UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Monsoon Forecast by IMD
Subject: Geography
Source: DTE
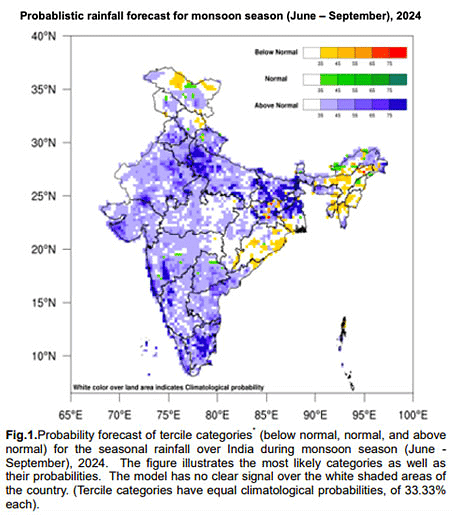
Why in News?
IMD predicts above normal monsoon for India from June to September this year.
- First time in a decade that IMD forecasts above normal rainfall 45 days in advance.
El Nino and La Nina
- El Nino: Ocean warming leading to below-average sea surface temperatures in the Pacific, causing reduced monsoon rainfall in India.
- La Nina: Ocean cooling resulting in better monsoon rainfall in India.
- Neutral: Neither El Nino nor La Nina, with Pacific SSTs close to average.
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- The IOD is defined by temperature differences in the Indian Ocean, affecting rainfall patterns.
- A positive IOD means cooler temperatures in the eastern Indian Ocean and warmer temperatures in the west.
- A negative IOD is the opposite, with warmer eastern and cooler western temperatures.
- The IOD was recognized as an independent system in 1999.
IMD Prediction for 2024
- India expected to receive 106% of long-period average (LPA) rainfall.
- LPA is the average rainfall over the past 50 years, with specific ranges indicating normal, deficient, below normal, and above normal rainfall.
- Factors contributing to above normal forecast include weakening El Nino, potential La Nina development, and positive IOD.
India's Arctic Imperative
Subject: Geography
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
India is looking to benefit from seabed mining and resource exploitation in the Arctic.
About the Arctic Region:
- The Arctic region boasts energy resources like oil, natural gas, and renewable energy sources.
- It spans approximately 8 million square kilometers and involves countries like Denmark, Canada, Iceland, and more.
Reasons for India's Arctic Focus:
- Climate Change Concerns: India is alarmed by the rapid warming of the Arctic.
- Trade Route Opportunities: India aims to utilize Arctic sea routes, especially the Northern Sea Route, for trade efficiency.
- Geopolitical Considerations: India is responding to China's and Russia's activities in the region.
- Historical Engagement: India has a historical connection dating back to the 1920 signing of the Svalbard Treaty.
Indian Initiatives:
- Arctic Council Participation: India, as an Observer, actively engages in Arctic Council discussions on governance issues.
- INS Himadri Expedition: India's first Arctic expedition in 2019 with the INS Himadri focused on climate change research.
- PAME Engagement: India's commitment to sustainable Arctic development is evident in its involvement with PAME initiatives.
Opportunities for Collaboration:
- Green Energy and Clean Industries: India emphasizes cooperation with Norway in green energy and clean sectors.
- Transformational Partnership: Collaboration with Norway could significantly benefit India in Arctic Council activities.
- Scientific Research and Environmental Protection: A partnership with Norway would prioritize research and environmental conservation.
GS-II
Easement Rights and Recent Supreme Court Ruling
Subject: Polity and Governance
Source: Live Law

Why in News?
The recent Supreme Court ruling clarified that a claimant of an Easementary Right cannot assert an Easement by necessity if there is an alternative route to access the property, known as the 'Dominant Heritage'.
- Reference was made to Section 13 of the Indian Easements Act of 1882, which addresses easementary rights by necessity.
What is Easement Right?
- An Easement represents the legal right to utilize another person's property for a specific purpose without owning it outright.
- It essentially entails permission granted by the owner of one property (the servient land) to another (the dominant land) to use the servient land in a particular manner.
Legal Basis for Easement Rights
- Section 13 of the Indian Easements Act, 1882, plays a pivotal role in resolving disputes related to easementary rights.
- This section specifies that such rights can only be claimed if there is no alternative access to the Dominant Heritage, offering clarity in legal proceedings.
- Understanding terms like 'Dominant Heritage' (representing the property for enjoyment) and 'Servient Heritage' (property over which rights are sought) is crucial in grasping easementary rights disputes.
Key Features of the Indian Easements Act, 1882
- Definition of Easements: The law defines easements and various types, such as rights of way, rights to light and air, and rights to use water.
- Acquisition of Easements: It explains how easements can be established, e.g., through agreement or prolonged usage.
- Rights and Liabilities: It delineates the rights and obligations of both the beneficiary and the servient owner, emphasizing responsibilities to avoid burden increase or obstruction.
- Termination of Easements: The circumstances under which an easement can end are described, like the cessation of its original purpose or the beneficiary's voluntary relinquishment.
- Customary Easements: Recognition of easements emerging from local customs or traditions.
Residency and Voter Status for Contesting Elections
Subject: Polity and Governance
Source: NDTV

Why in News?
Recently, Smriti Irani, the Union Minister for Women and Child Development, became an elector from her Lok Sabha constituency, Amethi. It's important to note that under election rules, a candidate isn't mandated to be a voter or a resident of the constituency they are contesting from.
Requirements for a Parliamentary Candidate
- Constitutional provisions:
- Candidates for both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha must be citizens of India according to Article 84 of the Constitution.
- The minimum age for Lok Sabha candidates is 25 years, while it is 30 for the Rajya Sabha.
- Candidates for state Assemblies must also be citizens, at least 25 years of age, and enrolled as electors.
- Additional qualifications may be required as per laws made by Parliament.
- Legal provisions:
- The Representation of the People Act, 1951, specifies that Lok Sabha candidates must be enrolled as electors from any constituency.
- Nomination papers require candidates to attach an extract of the electoral roll where they are enrolled.
Domicile Criteria in Rajya Sabha
- Historical Context:
- The Constituent Assembly deferred the decision on domicile and educational qualifications for MPs to the future Parliament.
- Candidates have the option to contest from two seats, eliminating the need for a domicile condition.
- Changes in Residency Rules:
- Originally, Rajya Sabha candidates were required to ordinarily reside in the state or Union territory they represented.
- In 2003, an amendment to the Representation of the People Act removed the domicile requirement for Rajya Sabha candidates.
- Arguments for and against:
- Supporters of the change believed it would broaden representation and prevent local biases.
- Opponents argued that it could weaken India's federal structure and lead to undesirable political practices.
- Legal Challenge:
- In 2006, the Supreme Court upheld the amendments, stating they were constitutionally sound.
- The court emphasized that Parliament had the authority to establish rules for the election process.
GS-III
Why Iran's Unprecedented Attack Failed Against Israel's Arrow Defence?
Subject: Defence and SecuritySource: NDTV

Why in News?
According to the Israel Defence Forces (IDF), the majority of the surface-to-surface missile launches from Iran were intercepted successfully by the Arrow Aerial Defense System.
What is the Arrow Aerial Defense System?
- The Arrow Aerial Defense System is a surface-to-surface missile system that serves as an upper tier in Israel's multi-layered air defense system, which includes Iron Dome, David's Sling, and the Arrow.
- Developed by Israel's Aerospace Industries in partnership with the US Missile Defense Agency, the Arrow 3 defense system, introduced in 2023, enhances Israel's ability to counter and eliminate long-range threats in the exo-atmosphere.
How Does the Arrow Defence System Work?
- The Green Pine radar identifies incoming threats heading towards Israeli territory, transmitting real-time data to the control center upon detection.
- Following target detection, a missile is launched vertically, propelled by a two-stage booster reaching speeds of Mach 9.
- The rocket's finned kill vehicle directs its explosion based on input from the missile seeker. In case of a miss, the fragmentation warhead can detonate within a 40-meter radius of the target.
Significance of the Arrow Aerial Defense System
- The Arrow Defense System equips Israel with the ability to intercept short, medium, and long-range missiles through a hit-and-kill strategy within the upper atmosphere, aiming to eliminate incoming threats before they descend.
How are hydrocarbons extracted from under the ground? | Explained
Subject: Economics
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The geological processes, extraction methods, and environmental impact of hydrocarbon extraction.
How Hydrocarbons are extracted?
- Damage to Marine Life and Ecosystems: The extraction process may release harmful substances, affecting marine life and ecosystems. For instance, toxic chemicals can lead to the death of fish and other marine animals, as well as habitat destruction.
- Deforestation and Destruction of Flora: Seeking hydrocarbon deposits often involves clearing large land areas, leading to deforestation and loss of plant life. This can significantly impact local ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Water Pollution: Extraction activities can contaminate groundwater and surface water sources.
- Destruction of Fertile Land: Extraction can harm fertile land, impacting agriculture and food production through soil erosion, desertification, and biodiversity loss.
Renewable sources as alternatives for hydrocarbons:
- Hydroelectricity: Represents 6% of the global renewable energy total.
- Solar Energy: Utilizes solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, with the U.S. experiencing rapid growth in this sector.
- Wind Energy: Utilizes wind turbines to generate electricity, with increasing popularity and efficiency.
- Biomass Energy: Derives from organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Geothermal Energy: Generated and stored in the Earth’s crust, usable for heating, cooling, and electricity.
- Renewable Natural Gas (RNG): High-quality gas sourced from methane waste like farm and landfills, interchangeable with traditional natural gas.
Conclusion
Hydrocarbons, found in underground rock formations, are extracted using petroleum geology methods. Extraction poses environmental risks like marine damage, deforestation, and water pollution. Renewable alternatives include hydroelectric, solar, wind, biomass, geothermal energy, and renewable natural gas.
Exercise DUSTLIK
Subject: Defense and Security
Source: PIB

Why in News?
Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of Exercise DUSTLIK in Uzbekistan.
Exercise DUSTLIK Overview
- Exercise DUSTLIK is an annual event that takes place alternately in India and Uzbekistan.
- It is named after Dustlik, a town located in the Jizzakh region of Uzbekistan.
- The inaugural edition of the exercise occurred in 2019 near Tashkent.
- The previous edition was conducted in Pithoragarh, India, in February 2023.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Focus on enhancing physical fitness, joint planning, and tactical drills.
- Emphasis on special skills related to various arms and multi-domain operations.
- Tactical drills involve activities like establishing command posts, intelligence centers, heliborne operations, and room intervention.
- Inclusion of combat support arms and services in addition to Infantry.
- Opportunity provided to exchange Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of joint operations.
- Enhancing interoperability and camaraderie among soldiers from both nations.
What is Net-zero, and What are India's Objections?
Subject: Environment and Ecology
Source: DTE

Why in News?
John Kerry, the US's Special Envoy on Climate, is currently on a three-day visit to India to explore if India can be nudged to drop its hard opposition to 2050 net-zero goal and pledge itself to it.
Net-Zero Goal and its Achievement
- Net-Zero Goal requires a country to offset its emissions by absorbing and removing atmospheric greenhouse gases (GHG).
- Absorption can be enhanced by creating more carbon sinks like forests.
- Removal necessitates advanced technologies such as carbon capture and storage.
- No emission reduction targets are specified for any country under this goal.
- Countries exceeding absorption and removal from actual emissions achieve negative emissions, as seen in Bhutan.
Importance of Net-Zero Goal
- Net-Zero Goal is crucial for meeting the Paris Agreement target of limiting global temperature rise to 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Current emission reduction efforts are insufficient to prevent a 3-4°C temperature increase by the end of the century.
India's Concerns and Objections
- India anticipates significant challenges due to its rapidly growing emissions, driven by the pursuit of higher economic growth.
- The country argues that afforestation and existing carbon removal technologies are inadequate to offset its emissions effectively.
- India advocates for a focus on fulfilling existing commitments rather than setting new net-zero targets outside the Paris Agreement.
- India aims to set an example by adhering to the Paris Agreement goals and does not commit in advance to achieving carbon-neutrality by 2050/2060.
|
61 videos|5403 docs|1144 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th April 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. How does the Indian Monsoon Forecast by IMD impact agriculture and economy in the country? |  |
| 2. Why is India's Arctic Imperative important for the country's strategic interests? |  |
| 3. What are easement rights, and how did a recent Supreme Court ruling impact them? |  |
| 4. What led to Iran's unprecedented attack against Israel's Arrow Defence, and why did it fail? |  |
| 5. How are hydrocarbons extracted from under the ground, and what are the key methods involved in the extraction process? |  |
















