps Sinensis, which is a fungal parasite that infects caterpillar larvae belonging to the ghost moth species.
- Habitat: This fungus is primarily found in the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding high Himalayan regions, typically at altitudes between 3,200 to 4,500 meters above sea level.
- Local Names: It is known by various names in different regions: Kira Jari in India, Yartsagunbu in Tibet, Yarso Gumbub in Bhutan, Dong Chong Xia Cao in China, and Yarsagumba in Nepal.
- Distribution in India: In the Indian Himalayas, it has been documented in alpine meadows within protected areas such as Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, Askot Wildlife Sanctuary, Kanchendzonga Biosphere Reserve, and Dehan-Debang Biosphere Reserve.
Conservation status
- IUCN Status: The caterpillar fungus is classified as Vulnerable according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
What researchers found?
- Cordycepin: The chemical Cordycepin has been identified as a substance that disrupts the overactive cell growth signals associated with cancer.
- Mechanism of Action: This chemical is transformed into cordycepin triphosphate, which has been shown to directly impact cancer cells, potentially providing a treatment option that minimizes harm to healthy tissues compared to existing therapies.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















