UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 12 July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Vizhinjam Port Welcomes its First Mothership
Source: Outlook India

Why in news?
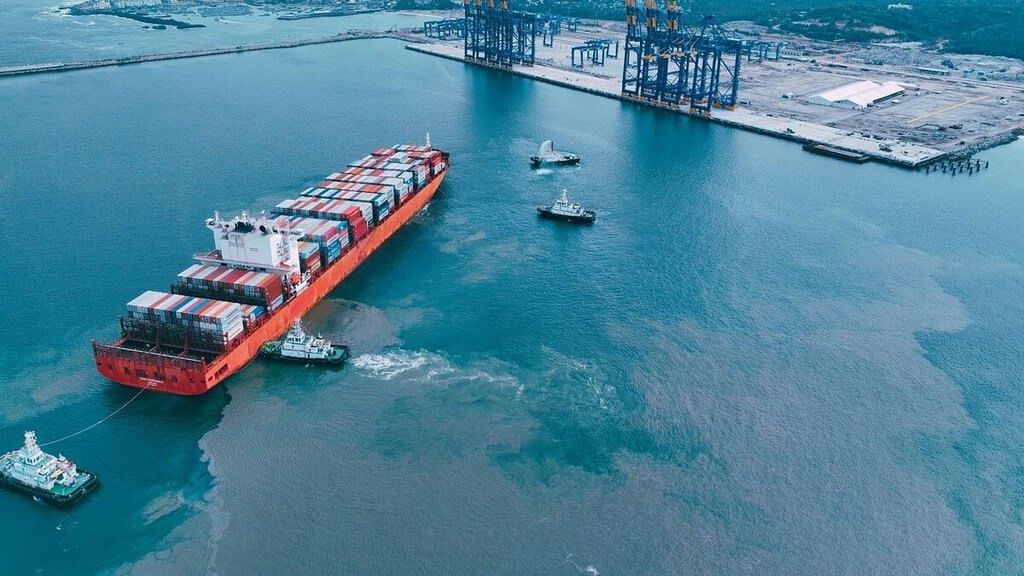
India's first deep-water transshipment port, the Vizhinjam international seaport near Thiruvananthapuram, received its first mothership (a mothership refers to a large cargo vessel that acts as a central hub for the transshipment of goods). The MV San Fernando, carrying 2,000 containers, was given a grand welcome at the port. The berthing of the ship was part of a trial run at the port before it is slated to open for commercial operations.
Deepwater port
- A deepwater port is a manmade structure that is used as ports or terminals to transport, store, or handle oil or natural gas.
- These structures can be fixed or floating, and are located beyond state seaward boundaries.
- They can include: Pipelines, Pumping stations, Service platforms, Mooring buoys.
Transshipment port
- A transshipment port is a port where goods are offloaded and loaded onto a different ship to continue their journey to their final destination.
Why India needs a container transshipment port?
- Lacks infrastructure to deal with ultra-large container ships
- India has 13 major ports. However, the country lacks a landside mega-port and terminal infrastructure to deal with ultra-large container ships.
- Hence, nearly 75 per cent of India's transshipment cargo is handled at ports outside India, mainly Colombo, Singapore, and Klang.
- In fiscal 2021-22, the total transshipment cargo of India was about 4.6 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units), out of which about 4.2 million TEUs were handled outside India.
Other benefits
- Developing such ports will accrue significant benefits such as forex savings, foreign direct investment, increased economic activity at other Indian Ports.
- It will also lead to the development of related logistics infrastructure, employment generation, improved operation/logistics efficiencies and increase in revenue share.
- Several other allied businesses ship chandlery-ship supplies, ship repair, crew change facility, logistics value-added services, warehousing and bunkering also come up at the transshipment port.
Increased economic activities
- A deepwater container transshipment port can attract a large share of the container transshipment traffic.
- Currently, this is being diverted to Colombo, Singapore and Dubai.
- It can also ensure India's economic development and open up immense job opportunities.
Vizhinjam International Seaport Project
- Located in Vizhinjam (near Thiruvananthapuram), Kerala, this transshipment deepwater multipurpose seaport project is being built by Adani Ports and SEZ Private Limited.
- It is being built on a design, build, finance, operate and transfer (DBFOT) model
- The DBFOT model is a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model. In this model, a private partner is responsible for:
- Designing the project
- Building the project
- Financing the project
- Operating the project during the contracted period
- According to the agreement, out of the total investment, Adani Group is supposed to invest Rs 2,454 crore and another Rs 1,635 crore will be mobilized from the state and central governments as viability gap funding.
- The Kerala government has also given 500 acres of land.
- DBFOT deal is for 40 years, with provisions extending for 20 years
Features of the Vizhinjam port
- India's first international deepwater transshipment port
- This is India's first international deepwater transshipment port with a natural depth of more than 18 meters, scalable up to 20 meters.
- This depth is crucial to get large vessels and mother ships.
- It is designed to cater to container transshipment, multi-purpose, and break-bulk cargo.
- The cost of movement of containers to and from foreign destinations is likely to come down.
- Strategic location
- The port is located ten nautical miles from the international shipping route
- The port is expected to compete with Colombo, Singapore, and Dubai for winning trans-shipment traffic.
- Increased capacity and minimum maintenance
- Its capacity in the first phase is one million TEU, which can be increased to 6.2 million TEU.
- Other features include minimal littoral drift along the coast and virtually no requirement for any maintenance dredging.
- Economic benefits
- The project is expected to generate 5,000 direct job opportunities, apart from giving a boost to an industrial corridor and cruise tourism.
- Vizhinjam port offers large-scale automation for quick turnaround of vessels with state-of-the-art infrastructure to handle Megamax container ships.
GS-III/Environment & Biodiversity
Zoological Survey of India’s Report on Animal Discoveries 2023
Source: Hindustan Times
 Why in news?
Why in news?
A report titled “Animal Discoveries 2023” by the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) highlights significant new species findings in Maharashtra and across India.
New Species in Maharashtra:
Maharashtra recorded 14 new animal species in 2023, with two species reported for the first time in India.
Notably, among the 25 Arachnid species reported for the first time in India, two belong to Maharashtra—
- Steatoda Erigoniformis
- Myrmarachne Spissa
Steatoda Erigoniformis:
- It is a species of spider known for its resemblance to the more dangerous black widow spiders. They are commonly referred to as “false widow spiders.”
Myrmarachne Spissa:
- It is part of a group of spiders that mimic ants in appearance and behavior, a trait known as myrmecomorphy. Previously reported in Sri Lanka, Myrmarachne Spissa’s discovery in Pune marks its first report from India, highlighting the region’s biodiversity significance.
Key Findings from the ZSI Report:
- National Discoveries: In 2023, Indian scientists reported a total of 641 new discoveries, including 442 new species and 199 new records for India. This includes the discovery of 19 new genera. As of January 1, 2024, India’s faunal diversity stands at 104,561 species, with the additions in 2023 constituting 6.65% of the global faunal diversity.
- Categories of Discoveries: Invertebrates accounted for the majority of new discoveries with 564 species, while vertebrates contributed 77 species. Among invertebrates, insects led with 369 new species, while vertebrates were dominated by fish with 47 species, followed by reptiles, amphibians, and mammals.
- Regional Distribution: Kerala reported the highest number of new discoveries (101), followed by West Bengal (72), Tamil Nadu (64), Arunachal Pradesh (45), Karnataka (45), and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (36). Southern India consistently reports the highest number of species.
Back2Basics: Zoological Survey of India
- The ZSI was set up by British zoologist Thomas Nelson Annandale in 1916. It is the premier taxonomic research organization in India based in Kolkata. It was established to promote surveys, exploration, and research leading to the advancement of our knowledge of various aspects of the exceptionally rich animal life of India.
- The ZSI had its genesis as the Zoological Section Indian Museum at Calcutta in 1875. Since its inception, the ZSI has been documenting the diversity and distribution of the fauna of India towards carrying out its mandate of conducting exploration-cum-taxonomic-research programs. The ZSI has published an extremely large amount of information on all animal taxa, from Protozoa to Mammalia.
PYQ:
[2020] With reference to India’s Biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet, and White-throated redstart are:
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
GS3/Economy
National Gopal Ratna Award, 2024
Source: AIR

Why in news?
The National Gopal Ratna Award (NGRA) 2024 has been awarded by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying. The awards are conferred annually on National Milk Day, which is celebrated on 26th November.
What is the National Gopal Ratna Award (NGRA)?
- NGRA is an initiative under the Rashtriya Gokul Mission, launched by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
Objective
- The award aims to promote the conservation and development of indigenous bovine breeds, crucial for the sustainability of the dairy sector in India.
Categories
- NGRA is awarded in several categories:
- Best Dairy farmer rearing indigenous cattle/buffalo breeds.
- Best Dairy Cooperative Society (DCS)/ Milk Producer Company (MPC)/ Dairy Farmer Producer Organization (FPO).
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT).
Other aspects of the Award
- Special Recognition: In recent years, a special award category has been included for the North Eastern Region (NER) states to encourage dairy development activities in these regions.
- Nomination and Recognition: Nominations for the NGRA are submitted online through the National Award portal.
- Award Details:
- NGRA 2024 will confer awards in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd ranks, and one Special Award for the NER States in each category.
- Cash prizes for Best Dairy Farmer and Best DCS/FPO/MPC categories:
- Rs. 5,00,000/- (1st rank)
- Rs. 3,00,000/- (2nd rank)
- Rs. 2,00,000/- (3rd rank)
- Rs. 2,00,000/- (Special Award for NER).
- Best AIT category:
- Certificate of merit and a memento, without any cash prize.
Back2Basics: Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- About:
- Implemented for development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- Continued under the umbrella scheme Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojana from 2021 to 2026 with a budget of Rs.2400 crore.
- Nodal Ministry:
- Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying
- Objectives:
- Enhance productivity of bovines and increase milk production sustainably using advanced technologies.
- Propagate the use of high genetic merit bulls for breeding purposes.
- Enhance artificial insemination coverage by strengthening the breeding network and providing services at farmers’ doorsteps.
- Promote indigenous cattle & buffalo rearing and conservation in a scientific and holistic manner.
PYQ
[2015] Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sector in India.
GS2/International Relations
India Pitches for Infusing New Energies into BIMSTEC Grouping
Source: The Tribune
Why in News?
India has called on the seven-nation Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) grouping to infuse new energies, resources, and a fresh commitment to bolster cooperation among the Bay of Bengal countries.
About BIMSTEC (Background, Objectives, Members, Focus Areas, Challenges, etc.)
News Summary
About BIMSTEC:
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional organization founded in 1997 to promote economic cooperation and technical collaboration among countries bordering the Bay of Bengal.
- The BIMSTEC region is home to more than 1.7 billion people which constitute around 23% of the global population.
Member Countries:
- Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand
Objectives:
- Foster economic growth and development.
- Enhance regional connectivity and integration.
- Promote cooperation across various sectors such as trade, technology, energy, and transportation.
Priority Sectors:
- Trade and Investment: Boosting intra-regional trade and investments.
- Technology: Sharing technological advancements.
- Energy: Collaborating on renewable and sustainable energy projects.
- Transportation: Improving regional connectivity.
- Tourism: Promoting cultural and tourism exchanges.
- Agriculture: Enhancing agricultural practices and ensuring food security.
- Fisheries: Ensuring sustainable fisheries management.
Trade Dynamics:
- According to industry insiders, intra-regional trade among BIMSTEC countries is above US$40 billion and the potential trade opportunity evolving the BIMSTEC nations seems to be as high as US$250 billion.
- BIMSTEC countries constitute around 3.8% of world trade meaning that it has an immense potential to be a game-changer of the global south economy.
- Presently, about 60% of BIMSTEC's combined GDP at present comes from trade.
- Currently, India's export share in BIMSTEC is about 50% (US$21 billion), followed by Thailand 30% (US$12.2 billion) and Myanmar 14% (US$6.1 billion).
- Over 40% of BIMSTEC's intra-regional trade is ocean-borne, demonstrating the need for maritime connectivity.
Challenges for BIMSTEC as an Organisation:
- Intra-regional trade and investment are relatively lower in the BIMSTEC region as compared to other regional blocs.
- One of the major reasons for this low level of trade and investment is inadequate infrastructure.
- Moreover, lack of connectivity and information dissemination in the region appears as a common barrier for tap BIMSTEC-led opportunities.
- Regarding border trade, lack of telecommunication links, parking space, warehouses and cold storage, accommodation facilities and power are major constraints.
News Summary:
- India has urged the BIMSTEC group to bring new energy, resources, and commitment to enhance cooperation among its member countries.
- This call was made by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar during a two-day retreat with his counterparts from the seven BIMSTEC nations: India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Discussions on the first day included topics such as connectivity, trade and business collaboration, health and space cooperation, digital public infrastructure, capacity building, and societal exchanges.
- Jaishankar emphasized that BIMSTEC aligns with India's 'Neighbourhood First' policy, 'Act East Policy,' and 'SAGAR' vision, focusing on the Bay of Bengal region. He highlighted the need to realize the collaborative potential of the region and conveyed a strong message of determination to enhance cooperation among the member countries.
GS3/Defence & Security
Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill 2024
Source: Economic Times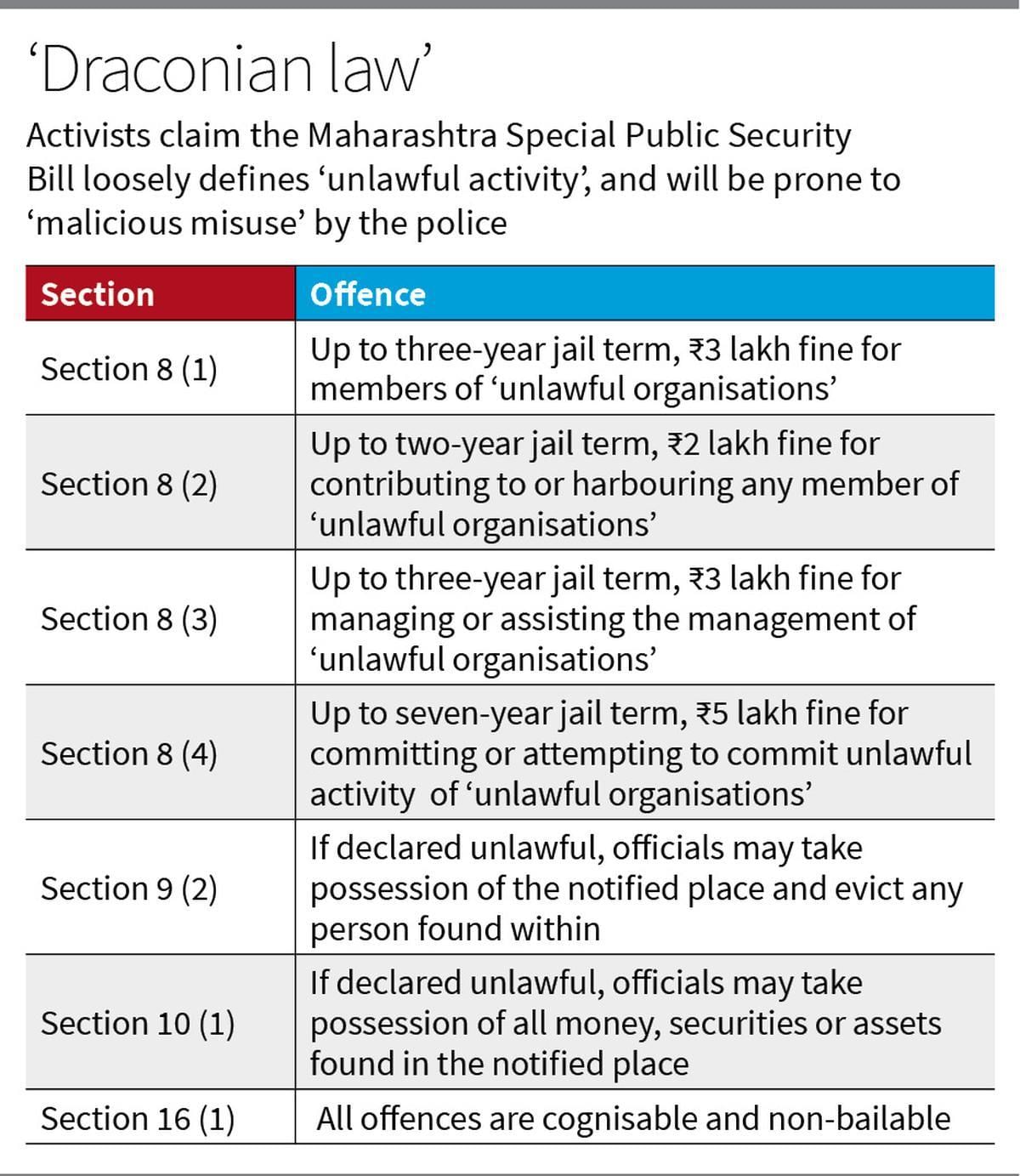
Why in news?
The Maharashtra government has introduced the Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, to tackle the increasing threat of Naxalism in urban areas, particularly through Naxal-affiliated organizations.
About
- The presence of and activities carried out by Naxalites or the CPI (Maoist) in urban areas are collectively referred to as Urban Maoism/Naxalism.
Maoist Document ‘Strategy and Tactics of Indian Revolution’:
- Urban movement is a vital source that provides cadres and leadership with essential capabilities for the people’s war and the establishment of liberated areas.
- The urban revolutionary movement is responsible for providing supplies, technology, expertise, information, and other support to the people’s war.
Three objectives of Maoist Urban work:
- Mobilizing and organizing masses.
- Building a United Front (Network of Mass Organizations).
- Performing Military Tasks.
Activities:
- Maintaining safe houses for leaders and cadres while in transit.
- Providing places for recuperation and holding meetings.
- Offering logistics support to underground squads.
- Mobilizing and recruiting youth, students, and workers from various sectors.
Purpose and Scope
- The Maharashtra government has introduced the Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, to combat the growing threat of Naxalism, particularly in urban areas through Naxal-affiliated organizations.
Declaration of Unlawful Organizations
- The state is empowered to declare an organization as "unlawful".
- An advisory board comprising three qualified individuals (current/former/qualified High Court judges) will review such decisions.
Definition of Unlawful Activities
- Activities that threaten public order, peace, and tranquility.
- Interference with law administration and public servants.
- Violence, vandalism, use of firearms, explosives, and disruption of transportation.
- Encouraging disobedience to law and institutions.
- Collecting funds or goods for unlawful activities.
Punishments
- Members of Unlawful Organizations: Imprisonment up to 3 years and fines up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Non-members Contributing or Aiding Unlawful Organizations: Imprisonment up to 2 years and fines up to Rs 2 lakh.
- Management or Promotion of Unlawful Organizations, Committing, Abetting, or Planning Unlawful Activities: Imprisonment up to 7 years and fines up to Rs 5 lakh.
Seizure and Forfeiture
- If an organization is declared unlawful, the District Magistrate or Commissioner of Police can notify and take possession of any place used for its activities.
- The government can confiscate money and assets intended for unlawful organizations.
Legal Review
- An advisory board must review the declaration of unlawful organizations within six weeks and submit a report within three months.
- The High Court can scrutinize government actions through revision petitions.
GS3/Science and Technology
Why are dengue cases on the rise worldwide?
Source: MSN
 Why in news?
Why in news?
In recent weeks, there has been an increase in dengue cases, notably in Karnataka, with rising numbers also observed in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
What is the global situation of dengue?
Epidemiological Burden:
- In 2024, over 7.6 million cases of dengue were reported globally, with 3.4 million confirmed cases and significant numbers of severe cases and deaths. Dengue affects approximately half of the world’s population, with an estimated 100-400 million infections occurring annually.
Geographical Distribution:
- Dengue transmission occurs in 90 countries worldwide, predominantly in tropical and subtropical regions. The disease is endemic in more than 100 countries across WHO regions, including Africa, the Americas, the Eastern Mediterranean, South-East Asia, and the Western Pacific.
Urbanization:
- Increased Population Density: Urban areas provide optimal conditions for the Aedes aegypti mosquito due to the availability of breeding sites like stagnant water in containers, tires, and other urban infrastructure.
- Expansion of Cities: Rapid urbanization leads to unplanned growth, inadequate waste management, and inadequate water supply, creating breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Human Movement: Urbanization facilitates increased human mobility, enabling the spread of the dengue virus through infected individuals travelling between urban centers.
Climate Change:
- Temperature and Rainfall Patterns: Warmer temperatures and altered rainfall patterns associated with climate change create favourable conditions for mosquito breeding and survival.
- Shifts in Geographic Distribution: Changing climate allows Aedes mosquitoes to expand their range to new regions previously unaffected by dengue, including temperate climates.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes and floods provide breeding opportunities for mosquitoes and facilitate virus transmission.
Impact:
- Health Impact: India accounts for an estimated 33 million clinically apparent dengue cases each year, contributing to a third of the global dengue burden.
- Economic Impact: A cost analysis study in southern India estimated the direct medical costs per hospitalized dengue patient at around ₹20,000 in 2017-18, with costs soaring to over ₹61,000 for complications requiring intensive care.
- Impact on Individuals: Dengue can cause a wide spectrum of illness, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe complications like internal bleeding, organ impairment, and potentially death if not treated promptly.
Way forward:
- Enhance Urban Infrastructure: Improve urban planning to include effective waste management, regular clearing of stagnant water sources, and sustainable water supply systems to reduce mosquito breeding grounds.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch comprehensive public awareness campaigns focusing on urban populations to promote community involvement in mosquito control measures and encourage responsible waste disposal practices.
Mains PYQ:
- Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector can help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives do you suggest? (UPSC IAS/2015)
GS3/Economy
Future investments in India's EV space
Source: Mint
Why in news?
The government plans to expand its EV policy to include retrospective benefits, incentivizing entities that have already invested, with a formal announcement expected in August.
Why is the government considering extending the EV policy?
- Retrospective Effect: To include a retrospective effect, extending benefits to entities that have already made investments, aiming to reward and encourage early movers in the EV sector.
- Encouraging Global Players: The policy seeks to prompt global players to localize production and invest in the domestic ecosystem.
- Inclusive Incentives: Earlier, entities were eligible for incentives only if they set up local facilities within three years of receiving approval. The extension aims to make these incentives more inclusive.
EV Policy of India:
- FAME Scheme:
The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme is India's flagship program to incentivize EV adoption. FAME-II, the current phase, provides incentives of:
- ₹15,000 per kWh for 2-wheelers, up to 40% of the vehicle cost
- ₹10,000 per kWh for 3-wheelers and 4-wheelers
- ₹20,000 per kWh for electric buses
- Phased Manufacturing Program (PMP):
To boost local manufacturing, the government has implemented a Phased Manufacturing Program that gradually increases import duties on EV components over time, incentivizing domestic production.
About the New EV Policy 2024:
- Reduced customs duty of 15% on imported EVs with a minimum CIF value of $35,000
- A cap of 8,000 imported EVs per year
- Requirement for manufacturers to invest at least ₹4,150 crore (~$500 million) and achieve 25% domestic value addition within 3 years, escalating to 50% in 5 years
- Duty waiver capped at the investment made or ₹6,484 crore (equal to the PLI scheme incentive), whichever is lower.
How does the revised policy align with India's goals of enhancing local manufacturing and technology adoption in the EV industry?
- Domestic Value Addition: The policy mandates that half of the value addition in manufacturing be done domestically within five years, boosting local manufacturing.
- Import Duty Reduction: Reducing import duty on EVs with a minimum CIF value of $35,000 from 70%-100% to 15% to make the transition commercially viable.
- Strengthening EV Ecosystem: By encouraging local production and investment, the policy aims to strengthen the entire EV ecosystem in India.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the global transition from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles by fostering a sustainable and technologically advanced manufacturing environment.
In what ways can the policy's focus on localization and production volume increase competition and lower costs?
- Economies of Scale: Higher volumes of production can lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost of EVs.
- Healthy Competition: Encouraging competition among EV players to innovate and improve efficiency, thereby lowering production costs and prices for consumers.
- Cost Reduction: Achieving higher production volumes and localized manufacturing will contribute to a significant decline in production costs, making EVs more affordable for Indian consumers.
- Comprehensive Ecosystem: The focus on localization ensures the development of a robust supply chain and after-sales service network, further enhancing the viability and attractiveness of EVs in India.
Way forward:
- Support Local Manufacturers: Provide incentives and support for domestic manufacturers to produce critical EV components such as batteries, motors, and controllers. This will reduce dependency on imports and enhance self-reliance.
- R&D Investment: Increase investment in research and development to drive innovation in EV technology, ensuring that India remains at the forefront of advancements in the industry.
Mains PYQ:
- 'Clean energy is the order of the day.' Describe briefly India's changing policy towards climate change in various international fora in the context of geopolitics. (UPSC IAS/2022)
GS3/Economy
Impose ‘Robot Tax’ for AI-induced Job Loss: RSS
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The Swadeshi Jagran Manch (SJM), affiliated with the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), advocates for a ‘robot tax’ to aid employees facing job displacement due to the implementation of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
SJM’s Proposals and Suggestions
- Robot Tax Proposal: SJM suggests a ‘robot tax’ to establish a fund supporting workers affected by AI adoption, assisting them in upskilling and adapting to new technologies.
- Tax Incentives for Job Creation: Suggestions include providing tax incentives to industries based on their employment-output ratio to promote job creation.
- Fund for Worker Upskilling: Emphasizes the importance of economic measures to address the human impact of AI. SJM proposes utilizing a ‘robot tax’ to finance worker upskilling programs.
Additional Budgetary Recommendations
- Incentivise job creation: SJM recommends tax incentives for industries that create more jobs, considering their employment-output ratio.
- Subsidies for Small Farmers: SJM proposes subsidies for micro-irrigation projects to enhance productivity among small-scale farmers. SJM suggests that micro-irrigation projects become eligible for CSR funding by incorporating them into Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Wealth tax on Vacant Lands: SJM suggests implementing a wealth tax on ‘vacant land’ to discourage unnecessary land hoarding for future needs.
What is a Robot Tax?
A robot tax refers to a proposed levy on companies utilizing automation and AI technologies to substitute human labor. The purpose is to generate revenue aimed at supporting workers impacted by automation. This can involve retraining initiatives, unemployment benefits, and other forms of social assistance.
Need for a Robot Tax
- Impact of Automation: AI and automation can result in significant job displacements across various sectors as machines and software take over tasks traditionally performed by humans.
- Worker Support: A robot tax can offer financial resources to aid displaced workers, facilitating their transition to new roles or acquisition of fresh skills.
- Wealth Distribution: Automation often concentrates wealth among technology owners, exacerbating economic inequality.
- Redistribution: Taxing companies benefiting from automation can support fairer wealth redistribution throughout society.
- Social Safety Nets: Proceeds from a robot tax can finance social safety nets like unemployment benefits, retraining programs, and other social services.
- Infrastructure: It can also aid public infrastructure developments and other initiatives benefiting society at large.
- Employment Decisions: By levying a tax on automation, companies may lean towards employing humans over robots for specific tasks.
- Balanced Approach: This strategy can help maintain equilibrium between technological progress and human employment.
Examples and Proposals
- Bill Gates’ Proposal: In 2022, Bill Gates advocated for a robot tax, suggesting that the generated revenue could finance job retraining and other societal benefits.
- European Parliament: In 2017, the European Parliament deliberated on a robot tax as part of broader AI and robotics regulations, though it was not ultimately implemented.
Criticisms and Challenges
- Implementation: Determining effective methods to implement and enforce a robot tax poses challenges.
- Innovation Stifling: Critics argue that a robot tax could impede innovation and technological advancements.
- Global Competition: There are concerns that companies might relocate to nations without such taxes, impacting global competitiveness.
Conclusion
A robot tax presents a contentious yet potentially advantageous approach to tackling the economic and social repercussions of AI and automation. It aims to provide assistance to displaced workers, reduce economic inequality, and ensure that the benefits of technological progress are equitably distributed.
PYQ 2013
Disguised unemployment generally implies:
(a)Large number of people remain unemployed
(b)Alternative employment is not available
(c)Marginal productivity of labor is zero
(d) Productivity of workers is low
GS3/Science and Technology
Breaking the taboo around men's reproductive health
Source: The Hindu
 Why in news?
Why in news?
Following World Population Day (July 11), amidst discussions on global population dynamics, it is essential to highlight a topic often overlooked in conversations about reproductive health: male infertility.
World Health Organization (WHO) Global Perspective on infertility:
- Prevalence: WHO estimates that 60 million to 80 million couples worldwide experience infertility.
- Male vs. Female Infertility: Globally, male infertility accounts for approximately 50% of all infertility cases.
Issues Specific to India:
- Data Deficiency: Unlike global estimates, specific prevalence data for infertility in India are outdated (from ICMR guidelines in 2005) and not comprehensive.
- Male Infertility: In India, male infertility constitutes a significant portion of all infertility cases, estimated to be around 50%, mirroring global trends.
- Contributing Factors: Unique challenges in India include environmental pollution, pesticide exposure in agriculture, lifestyle changes including late marriages and stress, which contribute to rising infertility rates.
- Access to Treatment: Disparities in access to advanced infertility treatments exist, with urban areas having better access compared to rural regions.
- Cultural and Social Stigma: Infertility remains stigmatized in Indian society, affecting mental health and social well-being of affected couples, and hindering open discussions and seeking timely medical help.
Male Factors:
- Low sperm count (oligospermia) or poor sperm motility (asthenozoospermia). Anatomical issues such as blocked sperm ducts or varicocele. Hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, and environmental influences like exposure to toxins.
Female Factors:
- Ovulation disorders, including hormonal imbalances like PCOS. Structural issues like blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities. Endometriosis, is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
Shared Factors:
- Age-related decline in fertility. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. Medical conditions like cancer and its treatments, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications affecting fertility.
Treatment options
- Semen Analysis: Essential for diagnosing male infertility, conducted after a period of sexual abstinence.
- Medical Consultation: Vital to identify underlying causes, whether physical (e.g., blocked sperm flow, anatomical issues) or genetic.
- Corrective Surgeries: Address issues like blocked sperm ducts, undescended testicles, or anatomical abnormalities affecting sperm production and flow.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): Effective for cases of severe male infertility where sperm count is extremely low.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Suitable when sperm motility is good but count is low, facilitating fertilization within the uterus.
- In vitro Fertilisation (IVF): Used when both sperm count and motility are low, involving fertilization outside the body before implantation.
- Donor Sperm Insemination or Adoption: Options for couples where male infertility is irreparable, providing alternative paths to parenthood.
Way forward:
- Enhanced Data Collection and Research: Update and expand prevalence data on infertility in India through national surveys and research initiatives. This should include both urban and rural populations to understand regional disparities.
- Public Awareness and Support Programs: Launch nationwide campaigns to raise awareness about infertility as a medical condition, debunk myths, and reduce stigma.
Mains PYQ:
In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care. Discuss. (UPSC IAS/2020)
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
















