UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 17th September 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
How do Emergency Provisions Impact Centre-State Relations?
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
The recent violence in Manipur has sparked renewed discussions on the dynamics of Centre-State relations in India, especially regarding the invocation of emergency provisions that enable the central government to intervene in state matters under certain conditions.
- India's federal system divides governance responsibilities between the central and state governments as outlined in the Constitution's Seventh Schedule. While law and order fall primarily under state jurisdiction, the Centre can intervene during governance breakdowns.
Understanding Emergency Provisions:
- Emergency provisions are detailed in Part XVIII of the Constitution.
- Article 355 mandates that the Centre must safeguard states from external threats and internal unrest while ensuring state governments adhere to constitutional mandates.
- Article 356 allows the Centre to impose President's Rule in states that do not comply with constitutional requirements.
- These provisions are distinctive to India; similar federal structures like the U.S. and Australia do not grant such removal powers to the central government.
Historical Context and Judicial Interpretation:
- B.R. Ambedkar, who was instrumental in drafting these provisions, hoped they would remain unused.
- Over time, Article 356 has been misused to dismiss state governments, often for political motives.
- The Supreme Court's 1994 ruling in the R. Bommai case established limitations on Article 356, indicating it should only be enacted during genuine constitutional crises, not merely for law-and-order issues.
- The court also confirmed that the imposition of President's Rule is subject to judicial review.
- Conversely, Article 355's applicability has broadened through various court decisions, such as the Naga People's Movement of Human Rights vs Union of India (1998), allowing for a wider range of actions by the Centre to protect states.
Recommendations from Various Commissions:
- Multiple commissions have examined emergency provisions in the context of Centre-State relations.
- The Sarkaria Commission (1987), National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2002), and Punchhi Commission (2010) all agree that Article 355 imposes a duty on the Union but that Article 356 should be a last resort.
- These commissions emphasize that such provisions should only be invoked in extreme circumstances.
The Case of Manipur:
- The recent unrest in Manipur has brought emergency provisions back into the spotlight.
- The state's turmoil, characterized by severe violence and looting of police resources, exceeds a mere law-and-order challenge.
- Despite the gravity of the situation, Article 356 has not been invoked, likely due to political factors, as the ruling party is the same at both the Centre and State levels.
- However, Article 355 is actively being employed, with the Centre taking various measures to restore order.
Conclusion:
India's federal structure underscores state autonomy; however, emergency provisions like Articles 355 and 356 empower the Centre to intervene when necessary. These provisions must be exercised cautiously to maintain the delicate balance between central authority and state autonomy. The Manipur situation highlights the complexities of this relationship, influenced by political, constitutional, and legal factors that shape the extent of Centre involvement.
GS3/Science and Technology
Rs 6,000-crore scheme to boost precision farming
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
The Centre is planning to earmark Rs 6,000 crore to promote precision farming. In this regard, a Smart Precision Horticulture Programme will be launched by the Union Ministry of Agriculture under the existing Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme.
About
- Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture, is an innovative agricultural method that utilizes advanced technologies such as GPS, sensors, data analytics, drones, and remote sensing to monitor and manage crop production with high precision.
The goal is to
- optimize inputs (such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides) based on specific site conditions to maximize yield, minimize waste, and lessen environmental impact.
Benefits
- Increased Productivity: By assessing field variability, farmers can customize inputs to address the specific needs of their crops, leading to enhanced yield and efficiency.
- Resource Optimization: This approach ensures the careful use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, which cuts down on waste and reduces production costs.
- Environmental Benefits: Lowering chemical use helps prevent soil and water contamination, fostering sustainable agricultural practices.
- Risk Management: Real-time data gathering and analysis enable farmers to make well-informed decisions, mitigating risks related to unpredictable weather and crop diseases.
Challenges
- High Initial Cost: The adoption of precision farming technologies requires substantial investment in tools and infrastructure, posing a barrier for smallholder farmers.
- Technical Expertise: Farmers must be trained to effectively use precision tools, analyze data, and apply findings in their farming practices.
- Digital Divide: Limited access to reliable internet, particularly in rural regions, hinders the widespread adoption of precision farming.
- Data Management: Handling and interpreting large volumes of data necessitate specialized software and expertise, which are often not available to smaller farmers.
Context
- As a contemporary farming strategy, precision agriculture addresses all elements of resources important for farming, such as soil, water, and nutrients.
- However, in India, the focus has primarily been on enhancing nutrient-use efficiency (NUE) and water-use efficiency (WUE).
- The integration of precision farming into mainstream agricultural systems in India remains limited.
Steps taken
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY), which emphasizes water-use efficiency and soil health monitoring.
- The government promotes the use of drones, soil health cards, and satellite-based monitoring.
- Additionally, a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture has been announced to provide farmers with access to technology and information.
- PF technology is developed and disseminated through 22 Precision Farming Development Centres across the country.
- The Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), initiated during the Covid-19 pandemic, includes provisions for financing infrastructure projects related to smart and precision agriculture.
- Funds are also allocated to states/UTs for projects integrating AI and machine learning under initiatives like the National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
- Area Under Precision Farming
- Currently, precision farming in India is at an early stage, with limited coverage primarily in states such as Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh.
- This technology is mainly utilized in large commercial farms and areas with advanced irrigation systems.
Challenges in India
- Fragmented Land Holdings: The small size of farms in India makes it difficult to implement precision farming technologies on a large scale.
- Cost and Awareness: Many small farmers are unaware of or lack the resources to invest in high-tech agriculture solutions.
- Infrastructure Gaps: The absence of strong digital infrastructure in rural India limits the accessibility of precision farming tools.
Scheme to promote precision farming
- The Indian government intends to allocate Rs 6,000 crore to enhance precision farming.
- This scheme will leverage smart technologies such as IoT, AI, drones, and data analytics to improve productivity and resource efficiency while minimizing environmental impacts.
Coverage: The initiative will encompass 15,000 acres of land over five years, from 2024-25 to 2028-29, and is projected to benefit around 60,000 farmers.
Role of Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) in promoting precision farming
- The AIF currently provides financial support for infrastructure projects focused on smart and precision agriculture.
- Individual farmers and farming communities, such as Farmer Producer Organizations, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, and SHGs are eligible for loans with a 3% interest subvention when adopting technological solutions in their farming practices.
- These practices include:
- Farm/harvest automation;
- Acquisition of drones and installation of specialized sensors on fields;
- Utilization of blockchain and AI in agriculture;
- Remote sensing and Internet of Things (IoT).
Collaboration with other countries to promote precision farming in India
- The government is collaborating with nations such as the Netherlands and Israel to implement advanced farming solutions, with plans to establish 100 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) within five years.
- To date, 32 Indo-Israel CoEs have been established in 14 states.
GS3/Environment
India’s Renewable Energy Revolution Story
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
At the 4th Global Renewable Energy Investors Meet and Expo (RE-INVEST 2024) in Gandhinagar, the PM declared that India's solar revolution story will be painted in gold when the history of the 21st century is written. This is because installed solar energy capacity in India has increased by 30 times in the last 9 years, reaching 89.43 GW (as of August 2024). The PM also highlighted that the government has taken many big decisions in the green energy sector.
Renewable Energy Installed Capacity in India:
As of August 2024, Renewable Energy (RE) sources (including large hydropower) have a combined installed capacity of 199.52 GW. The following is the installed capacity for Renewables:
| Source | Installed Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|
| Wind power | 47.19 |
| Solar Power | 89.43 |
| Biomass/Cogeneration | 10.35 |
| Small Hydro Power | 5.07 |
| Waste To Energy | 0.60 |
| Large Hydro | 46.92 |
As per REN21 Renewables 2024 Global Status Report, India stands 4th globally in RE installed capacity (including large hydro), 4th in Wind Power capacity, and 5th in Solar Power capacity.
Growth of Renewable Energy Installed Capacity in India:
India’s installed non-fossil fuel capacity has increased by 396% in the last 8.5 years and stands at more than 207.76 GW (including large hydro and nuclear), which is about 46% of the country’s total capacity. The country has set an enhanced target at the UNFCCC’s COP26 (Glasgow, 2021) of 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based energy by 2030 - the world's largest expansion plan in renewable energy under the Panchamrit Pledge.
Key Growth Drivers of Renewable Energy in India:
- Government commitments to reduce India’s total projected carbon emissions by 1 billion tonnes by 2030.
- Reduction of carbon intensity of the nation’s economy by less than 45% by the end of the decade.
- Achievement of net-zero carbon emissions by 2070.
- Approval of solar cities and parks by the government, along with the establishment of 57 solar parks with a total capacity of 39.28 GW across the nation.
- Promotion of Floating PV Projects.
- Launch of the National Green Hydrogen Mission aiming to produce 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen per annum with an associated renewable energy capacity of about 125 GW by 2030.
- Medium and long-term targets for offshore wind power capacity additions set at 5 GW by 2022 and 30 GW by 2030.
- Implementation of the Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy in 2018 to promote an extensive grid-connected wind-solar PV hybrid system.
- Introduction of the PLI scheme in Solar PV manufacturing under AatmaNirbhar Bharat.
- Allowing up to 100% FDI under the automatic route for renewable energy generation and distribution projects, complying with the Electricity Act 2003.
Union Budget 2024 Highlights:
- The Centrally Sponsored Scheme for Solar Power (Grid) has been allocated INR 10,000 Cr.
- PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has been allocated INR 6,250 Cr. This scheme aids in the installation of solar rooftops in households.
- Exemption of Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on imports of 25 critical minerals essential for the renewable energy sectors has also been announced.
About the RE-INVEST 2024:
Organised by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, RE-Invest is a global platform that brings together key players in the renewable energy sector. The conference will delve into the future of energy, exploring trends, technologies, and policies shaping the global renewable energy landscape and helping to achieve UN SDGs 7 and 13. This unique platform will foster collaboration, knowledge sharing, and investment opportunities to advance India's renewable energy goals.
Government Initiatives/Achievements in the Green Energy Sector Highlighted by the PM at the RE-INVEST 2024:
- A new Bio E3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) policy has been approved to promote high-performance bio manufacturing.
- A viability gap funding scheme for offshore wind energy projects has been approved with an outlay of ₹7000 crore.
- The Union government has set aside a ₹1 trillion research fund for initiatives in electric mobility and high-performance bio manufacturing.
- India is the first G-20 country to meet climate commitments made in Paris nine years before the deadline.
GS2/Polity
Laws regarding early elections to Delhi Assembly
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
Delhi CM, Arvind Kejriwal, is anticipated to resign from his position and will discuss this in a meeting with Delhi Lieutenant Governor Vinai Kumar Saxena. He has proposed that Delhi Assembly elections take place concurrently with those in Maharashtra, even though the current term of the Delhi Assembly is set to conclude on February 23, 2025.
Article 324 of the Indian Constitution
- Article 324 empowers the Election Commission of India (ECI) to oversee and manage elections.
- The ECI is tasked with ensuring the election process is completed before the Assembly's five-year term concludes.
The Representation of the People Act, 1951
- According to Section 15(2) of this Act, elections cannot be announced less than six months before the Assembly's term ends unless the Assembly has been dissolved earlier.
Factors Considered by the ECI for Election Schedule
- The new Assembly (or Lok Sabha) must be formed before the end of the current Assembly's term, necessitating that the election process, including all formalities, is completed in advance.
- The ECI schedules elections by considering various factors such as:
- Weather conditions
- Availability of security personnel
- Local festivals
- Training requirements for election officers
- Procurement of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs)
- Prior to finalizing the election schedule, the ECI consults with local administration and police, aiming to synchronize voting in neighboring states where elections are occurring simultaneously.
Article 174(2)(b) of the Constitution
- This article permits the Governor to dissolve the Legislative Assembly, and the Council of Ministers can recommend the early dissolution of the Assembly.
- Once dissolved, the ECI is required to conduct elections within six months.
- An example of this procedure occurred in 2018 when the Telangana Assembly was dissolved early upon the Cabinet's recommendation, leading to elections before the term expired.
Delhi's Status as a Union Territory
- Delhi is classified as a Union Territory governed by the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991.
- Under this Act, the Lieutenant Governor (LG) has the authority to dissolve the Assembly; however, the ultimate decision rests with the Central Government.
- Section 6(2)(b) of the Act states that the Lieutenant Governor may dissolve the Assembly at any time. Even if the Chief Minister advises dissolution, the final decision is made by the Centre (through the LG).
- Despite the current CM's intention to resign and request early elections, he has not yet suggested dissolving the Assembly.
- Any successor for the CM role may be determined following a meeting among AAP MLAs.
Current Preparedness for Elections in Delhi
- The ECI is presently focused on conducting elections for the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly, which will occur in three phases from September 18 to October 1.
- Subsequently, elections in Haryana are scheduled for October 5, with counting for both Haryana and J&K taking place on October 8.
- Upcoming Assembly elections are also planned for Maharashtra and Jharkhand, with their terms concluding in November 2024 and January 2025, respectively.
- A special summary revision of the electoral rolls occurs a few months prior to elections.
- The electoral rolls for J&K, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand were published in August, whereas Delhi's updated rolls will be released on January 6, 2025, as part of the annual revision.
- Thus, it can be concluded that Delhi is not currently a priority for the ECI.
GS2/International Relations
What is Line of Actual Control (LAC)?
Source: AIR

Why in News?
The Union Ministry of External Affairs recently said that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China on the military standoff along the Line of Actual Control in eastern Ladakh have been “sorted out”
Understanding the Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is the boundary that differentiates between territory controlled by India and territory controlled by China.
- Though not officially recognized as a border, it acts as a de facto divider between the two countries.
- India estimates the length of the LAC to be 3,488 kilometers, while China believes it to be around 2,000 kilometers.
Three Sectors of the LAC
- The LAC is divided into three main sectors:
- Eastern Sector: Includes Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim.
- Middle Sector: Covers Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh.
- Western Sector: Located in Ladakh.
Geographical Context
- The LAC runs along the Tibetan Autonomous Region and Xinjiang on the Chinese side.
Source of Tension
- The LAC has been a persistent source of tension between India and China.
- There are areas along the border where the two countries have different perceptions of where the LAC lies.
- Both India and China patrol up to their respective perceptions of the LAC, leading to occasional transgressions.
India’s Claim Line vs. LAC
- India’s claim line, as depicted in official maps from the Survey of India, includes Aksai Chin and Gilgit-Baltistan.
- This indicates that the LAC is not the same as India’s claim line.
China’s Perspective
- For China, the LAC serves as the claim line, except in the eastern sector.
- In the eastern sector, China claims the entire Arunachal Pradesh region as part of South Tibet.
GS2/Polity
Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954
Source: Business Standard
Why in News?
The promise of spectacular cures advertised in the media from time to time, in fact, prompted separate legislation to curb such claims: the Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act.
Overview of the Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954
The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954 is a legislative framework aimed at regulating the advertisement of drugs and prohibiting the claims of magical qualities in remedies. The Act covers various forms of advertisements, including written, oral, and visual.
Key Provisions of the Magic Remedies Act
- Definition of Drug: Under the Act, the term "drug" encompasses medicines intended for human or animal use, substances used for the diagnosis or treatment of diseases, and articles that affect the body's functions.
- Definition of Magic Remedy: The definition of "magic remedy" extends beyond articles meant for consumption to include talismans, mantras, and charms that are claimed to possess miraculous powers for healing or influencing bodily functions.
Regulations on Advertisements
- The Act imposes strict regulations on the publication of advertisements related to drugs.
- Advertisements that create false impressions, make false claims, or are misleading are prohibited.
- Violations of these provisions can lead to penalties, including imprisonment or fines, upon conviction.
- The term "advertisement" under the Act includes all notices, labels, wrappers, and oral announcements.
Scope of the Magic Remedies Act
- The Act applies to all individuals and entities involved in the publication of advertisements, including manufacturers, distributors, and advertisers.
- Both individuals and companies can be held accountable for contraventions of the Act.
- If a company violates the Act, individuals in charge of its business operations may also be deemed guilty unless they can prove lack of knowledge or show due diligence in preventing the offense.
- Directors, managers, or officers of the company may be held liable if they consented to or neglected the offense.
Penalties for Violating the Act
- Violating the Act can result in imprisonment, fines, or both.
- For a first conviction, the violator may face up to six months in prison, fines, or both.
- For subsequent convictions, imprisonment may extend to one year, fines, or both.
- The Act does not impose any limits on the fines that may be imposed on individuals or organizations.
GS3/ Science and Technology
Cellulitis Disease
Source: Deccan Chronicle
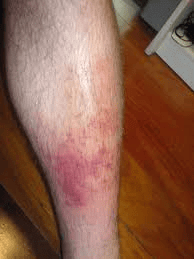
Why in News?
Cellulitis disease, which used to affect a few people during the rainy season, is now widespread in the erstwhile Karimnagar district, Telangana.
Understanding Cellulitis Disease
Cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin. It often occurs when bacteria, primarily streptococcus and staphylococcus, enter the body through a break or crack in the skin. This can happen after an injury, surgery, or even a small cut.
Common Areas Affected
- Cellulitis most frequently impacts the lower parts of the body, such as the legs,feet, and toes. However, it can also develop on other areas like the face,arms,hands, and fingers.
Symptoms of Cellulitis
- The skin affected by cellulitis becomes swollen, inflamed,painful, and warm to the touch.
- Some individuals might develop blisters, skin dimpling, or spots. Other symptoms of infection may include fatigue,chills,cold sweats,shivering,fever, and nausea.
Serious Complications
- If left untreated, cellulitis can spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream, leading to life-threatening complications.
Contagious Nature
- Cellulitis is not usually contagious. However, in rare cases, it can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact if an open wound from an infected person comes into contact with an open wound of another person.
Treatment for Cellulitis
- Treatment typically involves the use of antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection.
GS3/Science and Technology
Syntretus perlmani
Source: Hindustan Times

Why in News?
Researchers recently discovered a new species of parasitoid wasp named Syntretus perlmani that matures inside living adult fruit flies before bursting out, much like a scene from the Alien films.
About Syntretus perlmani:
- New species of parasitoid wasp has been discovered.
- This wasp is the first known to infect adult fruit flies, which is different from similar wasps that usually target the larvae and pupae stages of flies.
- The fruit fly invaders are called parasitoids because they always kill their hosts, unlike true parasites, which typically keep their hosts alive.
- Female S. perlmani wasps have a special tool called an ovipositor that allows them to place their eggs directly into the abdomen of adult fruit flies.
- After about 18 days, the eggs grow into wasp larvae, developing inside the host until they eventually kill the fly by emerging from its body.
- Researchers have found S. perlmani in several places across the eastern United States, including Mississippi, Alabama, and North Carolina.
|
38 videos|5283 docs|1116 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 17th September 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. How do emergency provisions in the Indian Constitution affect the relationship between the Centre and the states? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Rs 6,000-crore scheme for precision farming? |  |
| 3. How has India’s renewable energy revolution progressed in recent years? |  |
| 4. What are the legal provisions regarding early elections to the Delhi Assembly? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954? |  |
















