UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 19th October 2022 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Multidimensional Poverty Index

Context
As many as 41.5 crore people exited poverty in India during the 15-year period between 2005-06 and 2019-21, out of which two-thirds exited in the first 10 years, and one-third in the next five years, according to the global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
- Improvement in MPI for India has significantly contributed to the decline in poverty in South Asia.
Dimensions of Poverty:
- Absolute poverty – income below a certain threshold necessary to meet basic necessities of life (food, shelter, clothing, rent)
- Relative poverty – Individuals receiving income a certain level (e.g. 50%) below the median income of the general population.
- Persistent poverty – This is defined as a household which is below the poverty threshold line for 2 out of the past 3 years.
- Headcount Index – It is a widely-used measure, which simply indicates the proportion of the poor to total population. It does not indicate how poor the poor are.
- Poverty gap index – It is the ratio by which the mean income of the poor falls below the poverty line.
- The Sen index – It is a composite poverty measure, which combines incidence and intensity of poverty risk with the distribution of income among those at risk of poverty.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index:
- It is a report produced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI)
- The global MPI constructs a deprivation profile of each household and person through 10 indicators spanning health, education and standard of living. All indicators are equally weighted within each dimension.
- The global MPI identifies people as multidimensionally poor if their deprivation score is 1/3 or higher.
- The MPI is calculated by multiplying the incidence of poverty and the average intensity of poverty.
- The MPI ranges from 0 to 1, and higher values imply higher poverty.
- By identifying who is poor, the nature of their poverty (their deprivation profile) and how poor they are (deprivation score), the global MPI complements the international $1.90 a day poverty rate, which was revised by the World Bank last month to $2.15 per day.
- India ranked 62 in the Global MPI 2020 which ranked 107 countries.
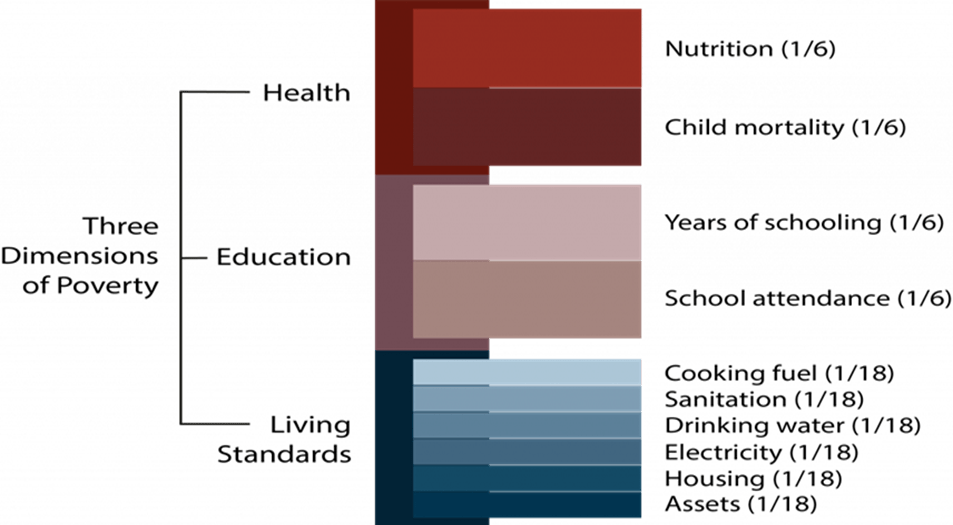
Findings of the report:
- The incidence of poverty fell from 55.1% in 2005/06 to 16.4% in 2019/21 in the country.
- Deprivations in all 10 MPI indicators saw significant reductions as a result of which the MPI value and incidence of poverty more than halved.
- Globally, of the total 610 crore people across 111 developing countries, 19.1% or 120 crore live in multidimensional poverty. Nearly half of them live in severe poverty.
- The report doesn’t fully assess the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on poverty in India as 71% of the data from the National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-2021) relied upon for MPI were collected before the pandemic.
- The report also notes that for India, the relative reduction from 2015/2016 to 2019/21 was faster: 11.9% a year compared with 8.1% from 2005/2006 to 2015/2016. This is unsurprising because relative poverty reduction is easier to achieve when starting levels of poverty are lower.
- Bihar, the poorest State in 2015/2016, saw the fastest reduction in MPI value in absolute terms. The incidence of poverty there fell from 77.4% in 2005/2006 to 52.4% in 2015/2016 to 34.7% in 2019/2021.
- Improvement in MPI for India has significantly contributed to the decline in poverty in South Asia.
- It is for the first time that India is not the region with the highest number of poor people, at 38.5 crore, compared with 57.9 crore in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Significance of MPI:
- Wide coverage across the length and breadth of the country and has international comparability.
- The MPI is, in principle, able to make statements about the extent of global multidimensional poverty in a way the World Bank’s $1 a-day poverty line makes about global absolute income poverty.
- More reliable database than the one used for the income poverty measure, where the comparability of survey instruments across country and over time is much less certain.
- Since it is based on household survey information, it is much more actionable and a policy-relevant indicator for countries and agencies than the HDI.
- One can decompose the MPI by region, by particular groups, and by indicator, thereby allowing countries to directly see which groups suffer most and in which dimensions they are deprived.
Poverty Challenges in India:
- India has by far the largest number of poor people worldwide at 22.8 crore, followed by Nigeria at 9.6 crore.
- Two-thirds of these people live in a household in which at least one person is deprived in nutrition.
- There were also 9.7 crore poor children in India in 2019/2021- more than the total number of poor people, children and adults combined, in any other country covered by the global MPI.
- Of the 10 poorest States in 2015/2016, only one (West Bengal) was not among the 10 poorest in 2019/2021. The rest— Bihar, Jharkhand, Meghalaya, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Rajasthan —remain among the 10 poorest.
- While poverty levels have not worsened, levels of under-nutrition are still very high. There is no marked acceleration in rate of improvement between NFHS-3 and NFHS-4 and NFHS-4 and NFHS-5. And the MPI mainly captures the pre-COVID situation because 71% of the NFHS-5 interviews were pre-COVID.
India’s Multidimensional Poverty Index:
- Steered by the Government of India’s Global Indices for Reforms and Growth (GIRG) initiative, the National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) for India is aimed at leveraging the monitoring mechanism and methodology of the globally recognised MPI to rigorously benchmark national and subnational performance and drive programmatic actions and reforms.
- It is released by NITI Aayog
Objectives:
- Enhanced high-level view of poverty at the national level
- Complements monetary poverty measures
- Information to shape policy
- Provides incentives for leaving no one behind and reaching the furthest behind first
- To track poverty over time
- To highlight “how” poor are the people in poverty
- To show the percentage of people who are multidimensionally poor
- To show the percentage of weighted deprivations the average multidimensionally poor person suffers from.
Way forward:
- The ongoing task of ending poverty remains daunting.
- The Sustainable Development Goal target 1.2 is for countries to reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women, and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions by 2030.
GS-II
Fateful Triangle China,USA and India and Changing World Order

Context
America’s national security strategy issued by the Joe Biden Administration last week and the Chinese Communist Party’s 20th Congress this week promise to reshape the geopolitics of Asia and the Indo-Pacific.
Historical background of USA-CHINA
- Context of World War II: Asia has seen multiple phases in the US-China relationship. In the second half of the 19th century, American missionaries began to arrive in China and began to generate empathy for the nation. During World War II, Washington backed Chinese nationalists in their fight against Japanese occupation.
- US efforts to isolation China: The US tried to isolate China from 1949 when the communists prevailed over the nationalists.
- Cooperation to counter Soviet: The 1970’s saw the US and communist China come together to counter the Soviet Union.
- Multiple Economic engagement: The 1980s saw the beginning of an economic engagement that turned into a huge commercial and technological partnership from the 1990s.
What is the USA’s assumption and China’s ambition?
- China as responsible stakeholder: The US establishment dismissed the idea of China as potential threat and bet that Beijing could become a “responsible stakeholder” in the world order.
- Democratization of Chinese society is inevitable: America also believed that China’s growing economic prosperity would inevitably lead to greater democratisation of its society.
- Visible decline of west: China, however, has steadily moved in the other direction, especially under Xi, who has convinced himself that the West is in terminal decline.
- China’s ambition to change the world order: Xi is determined to seize this moment to reshape the Asian as well as the global order to suit Chinese interests. At the same time, China has become increasingly repressive at home.
- Explicit expression of ambition: Xi made no effort to hide China’s new geopolitical ambition nor has he been defensive about his authoritarian rule. This, in turn, bestirred the US into rethinking its China policy in the second decade of the 21st century.
How China is asserting itself?
- Asserting own version of Global order: Beijing, argues that recent history points to the superiority of the Chinese system over the Western one. And it offers its own versions of a global order – economic, political and social. Since the end of the Cold War, ideological arguments had receded into the background but are now back in significant play.
- China offering model Economic Globalization: China continues to sing praises of the model of economic globalisation that has facilitated Beijing’s rise over the last four decades. But under Xi, China has emphasised the importance of self-reliance in the name of a “dual circulation strategy”.
- Leveraging world’s dependence for strategic gain: At the same time, Beijing has sought to enhance the world’s dependence on its economy and leverage it for strategic benefit. The profound political backlash against trade and economic cooperation with China in the US led to the questioning of economic globalisation in the Trump years.
- China building the powerful military: As China became a richer country, it also focused on building a powerful army. Using both the instruments of hard power, China under Xi has actively sought to undermine US alliances in Asia and mount pressure on American forward military presence in Asia.
How USA’s policy is changing towards China?
- Structured policy of rivalry: The traditional soft attitude to China yielded to a more confrontational approach during the Donald Trump presidency. Joe Biden has developed that into a more structured policy of competing with China.
- Combine challenge of China and Russia: The National Security Strategy of the Trump administration postulated the return of great power rivalry and the need to respond to the challenges presented by Russia and China. Biden’s NATIONAL SECURITY STRATEGY builds on that proposition and identifies China as the more demanding challenge than Russia, despite Moscow’s aggression against Ukraine.
- China is more capable than Russia: In his foreword to the National security strategy, Biden says “Russia poses an immediate threat to the free and open international system, recklessly flouting the basic laws of the international order today, as its brutal war of aggression against Ukraine has shown.” He names China, on the other hand, as “the only country with both the intent to reshape the international order and, increasingly, the economic, diplomatic, military and technological power to advance that objective”. While the European challenge is real, the Biden Administration now sees the Indo-Pacific as the principal strategic theatre.
- Projecting China as autocracy against the democracy: The US has sought to locate the conflict with China (and Russia) as a fundamental struggle between “democracies and autocracies”. Recognising the limited enthusiasm for the framing in Asia, the National security strategy now talks of broadening the coalition to include countries that may not be democratic. Beijing, on the other hand, argues that recent history points to the superiority of the Chinese system over the Western one.
- Building the bilateral alliances: The US is now pushing back. The principal instrument in the US response has been rebuilding the traditional bilateral alliances with Japan and Australia as well as constructing new partnerships with countries like India and developing new regional coalitions.
India’s role in shaping the world order
- Convergence of National interest wit USA: Today, Indian and American policies are converging. For both Delhi and Washington, Beijing presents the main national challenges.
- Reducing economic dependence on China: On the economic and technological front, both India and the US are trying to reduce their exposure to China.
- Keeping independent foreign policy: On the geopolitical front, a US plan to look beyond formal alliances suits Delhi, which is wedded to an independent foreign policy.
- Opportunity for cooperation: It is never easy to translate abstract convergence into concrete policies. The current churn in Asia provides Delhi and Washington with a historic opportunity to build on the new convergences in the areas of trade, technology, and geopolitics.
Conclusion
changing world order will have short term repercussion on economic front for developing country like India. India has a great opportunity to be the rule maker of new global order rather than just a rule follower. World order of 21st century will revolve around the fateful triangle of India, China and USA.
One Health Concept

Context
Recently, a new One Health Joint Plan of Action was launched by the Quadripartite-the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE).
- In April 2022 a pilot project in the state of Uttarakhand was launched to implement the One Health Framework by One Health Support Unit.
What is One Health Joint Plan of Action?
- About:
- The Action plan developed through a participatory process, provided a set of activities that aim to strengthen collaboration, communication, capacity building and coordination equally across all sectors responsible for addressing health concerns at the human-animal-plant-environment interface.
- The plan is valid from 2022-2026 and is aimed at mitigating the health challenges at global, regional, and country levels.
- Focus Areas of the Action Plan:
- One Health capacity for health systems
- Emerging and re-emerging zoonotic epidemics
- Endemic zoonotic
- Neglected tropical and vector-borne diseases
- Antimicrobial resistance and the environment
- Food safety risks
What is the One Health Concept?
- About:
- One Health is an approach that recognizes that the health of people is closely connected to the health of animals and our shared environment.
- One Health’ vision derives its blueprint from the agreement between the tripartite-plus alliance comprising the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE).
- It’s purpose is to encourage collaborations in research and sharing of knowledge at multiple levels across various disciplines like human health, animal health, plants, soil, environmental and ecosystem health in ways that improve, protect and defend the health of all species.
Why has the One Health Concept become more Important?
- Human Expansion: Human populations are growing and expanding into new geographic areas due to which close contact with animals and their environments provides more opportunities for diseases to pass between animals and people.
- Of the contagious diseases affecting humans, more than 65% are of zoonotic or animal to man origin.
- Environmental Disruptions: Disruptions in environmental conditions and habitats can provide new opportunities for diseases to pass to animals.
- International Travel & Trade: The movement of people, animals, and animal products has increased from international travel and trade due to which diseases can spread quickly across borders and around the globe.
- Viruses in Wildlife: Scientists have observed that there are more than 1.7 million viruses circulating in wildlife, and many of them are likely to be zoonotic.
- This implies that unless there is timely detection, India risks facing many more pandemics in times to come.
Way Forward
- The Covid-19 pandemic showed the relevance of 'One Health' principles in the governance of infectious diseases, especially efforts to prevent and contain zoonotic diseases throughout the world.
- India needs to scale up such a model across the country and to establish meaningful research collaborations across the world.
- There is a need to develop best-practice guidelines for informal market and slaughterhouse operation (e.g., inspections, disease prevalence assessments), and creating mechanisms to operationalise ‘One Health’ at every stage down to the village level.
- Awareness generation, and increased investments toward meeting ‘One Health’ targets is the need of the hour.
GS-III
Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)

Context
Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Housing & Urban Affairs inaugurated Asia’s largest Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) plant in Lehragaga, Sangrur, Punjab.
- The Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) plant inaugurated in Sangrur is a step in achieving objectives of the Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) scheme.
- This scheme was launched by Government of India in October 2018 to establish an ecosystem for production of Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) from various waste/ biomass sources in the country.
- The scheme aims to empower and unleash the rural economy by supporting farmers, increase India’s domestic energy production and self-sufficiency and also reduce the air pollution, and help India lead the world toward a clean energy transition.
What is Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)?
- Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) means the mixture of hydrocarbon gases and vapours consisting mainly of Methane in gaseous form, which has been produced by the decomposition of animal and plant waste, purified and compressed for use as an automotive fuel and industrial application.
- Biogas can be compressed after removal of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, the same way as natural gas is compressed to CNG, and used to power motor vehicles.
- Irrespective of technology, producing CBG from biomass involves a two-pronged approach:
- Biogas is produced through anaerobic decomposition of biomass.
- Since biogas contains 55 to 60 per cent methane, 40 to 45 per cent carbon dioxide (CO2) and trace amounts of hydrogen sulphide.
- The second process involves purifying the gas to remove carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide gases to prepare CBG.
- Chemically, CBG is the same as CNG — both are compressed methane — and has the same calorific value.
- The difference is that while CNG is a by-product of petroleum, CBG can be produced from any biomass.
- This makes CBG a commercially viable option as it can be directly used to replace CNG in transportation fuel.
- Just like CNG, CBG too can be transported through cylinders or pipelines to retail outlets.
- Its solid by-products can be used as bio-manure.
- It is a rich source of silica that not only aids in the growth and yield of crops but also bestows immunity against many diseases and prevents toxic material uptake by plants such as arsenic, cadmium, lead and other heavy metals.
- It can thus help reduce the requirement of chemical fertilisers.
- The other by-product is CO2.
- It can be tapped while purifying the biogas and used to produce liquid or solid CO2, which have high demand for food preservation or to be used in fire extinguishers.
- CBG and its by-products hold the chance for a circular economic growth.
Black Hole, Resolving the Mistry
Context
For the very first time, scientists noted that this observation of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave (LIGO) observatories coincided with the measurements made by other telescopes that measured visual and electromagnetic signals.
What is Black hole?
- A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying.
- Because no light can get out, people can’t see black holes. They are invisible. Space telescopes with special tools can help find black holes. The special tools can see how stars that are very close to black holes act differently than other stars.
What is the background?
- LIGO Observations: In 2017, astrophysicists observed an unusual feat among the stars. The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave(LIGO)observatories recorded a signal which indicated that two massive and dense stellar bodies had merged to form a third body, likely a black hole.
- Generation gravitational waves: In the process they gave off vibrations that quite literally shook the universe and its very fabric of space time.
- Neutron stars: Scientists, piecing together evidence from complementary measurements, surmised that the event they had observed was of two neutron stars merging and forming a black hole and, in the process, giving off light.
What are the observations through telescopes?
- The matter moving faster than light: An unusual jet of matter was observed that gave an illusion of travelling faster than light. These were all exciting phenomena observed for the very first time by telescopes and observatories.
- Confirmation by Hubble Space Telescope: Now, using data that had been recorded by the Global astro metric Interferometer for Astrophysics (GAIA) spacecraft and Hubble Space Telescope instruments, scientists have confirmed that the above picture is correct. They have made it more precise and descriptive.
- Seven times the speed of light: In a paper published in Nature, they describe measuring the “apparent speed” of the jet to be about seven times the speed of light.
- Lorenz factor: They have also measured more accurately a factor called the Lorenz factor which scales with the actual speed of the particles in the jet. Unlike earlier estimates which placed this factor at about 4, the present paper estimates this factor to be over 40. This is because they measure the speed of the relativistic jet to be close to 0.9997c, where “c” is the speed of light.
- Clarity about the source as neutron star in block hole generation: This resolves the earlier fuzziness about what the source was and puts the source clearly as massive neutron stars merging to give a black hole and throwing off relativistic jets of particles in the process.
Merging of Neutron stars
- Born out of Supernova explosion: Neutron stars are stellar corpses, left behind after a star has undergone a supernova explosion and reached the end of its lifetime. They are extremely dense, containing more mass than the sun in a sphere that is a few tens of kilometre wide.
- Produces fast moving material: This has been seen in many active galactic nuclei galaxy centres that harbour black holes and binary star systems within our galaxy, where one of the stars is a black hole. “Mostly, black holes are responsible for producing such fast moving material
Why present observations about black Hole are significant?
- Estimating changing position of sky: The present measurements and observations made with GAIA data are extremely challenging. They amount to measuring the position of an object in sky coordinates. These authors measured a change in sky position one millionth the span of the full moon. Normally, if one were making these measurements from earth-based telescopes, it would require data from radio telescopes spaced apart by intercontinental distances.
- VLBI technique: This technique is called Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) and was used in the earlier papers. “Here, the authors could beat VLBI in precision because they calibrated Hubble Space Telescope data with GAIA, which is a precision astrometry mission.
- It’s an estimate not a measurement: the researchers used both their Hubble Space Telescope and GAIA optical position measurement along with the earlier VLBI position measurement to get a better estimate of the speed of the source and angle (viewing angle) with which it is travelling with respect to us on earth. This estimate requires plugging in equations of the special theory of relativity. “So, it is an estimate as opposed to a measurement.
- Improvement in estimation: we have learnt that neutron star mergers can result in material moving with speeds as high as 0.9997c.Earlier results using Very Long Baseline Interferometry had pegged this value at about 0.938c. with the new results this lower limit has been improved. Even earlier, with VLBI, it was understood that it was a neutron star merger that produced such ultra-relativistic material. Before the VLBI results, there were several models that could replicate the observations.
- Explanation using ultra realistic material: The observations could be explained both by ultra-relativistic material and non relativistic material, with some differences in assumptions. That study indicated that the observed gamma ray bursts were produced along with the ultra-relativistic material.
Conclusion
Current discovery strengthens the hypothesis that such neutron star mergers are responsible for a class of gamma ray bursts. Gamma ray bursts are flashes of extreme gamma ray photons that release a huge amount of energy nearly 1047 They come from different galaxies in the universe and are observed here quite frequently.
Kamikaze Drone

Context
Recently, Ukraine’s capital region was struck by Iranian-made kamikaze drones.
- These kamikaze drones are not new, and have also been supplied by the US to Ukraine in its ongoing war with Russia.
What are Kamikaze Drones?
- About:
- These are small unmanned aircraft that are packed with explosives that can be flown directly at a tank or a group of troops that are destroyed when it hits the target and explodes.
- They are called Switchblade because their bladelike wings spring out on launch.
- The drones have the capability of going past traditional defences to strike its targets and also cost a fraction of what the larger counterparts do.
- These small lethal drones are difficult to detect on radar, and they can even be programmed to hit targets without human intervention, based on facial recognition.
- Countries Possess such Drones:
- Although the Kamikaze might be the most advanced form of this genre of drones, Russia, China, Israel, Iran and Turkey all have some version of it.
What are its Specifications?
- Light Weight:
- Weighing just five-and-a-half pounds, including its small warhead, the Switchblade can be taken into battle in a backpack and fly up to 7 miles to hit a target.
- Can Adjust Blast Radius:
- The Switchblade has a feature that allows the operator to adjust the blast radius. So, it can kill the driver of a vehicle but not a passenger, for example. The weapon can be “waived off” up to two seconds before impact.
- A blast radius is the distance from the source that will be affected when an explosion occurs.
- Cameras for Centralised View of Area of Operation:
- The Switchblade also has cameras that show a target seconds before impact.
- The drone cruises at 63 miles per hour and provides “operators with real-time video downlinks for a centralised view of the area of operation”.
Vision—Developed India: Opportunities and Expectations of MNCs

Context
According to the EY (Ernst & Young)- Confederation of Indian Industries (CII) report titled ‘Vision—Developed India: Opportunities and Expectations of MNCs’, India will attract FDI (Foregn Direct Investment) worth USD 475 billion in 5 years.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Overview:
- 71% of MNCs (Multinational Corporation) working in India consider the country an important destination for their global expansion.
- India has seen a consistent rise in FDI in the last decade, with FY22 receiving USD 84.8 billion, despite the impact of the pandemic and geopolitical developments.
- India is seen as an emerging manufacturing hub in global value chains, as a growing consumer market and as a hub for ongoing digital transformation.
- Over 60% of MNCs stated improvement in the business environment in the last three years.
- Against the backdrop of growth challenges MNCs consider India an attractive investment destination and are planning expansion.
- Cause of Optimism:
- The commitments for investments in the infrastructure sector offer assurance about India’s serious aspirations for providing best-in-class infrastructure and new opportunities for investments.
- Optimism on India’s growth is led by strong momentum in domestic consumption, a growing services sector, digitalization, and the government’s focus on manufacturing and infrastructure.
- The estimated real growth in consumption is the third highest behind only the US and China, while the fast-expanding digital economy is expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2025.
- Suggestions:
- It is high time India took the leap to the next level of economic development, including early closure of free trade agreements, continued reforms to enhance ease of doing business, faster implementation of infra projects and goods and services tax reforms.
What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- About:
- A FDI is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country.
- FDI lets an investor purchase a direct business interest in a foreign country.
- Investors can make FDI in a number of ways.
- Some common ones include establishing a subsidiary in another country, acquiring or merging with an existing foreign company, or starting a joint venture partnership with a foreign company.
- Apart from being a critical driver of economic growth, FDI has been a major non-debt financial resource for the economic development of India.
- It is different from Foreign Portfolio Investment where the foreign entity merely buys stocks and bonds of a company.
- FPI does not provide the investor with control over the business.
- Routes of FDI:
- Automatic Route:
- In this, the foreign entity does not require the prior approval of the government or the RBI (Reserve Bank of India).
- In India FDI up to 100% is allowed in non-critical sectors through the automatic route, not requiring security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Prior government approval or security clearance from MHA is required for investments in sensitive sectors such as defence, media, telecommunication, satellites, private security agencies, civil aviation and mining, besides any investment from Pakistan and Bangladesh.
- Government Route:
- In this, the foreign entity has to take the approval of the government.
- The Foreign Investment Facilitation Portal (FIFP) facilitates the single window clearance of applications which are through approval route. It is administered by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Automatic Route:
What is the Status of FDI Inflows in India?
- In 2021, FDI inflows increased from USD 74,391 million in FY 19-20 to USD 81,973 million in FY 20-21.
Top 5 FDI Sourcing Nation:
- Singapore: 27.01%
- USA: 17.94%
- Mauritius: 15.98%
- Netherland: 7.86%
- Switzerland: 7.31%
Top Sectors:
- Computer Software & Hardware: 24.60%
- Services Sector (Fin., Banking, Insurance, Non-Fin/Business, Outsourcing, R&D, Courier, Tech. Testing and Analysis, Other): 12.13%
- Automobile Industry: 11.89%
- Trading: 7.72%
- Construction (Infrastructure) Activities: 5.52%
Top Destinations:
- Karnataka: 37.55%
- Maharashtra: 26.26%
- Delhi: 13.93%
- Tamil Nadu: 5.10%
- Haryana: 4.76%
FDI Equity inflow in Manufacturing Sectors have increased by 76% in FY 2021-22 (USD 21.34 billion) compared to previous FY 2020-21 (USD 12.09 billion).
What has the Government done to boost FDI?
- New FDI norms
- Make in India
- Atmanirbhar Bharat
- India’s footing in global supply chains
- National technical Textile Mission
- Production Linked Incentive Scheme
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana
Polio eradication
Context
Global leaders committed to donating $2.54 billion (or Rs 19 crore) for eradicating polio at the World Health Summit.
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation pledged $1.2 billion to the largest international public health initiative, Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI).
About:
- Wild poliovirus is endemic in just two countries — Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- However, there has been new detections of polio this year in previously polio-free countries like the United States, Israel and the United Kingdom and southeast Africa.
- The funding will support vaccinating 370 million children annually over the next five years and continue disease surveillance across 50 countries.
- It also includes roll-out of the novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2) to stop outbreaks of type 2 circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) more sustainably.
- Additionally, outbreaks of cVDPV, variants of the poliovirus can emerge in places where not enough people have been immunized.
Significance:
- If fully funded, the strategy can save up to $33.1 billion in health cost savings this century compared to the price of controlling outbreaks.
- It would also be able to deliver additional health services and immunizations alongside polio vaccines to underserved communities.
About World Health Summit:
- World Health Summit is an international health conference held annually in Berlin, Germany.
- It was founded in 2009 and is traditionally held under the patronage of the German Chancellor, the French President, the President of the European Commission, and the Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Aim: to bring together stakeholders from politics, science, the private sector, and civil society from around the world to set the agenda for a healthier future by inspiring innovative solutions for better health and well-being for all.
About Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI):
- It is a public-private partnership led by national governments with six partners
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Rotary International
- the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- Gavi, the vaccine alliance.
- Its goal is to eradicate polio worldwide.
|
39 videos|4644 docs|996 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 19th October 2022 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the three main subjects covered in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of daily current affairs in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in relation to the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. How can candidates effectively prepare for the UPSC exam using the given article on daily current affairs? |  |
| 5. What is the role of UPSC in conducting the exam and selecting candidates for various government posts? |  |
























