UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 17 August 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Govt Notifies FEMA Amendments on Cross-Border Share Swaps
Source: Business Standard

Why in news?
The Department of Economic Affairs has amended the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) Rules, 2019, to support the global expansion of Indian companies through cross-border share swaps, mergers, and acquisitions. These changes, following the Union Budget's focus on simplifying foreign investment rules, aim to help Indian companies grow internationally.
About
FEMA came in 1999 as a successor to the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) of 1973, with changing economic conditions in a post-liberalisation India.
Objectives
- to facilitate external trade and payments
- to promote the orderly development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India
- to regulate the transactions related to foreign exchange/currency
Functions
- The FEMA regulates various aspects of foreign exchange transactions, including acquisition and holding of foreign exchange, payment and settlement of foreign exchange transactions, export and import of currency, and other related activities.
- The act also empowers the RBI to make rules and regulations to carry out the provisions of the act.
- Violation of the provisions of FEMA can result in penalties and fines.
Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA), 1973
- FERA was designed for an era in India marked by a shortage of foreign exchange.
- It was aimed at conserving forex to ensure it was utilized only in the interest of the development of the country.
- The act provided the Indian government with extensive powers to regulate foreign exchange transactions and payments in the country.
- This included the power to impose restrictions on the use of foreign exchange, to regulate the flow of foreign exchange, and to prohibit transactions that were deemed to be against the national interest.
Union Finance Ministry announced amendments includes
- mandatory government approvals for investments from countries sharing land borders with India
Key highlights
- The amendments simplify cross-border share swaps
- The amendments standardize definitions like "control"
- The amendments align the treatment of downstream investments by OCI-owned entities with those by NRIs on a non-repatriation basis, encouraging more NRI participation in Indian markets
- Non-repatriation refers to the funds that cannot be transferred back to the investor's home country. These funds must remain in India and can only be used within the country.
GS3/Environment
Existential Threats Faced by the Panama Canal
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
The decline in water levels of Lake Gatun, the artificial reservoir key to the Panama Canal system’s operation, as a result of climate change induced drought, is posing an existential threat to the canal.
About the Panama Canal:
- Location: It is an artificial 82-km waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean, cutting across the Isthmus of Panama.
- Construction: It was constructed by the US (at a cost of 375 million dollars) and the first ship passed through the canal on August 15, 1914.
- Ownership: The US government owned and operated the canal until 1999 when the Panamanian government took control of one of the most important shipping lanes in the world.
Significance:
- Vital strategic asset: The US has a vested interest in the secure, efficient, and reliable operation of the canal, as approximately 72% of transiting ships are either going to or coming from U.S. ports.
- Shorter transit routes: It saves approximately 12,600 km in a trip between New York and San Francisco, enabling ships to avoid the lengthy and hazardous voyage around Cape Horn at the southern tip of South America.
- Environmental benefits: By providing a shortcut, the canal contributes to the reduction of carbon emissions and helps mitigate the environmental impact of global maritime transportation.
- Global supply chain: The Canal connects 180 maritime routes that reach 1,920 ports in 170 countries, and about 5% of global maritime trade transits through it.
The Panama Canal System’s Operation:
- Engineering: The canal works on a highly-engineered system that uses locks and elevators to lift and drop vessels to the required sea level at either end of the canal.
- Locks: These locks are either flooded to gain elevation or drained to lose elevation, acting as water elevators and are serviced using artificial lakes and channels.
Potential Dangers the Panama Canal Faces from Climate Change:
- Water Requirements: The Panama Canal needs massive amounts of fresh water to facilitate the passage of ships, with a single ship requiring more than 50 million gallons of water.
- Impact of Drought: A drought driven by the El Niño meteorological phenomenon has reduced water levels in Lake Gatun, causing disruptions to international trade and supply chains.
- Long-term Solutions: Efforts are being made to address these challenges, such as using ocean water in the locks and creating a second source of water for the canal through infrastructure projects like the Rio Indio dam.
GS3/Science and Technology
ISRO launches SSLV
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the third and final developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- The SSLV-D3 placed the Earth observation satellite EOS-08 precisely into orbit.
- This also marks the completion of ISRO/Department of Space's SSLV Development Project.
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), ISRO's commercial arm, and India's private space industry can now produce SSLVs for commercial missions.
About
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 metres in length and 2 metres in diameter.
- It is a 3 stage Launch Vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages and liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) as a terminal stage.
- VTM is the last liquid-propellent based stage of the rocket which is used to correct the velocity just before injecting the satellites into orbit.
Uses
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
India's journey towards SSLV
- The first SSLV mission — SSLV-D1 — carrying two satellites, including EOS-02 and AzaadiSat, in August 2022, was a failure.
- In its second attempt with the SSLV-D2 in February 2023, ISRO tasted success by inserting three satellites onboard into the intended 450 km circular orbit following a 15-minute flight.
- SSLV-D3 has been launched recently.
Significance
- Seamless launch of small satellites.
- Suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- SSLV will shift the burden of commercial launches from Polar Satellite Launch Vehicles (PSLV).
- The SSLV is likely to cost a fourth of the current PSLV.
About the News
- ISRO successfully completed the third and final developmental flight of its SSLV, marking the vehicle's readiness for commercial launches and opening the door for industry-led manufacturing through technology transfer.
- The SSLV-D3 mission was launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- The mission placed two satellites—EOS-08, an earth observation satellite, and SR-0 Demosat—into a 475 km circular low-earth orbit.
Manufacturing and launch of SSLV for commercial purposes
- ISRO is exploring two routes for the commercial launch of this vehicle.
- One is through NSIL, which will fund and realise the rockets required for commercial purposes, and the other is through technology transfer, which InSpace will handle.
Payloads on SSLV-D3
- ISRO's EOS-08, the primary payload of the SSLV-D3 mission, is a 175-kg experimental satellite equipped with three new technologies.
- Electro-Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR) captures day and night images in mid-wave and long-wave infrared for various applications like surveillance, disaster and environmental monitoring, and fire detection.
- Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) payload demonstrates the use of reflected GPS signals for ocean wind analysis, soil moisture assessment, and flood detection.
- Additionally, the SiC UV Dosimeter payload will study UV radiation exposure on the crew module, aiding the Gaganyaan mission preparations.
Second spaceport in Kulasekarapattinam
- Second rocket launchport of the ISRO is being developed at Kulasekarapattinam in coastal Tamil Nadu's Thoothukudi district.
- This will be extensively and exclusively used for commercial, on-demand, and small satellite launches in the future.
- The existing Sriharikota spaceport will handle launches to orbits that require the rocket to fly eastwards.
GS3/Economy
Govt Launches Satellite-based Agricultural Decision Support System
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The Union government has introduced a satellite-based agricultural decision support system to furnish farmers with essential data for managing crops and enhancing productivity.
About Krishi-DSS:
- On August 16, 2024, the Indian government initiated the Krishi-Decision Support System (DSS), a groundbreaking digital geospatial platform aimed at transforming the agricultural sector.
- This platform is tailored to aid in various agricultural activities such as digital crop surveys, precise yield estimation, crop damage assessment, soil mapping, and processing weather-related data.
Advantages of Krishi-DSS:
- The Krishi-DSS platform signifies a notable departure from traditional methods like random sampling and visual assessments prevalent since the Mughal era.
- The innovative technology-based crop yield estimation system, YES-TECH, will offer more precise and reliable data, ensuring enhanced decision-making for farmers and stakeholders.
Comprehensive Data and Accessibility:
- Krishi-DSS will provide seamless access to a diverse range of data, including satellite images, weather forecasts, reservoir levels, groundwater data, and soil health information.
- This data will be showcased on the Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) at Krishi Bhawan, accessible to users nationwide.
Support for Agri Stack Implementation:
- The launch of Krishi-DSS represents a pivotal step towards implementing the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture, which will encompass farmers and their land records.
- This initiative aligns with Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman's announcement in the 2023 Budget, stressing the significance of digital crop surveys and the DPI in agriculture.
Enhanced Agricultural Practices:
- Krishi-DSS will bolster sustainable agriculture by encouraging diverse crop cultivation through crop monitoring and mapping.
- It will also amalgamate various data sources to formulate farmer-centric solutions, including early disaster alerts and individual advisories.
Data Integration and Future Prospects:
- The platform will integrate data from the FASAL 2.0 initiative, encompassing key crops like paddy, sugarcane, wheat, cotton, soybean, mustard, gram, lentil, and potato.
- This integration will enhance crop production forecasting, drought monitoring, and crop health evaluations, ultimately contributing to improved crop insurance solutions.
Conclusion
Krishi-DSS signifies a significant leap in the utilization of technology in Indian agriculture, offering a comprehensive and accessible tool to enhance farming practices and ensure better outcomes for farmers nationwide.
GS3/Environment
National Green Tribunal (NGT)
Source: Deccan Herald
Why in News?
The southern bench of National Green Tribunal has set aside the environmental clearance granted to a pharmaceutical company to expand its unit in Krishnapatnam Industrial Area in Nellore, Andhra Pradesh.
About National Green Tribunal (NGT):
- NGT (National Green Tribunal) was created in 2010 to quickly handle cases about protecting the environment and conserving natural resources.
- New Delhi is the main location for the tribunal, while Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai are other locations where it operates.
- Composition:
- The NGT consists of the Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members.
- The Chairperson is a retired Supreme Court Judge, and other judicial members are retired High Court Judges.
- Each NGT bench must have at least one judicial member and one expert member.
- Expert members must have a professional qualification and 15 years of experience in environmental/forest conservation.
- Powers: NGT can address civil cases concerning environmental issues and issues related to laws in Schedule I of the NGT Act. These include laws like:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Cess Act, 1977
- The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- The Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- NGT can hear appeals like a court, and it doesn't have to follow the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 but should consider natural justice principles.
- NGT must resolve applications or appeals within 6 months of filing.
GS1/Geography
Solar Cycle
Source: CNN
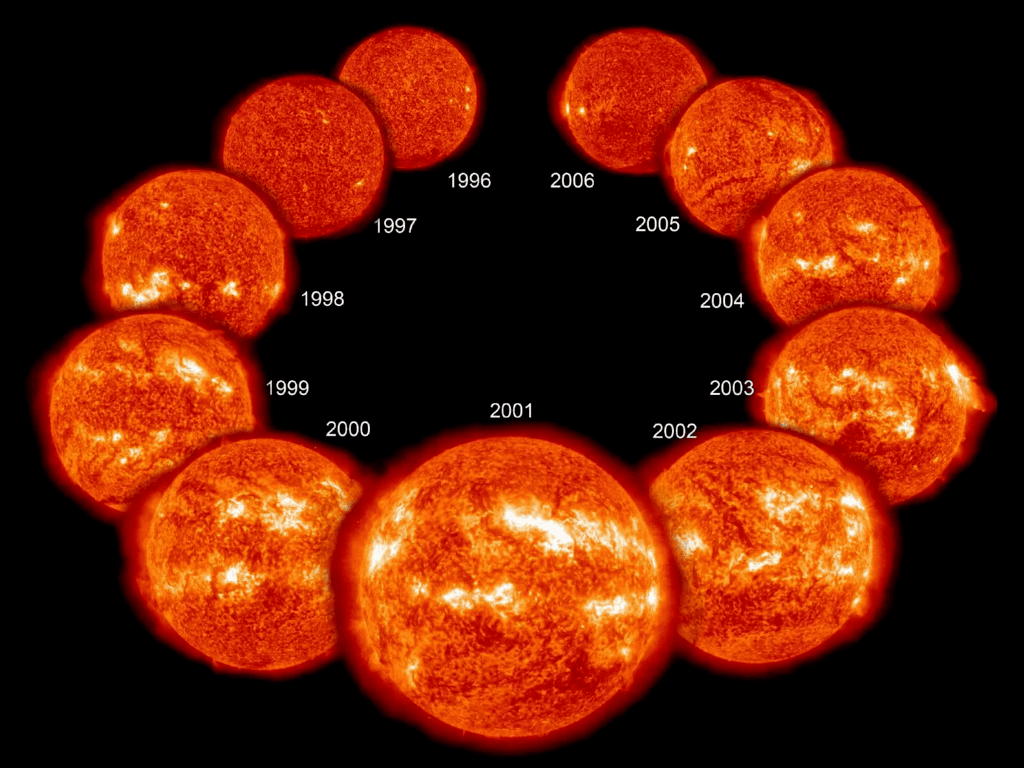
Why in News?
Astronomers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have found a new method to predict the amplitude of the upcoming solar cycle.
About Solar Cycle:
- Our Sun is a large sphere of hot, electrically charged gas.
- This charged gas moves around, creating a strong magnetic field.
- The Sun experiences a pattern called the solar cycle, which lasts about 11 years.
- Approximately every 11 years, the Sun's magnetic field completely switches direction.
- It then takes another 11 years for the Sun's magnetic poles to return to their original positions.
- Therefore, the solar cycle is a process where the Sun's magnetic field changes direction over an 11-year period.
- The solar cycle impacts activities on the Sun's surface, like sunspots, formed by its magnetic fields.
- Changes in the magnetic fields lead to variations in solar surface activities.
- One method to monitor the solar cycle is by counting sunspots.
- The start of a solar cycle is a solar minimum, with the least number of sunspots.
- Over time, solar activity and sunspot numbers increase.
- The peak of the solar cycle is the solar maximum, with the highest number of sunspots.
- As the cycle concludes, it returns to the solar minimum before a new cycle starts.
- During the solar cycle, significant eruptions occur on the Sun, like solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- These eruptions release intense bursts of energy and matter into space.
- Such activity can impact Earth, causing phenomena like auroras or affecting radio communications.
- Severe eruptions might even disrupt Earth's power grids.
GS3/Environment
Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve (NNP&TR)
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Fifty-seven casual employees of Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve have been reinstated three months after their services were terminated.
About Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve (NNP&TR):
- Location: The park is situated in the Changlang District of Arunachal Pradesh, bordered by Myanmar in the Southeast. It lies at the meeting point of the Indian Sub-Continent Biogeographic Region and the Indo-China Biogeographic Region, resulting in a wide range of plant and animal life.
- Surrounding Geography: Namdapha is nestled between the Dapha Bum ridge of Mishmi Hills in the North Eastern Himalayas and the Patkai Ranges. It shares boundaries with Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary to the southwest and Nampong Forest Division in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Altitude: The park varies in altitude from 200 m to 4,571 m at Dapha Bum, its highest point. The park is named after the Namdapha River, originating from Dapha Bum and merging with the Noa-Dehing River, a tributary of the Brahmaputra.
- Vegetation: Various biomes like evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, sub-tropical forests, temperate forests, and alpine regions are present. Notable flora includes 150 timber species, unique orchids like Blue Vanda, and medicinal plants like Mishimi Teeta.
- Wildlife: Namdapha is home to a diverse range of animals. It boasts all four big cat species - Tiger, Leopard, Snow Leopard, and Clouded Leopard, along with Lesser cats. The park is also inhabited by Hoolock Gibbons, elephants, black bears, Indian Bison, macaques, various deer species, reptiles, and arboreal creatures.
GS2/Polity and Governance
National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS)
Source: AIR

Why in News?
The Union Government recently launched the AI-based National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS).
About National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS):
- It is a digital project by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare using AI and ML to give timely advice on managing pests to farmers nationwide.
- NPSS aims to change how farmers deal with pests and help farmers in India.
- The main aim of NPSS is to lessen farmers' dependence on pesticide sellers and promote a scientific way of controlling pests.
- This system includes an easy-to-use mobile app and a website, making it accessible for all farmers.
- NPSS uses real-time information and advanced analysis to accurately identify, monitor, and manage pests.
- With NPSS, farmers can quickly tackle pest attacks and crop diseases, cutting down on crop losses and boosting productivity.
- The system's detailed data on pest occurrences and automated advice will give farmerspractical insights to help them decide and protect their crops.
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 17 August 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the recent amendments notified by the government in FEMA regarding cross-border share swaps? |  |
| 2. What are some existential threats faced by the Panama Canal? |  |
| 3. What is SSLV and who launched it recently? |  |
| 4. What is the Satellite-based Agricultural Decision Support System launched by the government and what are its objectives and advantages? |  |
| 5. Why is the Krishi-DSS system significant for the agriculture sector in India? |  |





















