UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15 July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Shigella Infection
Source: MSN
Why in news?
Recently, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has found an Indian partner to manufacture the breakthrough vaccine for shigella infection. This development is a crucial step towards combating shigellosis, especially in low- and middle-income countries where the disease burden is highest.
About shigella infection:
- It is an intestinal infection caused by a family of bacteria known as shigella.
- The four species of Shigella are Shigella sonnei, Shigella flexneri, Shigella boydii and Shigella dysenteriae.
Key Points:
- Symptoms: Diarrhea, Stomach pain or cramps, Fever, Nausea or vomiting.
- Transmission:
- It is very contagious. Shigella is transmitted via the fecal–oral route, through direct person-to-person contact, or indirectly through contaminated food, water, or fomites.
- Spread of Shigella through both direct and indirect sexual contact has been widely reported, primarily among men who have sex with men (MSM).
- Humans are the primary natural reservoir, although nonhuman primates also can be infected.
- Vulnerable Groups: Children under age 5 are most likely to get shigella infection, but it can occur at any age.
- Vaccine: Currently, no vaccines are available for shigella.
- Precautions:
- Wash hands thoroughly before and after meals.
- Wash hands properly after bowel movements.
- Ensure drinking water is clean.
- Consume fresh fruits and vegetables.
GS1/Indian Society
Asur Tribes to get Forest Land Rights
Source: Times of India
Why in news?
The Gumla district administration in Jharkhand has announced that the Asur community, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) residing in the Netarhat plateau region of Gumla, will soon benefit from the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006.
About Asur Community
- The Asur tribe primarily resides in the districts of Gumla, Lohardaga, Palamu, and Latehar in Jharkhand, India.
- They speak Asuri, a Munda language belonging to the Austroasiatic language family.
- Traditionally, the Asur were skilled iron-smelters, practicing metallurgy using indigenous techniques.
- Over time, many have shifted to agriculture, although some are still involved in mining work.
- The Asur community has a traditional council (jati panch) to settle disputes.
- They maintain kinship ties with neighboring tribes like Kharwar and Munda.
Social Structure of Asur Community:
- They live in forest-surrounded clearings called pats, with houses made of mud walls, wooden poles, and roofs covered with paddy straw.
- Asurs follow a religion that combines animism, animatism, naturalism, and ancestral worship.
- Their chief deity is Singbonga, and they celebrate festivals like Sarhul and Karma.
- Marriage is significant, following rules of monogamy with exceptions for barrenness or widowhood.
- Widow remarriage is allowed, and marriages occur within the tribe (endogamy).
Back2Basics: Forest Rights Act, 2006
- Purpose: Recognizes and vests forest rights in Forest Dwelling Scheduled Tribes (FDST) and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFD).
- Eligibility: Individuals or communities residing in forest land for at least 3 generations (75 years) prior to December 13, 2005.
- Rights Recognized:
- Title Rights: Ownership up to 4 hectares for cultivation.
- Use Rights: Includes Minor Forest Produce and grazing areas.
- Relief and Development Rights: Rehabilitation and basic amenities in case of eviction.
- Forest Management Rights: Conservation and sustainable use of community forest resources.
- Authority: Gram Sabha initiates the process of determining Individual Forest Rights (IFR) or Community Forest Rights (CFR).
GS3/Science and Technology
India-based Neutrino Observatory
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) project, supported by Nobel laureate Takaaki Kajita, is crucial despite challenges.
Who is Takaaki Kajita?
Japanese physicist Takaaki Kajita, awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2015, discovered neutrino oscillations, proving their mass.
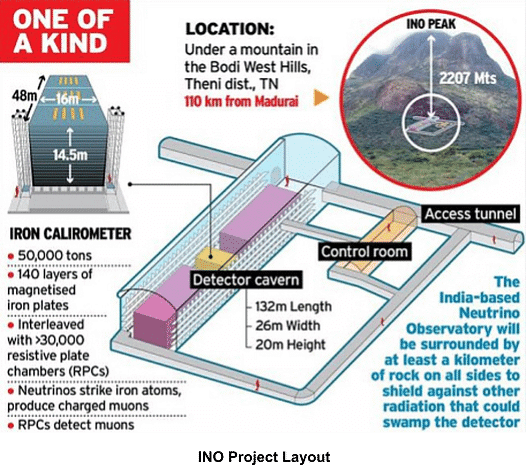
About India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO):
Details
Located at INO Peak near Theni, Tamil Nadu, it aims to study atmospheric neutrinos and measure neutrino mixing parameters precisely.
Project Scope
One of India's largest experimental particle physics projects with delayed completion due to local opposition and environmental concerns.
Key Equipment
Includes the Iron Calorimeter (ICAL) Detector for studying neutrino propagation effects and determining oscillation parameters. Additionally, it houses the world's largest magnet, crucial for research.
Research Goals
- Neutrino Oscillation Parameters: Determining parameters accurately using atmospheric neutrinos.
- Matter Effects: Investigating mass differences through charge identification.
- CP Violation: Studying parity violations in the leptonic sector.
- CPT Violation: Possible investigations on time-reversal violations.
- Kolar Events: Exploring very-high-energy neutrinos and multi-muon events.
Back2Basics: Neutrinos
Definition
Neutrinos, known as "ghost particles," are subatomic particles with minimal mass and no charge.
Detection Challenge
Due to their weak interactions, detecting neutrinos is immensely challenging.
Properties
Neutrinos, abundant in the universe, behave similarly to electrons in weak nuclear forces.
They are produced in stars and reactors during nuclear fusion and fission, respectively.
Interactions
Neutrinos have weak interactions with matter, making them elusive and hard to detect directly.
GS3/Defence & Security
EXERCISE PITCH BLACK
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
Indian Air Force (IAF) is all set to participate in Exercise Pitch Black 2024. This edition is slated to be the largest in the 43-year-long history of Ex Pitch Black, which includes participation by 20 countries, with over 140 aircraft and 4400 military personnel of various air forces.
About Exercise Pitch Black
- Exercise Pitch Black is a biennial warfare exercise hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
- The exercise is normally held in Northern Australia, primarily at RAAF Bases Darwin and Tindal.
- The aim of the exercise is to practice Offensive Counter Air (OCA) and Defensive Counter Air (DCA) combat in a simulated war environment.
- The name 'Pitch Black' was derived from the emphasis on night time flying over large unpopulated areas.
- The exercise provides an excellent opportunity for strengthening the ability of the participating nations to deploy over large distances, support integrated operations in the Indo-Pacific region, and build strong aviation associations in a highly challenging environment.
- The IAF has previously participated in the 2018 and 2022 editions of this exercise.
GS3/Environment
SALVINIA MOLESTA
Source: Down to Earth

Why in news?
An exotic beetle released into a vast reservoir in Betul district (Madhya Pradesh) has successfully eradicated an invasive weed species, Salvinia molesta, within 18 months.
- Cyrtobagus salvinia, the exotic beetle, was imported to India after thorough research and with the necessary governmental approvals. Within 15 to 18 months, its population multiplied significantly, effectively consuming and destroying the weed.
SALVINIA MOLESTA :
- Salvinia molesta, commonly known as giant salvinia, or as kariba weed after it infested a large portion of Lake Kariba between Zimbabwe and Zambia, is an aquatic fern, native to south-eastern Brazil.
- It is a free-floating plant that does not attach to the soil but instead remains buoyant on the surface of a body of water.
- It thrives in slow-moving, nutrient-rich, warm freshwater. A rapidly growing competitive plant, it is dispersed long distances within a waterbody (via water currents) and between waterbodies (via animals and contaminated equipment, boats, or vehicles).
- Salvinia molesta may form dense vegetation mats that reduce water flow and lower the light and oxygen levels in the water. This stagnant dark environment negatively affects the biodiversity and abundance of freshwater species, including fish and submerged aquatic plants.
- Salvinia molesta can alter wetland ecosystems and cause wetland loss and also poses a severe threat to socio-economic activities dependent on open, flowing and/or high-quality waterbodies.
- It is on the list of the World's 100 Most Invasive Species.
GS3/Economy
SDG INDIA INDEX 2023-24
Source: The Print

Why in news?
NITI Aayog recently unveiled the SDG India Index 2023-24, assessing India's progress on the 16 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This index reflects India's dedication to the SDGs following the adoption of the 2030 Agenda on Sustainable Development. NITI Aayog has been actively involved in SDG localization efforts, collaborating closely with states and union territories.
About SDG India Index :
The SDG India Index offers a comprehensive snapshot of the social, economic, and environmental status of India, including its states and union territories. Developed in partnership with the United Nations in India, the index serves as a tool to monitor and evaluate advancements towards the 16 SDGs set by the United Nations in 2015. It relies on a set of 113 indicators to gauge performance across key areas such as health, education, gender equality, climate action, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
SDG India Index 2023-24 Highlights:
- Overall Score: India's overall SDG score rose to 71 in 2023-24, marking an improvement from 66 in 2020-21 and 57 in 2018.
- Top Performing States: Kerala and Uttarakhand achieved the highest scores of 79 each.
- Significant Progress: Notable advancements were made in Goals 1 (No Poverty), 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), 13 (Climate Action), and 15 (Life on Land).
- Fastest Moving States: Uttar Pradesh saw a remarkable increase of 25 points, followed by J&K (21), Uttarakhand (19), Sikkim (18), Haryana (17), Assam, Tripura, and Punjab (16 each), Madhya Pradesh and Odisha (15 each).
- New Entrants in Front-Runner Category: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Manipur, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
- Key Initiatives Contributing to Progress:
- Government Programs: Initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, Ujjwala, Swachh Bharat, Jan Dhan, Ayushman Bharat-PMJAY, Ayushman Arogya Mandir, PM-Mudra Yojana, Saubhgaya, and Start-up India.
- SDG Localisation: NITI Aayog's efforts in promoting competitive and cooperative federalism by collaborating with States and UTs.
GS1/History & Culture
Ratna Bhandar of Puri Jagannath Temple, opened after 46 years
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
After 46 years, the sacred treasury of Shree Jagannath Temple, Puri, known as Ratna Bhandar, was reopened amid years of legal battles, controversies, and debates.
About the Ratna Bhandar
- The Ratna Bhandar stores the gold and jewels offered by devotees to the deities Lord Jagannath, Lord Balabhadra, and Goddess Subhadra.
- It is located adjacent to the prayer hall on the north side of the temple.
- It consists of two sections: the 'Bhitar Bhandar' (Inner Treasury) and the 'Bahar Bhandar' (Outer Treasury), with the last inventory in 1978 noting significant amounts of gold and silver items in both chambers.
- Legend says, Odisha's King Anangabhima Dev (1211 to 1238) donated 2.5 lakh madhas of gold to prepare jewellery for the almighty.
Recent Developments
- The safety of the Ratna Bhandar is managed by the Temple's Committee chaired by the titular 'King of Puri' and includes IAS officers and other state-appointed members.
- Originally, keys to the Ratna Bhandar were held by the Puri royal family temple committee, with significant changes in ownership and access protocols over the years due to legal rulings.
- The recent reopening involved breaking the locks of the inner chamber as they could not be opened traditionally, following strict procedures.
About Jagannath Puri Temple
- The Jagannath Temple is an important Vaishnavite temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Sri Krishna in Puri in Odisha.
- The present temple was rebuilt from the 10th century onwards, on the site of an earlier temple, and begun by Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva, the first king of the Eastern Ganga dynasty.
- The Puri temple is famous for its annual Ratha Yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal deities are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars.
Its Architecture
- With its sculptural richness and fluidity of the Oriya style of temple architecture, it is one of the most magnificent monuments of India.
- The huge temple complex covers an area of over 400,000 square feet and is surrounded by a high fortified wall.
- This 20 feet high wall is known as Meghanada Pacheri.
- Another wall known as kurma bedha surrounds the main temple.
The temple has four distinct sectional structures:
- Deula, Vimana or Garba griha (Sanctum sanctorum) where the triad deities are lodged on the ratnavedi (Throne of Pearls) in Rekha Deula style.
- Mukhashala (Frontal porch).
- Nata mandir/Natamandapa, which is also known as the Jagamohan (Audience Hall/Dancing Hall), and Bhoga Mandapa (Offerings Hall).
GS3/Economy
VIBRANT VILLAGES PROGRAMME
Source: Business Standard

Why in news?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah recently reviewed the implementation of Vibrant Villages Programme.
Vibrant Villages Programme was first announced in the 2022 Budget. The programme's targets are to provide comprehensive development of villages on the border with China and improvement in the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
About Vibrant Villages Programme- Government approved Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in February 2023, with financial outlay of ₹4800 crore for the FY 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- It aims for comprehensive development of the select villages in 46 blocks in 19 districts abutting northern border in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand and UT of Ladakh.
- The objective of the programme is comprehensive development of these villages to improve the quality of life of people & thereby reversing outmigration.
- The programme envisages focused areas of interventions in the select villages for creation of opportunities for livelihood generation through promotion of tourism & cultural heritage, skill development & entrepreneurship and development of cooperative societies including agriculture/horticulture, cultivation of medicinal plants/herbs etc. the interventions also include providing road connectivity to unconnected villages, housing & village infrastructures, energy including renewable energy, television & telecom connectivity.
- VVP has been conceived as an outcome oriented programme with outcome indicators at three levels- village, household & individual beneficiary.
GS2/Polity
The SC ruling on the portrayal of disability in films
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
On July 8, the Supreme Court issued guidelines against stereotyping and discriminating persons with disabilities in visual media, prompted by a plea to ban Aaankh Micholi.
Background:
- The Supreme Court’s guidelines came in response to a plea filed by activist Nipun Malhotra challenging the alleged insensitive portrayal of differently-abled individuals in the Film ‘Aaankh Micholi’.
- The petitioner argued that the film contained derogatory references and stereotyping of persons with disabilities.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Ruling:
- Avoiding Derogatory Language:
- The court asked creators to avoid words like “cripple”, “spastic”, “afflicted”, “suffering”, and “victim” as they contribute to negative self-image and perpetuate discriminatory attitudes.
- Accurate Representation:
- The court said stereotyping differently-abled persons in visual media and films must end, and creators should provide an accurate representation of disabilities rather than mocking or mythifying them.
- Involvement of Persons with Disabilities:
- The court asked creators to practice the principle of “nothing about us, without us” and involve persons with disabilities in the creation and assessment of visual media content.
- Training and Collaboration:
- The court emphasized the need for training programs for writers, directors, producers, and actors to sensitize them on the impact of portrayals on public perceptions.
What are the laws which grant disability rights?
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (RPwD Act), 2016:
- This is the primary legislation that comprehensively addresses the rights and entitlements of persons with disabilities in India. It replaced the earlier Persons with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities, Protection of Rights and Full Participation) Act, of 1995.
- The National Trust Act, 1999:
- It provides legal support to persons with autism, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, and multiple disabilities. It focuses on enabling guardianship and providing support to those who may not have guardians.
- Rehabilitation Council of India Act, 1992:
- Regulates the training of rehabilitation professionals and promotes research in rehabilitation and special education.
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017:
- While primarily focusing on mental health issues, this Act also includes provisions related to the rights and treatment of persons with mental disabilities.
Are the laws governing the ‘Rights of Differently-abled’ persons being implemented properly?
- Implementation Gaps:
- There are significant gaps between the provisions laid out in laws like the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016, and their actual implementation on the ground. Many disabled persons continue to face barriers to accessing their entitlements and rights.
- Awareness and Sensitization:
- There is a lack of awareness among the general public, as well as within government bodies and institutions, about the rights and needs of persons with disabilities.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility:
- Despite legal mandates for accessibility in public places, transportation, and buildings, implementation remains uneven.
- Employment Opportunities:
- While laws mandate employment quotas for persons with disabilities in government and private sectors, these quotas are often not met.
What is the way forward?
- Enhanced Monitoring and Accountability:
- Implement regular audits and monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with disability rights laws at all levels of governance and across sectors.
- Need to Increase Awareness and Sensitization:
- Launch nationwide awareness campaigns targeting both the general public and stakeholders within government and private sectors to promote understanding of disability rights.
Mains PYQ:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 remains only a legal document without intense sensitisation of government functionaries and citizens regarding disability. Comment. (UPSC IAS/2022)
GS3/Science and Technology
India Could Soon Allow Weight-Loss Drug Tirzepatide
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
In a groundbreaking move, a panel of experts from India’s drug regulatory body, CDSCO (which operates under DCGI), has given its endorsement to the weight reduction medication tirzepatide. This decision paves the way for the final regulatory approval, following a review, which will enable its manufacturer, the US-based Eli Lilly, to introduce this product to the Indian market.
The Development of Various Weight Loss Drugs:
- The evolution of diverse weight loss medications has revolutionized obesity treatment, particularly in the US and Europe.
- The US FDA has sanctioned Wegovy (semaglutide) and Zepbound (tirzepatide) for chronic weight control in adults.
- These medications are suitable for individuals who are Obese (with a BMI over 30) or Overweight (with a BMI between 27 and 30) and have at least one other health condition related to their weight, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or type 2 diabetes.
About Semaglutide and Tirzepatide Drugs:
- Semaglutide and tirzepatide (both administered via subcutaneous injections) are polypeptides - small proteins that enhance the levels of naturally-occurring hormones in the body.
- These hormones, including glucagon-like-peptide 1 (GLP-1), regulate weight through the brain and digestive tract.
- Elevated GLP-1 levels (released in the gut) stimulate the feeling of satiety in the brain, indicating satisfaction and satiation after eating.
- These drugs aid in managing glucose levels, making them effective for diabetes treatment as well.
- While semaglutide targets GLP-1 receptors exclusively, tirzepatide also enhances a second hormone: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP).
- GIP also controls weight through receptors in the brain and fat cells, and the synergistic action of GLP-1 and GIP amplifies their effects.
- Global trials involving Zepbound, in which Indian subjects participated, have produced promising outcomes.
- Based on the trial data, Zepbound has received regulatory clearance in India, with a mandatory phase IV trial (post-marketing surveillance) to monitor side effects.
- Zepbound is a prescription medication and not intended for cosmetic weight reduction.
- Common side effects of Zepbound, as highlighted by Eli Lilly, include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, indigestion, injection-site reactions, fatigue, allergic reactions, belching, hair loss, and heartburn.
- Eli Lilly specifically mentions the risk of thyroid tumors, including thyroid cancer.
- Obesity drugs are not quick-fix solutions for weight loss; consistent usage is necessary for sustained weight loss and other benefits, given the complex and chronic nature of obesity.
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
















