UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th March 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| GS-II |

|
| Move to benefit Indian lawyers |

|
| How foreign lawyers can begin operating in India? |

|
| GS-III |

|
GS-II
China-India: Facilitating an Asian Century

Why in News?
China’s recent developments in steady growth, people’s well-being, opening up, and win-win cooperation, as well as its willingness to strengthen communication and coordination with India, can provide new opportunities for all countries in the world, especially neighbouring countries. importance of China-India relations and their role in facilitating an Asian Century.
China’s focus areas of development
- Modernization: China is currently advancing modernization in all fronts, based on its practices, and a focus on high-quality development.
- Overall development: The country aims to modernize its huge population, ensuring common prosperity for all, material and cultural-ethical advancement, harmony between humanity and nature, and peaceful development.
- New opportunities: China’s development will create new opportunities for all countries, especially neighbouring countries.
The development of China in recent years
- Steady Growth:
- In 2022, China’s economy grew by 3%, and the country added a total of 12.06 million urban jobs.
- The country’s GDP increased to 121 trillion yuan (approximately $18 trillion), registering an annual growth rate of 5.2% over the past five years and an annual growth of 6.2% over the past decade, with GDP increasing by nearly 70 trillion yuan.
- People’s Well-being:
- China has historically resolved absolute poverty, with the alleviation of close to 100 million rural residents from poverty.
- Over 70% of the government’s expenditure went toward ensuring people’s well-being.
- Basic old age insurance covers 1.05 billion people, an increase of 140 million. Living standards continue to witness new improvements.
- Opening Up:
- In 2022, China’s total volume of trade in goods exceeded 40 trillion yuan, registering an annual growth rate of 8.6%.
- China’s actual use of foreign capital was up by 8%, and the country remained one of the top destinations for foreign investors.
- The overall tariff level continues to fall, from 9.8% to 7.4%. China’s doors to the outside world are opening even wider.
- Win-Win Cooperation
- In the period 2013-2021, China’s contribution to global economic growth averaged 38.6%, higher than that of G7 countries combined (25.7%).
- More than 100 countries have expressed their support, and over 60 countries have joined the Group of Friends of the Global Development Initiative (GDI) since Chinese President, Xi Jinping, proposed it in a speech at the United Nations General Assembly in 2021.
China-India Relations
- Emerged as Representatives: As neighboring and ancient civilizations, China, and India are representatives of developing countries and emerging economies.
- National rejuvenation: Both countries are currently in the process of national rejuvenation and a crucial period of modernization where challenges need to be overcome and problems need to be solved.
- Interests than differences: China and India have far more common interests than differences.
China- India Trade
- China and India are important trading partners, with bilateral trade volume reaching $135.984 billion in 2022.
- Although there is a trade deficit, India’s import of equipment and materials from China reduces the overall cost of Made-in-India products, benefits Indian downstream industries and consumers, enhances the competitiveness of Indian exports, and in turn facilitates India’s integration into global industrial and supply chains.
Facilitating an Asian Century
- Chinese Foreign Minister recently stated that the development and revitalization of China and India embody a boost to the force of developing countries, which will change the destiny of a third of the world’s population and have a bearing on the future of Asia and beyond.
- This echoes what India’s External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar had expressed in 2022 that the Asian Century will happen when China and India come together.
Conclusion
- China’s development and its relationship with India are important for the region and the world. Both countries are in the process of modernization and face challenges that need to be overcome. China and India are important trading partners, and their cooperation can facilitate an Asian Century and contribute to peace and stability in the region and beyond.
Source: The Hindu
Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act)
Why in News?
The Delhi High Court recently disposed of a plea seeking direction to the Bar Council of India (BCI) to make the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act) a compulsory subject in all law schools.
About Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act):
- The Constitution (Eighty-sixth Amendment) Act, 2002 inserted Article 21-A in the Constitution of India to provide free and compulsory education of all children in the age group of six to fourteen years as a Fundamental Right.
- RTE Act is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted on 4 August 2009 as envisaged under Article 21-A.
- Main Features of the RTE Act:
- Free and compulsory education to all children of India in the 6 to 14 age group.
- It clarifies that ‘compulsory education’ means the obligation of the appropriate government to provide free elementary education and ensure compulsory admission, attendance, and completion of elementary education to every child in the six to fourteen age group.
- No child shall be held back, expelled, or required to pass a board examination until the completion of elementary education.
- It makes provisions for a non-admitted child to be admitted to an age-appropriate class.
- It specifies the duties and responsibilities of appropriate Governments, local authorities, and parents in providing free and compulsory education and sharing of financial and other responsibilities between the Central and State Governments.
- It lays down the norms and standards relating inter alia to Pupil Teacher Ratios (PTRs), buildings and infrastructure, school-working days, and teacher-working hours.
- It provides for the appointment of appropriately trained teachers, i.e., teachers with the requisite entry and academic qualifications.
- It prohibits physical punishment and mental harassment, screening procedures for admission of children, capitation fee, private tuition by teachers, and running of schools without recognition.
- It provides for the development of a curriculum in consonance with the values enshrined in the Constitution.
Source: Indian Express
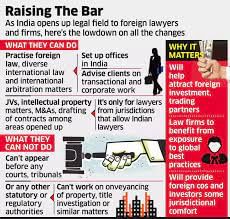
Foreign lawyers, firms can operate in India: Bar Council
Why in News?
The Bar Council of India (BCI) has opened up law practice in India to foreign lawyers and law firms. It has framed the ‘Bar Council of India Rules for Registration of Foreign Lawyers and Foreign Law Firms in India, 2021’.
Why such move?
- The BCI notification also stated that the Rules would help to address the concerns expressed about the flow of Foreign Direct Investment into the country.
- The Rules would also help make India a hub for international commercial arbitration.
Move to benefit Indian lawyers
- The rules enable foreign lawyers and law firms to “practice foreign law, diverse international law and international arbitration matters in India on the principle of reciprocity in a well-defined, regulated and controlled manner”.
- The BCI said that the move would benefit Indian lawyers, whose standards of proficiency in law are comparable with international standards.
- The legal fraternity in India is not likely to suffer any disadvantage since the move would be mutually beneficial for lawyers from India and abroad.
How foreign lawyers can begin operating in India?
- The Rules prescribe that foreign lawyers and firms would not be entitled to practice law in India without registration with the BCI.
- Foreign lawyers and law firms are not allowed to practice Indian law in any form or before any court of law, tribunal, board or any other authority legally entitled to record evidence on oath.
- However, the restriction does not apply to law practice by a foreign lawyer or foreign law firm on a ‘fly in and fly out basis’ for the purpose of giving legal advice to a client in India on foreign law or international legal issues.
- In such a case, the lawyer or firm cannot have an office in India, and their practice cannot exceed 60 days in any 12-month period.
Requirements for foreign lawyers and firms
A primary qualification required from foreign lawyers and firms is-
- Certificate from the competent authority of their country that they are entitled to practice law in that country.
- Undertaking that they shall not practice Indian law in any form or before any court of law, tribunal, board or any other authority legally entitled to record evidence on oath.
Source: Indian Express
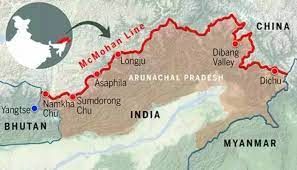
What is McMahon Line
Why in News?
A recent bipartisan Senate resolution in the United States recognizes the McMahon Line as the international boundary between China and Arunachal Pradesh.
About McMahon Line:
- It is a geographical border between Northeast India and Tibet.
- It is the boundary between China and India, although its legal status is disputed by the Chinese
- It was negotiated between Tibet and Great Britain at the end of the Shimla Conference in 1914.
- It is named after Henry McMahon, who was the foreign secretary of British India and the chief negotiator of the convention at Simla.
- The length of this boundary is 890 kilometers.
- It runs from the eastern border of Bhutanalong the crest of the Himalayas until it reaches the great bend in the Brahmaputra River, where that river emerges from its Tibetan course into the Assam Valley.
- Though India considers the McMahon Line as the legal national border, China rejects it, contending that Tibet was not a sovereign state and therefore did not have the power to conclude treaties.
What is The Shimla Treaty of 1914?
- It was signed in 1914 by delegates from India and Tibetto establish a clear demarcation between the two countries.
- China was not present in this treaty since Tibet was an autonomous region at the time.
- According to the treaty the McMahon Line is the clear boundary line between India and China.
- The British rulers, on behalf of India, considered Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh and the southern portion of Tibet to be part of India, which the Tibetans consented to.
- As a result, Arunachal Pradesh's Tawang region became a part of India.
What is LAC?
- LAC is a demarcation line that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory.
- India considers the LAC to be 3,488 km long, while the Chinese consider it to be only around 2,000 km.
- It is currently the de-facto border between the two countries.
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC), is divided into three sectors:
- Western (Ladakh, Kashmir),
- Middle (Uttarakhand, Himachal) and
- Eastern (Sikkim, Arunachal): Here, the alignment of the LAC is along the McMahon Line.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Wild Ass Sanctuary
Why in News?
Gujarat High Court recently sought a report from the state government on the licenses and permissions it has granted for mining activities within Wild Ass Sanctuary in the Little Rann of Kutch.
About Wild Ass Sanctuary:
- Location: It is located in the Little Rann of Kutch of the Gujarat State in India.
- It is the only place where the Indian wild ass, locally called Khacchar, is found.
- The sanctuary is home to a sizeable population of Rabari and Bharwad tribes.
- Topology:
- It can be considered a large ecotone, a transitional area between marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
- It is a continuum of a dry area of dark silt with salt encrustation.
- It is dotted with about 74 elevated plateaus or islands, locally called 'bets'.
- During the monsoon, large parts are flooded to depths of up to 2m.
- Flora:
- It is full of dry thorny scrub, and there are no large trees except on the fringes and bets.
- Some of the plants and trees that are found in this sanctuary are Morad, Unt morad, Theg, Dolari, Khijdo, Kerdo, Mithi jar, Kheri pilu, Akado, etc.
- Fauna:
- Besides Indian Wild Ass, the other mammals found here include Blackbuck, Nilgai, Bluebull, Hare, Wolf, Foxes, Desert Cat, Indian fox, Jackal, Hyena, Wild boar, etc.
- There is rich birdlife, including the Houbara bustard, Sandgrouse, Pale harrier, Black-shouldered kite, Pelican, etc.
Key Facts about Indian Wild Ass:
- It is a sub-species of Asian Wild Ass, i.e., Equus hemionus.
- Scientific name: Equus hemionus khur
- It is characterized by distinctive white markings on the anterior part of the rump and on the posterior part of the shoulder and a stripe down the back that is bordered by white.
- Distribution: World’s last population of Indian WildAss is restricted to Rann of Kachchh, Gujarat.
- Habitat: Desert and grassland ecosystems.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened.
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Schedule-I
Source: Indian Express
Women Leadership: Conditions To Unleash Her Potential
Why in News?
Today the world is home to a transformative generation of 900 million adolescent girls and young women poised to shape the future of work and growth. If this cohort of young women could be equipped with the right resources and opportunities to nurture the 21st century skills, they would become the largest segment of women leaders, change-makers, entrepreneurs, and innovators in history.
Women In India
- India is home to one of the largest generations of girls and young women, has made significant progress across various domains, such as education, health, digital and financial inclusion, and leadership building, to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 5, which envisions a more gender-equal world by 2030.
- To unleash the gender dividend and create conditions for female leadership to flourish, women at all levels of society must have inclusion in the Information and Communications Technology (ICT), bodily autonomy and safety, shared responsibility within the household, and equal participation in decision-making spaces.
What are the necessary conditions that must be in place for Women leadership to thrive?
- Cultivating Agency:
- Given the socio-economic barriers that adolescent girls confront from their earliest years that the work to cultivate their agency must begin early.
- India’s initiatives across various domains, such as education, health, digital and financial inclusion, and leadership building, to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 5, which envisions a more gender-equal world by 2030.
- Inclusion in ICT:
- Inclusion in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) for women at all levels of society is very important.
- As access to digital technology increasingly becomes an arena of opportunity and basic service, EdTech can bridge the accessibility gap in education through hybrid learning models, even where girls’ access to schooling is restricted by harmful norms.
- STEM Education:
- The prevailing stereotypes that characterize STEM education as a traditionally masculine domain, even though over 43% of Indian STEM graduates are women.
- The gender norms that disproportionately allocate domestic and care responsibilities to women, representation of men as leaders of STEM, finance, and entrepreneurial fields in the public perception, and institutional mechanisms are some of the barriers that explain why increased women’s representation in STEM education does not translate into work participation.
- There is need of inclusion of grade-appropriate STEM, financial education, and entrepreneurship syllabi into the educational curriculum for girls to counter these stereotypes actively.
- Bodily Autonomy and Safety
- Empowering women to make decisions about their bodies and be free from all forms of violence and harassment is very important.
- These basic conditions are critical to enable women and young girls to chart the trajectory of their personal and professional lives.
- Sport for Leadership
- The sporting activities can promote leadership, self-sufficiency, and teamwork. The inclusion of adolescent girls and young women in sports can build their self-confidence, strengthen self-belief, and impart the nuances of teamwork.
- The National Sports Policy and inclusion programs for children from vulnerable communities, which have seen remarkable success.
- Redistribute Care Work
- The backbone of thriving families, communities, and economies largely falls on women, increasing in times of crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It is crucial to recognize, reduce and redistribute unpaid care and domestic work, so that women may enjoy economic opportunities and outcomes on an equal footing to men.
- The policies that provide services, social protection and basic infrastructure, promote sharing of domestic and care work between men and women, and create more paid jobs in the care economy, which are urgently needed to accelerate progress on women’s economic empowerment.
Do you know? STEM education
- STEM education refers to a curriculum that focuses on four academic disciplines: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics.
- STEM education is designed to promote and enhance the critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills of students, while also encouraging their creativity and innovation.
- The curriculum typically integrates these four subjects to show how they are interconnected and applicable to real-world problems.
- STEM education is becoming increasingly important in today’s world, as technology continues to advance and the demand for skilled workers in these fields grows.
Conclusion
- Nurturing the leadership abilities of adolescent girls and young women is crucial for breaking down restrictive gender norms and barriers and accelerating progress across the Sustainable Development Goals. By working together to empower girls and women, we can create a more gender equal world and unlock the full potential of the next generation of female leaders.
Source: PIB
What is MQ 9 Reaper

Why in News?
An MQ-9 Reaper drone belonging to the United States Air Force recently crashed into the Black Sea due to collision with a Russian Su-27 jet fighter.
About MQ 9 Reaper:
- The MQ-9 Reaper, also known as Predator B, is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) capable of remotely controlled orautonomous flight operations.
- It is developed by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI), primarily for the United States Air Force (USAF).
- It is remotely operated by a two-person team consisting of a pilot and an aircrew member who operates sensors and guides weapons.
- The US uses the MQ-9 Reaper for both surveillance and strikes.
- Features:
- It is 11 metres long with a wingspan of over 22 metres.
- Reapers can be armed with air-to-ground Hellfire missiles as well as laser-guided bombs.
- It carry as many as 16 Hellfire missiles, equivalent to the payload capacity of an Apache helicopter.
- It can fly at an altitude of 50,000 ft (15 km) and can loiter over targets for for over 27 hours.
- Top speed: 275 mph.
Source: Economic Times
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th March 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-II in UPSC exams? |  |
| 2. What are some commonly asked topics in GS-II for UPSC exams? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for GS-II in UPSC exams? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific resources or study materials available for GS-II preparation? |  |
| 5. How much weightage does GS-II carry in the UPSC exams? |  |