UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 17th June 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/International Relations
Under Kafala, workers are dispensable
Source: DNA

Why in news?
Shortly after a fatal fire claimed the lives of 49 migrant workers, predominantly Indians, in the Mangaf area of Al Ahmadi municipality, Kuwait
About the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
- It is a regional intergovernmental organization that aims to promote economic, political, and cultural cooperation among its member states.
- The GCC was established in 1981 and currently consists of six Arab countries: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The council’s main headquarters is located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
What is the Kafala system?
- The Kafala system is a sponsorship system used in several Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, including Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates.
- It governs the legal status of migrant workers, particularly those from other countries in Asia and Africa, who come to work in these countries. It binds migrant workers to a specific employer, known as the “kafeel,” who is responsible for the worker’s visa and legal status.
Migrants' Rights in GCC countries
- Vulnerabilities of Migrant Workers: Migrant workers in GCC countries face systemic vulnerabilities due to the Kafala system, tying their legal status to employers who control their accommodation, wages, and freedom of movement. Lack of independent legal status and dependency on employers make them susceptible to exploitation, poor living conditions, and arbitrary deportations.
- Living Conditions and Safety: Many migrants live in crowded and substandard accommodations, which exacerbate risks during emergencies such as fires, as seen in the Mangaf tragedy. Safety standards in workplaces and living spaces often fall short, posing significant risks to migrants’ health and well-being.
- Legal Protections and Access to Justice: Legal protections for migrant workers vary, with some categories like domestic workers often excluded from labor laws and protections. Limited access to justice and the ability to organize or unionize further restrict their ability to advocate for improved rights and conditions.
India’s Relationship with GCC Countries
- Economic Dependence and Migrant Workforce: India has a significant economic relationship with GCC countries, with millions of Indian migrants working across sectors such as construction, healthcare, and services. Remittances from GCC countries contribute significantly to India’s economy, highlighting the mutual economic interdependence.
- Diplomatic and Policy Engagements: India engages diplomatically with GCC countries to safeguard the interests and welfare of its migrant workers, advocating for better working conditions, legal protections, and safety measures. Bilateral agreements and negotiations focus on labor rights, remittance flows, and crisis management during emergencies affecting Indian migrants.
What India can do? (Way forward)
- Diplomatic Engagement and Advocacy: Strengthen diplomatic ties with GCC countries to advocate for better working conditions, legal protections, and safety measures for Indian migrants.
- Consular Services and Support: Enhance consular services and support networks in GCC countries to provide timely assistance, legal aid, and emergency relief to Indian migrant workers.
- Skill Development and Empowerment: Collaborate with GCC governments and employers to ensure skill development programs for Indian migrants, enhancing their employability and negotiating power.
Mains PYQ
Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South-East Asian countries’ economy and society. Appraise the role of the Indian Diaspora in South-East Asia in this context. (UPSC IAS/2017)
GS-I/Indian Society
India needs to close the gender gap in education and politics
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
While global gender parity has improved to 68.5% in 2024 from 68.4% in 2023, progress remains slow. The World Economic Forum’s report indicates it will take 134 years to achieve full parity at this rate.
The Global Gender Gap Report 2024
It is released by the World Economic Forum (WEF), and highlights significant disparities in gender parity across various sectors.
Present Scenario:
- Global Gender Gap Report 2024:
- The global gender gap stands at 68.5% closed, indicating slow progress towards gender parity.
- Iceland leads with over 90% closure, while India has slipped to 129th position out of 146 countries, with 64.1% closure.
- India’s slight regression is attributed to declines in education and political empowerment indices.
Challenges in India:
- Despite improvements in economic participation, India needs to bridge gaps in education and political representation.
- The labour force participation rate for women is 45.9%, indicating significant untapped potential.
- Gender disparity in literacy rates persists, with women lagging 17.2 percentage points behind men, impacting India’s global ranking.
Significance of Low Gender Gap in the Education Sector:
- Bridging the gender gap in education is crucial for enhancing women’s economic opportunities.
- Measures such as preventing dropout rates among girls, imparting job skills, and ensuring workplace safety are essential.
- Improving literacy rates and educational attainment levels for women can lead to higher economic productivity and empowerment.
Significance of Low Gender Gap in Political Representation:
- India shows low representation of women in political bodies despite some progress. Women constitute only 13.6% of the Lok Sabha members, reflecting inadequate political empowerment.
- Implementation of the Women’s Reservation Bill, aimed at reserving one-third of seats in legislative bodies, remains crucial for enhancing women’s political participation and influence.
Way forward:
- Enhancing Education Access and Quality: Implement targeted policies to reduce the gender gap in education, focusing on increasing girls’ enrollment and retention rates.
- Promoting Women’s Political Empowerment: Implement initiatives to encourage women’s active participation in politics, such as leadership training programs, awareness campaigns, and support networks.
Mains PYQ:
Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (UPSC IAS/2021)
GS3/Science and Technology
What is an Electromagnet?
Source: The Hindu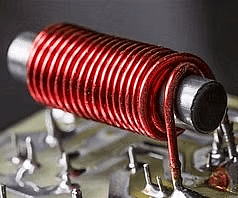
Why in news?
Recently Scientists have designed a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner that costs a fraction of existing machines, setting the stage for improving access to this widely used diagnostic tool. So we need to know about the Electromagnet.
Invented in 1824 by William Sturgeon
William Sturgeon was an English physicist and inventor who discovered that wrapping a coil of wire around a piece of iron and passing an electric current through the wire produced a magnetic field.
Electromagnets are used in Loudspeakers for sound reproduction, Motors for mechanical movement, and MRI machines for medical imaging, etc.
How Electromagnets Work?
- Electric current flowing through a wire generates a magnetic field around the wire.
- Coiling the wire enhances this magnetic field by concentrating it within the coil’s core. This configuration creates an electromagnet, where the strength of the magnetic field is directly proportional to the current flowing through the coil. The magnetic flux density so generated is measured in ‘Tesla’.
Enhancing Magnetic Strength with a Core
- Coiling the wire around a magnetic material (core), such as iron or steel:
- Amplifies the magnetic field produced by the electric current.
- Ferromagnetic materials like iron align their internal magnetic domains with the external magnetic field generated by the coil.
- This alignment significantly increases the overall magnetic strength of the electromagnet compared to a non-magnetic core.
Persistence of Magnetization
- It refers to the property of a material to retain a certain amount of magnetization even after the removal of an external magnetic field.
- Certain core materials exhibit retained magnetization even after the current ceases. Residual magnetism is useful in applications requiring sustained magnetic fields.
- Superconducting electromagnets used in, are capable of producing magnetic fields up to 30 Tesla.
- Research electromagnets like those used in particle physics, which require stable and powerful magnetic fields.
Who was Michael Faraday (1791-1867)?
- Michael Faraday was a pioneering English scientist and physicist who made substantial contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry.
- Faraday is best known for his experiments and discoveries in electromagnetism, which laid the groundwork for the principles of electromagnetic induction and the laws of electrolysis.
Key achievements of Michael Faraday include:
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction in 1831, showing that a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a nearby conductor.
- Electrochemistry: Faraday formulated the laws of electrolysis, which describe the quantitative relationship between the amount of material produced or consumed during electrolysis and the amount of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
- Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction: These laws describe the fundamental principles of generating electricity using magnetic fields, forming the basis for the development of electric generators and transformers.
- Faraday Cage: He invented the Faraday cage, a device used to block electromagnetic fields.
GS2/International Relations
Swiss Peace Summit
Source: Times of India

Why in news?
The two-day Summit on Peace in Ukraine at the Bürgenstock resort in Switzerland concluded recently with hopes for an end to the Russia-Ukraine war. Out of the 100 attending delegations, 80 countries and four organizations supported the final joint communiqué from the Path To Peace Summit, which focused on finding ways to end the Russia-Ukraine war that has been ongoing since February 2022.
About
The Swiss Peace Summit, also known as the Summit on Peace in Ukraine, is an international conference aimed at addressing and finding solutions to the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Held at the Bürgenstock resort in Switzerland, this summit gathers representatives from various countries and organizations to discuss and promote peace initiatives.
Objective
The primary goal of the Swiss Peace Summit is to facilitate dialogue and negotiations aimed at ending the war between Russia and Ukraine, which has been ongoing since February 2022.
Participants
The summit brings together a wide range of participants, including representatives from numerous countries, international organizations, and peace advocacy groups. In the recently held summit, 80 countries and four organizations supported the final joint communiqué.
Key outcome of Swiss Peace Summit
- Joint Communiqué: A final joint communiqué was issued, supported by 80 countries and four organizations out of the 100 attending delegations. This document outlines the collective consensus and recommendations for achieving peace between Russia and Ukraine.
- Territorial integrity of Ukraine should be respected: According to the communique, the territorial integrity of Ukraine should be the basis for any peace agreement to end Russia's war.
Important themes featured in the final statement
- Any threat or use of nuclear weapons in the context of the ongoing war against Ukraine is inadmissible;
- Food security must not be weaponized in any way. Ukrainian agricultural products should be securely and freely provided to interested third countries;
- All prisoners of war must be released by complete exchange; All deported and unlawfully displaced Ukrainian children, and all other Ukrainian civilians who were unlawfully detained, must be returned to Ukraine.
Commitment to Peace
Participants expressed a strong commitment to ending the war, emphasizing the need for continued dialogue and diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict.
Humanitarian Aid
The summit underscored the importance of providing humanitarian aid to those affected by the conflict, including displaced persons and civilians in war-torn areas.
International Cooperation
The summit facilitated international cooperation and solidarity, with countries and organizations pledging to work together to promote peace and stability in the region.
India attended the summit
India had joined the summit to explore the way forward to a negotiated settlement of a very complex and pressing issue. India was represented by the Secretary (West) in the Ministry of External Affairs. Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelenskyy had asked Prime Minister Narendra Modi to attend the summit. However, India, which has strategic ties with Moscow and a strong dependence on Russia for defence supplies, decided to send a Secretary-level official for the summit. Ever since the war began, India has also been buying Russian oil at discounted prices to cushion the inflationary impact of rising oil prices.
Decided not to sign the joint communique
- India decided to not sign the joint communique by saying that only those options acceptable to both parties can lead to abiding peace. It underlined that enduring peace can be achieved only through dialogue and diplomacy.
Reasons behind the Indian position of not becoming a signatory to the joint communique
- Russia - one of the two warring parties - declined to attend the summit in Burgenstock in central Switzerland. With Russia not attending the Swiss summit on peace in Ukraine, there cannot be a lasting peace on this issue.
- Besides India, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Thailand, Indonesia, Mexico and UAE were among countries participating at the summit on peace for Ukraine but did not sign a final communique. Brazil, which was listed as an observer on the list of attendees, also did not feature as a signatory.
GS-III/Economy
PM-Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana
Source: India TV

Why in news?
The Prime Minister will release the 17th instalment of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN), amounting to over ₹20,000 crore, for 92.6 million beneficiary farmers across the country.
About:
- Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India
- Implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare
- Launched in February 2019
- Aim to help procure various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle
- Objective is to provide eligible farmers with an annual financial assistance of ₹6,000, distributed in three equal instalments of ₹2,000 each every 4 months via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)
- Beneficiaries include farmer families that hold cultivable land, specifically Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs)
- The PM-KISAN scheme was first implemented by Telangana government as the Rythu Bandhu scheme
Impact of the Scheme
- Beneficiaries outreach extends to over 11 crore farmers across the country, indicating its widespread reach and impact
- Financial aid helps farmers meet agricultural expenses, purchase seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs
- Contributes to improved agricultural practices, food security, and growth of the agricultural sector
- Plays a crucial role in poverty alleviation among small and marginal farmers, providing them with a steady source of income
- Supports farmers’ livelihoods during agricultural distress or economic uncertainties, ensuring a better quality of life for rural communities
PYQ
- Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for various purposes such as working capital, purchase of farm assets, post-harvest expenses, and more
GS3/Environment
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary: India's Second Home for Cheetahs
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
The Madhya Pradesh government has completed its preparations for the reintroduction of the cheetahs in the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary, which will be the second home for cheetahs in India, after the Kuno National Park (KNP).
Under the ambitious cheetah reintroduction project, 8 Namibian cheetahs were released into enclosures at KNP in MP's Sheopur district on September 17, 2022. Later (in February 2023), 12 more cheetahs were brought from South Africa.
About the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: The sanctuary (notified in 1974) is spread across an area of 368.62 sq km in the districts of Mandsaur (187.12 sq km) and Neemuch (181.5 sq km) in western MP, right on the border with Rajasthan.
- Ecosystem: Due to the rocky terrain and shallow topsoil, the savanna ecosystem - comprising open grasslands interspersed with dry deciduous trees and shrubs, belongs to the sanctuary. However, the riverine valleys of the sanctuary are evergreen.
Why is Gandhi Sagar an ideal habitat for cheetahs?
- According to MP's wildlife officials, the sanctuary makes for perfect cheetah habitat as it looks like Maasai Mara - a national reserve in Kenya known for its savanna wilderness and wildlife.
Preparations for the Introduction of Cheetahs in Gandhi Sagar:
- Currently, an area of 64 sq km has been developed for the cheetahs, at a cost of Rs. 17.72 crores.
- A soft release enclosure (or boma, which is 1 sq km in area) has been constructed to ensure a suitable and secure habitat for the cheetahs upon their arrival.
- A hospital has also been constructed to cater to the needs of cheetahs.
- In order to gauge the existing ecological dynamics, the wildlife officials are currently in the process of conducting a comprehensive status assessment of herbivores and predators in the sanctuary.
Challenges in Making Gandhi Sagar a Viable Cheetah Habitat:
- Food: For cheetahs to sustainably survive in Gandhi Sagar, the first step is prey base augmentation, i.e. increasing the number of animals that the wild cats can prey upon.
- Leopard and other co-predators: Just like in Kuno, the leopard population in Gandhi Sagar will pose a threat to cheetahs, with the two feline predators possibly clashing with each other for the same prey.
- Human habitation: Unlike Kuno, highways and human habitation pass right outside the boundary of the protected area in Gandhi Sagar.
- Inter and intra state coordination: The potential of expanding the cheetah habitat in Gandhi Sagar to an area of around 2,000 sq km will depend on the coordination between Rajasthan's Bhainsrodgarh sanctuary, as well as the territorial divisions of Mandsaur and Neemuch.
- Infection: The final call on when the cheetahs will be imported from Namibia and South Africa will be made after the monsoons, during which the cats may be vulnerable to infection.
GS3/Environment
INCOIS’ New Product to Forecast El Nino and La Nina
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Hyderabad-based Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) has developed a new product to predict the emergence of El Nino and La Nina conditions.
About INCOIS (Meaning, Objective, Activities)
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) is an autonomous organization, established in 1999, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO).
- To provide ocean data, information and advisory services to society, industry, the government and the scientific community.
Activities of INCOIS Include
- Provides round-the-clock monitoring and warning services for the coastal population on tsunamis, storm surges, high waves, etc.
- Provides daily advisories to fisher folk to help them easily locate areas of abundant fish in the ocean while saving on both fuel and time used to search for the same.
- Short term (3-7 days) Ocean State Forecasts (waves, currents, sea surface temperature, etc.) are issued daily.
- Deploys and maintains a suite of Ocean Observing Systems in the Indian Ocean to collect data on various oceanic parameters to understand the processes in the ocean and to predict their changes.
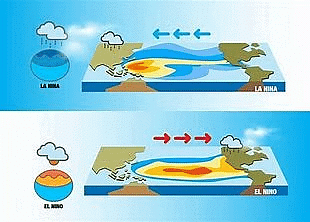
What is ENSO (El Nino and Southern Oscillation)?
- ENSO is one of the most important climate phenomena on earth due to its ability to change the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn, influences temperature and precipitation across the globe.
- El Nino:
- This phase is characterized by unusually warm sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
- El Nino typically leads to altered weather patterns around the world, including increased rainfall in the southern United States and Peru, and drought conditions in Australia, Indonesia, and India.
- It can also affect marine life due to changes in nutrient availability in the ocean.
- La Nina:
- This phase features unusually cold sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
- La Nina generally causes the opposite weather effects of El Nino.
- For instance, it can lead to increased rainfall in Australia and Indonesia, and drier conditions in the southwestern United States.
- Neutral:
- In this phase, sea surface temperatures and atmospheric conditions in the equatorial Pacific are near average.
- This phase is also sometimes referred to as ENSO-neutral.
- During this phase, the global weather patterns are more stable and not significantly influenced by the extreme conditions seen during El Nino or La Nina.
New Product to Forecast El Nino and La Nina
- Known as Bayesian Convolutional Neural Network (BCNN), the new product uses the latest technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), deep learning, and machine learning (ML) to improve forecasts related to the ENSO phases.
- Working of BCNN:
- The model predicts El Nino or La Nina by observing slow changes in the ocean and how they interact with the atmosphere.
- This interaction allows enough time to make early forecasts.
- The prediction uses the Nino3.4 index, which helps identify the different ENSO phases.
- This index is calculated by averaging the sea surface temperature (SST) anomaly in a specific part of the central equatorial Pacific, ranging from 5°N to 5°S latitude and 170°W to 120°W longitude.
GS3/Economy
What is SWM Cess and Why is It Levied on Waste Generators?
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The Bruhat Bengaluru Mahangara Palike (BBMP) has proposed a Solid Waste Management (SWM) Cess of ₹100 per month for each household.
What is Cess?
- A cess is a form of tax or levy imposed by governments to fund specific services or purposes, such as waste management or infrastructure development.
Purpose of SWM Cess:
- SWM Cess is intended to cover a portion of the costs incurred by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in providing SWM services, which are resource-intensive and crucial for maintaining cleanliness and health standards in urban areas.
Legal Provisions:
- According to the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016, ULBs are mandated to collect user fees/cess for SWM services. The proposed increase reflects the rising costs and challenges faced by ULBs in managing solid waste effectively.
Why has it hit the headlines suddenly?
- The proposed SWM Cess represents a substantial increase from the previous user fees typically charged by ULBs (Urban Local Bodies) across India, which are generally in the range of ₹30-50 per month.
- Such a significant rise in fees has garnered attention and sparked debate among residents and stakeholders in Bengaluru.
Impact on Residents:
- The SWM Cess directly affects every household in Bengaluru, potentially adding financial burden on residents.
- This has led to widespread discussions and concerns among citizens about the affordability and justification of the proposed increase.
How has Bengaluru been handling its solid waste management?
- Bengaluru faces significant challenges in solid waste management (SWM) due to its large population and high daily waste generation of approximately 5,000 tonnes.
- Managing such volumes requires extensive resources and infrastructure.
Operational Focus:
- The Bruhat Bengaluru Mahangara Palike (BBMP) primarily focuses its SWM efforts on the collection and transportation of waste.
- These activities are labour-intensive and consume a major portion of BBMP's budget allocated for SWM services.
Financial Strain:
- SWM services constitute a substantial portion of BBMP's budget, with limited revenue generated from these services.
- This financial strain necessitates the proposal of initiatives like the SWM Cess to bridge the funding gap and ensure sustainable service delivery.
What is about to change going forward?
- Going forward, Bengaluru plans to implement several changes in its SWM strategy.
- These include revising user fees and potentially increasing charges on bulk waste generators to better cover operational costs and enhance service efficiency.
Strategies for Improvement:
- BBMP aims to enhance waste management practices through initiatives such as waste segregation at source, promoting decentralized composting centres, and launching public awareness campaigns.
- These efforts are aimed at optimizing resource utilization and improving overall SWM effectiveness in the city.
Mains PYQ:
- What are the impediments in disposing of the huge quantities of discarded solid wastes which are continuously being generated?
- How do we remove safely the toxic wastes that have been accumulating in our habitable environment?
GS2/International Relations
India refuses to endorse Ukraine meet statement
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
India emphasized that only proposals acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine can lead to peace as it decided to disassociate from the final document issued on June 16 at the conclusion of the Peace Summit in Switzerland.
What is a Joint Communique on a Peace Framework?
The Joint Communique on a Peace Framework is a formal document issued at the conclusion of the Peace Summit in Switzerland, held on June 16, 2024. This communique outlines the collective stance and proposed guidelines for achieving peace in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Key Highlights of the Ukraine Peace Summit in Switzerland
- Attendance and Endorsement:
- More than 80 countries attended the summit and endorsed the “Joint Communique on a Peace Framework.”
- The communique emphasized the protection of Ukraine’s territorial integrity, based on Ukraine’s peace formula and the UN charter.
- Non-Endorsing Countries:
- India, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Thailand, Indonesia, Mexico, and the United Arab Emirates did not sign the communique. Brazil maintained an observer status, and China declined the invitation altogether.
- India’s Participation and Stance:
- India attended the summit but chose not to endorse the final document. India’s stance is rooted in the belief that any peace proposal must be acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine for it to be sustainable. The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) emphasized India’s commitment to understanding different perspectives to find a lasting resolution through dialogue and diplomacy.
Why did India Refuse?
- Neutrality and Balanced Approach: India maintains a policy of neutrality and balanced diplomacy, avoiding taking sides in the Russia-Ukraine conflict to preserve its diplomatic relations with both nations.
- Mutually Acceptable Solutions: India believes that any peace proposal must be acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine to be sustainable, emphasizing dialogue and practical engagement between the conflicting parties.
- Strategic and Diplomatic Considerations: By not endorsing the communique, India retains its potential role as a trusted mediator, protecting its strategic ties with Russia and considering broader geopolitical concerns such as food and energy security.
Conclusion:
India’s decision reflects its stance on neutrality, advocating for peace proposals acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine while preserving diplomatic relations and strategic interests amid global geopolitical dynamics.
Mains PYQ:
What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region (UPSC IAS/2020)
GS2/Polity
Madras High Court's Interpretation of POSH Act, 2013
Source: The Print

Why in news?
Madras HC upheld the 'Right to Report' serious incidents of sexual harassment at any time, rejecting the 3-month deadline under the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act (POSH), 2013. Long-term emotional and psychological damage on victims underscored the need for a broader application of the law.
Right to Report under POSH Act, 2013
- Case Background: The decision came while addressing a police officer's petition to quash an enquiry report for alleged sexual assault against a female colleague.
- Madras HC Reasoning: Serious allegations leading to "grave mental trauma" and "stress" constitute a "continuing offence" under POSH, allowing victims to report and investigate at any time.
- Notable Observations: The Madras HC distinguished between isolated incidents and serious allegations like assault or molestation.
- Isolated Incidents: Must adhere to strict deadlines under POSH.
- Serious Allegations: Treated as continuous misconduct until addressed, allowing flexibility in reporting timelines due to fear of victimization.
What is the POSH Act?
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act was passed in 2013.
- It defined sexual harassment, laid down the procedures for a complaint and inquiry, and the action to be taken.
- It broadened the Vishakha Guidelines, which were already in place.
- The POSH Act broadened these guidelines:
- It mandated that every employer must constitute an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) at each office or branch with 10 or more employees.
- It lays down procedures and defines various aspects of sexual harassment, including the aggrieved victim, who could be a woman "of any age whether employed or not", who "alleges to have been subjected to any act of sexual harassment".
Definition of Sexual Harassment
- Under the 2013 law, sexual harassment includes "any one or more of the following unwelcome acts or behavior" committed directly or by implication:
- Physical contact and advances
- A demand or request for sexual favors
- Sexually colored remarks
- Showing pornography
- Any other unwelcome physical, verbal or non-verbal conduct of a sexual nature.
Procedure for complaint
- Description
- Filing a complaint
- The aggrieved victim has the option to file a complaint with the ICC, but it is not compulsory for the ICC to act.
- Assistance in filing a complaint
- Any member of the ICC must provide reasonable assistance to the victim in filing a written complaint.
- Filing a complaint on behalf of the victim
- If the victim is unable to file a complaint due to incapacity, death, or other reasons, her legal heir may file it on her behalf.
Monetary settlement and conciliation
- Yes. It is possible.
Forwarding complaint or initiating an inquiry
- Must be completed within 90 days.
Confidentiality of information
- The act ensures the confidentiality of the woman's identity, respondent's identity, inquiry details, recommendations, and actions taken.
Requirements imposed on employers
- Employers with more than 10 employees must establish an ICC to address sexual harassment complaints.
Composition of ICC
- The ICC must include women employees, another employee, and a third-party member familiar with sexual harassment issues.
Local Committee (LC) for smaller organizations
- Organizations with fewer than 10 employees must create an LC to receive complaints from the informal sector.
Complaint filing process
- Women can file written complaints to either the ICC or LC within three to six months of the incident.
Resolution methods
- The Act provides two resolution methods: conciliation between the parties involved or conducting an inquiry by the committee.
Non-compliance penalties
- Non-compliance with the Act can result in penalties, including fines.
|
53 videos|5389 docs|1140 tests
|
















