UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 11th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Nutrient Based Subsidy scheme
Why in News?
Recently, the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) has recommended the Centre to bring urea under the nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) regime to address the problem of imbalanced use of nutrients.
About Nutrient Based Subsidy scheme:
- It is being implemented in 2010 by the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
- A fixed amount of subsidy decided on annual basis, is provided on each grade of subsidized Phosphatic & Potassic (P&K) fertilizers depending on its Nutrient Content.
- In case of phosphate (P) and potassic (K)fertilisers, subsidy is fixed under this scheme by an inter-ministerial committee taking into account the benchmark international prices of finished fertilisers as well as raw materials.
- The subsidy is given to registered to P&K fertiliser manufacturers/importers which provides these fertilisers at subsidised rates to farmers.
- Benefits of the scheme
- It helps farmers in ensuring availability of essential nutrients at subsidized prices.
- It rationalizes the subsidy on P&K fertilizers, ensuring effective and efficient utilization of government resources.
Source: DTE
National Training Conclave

Why in News?
Prime Minister will inaugurate the first National Training Conclave at the International Exhibition and Convention Centre Pragati Maidan, New Delhi.
About National Training Conclave:
- The conclave is part of the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) - ‘Mission Karmayogi’.
- Objective: To foster collaboration among civil services training institutes and strengthen the training infrastructure for civil servants across the country.
- The Conclave is being hosted by the Capacity Building Commission.
- More than one thousand 500 representatives from various training institutes, including Central Training Institutes, State Administrative Training Institutes, Regional and Zonal Training Institutes, and Research institutes, will participate in the conclave.
- Civil Servants from the Central government departments, State governments, and local governments, as well as experts from the private sector, will take part in the deliberations.
- The Conclave will have eight-panel discussions, each focusing on key concerns related to Civil services training institutes such as faculty development, training impact assessment, and content digitisation.
What is Mission Karmayogi?
- Mission Karmyogi, or National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), aims to prepare Civil Servants for the future by making them more creative, constructive & innovative through transparency and technology.
- This unique programme will help to lay the foundation for civil servants in the country.
- There will be more focus on 'on-site learning' in complementing "off-site learning".
- Executing Bodies:
- It will be steered by four new bodies.
- The new entities will be a Prime Minister’s Public Human Resources Council, a Capacity Building Commission, a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that will own and operate the digital assets and technological platform for online training, and a Coordination Unit, which will be headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
Source: Newsonair
GS-II
India’s G20 Presidency: Embracing Inclusivity, Ambition, and Action
Why in News?
India’s G20 presidency, characterized by the keywords “inclusive, ambitious, and action-oriented,” has made substantial progress in delivering on its promise of inclusivity. By prioritizing the basic necessities of life for every citizen, India has exhibited a strong commitment to social security support and people-centric development.
Inclusive Development Initiatives during India’s G20 presidency
- Digital Public Infrastructure: India’s robust digital infrastructure has played a crucial role in delivering the benefits of development directly to citizens across the country. This transparent and corruption-free system has ensured that developmental programs reach every corner of the nation, bridging the digital divide and empowering citizens.
- Access to Basic Necessities: The government has prioritized providing every citizen with access to basic necessities. For example, around 110 million rural households have been provided with access to clean drinking water at their homes. Additionally, more than 110 million sanitation facilities have been constructed across the country, improving public health and hygiene.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana: This flagship financial inclusion program has been instrumental in providing banking services to previously unbanked sections of society. With a focus on women-led development, the scheme has witnessed significant participation, with 56% of Jan Dhan account holders being women, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Women-Led Development: Recognizing the pivotal role of women in driving development, India’s G20 presidency has prioritized women’s empowerment. Policies and initiatives have been designed to foster gender equality, enhance women’s participation in various sectors, and promote their overall well-being.
How India’s Foreign Policy consistently prioritized working for the global public good?
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief: India has a long-standing tradition of providing humanitarian assistance and disaster relief to countries in need. In times of crises India has extended its support by offering medical aid and supplies. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, India provided essential medical supplies to over 190 countries and shared vaccines through the Vaccine Maitri program with more than 150 countries.
- Development Cooperation: Through programs such as the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) and the Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS), India has offered capacity building, technical assistance, and development projects in various sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- Multilateral Engagements: India actively collaborates with other nations to find collective solutions to issues like climate change, sustainable development, peacekeeping, and poverty eradication. India’s engagement in forums such as the United Nations, G20, BRICS, and regional organizations like SAARC and ASEAN reflects its commitment to multilateralism and working towards common goals.
- Peacekeeping Operations: India has consistently been one of the largest contributors to UN peacekeeping missions. Indian peacekeepers have played a crucial role in maintaining peace and stability in conflict-affected regions around the world.
- South-South Cooperation: India actively engages in South-South cooperation, which involves sharing knowledge, experiences, and resources among developing countries. India has partnered with other developing nations to address common challenges, share best practices, and promote mutual growth and development.
What is Pro-Planet People’s Movement?
- Prime Minister Modi’s call for a “pro-planet people’s movement” to combat climate change epitomizes inclusivity in its true essence.
- Aligned with this year’s G20 theme of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam or One Earth, One Family, One Future, India demonstrates its holistic worldview, emphasizing collective efforts for global good.
- Derived from the ancient Sanskrit text, the Maha Upanishad, this theme underscores the interconnectedness and value of all life forms, emphasizing the planet Earth’s broader universe
Inclusivity at the Core of India’s G20 Presidency
- Geographic Representation: India has taken steps to ensure geographic inclusivity by holding G20 meetings in different locations across the country, covering all states and Union Territories.
- African Representation: India has actively invited African nations to participate in its G20 Presidency, demonstrating a commitment to inclusivity and engagement with the African continent. Countries such as South Africa, Comoros (African Union Chair), Nigeria, Egypt, and Mauritius have been invited, giving a strong voice to Africa within the G20 discussions.
- Engagement of Non-G20 Members: India has extended invitations to non-G20 member countries, regional organizations, and international organizations for specific G20 meetings. This initiative enriches the discussions by incorporating perspectives and expertise from a wider range of stakeholders. For example, Norway, known for its expertise in the blue economy, has been invited to contribute to the G20 meeting on ocean health.
- Regional and International Organizations: In line with the inclusive approach, India has invited regional and international organizations to participate in specific G20 meetings. This facilitates dialogue and collaboration with organizations such as the United Nations, World Bank, IMF, and other relevant institutions.
- People-Oriented Approach: India’s G20 Presidency adopts a people-oriented approach, encouraging the active participation and engagement of citizens. Various events, including seminars, conferences, and festivals, have been designed to involve the public and make them stakeholders in India’s G20 Presidency.
Conclusion
- India’s G20 presidency embodies the values of inclusivity, ambition, and action. By prioritizing the most vulnerable citizens of the world, India aims to foster human-centric development. In an era of global crises, the significance of upholding the sentiment of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam has never been more crucial. India remains committed to inclusivity, ensuring the participation of all in the path to growth and prosperity.
Source: The Hindu
Revitalizing India-Nepal Bilateral Relations through Pragmatism and Cooperation

Why in News?
Nepal’s democracy, governance, and stability face numerous challenges, along with persistent bilateral irritants with India. However, the recent bilateral visit of Prime Minister Pushpa Kamal Dahal Prachanda to India has highlighted the potential of a pragmatic approach and mutual sensitivity in re-energizing the relationship between the two nations.
The challenge faced by Nepal in depoliticizing cooperation with India
- Political Influence: Nepal’s domestic political dynamics often influence the country’s engagement with India. Political parties and leaders may prioritize their own interests or use cooperation with India as a political tool, leading to the politicization of bilateral issues and hindering effective collaboration.
- Water Resources Cooperation: One area where depoliticization is crucial is water resources cooperation. The development of hydropower projects and the management of shared rivers require technical and practical solutions that are free from political interference. Depoliticizing water resources cooperation is essential to ensure long-term sustainability and mutual benefits.
- Quality of Democracy and Governance: Strengthening the quality of democracy and governance within Nepal is vital to reduce the influence of political factors on bilateral relations. By promoting transparent and accountable governance structures, Nepal can create an environment that prioritizes national interests over political considerations.
- Perception of Foreign Policy Priority: There is a perception among some in Nepal that India no longer considers the country a foreign policy priority. Addressing this perception and reaffirming Nepal’s importance to India’s foreign policy agenda can help build trust and create a sense of shared ownership in bilateral cooperation.
- Inclusive Approach: Nepal needs to ensure that cooperation with India is not limited to the government of the day but involves all stakeholders across the political spectrum. Providing a sense of ownership, equality, and credit for major advancements to all parties fosters a more inclusive approach and reduces the politicization of bilateral relations
Significance of the recent bilateral visit
- Re-energizing Bilateral Relations: The visit signifies a renewed commitment to re-energizing and strengthening bilateral relations between Nepal and India. It highlights the willingness of both nations to address challenges, enhance cooperation, and foster a positive trajectory in their relationship.
- Comprehensive Review of Bilateral Agenda: Discussions covered various areas such as politics, economics, trade, energy, security, and developmental cooperation, allowing both sides to identify priorities and areas of mutual interest.
- Addressing Daunting Challenges: Despite the daunting challenges faced by Nepal’s democracy, governance, and stability, the visit demonstrated that pragmatic approaches and mutual sensitivity can help overcome these challenges.
- Economic Integration: The visit underscored the significance of economic integration between the two nations. Emphasis was placed on “game changers” such as hydropower projects, infrastructure development, tourism circuits, and improved connectivity.
- Power Sector Cooperation: Cooperation in the power sector, including the transmission passage from Nepal to Bangladesh through India, was an important aspect of the visit. Agreements and efforts to increase power trade and collaboration in this sector have the potential to bring prosperity to the entire sub-region.
- Digital Connectivity and Space Cooperation: The visit also focused on enhancing digital financial connectivity and regional cooperation in the space sector. Initiatives such as facilitating cross-border digital payments and providing satellite services highlight the potential for collaboration in telecommunication, broadcasting, tele-medicine, tele-education, and other areas.
- Building Trust and Confidence: The visit helped in building trust and confidence between the leaders of both countries. Reassurances regarding the resolution of differences on border issues and avoiding attempts to justify official versions of the border as the correct one contributes to a more positive atmosphere.
Realistic Handling of Bilateral Issues
- Political Courage: Despite being in a weak position as the leader of the third-largest party in Parliament, Prachanda demonstrated political courage by considering the costs and benefits of various approaches to bilateral issues.
- Calculated Decision-making: Prachanda shrewdly calculated the costs of paying heed to political noises cautioning against being soft on irritants like the 1950 Treaty, border differences, and India’s reluctance to receive the report of the Eminent Persons Group (EPG).
- Listening to Voices of Reason and Moderation: Rather than succumbing to the spectrum of political dissent, Prachanda chose to listen to the few voices of reason and moderation. This approach helped him focus on opportunities for building a better future.
- Pragmatic Approach: Prachanda’s approach was pragmatic, taking into account the challenges presented by the post-COVID-19 world, current realities, and the significant opportunities for bilateral cooperation.
- Focus on Opportunities: Instead of getting caught up in political instability and distractions, Prachanda focused on the opportunities for cooperation and collaboration between India and Nepal.
Cooperation in the Power Sector and Digital Connectivity
- Power Sector Cooperation: The visit highlighted the transmission passage from Nepal to Bangladesh through India, enabling trilateral power transactions. Agreements were made to increase the quantum of power export from Nepal to India to 10,000 MW within a timeframe of 10 years, presenting significant opportunities for economic growth and energy security in the region.
- Hydropower Projects: The development of hydropower projects in Nepal can not only meet the increasing energy demands of India but also contribute to Nepal’s economic growth. The visit highlighted the importance of hydropower projects that can supply energy to India and potentially to Bangladesh, opening new avenues for regional collaboration and prosperity.
- Digital Connectivity: The memorandum of understanding (MoU) between the National Payments Corporation of India and the Nepal Clearing House Ltd. facilitates cross-border digital payments, promoting seamless financial transactions and facilitating trade between the two countries.
- Space Sector Cooperation: India offered to create a ground station and supply user terminals to provide satellite services of the South Asia Satellite to Nepal. This cooperation can have wide-ranging applications in telecommunication, broadcasting, tele-medicine, tele-education, disaster response, and meteorological data transmission. It promotes regional cooperation in space technology and its practical applications across various sectors.
Way ahead
- Dialogue and Engagement: Sustained and regular dialogue between the leaders and officials of both countries is crucial. This helps address concerns, build trust, and foster a deeper understanding of each other’s perspectives. Regular high-level visits, diplomatic exchanges, and people-to-people interactions can help maintain open channels of communication.
- Depoliticize Cooperation: Nepal should strive to depoliticize cooperation with India, particularly in critical areas such as water resources management. By prioritizing technical expertise, scientific assessments, and mutual benefits, both countries can work towards sustainable solutions that are not influenced by short-term political considerations.
- Economic Integration: Enhancing economic integration is vital for strengthening bilateral relations. Efforts should focus on facilitating trade, investment, and cross-border connectivity. Expanding infrastructure, improving border infrastructure, and streamlining customs procedures can promote seamless economic cooperation and foster shared prosperity.
- People-to-People Exchanges: Encouraging cultural and educational exchanges between India and Nepal can promote greater understanding and friendship at the grassroots level. Encouraging tourism, promoting student exchanges, and facilitating cultural events can contribute to stronger people-to-people bonds.
- Addressing Perception Issues: India needs to address the perception in Nepal that it is no longer a foreign policy priority. Demonstrating a consistent commitment to bilateral relations, engaging with diverse stakeholders, and providing equal opportunities for cooperation can help overcome this perception and build trust.
- Collaboration in Regional Forums: Both countries can collaborate within regional forums such as the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC). Active participation in these platforms can foster greater regional cooperation and provide opportunities for addressing common challenges.
- Good Governance and Anti-corruption Measures: Nepal should prioritize good governance and anti-corruption measures. Strengthening institutions, promoting transparency, and curbing corruption will not only enhance domestic governance but also inspire confidence in India and other partners for increased cooperation.
Conclusion
- Despite the daunting challenges, the recent bilateral visit between the Prime Ministers of Nepal and India highlights the potential for re-energizing their relations through pragmatism and cooperation. By prioritizing development and cooperation, both nations can pave the way for a prosperous future in the sub-region.
Source: Indian Express
Jal Jeevan Mission: Saving Lives through Access to Piped Water
Why in News?
Potable water: The Jal Jeevan Mission aims to provide piped potable water to all of India.
- Potential Life-Saving Impact: If successful, the mission could avert nearly 400000 deaths from diarrhoea.
- Reduction in Disease Burden: The mission could avoid 14 million DALYs (Disability Adjusted Life Years) related to diarrhoea.
About Jal Jeevan Mission
- Launch: Government initiative launched in 2019
- Goal: Provide access to clean and piped drinking water to every rural household
- Focus: Water supply infrastructure development, community participation, water quality monitoring
- Objective: Improve health, well-being, and productivity of rural communities, Addressing challenges of water scarcity, contamination, and inadequate infrastructure
- Target: Achieve 100% coverage by 2024 for reliable and sustainable water supply
- Definition of functional Connection: A fully functional tap water connection means receiving at least 55 litres of potable water per capita per day throughout the year
The key objectives of the Jal Jeevan Mission include:
- Universal coverage: Mission aims to achieve tap water connections for all rural households, ensuring access to potable water within premises.
- Sustainability: Focus on long-term sustainability through community participation, water resource management, and water conservation practices.
- Quality assurance: Prioritizing safe and clean drinking water by implementing water quality monitoring systems and adhering to prescribed standards set by BIS.
- Convergence and coordination: Emphasis on collaboration among stakeholders to effectively achieve mission objectives.
Socioeconomic Benefits of the Mission
- Economic Savings: The study suggests that the mission could save close to $101 billion.
- Time Savings: It could save 66.6 million hours per day that would have been spent collecting water, primarily by women.
- Improved Quality of Life: Access to piped water connections would enhance convenience and overall well-being.
- Sanitation benefits: Every dollar invested in sanitation interventions yields a $4.3 return in reduced healthcare costs.
Progress status of the scheme
- Current Coverage Levels: Around 62% of rural households have piped water connections.
- States and UTs at Full Coverage: Five states and three Union Territories have reported 100% coverage.
- Progress of states: Himachal Pradesh is at 98.87% coverage, while Bihar is at 96.30% and nearing saturation.
Limitations and Considerations of the Study
- Extrapolation of Data: The study extrapolates data and does not compute current levels of coverage.
- Contamination Concerns: The study does not account for the degree of contamination in the piped water provided.
- Data Sources: The authors used population data from the United Nations, the 2018 National Sample Survey, and water quality data collected by the Jal Jeevan Mission.
Challenges Addressed by the Mission
- Water scarcity: Mission aims to tackle the challenge of inadequate water availability in rural areas.
- Contamination: Focus on improving water quality and addressing issues of waterborne diseases.
- Infrastructure gaps: Efforts to bridge the gap in water supply infrastructure in rural regions.
Way forward
- Enhancing Capacity of Local Bodies: Provide support and resources to strengthen the capacity of local governance institutions in effectively managing and governing rural water supply systems.
- Promoting Community Participation: Foster active community participation in decision-making processes related to water infrastructure planning, implementation, and maintenance.
- Empowering Local Water User Committees: Strengthen the role of local water user committees in monitoring and regulating water supply services, promoting their active involvement in decision-making.
- Participatory Planning: Facilitate participatory planning processes, where water user associations actively contribute to the development of water management plans, considering local needs and priorities.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Operation Amanat

Why in News?
The Railway Protection Force (RPF) recently conducted a successful operation named "Amanat," resulting in the retrieval of lost or left-behind luggage and valuable articles.
About Operation Amanat:
- Under the Operation Amanat initiative, the Railway Protection Force has taken a novel initiative to make it easier for the passengers to get back their lost luggage.
- It helps to track lost belongings of passengers.
- The details of lost luggage along with photos are uploaded by RPF personnel of the respective Divisions. The details are uploaded in the web portal https://wr.indianrailways.gov.in/ in the tab of divisions under the link “Mission Amanat – RPF”.
- Passengers can check whether their luggage which went missing or was lost in railway premises or trains is available at the Lost Property Office centres at stations.
Key facts about Railway Protection Force (RPF):
- RPF is a security force of India entrusted with protecting railway passengers, passenger area and railway property of the Indian Railways.
- It was established by the Railway Protection Force Act, 1957.
- This is only central armed police force (CAPF, commonly known as Para-Military force) which has power to arrest, investigate and prosecute criminals.
- It is under the authority of Ministry of Railways (India).
- All the officers of RPF are members of the Indian Railway Protection Force Service (IRPFS) and are recruited through UPSC Civil Services Examination.
- It is headed by the Director General (DG). However, the post of Director-General of RPF is held on deputation by a senior Indian Police Service (IPS) officer.
Source: PIB
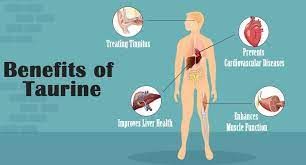
Taurine
Why in News?
A recent study suggests that ageing mice, worms and monkeys can live longer or healthier lives when fed large amounts of taurine.
About Taurine:
- It is a naturally occurring sulfur-containing amino acid.
- It’s particularly concentrated in your brain, eyes, heart, and muscles.
- Sources: Taurine occurs naturally in foods with protein, such as meat or fish.
- Functions:
- The human body uses taurine for actions in cells. One example is that taurine is used for energy production.
- Taurine also helps the body process bile acid and balance fluids, salts and minerals, among other actions.
- It has important functions in the heart and brain. It helps support nerve growth.
- It might also benefit people with heart failure by lowering blood pressure and calming the nervous system.
- It is also used for obesity, athletic performance, fatigue, diabetes, and many other conditions.
What are Amino Acids?
- An amino acid is the fundamental molecule that serves as the building block for proteins.
- There are 20 different amino acids.
- A protein consists of one or more chains of amino acids (called polypeptides) whose sequence is encoded in a gene.
- Some amino acids can be synthesized in the body, but others (essential amino acids) cannot and must be obtained from a person’s diet.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5283 docs|1116 tests
|