UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13 July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Samvidhaan Hatya Diwas’ on 25th June Every Year
Source: Hindustan Times
Why in news?
The Government of India has decided to observe every year as ‘Samvidhaan Hatya Diwas.’ National Emergency imposition in India on June 25, 2025, will mark fifty years since the imposition of the Emergency. The Emergency lasted from June 25, 1975, to March 21, 1977. It was characterized by the suspension of civil liberties, press freedom, mass arrests, the cancellation of elections, and rule by decree.
What was the Emergency?
- PM Indira Gandhi’s government used constitutional provisions to impose sweeping executive and legislative control.
- Opposition leaders were jailed, fundamental rights, including freedom of speech and expression, were curtailed, leading to press censorship.
- The federal structure was effectively converted into a unitary one, with the Union controlling state governments.
- Parliament extended its term, made laws on state subjects, and extended the Union’s executive powers to the states.
Legal and Constitutional Sanction
- Article 352 allowed the President to proclaim an emergency if India’s security was threatened by war, external aggression, or armed rebellion.
- In 1975, “internal disturbance” was used as grounds for the Emergency, citing incitements against the police and armed forces. This was the only instance of emergency due to “internal disturbance,” later removed by the 44th Amendment in 1978.
- Article 358 suspended limitations on Article 19 (“Right to freedom”).
- Article 359 allowed the President to suspend the right to court enforcement of rights during an emergency.
Political and Social Circumstances: A Timeline
- In 1974, the Navnirman movement against corruption in Gujarat led to President’s Rule.
- Inspired by Navnirman, a student movement in Bihar, led by Jayaprakash Narayan (JP), aimed to cleanse the country of corruption and misgovernance.
- In May 1974, George Fernandes led a massive railway workers’ strike.
- On June 5, 1974, JP called for “Sampoorna Kranti” (total revolution).
Impact on Opposition Leaders, Media, and Political Dissenters
- Almost all opposition leaders, including JP, were detained under the Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA).
- Newspapers faced pre-censorship, with UNI and PTI merged into a state-controlled agency, Samachar.
- More than 250 journalists were jailed, and The Indian Express resisted by printing blank spaces when stories were censored.
Sanjay Gandhi’s “Five-Point Programme”
- Sanjay Gandhi, the younger son of then PM, Mrs. Indira Gandhi had come forward with a programme to ‘improve’ the condition of the poor people.
- His programme can be divided under five Headings, i.e. Adult Education, To abolish Dowry, To Grow more trees, Family planning – only two children, Eradication of caste system.
Legal Changes during the Emergency
- With opposition leaders in jail, Parliament passed amendments barring judicial review of the Emergency and securing the Prime Minister’s election.
- The 42nd Amendment expanded Union authority over states and gave Parliament unbridled power to amend the Constitution.
- In ADM Jabalpur vs. Shivkant Shukla (1976), the Supreme Court ruled that detention without trial was legal during an emergency, with Justice H.R. Khanna dissenting.
Lifting the Emergency and Aftermath
- Indira Gandhi lifted the Emergency in early 1977, leading to her defeat in the elections. Janata Party emerged victorious, with Morarji Desai becoming India’s first non-Congress Prime Minister.
- The Janata government reversed many constitutional changes from the 42nd Amendment, made judicial review of emergency proclamations possible, and removed “internal disturbance” as grounds for emergency imposition.
GS3/Environment
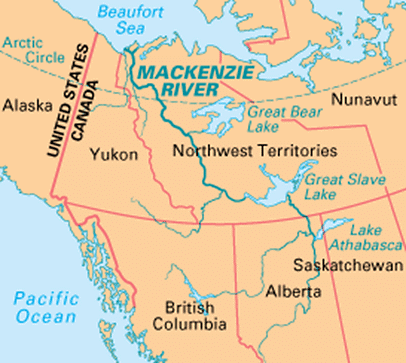
Mackenzie River
Source: Times Now
Why in news?
The Mackenzie River is currently facing unprecedented low water levels caused by intense heat and minimal precipitation, resulting in substantial evaporation. This situation has adversely affected local communities dependent on the river for transportation and fishing.
About MACKENZIE RIVER
- The Mackenzie River, situated in Canada, flows through the Northwest Territories.
- It stands as Canada's longest river system, stretching approximately 1,650 km (1,025 miles).
- Originating from Great Slave Lake, it terminates at the Beaufort Sea in the Arctic Ocean.
- Historically, the river has been vital for transportation and the utilization of natural resources.
GS3/Environment
Chromium Contamination
Source: New Indian Express

Why in news?
The Odisha government has been directed by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) to provide safe drinking water in areas where groundwater has been contaminated by chromium pollution.
About chromium contamination
- Chromium is a metallic element that is both odorless and tasteless.
- Naturally occurring in rocks, plants, soil, and volcanic dust, chromium exists in two primary forms:
- Trivalent chromium (chromium-3): Essential in the human diet and found in various foods such as vegetables, fruits, meats, grains, and yeast.
- Hexavalent chromium (chromium-6): Found naturally through environmental erosion of chromium deposits or through industrial processes. Industrial activities like leather and tanning, petroleum and ore refining, electroplating, and pulp industries contribute to chromium pollution in water sources.
- Hexavalent chromium poses significant health risks due to its high solubility and mobility. It can lead to health issues like pulmonary congestion, vomiting, diarrhea, and liver damage.
GS2/Polity
The Delhi Urban Land and Immovable Property Records Bill 2024
Source: New Indian Express

Why in news?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry (MoHUA) is working on a law - the Delhi Urban Land and Immovable Property Records Bill 2024, that would bring all urban land and building records in the national capital under a single Authority.
Major Impediments in the Urban planning in India
- Accurate and usable maps are lacking for many major cities.
- Record of Rights (RoR) in some states is either non-existent or not updated post urbanization.
- Maintaining urban records is often not seen as the responsibility of Revenue Departments.
- Alignment of spatial plans with land records is crucial for effective urban planning.
Current Situation in the National Capital
- Delhi sprawls over 1,483 sq km, with 1,114 sq km designated as urban.
- Rural land records are maintained separately under different acts.
- Currently, there is no comprehensive urban land and buildings records system in Delhi.
- Multiple agencies are responsible for land-related matters in Delhi.
Proposals in the Delhi Urban Land and Immovable Property Records Bill 2024
- Establishment of the Delhi Urban Land and Immovable Property Records Authority.
- Creation of guidelines for urban land records maintenance.
- Inclusion of various stakeholders in the authority.
- Provisions for an urban Record of Rights (RoR) with detailed information.
Significance of the Delhi Urban Land and Immovable Property Records Bill 2024
- Ensuring uniformity in records across governance bodies for easier property searches.
- Coverage of all notified urban areas within the NCT of Delhi under the new authority.
- No fundamental change in land policy control due to Delhi's special status.
GS-III/& Biodiversity
Weed control using ‘Cyrtobagus salvinia’ Insect
Source: DTE
Why in news?
The Sarani reservoir in the Betul district has been successfully cleaned following the release of an exotic beetle to eradicate the invasive weed Salvinia molesta. The weed was completely eliminated within 18 months, transforming the 2,800-acre reservoir.
Case Study: Salvinia Molesta eradication from Sarani Reservoir
- Salvinia molesta, an aquatic fern, had overtaken the Sarani reservoir on the Tawa River in Madhya Pradesh.
- Locally known as “Chinese Jhalaar,” the invasive species was first noticed in 2018 and covered the reservoir by 2019.
- This project is the largest and most successful experiment by ICAR-DWR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Directorate of Weed Research).
Initial Challenges
- The invasive species had covered water bodies, depleting oxygen and destroying fish populations.
- The company initially considered manual removal of the weed, estimated to cost Rs 15 crore.
- Manual removal was deemed ineffective due to the likelihood of the weed’s resurgence.
Biological Control using ‘Cyrtobagus salvinia’
- ICAR-DWR proposed using the exotic insect Cyrtobagus salvinia, a bio-agent from Brazil, specifically targeting Salvinia molesta.
- ICAR-DWR, after thorough research and government approvals, released the insect into the reservoir in April 2022.
- This insect feeds exclusively on Salvinia molesta and dies naturally once the weed is eradicated, posing no environmental threat.
- Within 15 to 18 months, the insect population eradicated the weed.
About
- Establishment: Founded in 1989 and located in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India.
- Mandate: Focuses on research and development in weed management, aiming for sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
- Research Areas: Includes weed ecology and biology, herbicide resistance, non-chemical weed management, and weed utilization.
- Facilities: Equipped with modern laboratories, experimental farms, a herbarium, and a comprehensive library.
Economic and Social Benefits
- The elimination of Salvinia molesta has relieved fishermen in surrounding villages, restoring their livelihoods.
- The infestation had forced many fishermen to migrate and work as laborers due to the loss of fish populations.
- With the reservoir clear, fishermen are optimistic about regaining their income through reintroduced fish populations.
PYQ
[2018] Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in the news?
(a) Its extract is widely used in cosmetics.
(b) It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows.
(c) Its extract is used in the synthesis of pesticides.
(d) None of the above.
GS3/Science and Technology
ISRO's plans to venture into planetary defence
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
Last week, ISRO Chairman S Somanath expressed the possibility of engaging with the asteroid Apophis during its close approach to Earth at a distance of 32,000 km in 2029. However, the specific manner of ISRO's involvement has not yet been determined.
Space objects:
The asteroid Apophis may pose a threat:
- Initial Concerns: Discovered in 2004, Apophis initially posed a 2.7% chance of colliding with Earth, raising alarms due to its size (about 450 m wide).
- Revised Risk: Subsequent observations ruled out immediate collision risks in 2029, 2036, and 2068, but it will pass close to Earth in 2029 at 32,000 km.
- Potential Impact: Its size could cause significant damage if it were to collide with Earth, though recent observations suggest no imminent danger.
Other possible incoming threats from space:
- Daily Encounters: Thousands of asteroids enter Earth's atmosphere daily, most burning up due to friction, causing phenomena like fireballs.
- Russian Example: In 2013, a 20-meter asteroid exploded above Russia, releasing significant energy and causing damage and injuries.
- Detection Challenges: Some asteroids are detected only upon entering the atmosphere, especially those coming from the direction of the Sun, which can obscure detection.
ISRO's plan: From sci-fi to reality:
- Planetary Defense Initiative: ISRO aims to develop capabilities in planetary defense, potentially participating in missions to study and potentially deflect asteroids.
- Collaboration: Considering sending its own spacecraft or collaborating with other space agencies, like NASA, which has already redirected a spacecraft to study Apophis in 2029.
- Evolution of ISRO: Reflects ISRO's evolution as a space agency, transitioning from aspirations to reality in tackling global space objectives, demonstrating growing confidence and capabilities.
Way forward:
- Form Partnerships: ISRO should actively seek partnerships with leading space agencies like NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and others involved in asteroid detection and planetary defense.
- Joint Missions: Collaborate on joint missions to study and potentially mitigate asteroid threats. This could include sharing resources, technology, and expertise to maximize effectiveness and minimize costs.
Mains PYQ:
What is India's plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (UPSC IAS/2019)
GS3/Defence & Security
Control of nodal cyber security watchdog CERT-IN
Source: New Indian Express

Why in news?
Two ministries, Information Technology and Home Affairs, are vying for control of Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-IN), the country's primary cybersecurity watchdog. Currently, CERT-IN operates under the IT Ministry's administration.
About
The Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-IN) is an entity under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India, functioning since 2004. According to the Information Technology Amendment Act, 2008, CERT-IN is mandated to:
- Respond to computer security incidents promptly.
- Enhance the security of India's communication and information infrastructure.
Functions
- Incident Response: CERT-IN offers technical guidance and support to individuals and organizations facing cyber incidents. It also coordinates responses to security breaches at the national level.
- Cyber Security Awareness and Training: The organization conducts programs, workshops, and conferences to educate stakeholders about cyber threats and best practices. It also shares information on threats and protective measures.
- Vulnerability Handling and Coordination : CERT-IN identifies and analyzes vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. It collaborates with stakeholders to mitigate vulnerabilities and recommends preventive actions.
- Security Quality Management Services: CERT-IN provides various security services, including risk assessment and security audits. It also formulates guidelines for information infrastructure protection.
- Cyber Threat Monitoring: The organization continuously monitors cyber threats to India's information infrastructure. It issues alerts and warnings regarding potential threats.
- Collaboration and Coordination: CERT-IN collaborates with national and international cyber security bodies, law enforcement, and industry partners. It shares information to bolster collective cyber defenses.
- Policy Development and Implementation: The organization aids in forming national cyber security policies and ensures their implementation. It engages in research to innovate cyber security technologies.
Few notable works of CERT-IN
- CERT-IN has been engaged in significant investigations such as the 2022 cyberattack on AIIMS Delhi. In 2022, it issued a directive mandating VPN and cloud service providers to retain customer data for five years.
- In 2022, CERT-IN managed around 1.4 million cyber incidents, with the mitigation of vulnerable services being a common focus.
Positions of the Ministries
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA): MHA advocates for bringing CERT-IN under its jurisdiction to boost law enforcement capabilities, especially in cyberspace. They believe this integration would streamline cybercrime investigations.
- Ministry of Information Technology (IT): IT Ministry argues that CERT-IN's role primarily involves technical functions beyond law enforcement, focusing on incident reporting and security advisories. They emphasize the distinct nature of CERT-IN's technical duties from investigative powers held by MHA.
Background
- Currently, CERT-IN operates under the IT Ministry, providing technical services like incident analysis and alerts. It lacks investigative powers such as search and seizure, which the MHA concentrates on through the Indian Cyber-crime Coordination Centre (I4C).
- The dispute arises partly due to ambiguous Allocation of Business Rules (AoBR), leading to overlapping responsibilities among various ministries.
GS-III/Enviro & Biodiversity
Squalus hima: A new deep-water Dogfish Shark discovered in Kerala
Source: The Hindu
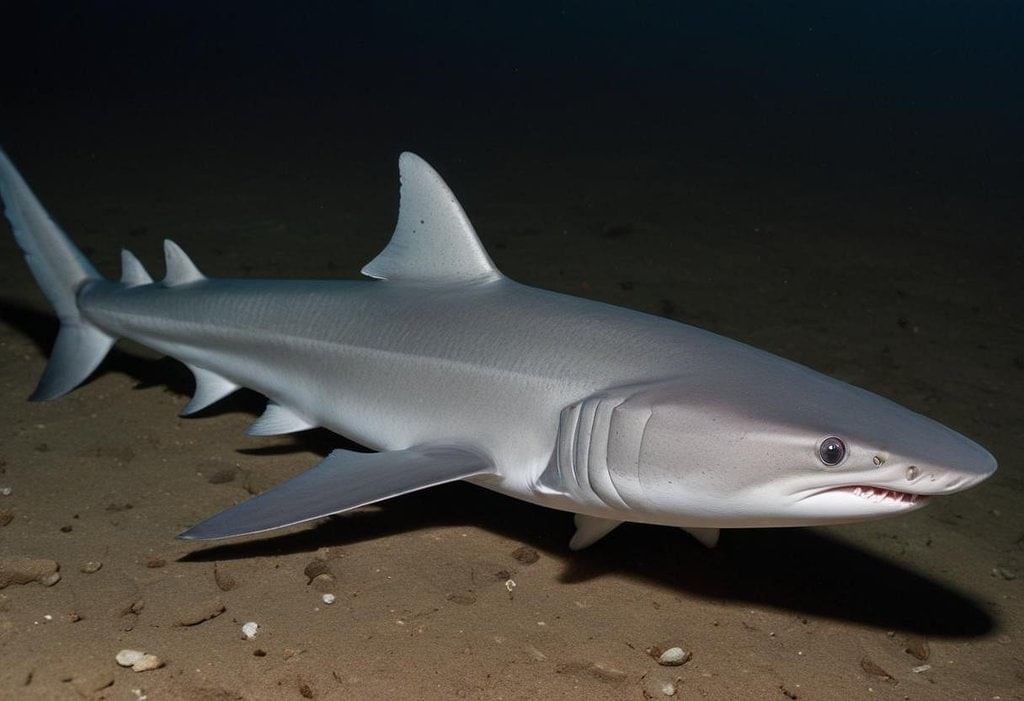

Why in news?
Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have discovered a new species of deep-water dogfish shark, Squalus hima, from the Sakthikulangara fishing harbour in Kerala along the Arabian Sea.
About Squalus hima
- Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae, commonly known as spurdogs, characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines. The new species, Squalus hima sp. nov., has been misidentified with S. mitsukurii and S. lalannei in the past, differing from other species by the number of precaudal vertebrae, total vertebrae, teeth count, trunk and head heights, fin structure, and fin color.
Comparison with Other Species
- On the Indian coast, two species of Squalus are found from the southwest coast of India.
- Squalus hima n.sp., is very similar to Squalus lalannei but differs in many characteristics.
- Species in the Squalus megalops group are characterized by an angular short snout, a small mouth almost as wide as the snout, the first dorsal fin origin behind the pectoral fins, and a body without any spots.
Economic and Conservation Implications
- Sharks in the genus Squalus and Centrophorus are exploited for their liver oil, which contains high levels of squalene, used in high-end cosmetic and anti-cancer products.
- Fishermen from southern India and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands harvest these sharks for their liver oil, making conservation of these species critical.
Importance of the Discovery
- The discovery of Squalus hima is significant for the conservation of shark species exploited for commercial purposes.
- Dogfish sharks are commercially important for their fins, liver oil, and meat and are sometimes caught as by-catch in fisheries targeting other species.
GS2/Polity and Governance
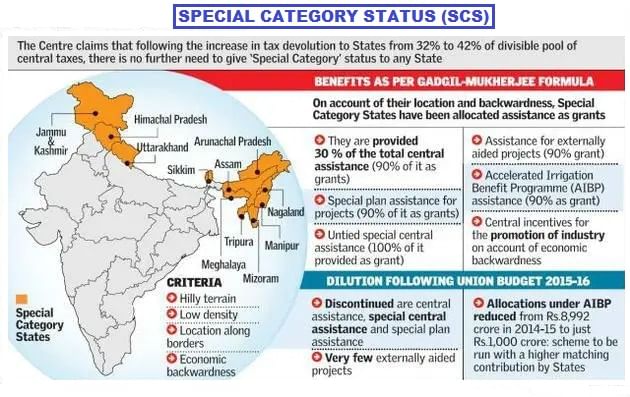
Why States Must Reconsider Their Demand for Special Category Status
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
Special Category Status (SCS) has been crucial in addressing regional disparities, but its future is uncertain given the changing political and economic landscapes. Leaders of aspiring states often advocate for SCS without fully assessing its net benefits. The challenge lies in finding a balanced approach that supports underprivileged states while ensuring equitable development nationwide.
The Concept of SCS and Role of NDC and FC
- The concept of SCS originated in 1969 during the Fourth Five-Year Plan by the Planning Commission to tackle development disparities among Indian states.
- NDC played a significant role by providing plan assistance to states via the Gadgil formula, which prioritized population and economic deprivation.
- 30% of funds were reserved for SCS states under this formula.
- FC recognized the importance of SCS, integrating it into budgetary deficit considerations and tax devolution criteria.
Additional Benefits of SCS
- Concession in Taxes: SCS states receive relief in excise duties, lowering the tax burden on local industries and encouraging investment.
- Concessions in customs duties: These reduce the cost of imported raw materials for industries in SCS states, fostering economic growth.
- Higher Central Plan Status: SCS states receive 90% of funding for centrally sponsored schemes as grants, providing greater flexibility in project implementation.
- Enhanced Financial Transfers: FC's criteria for tax devolution favor SCS states, ensuring a higher share of central taxes is transferred to them.
Transition to NITI Aayog and Current Scenario
- The shift to NITI Aayog altered the mechanism for central plan assistance, emphasizing performance-based incentives and outcome-oriented funding.
- Despite structural changes, the fundamental benefits for SCS states in terms of financial support and tax concessions persist.
Recommendations of the 14th and 15th Finance Commissions
- The 14th Finance Commission didn't address SCS explicitly but allocated higher grants to northeastern states, Uttarakhand, and Himachal Pradesh.
- The 15th Finance Commission allocated a significant portion of devolved taxes to northeastern and hilly states.
Challenges and Future Considerations
- Political Controversies and Bargaining: SCS can become a tool for political bargaining, intensifying demands, and complicating objective assessments of state needs.
- Fiscal Implications: Balancing support for SCS states with other fiscal responsibilities can strain the central government's budget and create regional tensions.
- Administrative Challenges: Ensuring effective fund utilization in SCS states is crucial to prevent mismanagement and underutilization.
- Establishing Clear, Updated Criteria: An inclusive framework considering various factors is needed, along with regular reviews to address emerging challenges.
Strengthening Institutional Mechanisms
- Enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficient resource utilization is vital for the successful implementation of SCS benefits.
- Implementing robust monitoring systems and building state government capacities are essential to realize the full benefits of SCS.
Conclusion
The future of SCS in India hinges on addressing current challenges, evolving frameworks, and ensuring equitable growth, transparency, and accountability for balanced regional development.
GS2/International Relations
The Forum for India-pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC)
Source: Mint

Why in news?
Last month, India provided humanitarian aid to Papua New Guinea following a severe landslide in Enga province. This act highlights the increasing interaction between India and the Pacific Island countries through the Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC).
- India has consistently extended support to Papua New Guinea during times of adversity and natural calamities, including the earthquake in 2018 and volcanic eruptions in 2019 and 2023.
About Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation
- Established in 2014
Members:
- India and 14 Pacific Island nations:
- Cook Islands
- Fiji
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia
- Nauru
- Niue
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Objectives:
- Strengthen diplomatic, economic, cultural, and technical ties between India and the Pacific Island nations.
- Promote sustainable development and address common challenges like climate change, health, and education.
Key Summits:
- First Summit: Suva, Fiji (2014)
- Second Summit: Jaipur, India (2015)
- Third Summit: Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea (2023)
Significance for India:
- Geopolitical: Boosts India's strategic presence in the Pacific region.
- Economic: Creates new avenues for trade and investment.
- Cultural: Strengthens interpersonal connections and encourages cultural exchanges.
Recent Initiatives:
- Healthcare: Establishment of a specialized cardiology hospital in Fiji, along with the introduction of dialysis units and sea ambulances in all 14 Pacific Islands Countries.
- Clean Energy: Support for projects related to renewable energy.
- Water Scarcity: Provision of desalination units to tackle water scarcity challenges.
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
















