UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 1st December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
What is C-PACE (Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit)?
Source:Business Standard

Why in News?
Recently, the Central Government informed the Lok Sabha that corporate exits are now happening in 70-90 days under the Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE).
About C-PACE (Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit):
- C-PACE has been established to centralize the process of removing companies from the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) Register.
- It operates through the Registrar of Companies (RoC) to manage the processing and disposal of applications.
- C-PACE functions under the supervision of the Director General of Corporate Affairs (DGCoA).
- The initiative is aimed at expediting the voluntary winding up of companies to under six months through process re-engineering.
- This is part of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs' efforts to improve the ease of doing business and facilitate smoother exits for companies.
- C-PACE is located at the Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs in Gurgaon.
Significance of C-PACE:
- C-PACE aims to alleviate the burden on the registry, providing stakeholders with a streamlined filing process.
- It ensures timely and structured removal of company names from the register, making the process hassle-free.
Rules to Remove a Company from the Registrar of Companies:
- According to Section 248 of the Companies Act, a company's name can be removed from the RoC if it has not been conducting any business or operations for the preceding two financial years.
- If the company has not applied for dormant status within this period, it is eligible for removal.
GS3/Health
What is Aortic Stenosis?
Source:News Medical
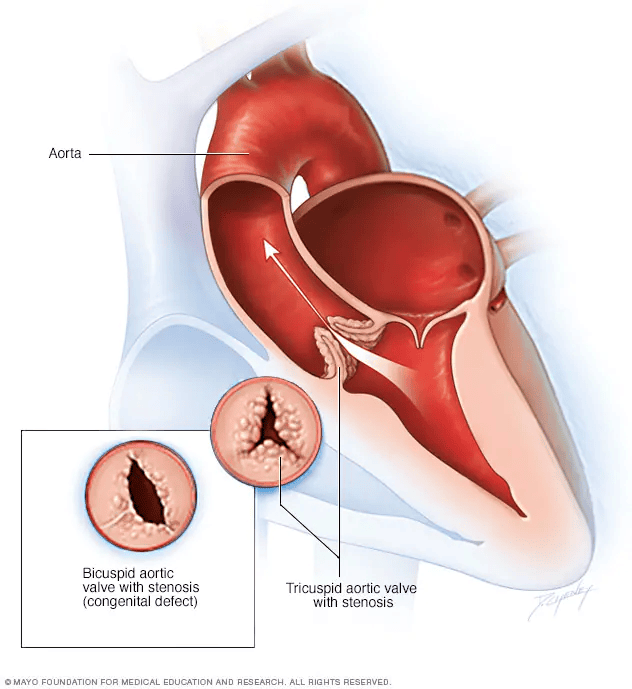
Why in News?
A large population study indicates that insulin resistance may be an important risk factor for the development of heart valve disease — aortic stenosis.
About Aortic Stenosis:
- The aortic valve is crucial for maintaining blood flow from the heart's lower left chamber (left ventricle) to the aorta, the primary artery that carries blood to the body.
- Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve narrows, resulting in abnormal blood flow. This condition can range in severity from mild to severe.
- Over time, this narrowing forces the left ventricle to exert more effort to pump blood through the valve, potentially leading to thickening, enlargement, and weakening of the heart muscle.
- If left untreated, aortic stenosis can progress to heart failure.
Main Cause
- The most common cause of aortic stenosis is atherosclerosis, which involves the buildup of calcium deposits on the aortic valve as a person ages.
- These calcium deposits make the valve tissue stiff and less flexible, contributing to the narrowing of the valve.
Symptoms
- Many individuals with aortic stenosis may not display noticeable symptoms until blood flow is significantly restricted.
- Possible symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Rapid or fluttering heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Dizziness or light-headedness, which may lead to fainting
- Challenges in walking short distances
- Reduced overall activity level or diminished capacity to perform daily tasks
Treatment
- Treatment options for aortic stenosis are determined by the severity of the condition, which may include surgical interventions to repair or replace the affected valve.
GS1/History & Culture
Key Facts about Lothal
Source:Hindustan Times
Why in News?
Recently, a tragic incident occurred near the archaeological site of Lothal in Gujarat, where an IIT Delhi student lost their life and three others sustained injuries due to a soil collapse while they were conducting research in a pit.
About Lothal:
- Lothal is an archaeological site located in the Bhal region of Dholka, Ahmedabad, Gujarat.
- It is recognized as one of the significant cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization (IVC).
- The history of Lothal dates back to approximately 2400 BC.
- It was one of the southern cities of the IVC, positioned in the Gulf of Khambat region.
- Lothal is notable for being the only port town of the IVC, discovered by Indian archaeologist SR Rao in 1954.
- The name Lothal translates to 'Mound of the Dead', indicating its historical significance and ancient ruins.
- This city provides valuable insights into the Harappan culture and the broader Indus Valley Civilization.
- Like other cities within the IVC, Lothal exhibited remarkable architecture and urban planning.
- Excavations have shown that the town was organized into two distinct sections:
- The upper section, known as the acropolis, was inhabited by the ruler and other prominent residents.
- The lower section catered to the common populace.
- The entire city was equipped with an advanced drainage system, well-constructed paved roads, and many homes featured baths, some of which were constructed as double-storied buildings on mud platforms.
- The most architecturally advanced portion of Lothal was its dockyard, which provided docking facilities for ships.
- It is recognized as the world's oldest known artificial dock, connected to a former channel of the Sabarmati River.
- Lothal was historically a leading center of trade.
- The city was actively involved in trading goods such as beads, gems, and luxury ornaments, which were exported to regions in West Asia and Africa.
- Pottery was another significant industry in Lothal.
- Archaeological findings of a fire altar suggest that the inhabitants worshipped both the fire god and the sea god.
GS1/History & Culture
Notre-Dame Cathedral
Source:BBC
Why in News?
Recently, the French President commended over 1,000 artisans who played a crucial role in the restoration of Paris' Notre-Dame Cathedral, referring to it as "the project of the century." This comes five and a half years after the catastrophic fire that severely damaged this Gothic architectural marvel.
About Notre-Dame Cathedral:
- Notre-Dame Cathedral is a prominent church located in Paris, France.
- It is renowned as one of the most significant Gothic cathedrals from the Middle Ages, recognized for its vast size, ancient history, and architectural significance.
- The cathedral's intricate sculptures and stunning stained-glass windows showcase a strong influence of naturalism, contrasting with the earlier Romanesque style.
Construction
- Notre-Dame is among the earliest examples of Gothic cathedrals, with construction spanning the entire Gothic period.
- The cathedral exhibits various Gothic styles, from the early phase to the rayonnant style.
- The project was initiated by Maurice de Sully, the Bishop of Paris.
- The foundation stone was laid by Pope Alexander III in 1163, and the high altar was consecrated in 1189.
- By 1250, significant parts, including the choir, western facade, and nave, were completed. Additional features such as porches and chapels were added over the next century.
Historical Significance
- Notre-Dame has been the venue for numerous historical milestones, including the coronation of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1804.
- It has also hosted the weddings of multiple French monarchs, such as Francis II in 1558 and Henry IV in 1572.
Fire Incident
- On April 15, 2019, Notre-Dame Cathedral suffered a devastating fire that destroyed its roof and iconic spire.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
Notre-Dame Cathedral is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, highlighting its cultural and historical importance.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Tungsten?
Source:The Hindu
Why in News?
The Tamil Nadu Chief Minister recently wrote to the Prime Minister seeking the cancellation of rights granted by the Centre to a private firm to mine tungsten in Nayakkarpatti Tungsten Block in Madurai district.
About Tungsten:
- Tungsten is a chemical element represented by the symbol W and has the atomic number 74.
- It is classified as a transition metal and exists as a solid at room temperature.
- This element occurs naturally in the earth and is found in various rocks and minerals, but it is never found in its pure metallic form.
- Common mineral forms of tungsten include wolframite and scheelite.
- Elemental tungsten appears as a white to steel gray metal, depending on its purity, and can be utilized in its pure form or as part of various metal alloys.
Features:
- It is one of the densest metals, with a density of 19.3 g/cc.
- Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, reaching 3410 °C.
- It possesses the lowest vapor pressure of all metals at 4.27 Pa at 3410 °C.
- The metal also exhibits the highest tensile strength of any metal when heated over 1650 °C.
Uses:
- Tungsten alloys are noted for their strength and flexibility, wear resistance, and good electrical conductivity.
- This metal is used in a variety of products, including:
- X-ray tubes
- Light bulbs
- High-speed tools
- Welding electrodes
- Turbine blades
- Golf clubs
- Darts
- Fishing weights
- Gyroscope wheels
- Phonograph needles
- Armor-piercing bullets
- Tungsten is also utilized as a catalyst to accelerate chemical reactions.
- Chemical compounds of tungsten serve various purposes, such as:
- Cemented tungsten carbide, a hard material used for grinding wheels and cutting or forming tools.
- Other compounds are applied in ceramic pigments, fire retardant coatings for fabrics, and color-resistant dyes for textiles.
Major producers:
- China is the leading global producer of tungsten.
- Other significant producers include Vietnam, Russia, and North Korea.
- Tungsten has been classified as a Critical Mineral by the Government of India.
GS3/Science and Technology
WOH G64 Star
Source:Indian Express
Why in News?
Recently, for the first time, scientists have succeeded in taking a zoomed-in picture of the WOH G64 star which is located in another galaxy.
About WOH G64 Star:
- WOH G64 is a massive star that has been imaged with remarkable clarity by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (ESO’s VLTI).
- This star resides in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy that orbits the Milky Way and is one of our closest galactic neighbors.
- It was discovered in the 1970s by astronomers Bengt Westerlunds, Olander, and Hedin, with "WOH" being an acronym for their names.
- WOH G64 is approximately 160,000 light years away from Earth and is classified as a red supergiant due to its immense size, which is about 2,000 times larger than that of the Sun.
- The recent imaging has shown that WOH G64 is transitioning into the final stages of its life cycle, having shed its outer layers and now surrounded by gas and dust formations.
What are Magellanic Clouds?
- The Magellanic Clouds are irregular galaxies that share a gaseous envelope and are located about 22 degrees apart in the southern sky.
- They consist of two main galaxies: the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), both of which orbit the Milky Way approximately every 1.5 billion years and each other every 900 million years.
- These galaxies are named after the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan, whose crew first identified them during their circumnavigation of the globe between 1519 and 1522.
- Formed around the same time as the Milky Way, roughly 13 billion years ago, the Magellanic Clouds are currently bound to the Milky Way and have undergone numerous tidal interactions with each other and with our galaxy.
- They host a rich population of young stars and star clusters, alongside some older stellar formations.
GS2/International Relations
Exercise AGNI WARRIOR
Source:PIB

Why in news?
Recently, the 13th edition of Exercise AGNI WARRIOR (XAW-2024) concluded at Field Firing Ranges, Devlali (Maharashtra).
About Exercise AGNI WARRIOR:
- Exercise AGNI WARRIOR is a collaborative military exercise involving the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces.
- This edition saw the participation of personnel from the Singapore Artillery and members of the Indian Army’s Regiment of Artillery.
Aims of XAW-2024:
- The primary goal of the exercise was to enhance mutual understanding of operational drills and procedures.
- It aimed to foster jointness among the multinational forces operating under the United Nations Charter.
Key Activities:
- The exercise involved joint firepower planning, execution, and the utilization of New Generation Equipment by both armies' artillery units.
- Extensive preparation and coordination were crucial for understanding each other’s capabilities and procedures.
- It facilitated the development of a common interface between the artillery procedures of India and Singapore.
Training Outcomes:
- This exercise marked the successful culmination of training for the Singapore Armed Forces, focusing on the intricacies of firepower planning.
- Both sides leveraged advanced technologies during the exercise and shared best practices as part of their joint training efforts.
GS1/History & Culture
Ramappa Temple
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
The Union Government has sanctioned loans under the Special Assistance to States/Union Territories for Capital Investment (SASCI) scheme aimed at developing the Ramappa Region Sustainable Tourism Circuit.
About Ramappa Temple:
- Also recognized as the Rudreshwara temple, it is a Kakatiya style Hindu temple devoted to Lord Shiva, situated in Telangana.
Patronage:
- This medieval temple, dating back to 1213 AD, was constructed under the patronage of Kakatiya ruler Kakati Ganapathi Deva.
- The temple was built by his Chief Commander, Rudra Samani, and is named after its chief sculptor, Ramappa.
- Remarkably, Ramappa Temple is possibly the only temple in India named after its architect.
Architectural features:
- Earthquake-proof:
- The bricks used in constructing the gopuram are made from a mixture of clay, acacia wood, chaff, and myrobalan fruit, making them lightweight and capable of floating on water.
- This innovative construction method significantly reduces the risk of collapse during earthquakes.
- Sandbox technique:
- The temple was built using the sandbox technique, where the foundation pit is filled with a mixture of sand-lime, jaggery, and black myrobalan fruit.
- This mixture acts as a cushion, enhancing the temple's resilience against earthquakes.
- The temple's pillars are designed to produce musical notes, adding to its unique architectural features.
- In 2021, Ramappa Temple was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site under the name "Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple, Telangana."
GS3/Environment
Cyclone Fengal makes landfall
Source:Mint
Why in News?
Cyclone Fengal made landfall near Puducherry on November 30, bringing heavy rainfall and gusty winds to Tamil Nadu's coastal belt, including Chennai and Puducherry. This is the second cyclone to impact India’s east coast in two months after Cyclone Dana. Cyclone Fengal, initially stagnant, intensified as it moved closer to land, reaching about 120 km east of Puducherry and 110 km southeast of Chennai before landfall. The cyclone made landfall between Mahabalipuram and Karaikal with wind speeds of 70-80 km/hr, gusting to 90 km/hr. Heavy rainfall and gusty winds disrupted public transport, with buses, trains, and flights affected.
What is a Cyclone?
- A cyclone is a large-scale atmospheric system that rotates around a low-pressure area, often bringing storms and severe weather.
- Cyclones are characterized by spiraling winds that rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Characteristics of a Tropical Cyclone:
- The center of a cyclone, known as the eye, is calm and features very low air pressure.
- The average wind speed can reach up to 120 km/h.
- Cyclones have closed isobars, which indicate consistent pressure and contribute to increased wind velocities.
- They form over oceans and seas only.
- Cyclones generally move from east to west under the influence of trade winds.
- They are typically seasonal phenomena.
Classification of Cyclones:
- Cyclones are categorized based on wind speed by the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD):
Classification Wind Speed (km/h) Depression 31–49 Deep Depression 50–61 Cyclonic Storm 62–88 Severe Cyclonic Storm 89–117 Very Severe Cyclonic Storm 118–166 Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm 167–221 Super Cyclonic Storm Above 222
What Does Landfall Mean?
- Landfall refers to the moment a tropical cyclone moves from water onto land.
- A cyclone is considered to have made landfall when the center, or eye, of the storm reaches the coast.
- The eye of the cyclone is characterized by relatively calm weather and light winds, typically having clear or partly cloudy skies.
- The size of the eye can vary greatly, ranging from a few kilometers to over 50 kilometers in diameter in larger storms.
- During landfall, the outer bands of the cyclone may already impact the coast, causing strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
- Landfall should not be confused with a direct hit, where the core of high winds (the eyewall) makes landfall but the center of the storm remains offshore.
Bay of Bengal: A Cyclone Hotspot
- Historical data shows that the Bay of Bengal is particularly prone to cyclones, with around 58% of cyclones making landfall on India's eastern coast, in contrast to only 25% in the Arabian Sea.
- The Arabian Sea experiences fewer cyclones due to its narrower and deeper nature, cooler temperatures, and higher salinity, alongside its partially landlocked geography.
Cyclone Management – Steps Taken by India:
- The National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP) was launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs to enhance the resilience of coastal communities and infrastructure against cyclones and storm surges.
- This project emphasizes building capacity, establishing early warning systems, creating cyclone shelters, planning evacuations, and raising community awareness.
- The IMD uses a color coding system to alert the public about cyclone severity, using four colors: Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red.
- Other initiatives include Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) and regulations under Coastal Regulation Zones (CRZ).
- Additional measures involve the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), the National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP), and state-level disaster management authorities.
GS3/Environment
Road Accident Fatalities in India
Source:Indian Express
Why in News?
India continues to face a significant road safety crisis, as highlighted by Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways, Nitin Gadkari, who presented alarming statistics for 2023. During a road safety event in Lucknow, he discussed the scale of road accidents, their causes, and the measures being taken to address this urgent issue.
Road Accidents in India (Fatalities, Key Causes, About UP, Govt. Initiatives, Global Learnings)
Road Accident Statistics for 2023:
- Total Crashes:In 2023, there were over 4.80 lakh road accidents, which represents a 4.2% increase compared to 2022.
- Deaths:The reported fatalities amounted to 1.72 lakh, marking a 2.6% rise from 2022's figure of 1.68 lakh deaths.
- Daily Impact:On average, there were 1,317 crashes and 474 deaths each day in 2023, equating to approximately 55 crashes and 20 fatalities every hour.
- Crash Severity:The rate of fatalities per 100 crashes slightly decreased from 36.5 in 2022 to 36 in 2023.
Key Causes for Road Accidents:
- Human Behaviour:The leading cause of road accidents is human error, often stemming from a disregard for traffic laws and unsafe behaviors such as speeding and reckless driving.
- Over-speeding:Responsible for 68.1% of road crash deaths in 2023.
- Helmet and Seatbelt Non-Usage:Not wearing helmets resulted in 54,000 deaths, while 16,000 fatalities were linked to the lack of seatbelt use.
- Pedestrian and Two-Wheeler Vulnerability:Pedestrians accounted for 20% of road crash fatalities, and two-wheeler users represented 44.8% of the total deaths.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:Issues such as potholes, lack of underpasses, and insufficient foot overbridges contribute significantly to accidents.
- Black Spots:High-risk areas on national highways are being addressed with a budget of ₹40,000 crore for improvements.
- Other Factors:Overloaded vehicles accounted for 12,000 deaths, while unlicensed driving contributed to 34,000 accidents. The prevalence of old vehicles and outdated technology further increases risks.
Regional Disparities:
- Uttar Pradesh (UP): UP has the highest incidence of road accidents and fatalities in India, recording 44,000 accidents and 23,650 deaths.
- Notable figures: Among these fatalities, 1,800 involved individuals under 18 years of age, while 10,000 deaths pertained to pedestrians and two-wheeler users.
- Over-speeding: Contributed to 8,726 deaths in the state.
Government Initiatives:
- Infrastructure Improvements:The government is focusing on identifying and rectifying black spots on highways, enhancing road designs, and adding safety features like underpasses and foot overbridges.
- Automobile Engineering:There are directives aimed at improving vehicle safety features to help reduce fatalities.
- Awareness Campaigns:Efforts are being made to promote road safety through public awareness initiatives, including advocating for the inclusion of traffic rules in school curriculums.
- Ambitious Goals:Despite the goal to cut accidents by 50% by 2024, progress has been slow, highlighting the need for intensified efforts.
Global Context & Learnings:
- India's road safety challenges rank among the most severe in the world. According to the World Bank, inadequate road infrastructure, rapid urbanization, and increasing vehicle traffic exacerbate these issues.
- Successful Models: Countries like Sweden and the Netherlands have implemented the Vision Zero initiative, which aims for zero road fatalities through strict policies and advanced road designs.
- India can learn from these approaches to enhance road safety and reduce fatalities.
GS3/Economy
Rising Stress in Microfinance and Small Loans in India
Source:Indian Express
Why in News?
The microfinance sector, which includes small finance lenders and unsecured personal loans in India, is currently exhibiting early signs of stress due to increasing borrower indebtedness. Key indicators are showing a rise in delinquencies, which threatens both asset quality and profitability in these segments.
Microfinance in India:
- Evolution:
- The Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) Bank, established in Gujarat in 1974, marked the beginning of microfinance in India. It celebrated its 50th anniversary in 2024.
- NABARD introduced the Self-Help Group (SHG) linkage model in 1984 to address poverty issues.
- In 2004, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) classified microfinance as a priority sector.
- The Andhra Pradesh crisis in 2010, which was sparked by aggressive debt recovery methods, led to significant regulatory reforms.
- The RBI formed the Malegam Committee in 2012 to tackle concerns in the microfinance sector after the Andhra Pradesh crisis.
- The launch of MUDRA Bank in 2015 improved credit access for small businesses, thereby enhancing the microfinance ecosystem.
- Microfinance Business Models:
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs): Typically comprising 10-20 members, SHGs emphasize collective savings and use these savings to obtain bank loans under NABARD’s SHG-Bank Linkage Programme.
- Microfinance Institutions (MFIs): MFIs provide financial services such as credit, insurance, and remittances through Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) of 4-10 members engaged in similar economic activities. They operate on structured repayment schedules and generate interest like traditional banks.
- Types of Microfinance Lenders:
- NGO-MFIs: These organizations are registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, or the Indian Trusts Act, 1880.
- Co-operative Societies: Examples include Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) that provide microfinance services.
- Section 8 Companies: These are non-profits established under the Companies Act, 2013, offering microfinance services.
- NBFC-MFIs: Comprising 80% of the market, these institutions are regulated by the RBI and depend on bulk loans from banks or their own resources to lend to JLGs.
- Current Status:
- The microfinance sector has expanded significantly, with 168 MFIs serving over 30 million clients.
- This sector plays a vital role in job creation, contributing to 1.3 million jobs and 2% of India’s Gross Value Added (GVA).
- The RBI defines microfinance as collateral-free loans for households with an annual income of up to ₹3 lakh.
Signs of Stress in the Microfinance Sector:
- Rising Delinquencies and Asset Quality Risks:
- Increased non-performing assets (NPAs) have been observed; for instance, ESAF Small Finance Bank’s gross NPAs rose to ₹1,279.3 crore (6.9% of advances) in September 2024, up from ₹399.1 crore (2.6%) the previous year.
- CRISIL forecasts that SFB NPAs will increase to 2.9% by FY25, compared to 2.3% in FY24.
- Early-stage delinquencies have surged, with collection efficiency dipping to 94% in Q2 FY25 from 98% in the previous fiscal year.
- Challenges with Borrower Indebtedness:
- Outstanding credit card debt skyrocketed to ₹2.71 lakh crore in September 2024, up from ₹2.30 lakh crore the previous year.
- Due to predatory pricing and insufficient borrower assessments, the RBI has imposed restrictions on NBFC-MFIs, signaling regulatory intervention to mitigate growing risks.
Factors Driving Stress in the Microfinance Sector:
- Operational and Structural Issues:
- Over-leveraged borrowers have emerged because aggressive lending practices have resulted in loans being granted without adequate evaluation of repayment capacities.
- The Joint Liability Group (JLG) model is facing challenges, with declining attendance and accountability leading to increased defaults.
- High turnover rates among staff and instances of fraud have created operational disruptions, complicating recovery efforts.
- External Challenges:
- Socio-political factors, such as debt-waiver movements and general elections, along with natural disasters, are putting additional strain on borrowers’ ability to repay loans.
- Economic hardships in rural and semi-urban areas continue to limit small borrowers' repayment capacities.
Regulatory and Institutional Responses to Deal with the Stress in the Microfinance Sector:
- Regulatory Actions:
- The RBI has issued "cease and desist" orders to certain NBFC-MFIs to address issues like loan netting and lending to ineligible borrowers.
- It has tightened lending norms for unsecured loans and emphasized the need for institutions to adopt sustainable risk management frameworks.
- Institutional Adjustments:
- Banks and NBFCs are re-assessing their underwriting standards and concentrating on risk mitigation strategies.
- The sector is experiencing a slowdown in growth, with MFIs’ assets under management (AUM) projected to decline to 17-19% in FY25 from 29% in FY24.
Sector Resilience Amid Challenges and Future Outlook:
- Strengths of the Microfinance Sector:
- Despite current vulnerabilities, the microfinance sector has historically demonstrated resilience, recovering from shocks such as demonetization and the pandemic.
- Investor confidence remains high, highlighting the sector's crucial role in promoting financial inclusion.
- Future Outlook:
- Analysts anticipate ongoing stress in FY25, with delinquencies expected to rise across unsecured and microfinance loans.
- A cautious approach to new loan approvals and enhanced recovery efforts will be vital for stabilizing the sector.
- Effective regulatory oversight and institutional flexibility will be essential in navigating these challenges.
Conclusion:
With strategic reforms, robust risk management practices, and supportive regulatory measures, the microfinance sector can overcome current stresses and continue to effectively serve underserved communities.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















