UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 1st June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Mo Ghara (My Home) Scheme
Why in News?
Odisha Chief Minister recently announced new credit-linked housing scheme for rural poor.
About Mo Ghara Scheme:
- Odisha government announced a new initiative, Mo Ghara (My Home).
- Mo Ghara is a credit-linked housing scheme for rural poor in the state with an aim to convert all kutcha houses into pucca ones.
- The scheme will have a financial implication of around Rs.2, 150 crore over a period of two years and it will be fully funded from the state budget.
- Under the Mo Ghara scheme, a beneficiary can avail housing loan of up to Rs. 3 lakh that can be repaid in 10 years in easy instalments excluding one-year moratorium period.
- “The state government will release capital subsidy to the loan account of the beneficiaries on completion of the house.
- There will be four slabs of loan amount.
- The rates of the subsidy will be Rs 30,000 for a Rs 1 lakh loan, Rs 45,000 for Rs 1.5 lakh loan, and Rs 60,000 for a loan amount of Rs 2 lakh and Rs 3 lakh.
- The subsidy will be Rs 10,000 more across slabs for those belonging to the SC/ST category and for the differently abled.
- “The capital subsidy released to the loan accounts of the beneficiaries will result in a significant reduction in EMI for repayment and thus make the repayment more affordable,”
- A family staying in a kutcha house or one pucca room with a concrete roof is eligible to get the loan under the Mo Ghara scheme.
- Families that have not availed of any government housing assistance or have availed assistance of below Rs 70,000 in the past with a monthly income below Rs 25,000 will also be eligible under the scheme.
- Families having four-wheelers or any member in government service or irrigated land of five acres or more will not be eligible for the loan.
- While banks have been asked not to charge any processing fee from beneficiaries, the Odisha government has also waived off registration fees and stamp duties required during the mortgage of the title deed to further reduce the financial burden for the beneficiaries, said the chief secretary.
- The state government will start receiving applications from beneficiaries on its dedicated portal from June 16, 2023.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
All India Survey of Higher Education
Why in News?
The All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) Survey 2020-21 conducted under the Ministry of Education found that the Muslim community’s enrolment in higher education declined at a time when the enrolment of SCs, STs and OBCs improved.
About All India Survey of Higher Education
- All India Survey of Higher Education is an annual web-based survey, which started in 2010-11 and was conducted by Ministry of Education.
- Various parameters of data collection includes teachers, student enrolment, programmes, examination results, education finance, and infrastructure.
- For the first time, the Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) of India have filled their data using an entirely online data collection platformthrough the Web Data Capture Format (Web DCF) developed by the Department of Higher Education and the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
Key findings from the report:
- Gross Enrolment Ratio(GER) for all enrolments (as per 2011 Census) increased by over 2 points to 27.3.
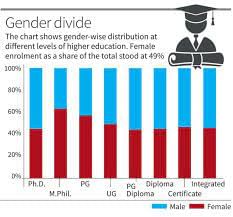
- The female enrolment in higher educationprogrammes had increased to 49% of total enrolments in 2020-21 compared to 45% in 2019-20.
- SC: More SC students who were enrolled in 2020-21 compared two lakh to the previous year.
- ST: The year also saw about three lakh more ST students and six lakh more OBC students being enrolled for higher education.
- The proportion of Muslim students enrolling for higher education dropped to 4.6% in 2020-21 from 5.5% in 2019-20
- During2020-21, the number of universities has increased by 70, and the number of colleges has increased by 1,453.
- The female per 100 male faculty has improved to 75 in 2020-21 from 74 in 2019-20 and 63 in 2014-15.
Other points
- Be it learning or teaching, the Muslim community is lagging behind all communities, including the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, in higher education
Reasons
- It’s caused partially by the COVID-19 pandemic, points to the relative economic impoverishment of the community, which forces its talented students to pursue earning opportunities after completing schooling rather than enrolling for higher education, beginning at the graduation level.
Source: The Hindu
UAE withdraws from Combined Maritime Forces (CMF)

Why in News?
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has announced its withdrawal from the U.S.-led Combined Maritime Forces (CMF), a maritime coalition responsible for securing Gulf waterways crucial to global oil trade.
What is Combined Maritime Forces (CMF)?
| Establishment | 2002 |
| Location | Bahrain |
| Objective | Promoting security, stability, and prosperity across maritime regions |
| Member Nations | Over 30 member nations |
| Primary Task Forces | Combined Task Force 150 (CTF 150), Combined Task Force 151 (CTF 151), Combined Task Force 152 (CTF 152) |
| Operations | Counter-terrorism, counter-piracy, maritime security, and cooperation |
| Collaborations | United Nations, European Union, NATO, and regional partners |
| Contributions | Naval assets including warships, aircraft, and maritime patrol vessels |
| Focus Areas | Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, Gulf of Aden, Red Sea, Indian Ocean, Arabian Gulf, and surrounding areas |
Reasons for UAE’s withdrawal
- UAE has not provided specific reasons for its withdrawal from the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) in the official statement.
- One potential factor could be a desire to distance themselves from perceived dependencies or entanglements with the US.
- This could be part of a broader strategy by the UAE to assert its own regional influence, pursue independent foreign policies, or rebalance its relationships with China and Iran.
Recent incidents and tensions in Gulf Waters
- In late April and early May, Iran seized two tankers, one of which was empty and travelling between the UAE ports of Dubai and Fujairah.
- Iran was also accused of launching a drone attack on an Israeli-owned tanker in November 2022, escalating tensions with the United States.
- As a response to increasing harassment by Iran, the US announced the deployment of reinforcements to the Gulf, a vital route for a significant portion of the world’s sea-borne oil.
Source: The Hindu
Mandatory Anti-Tobacco Warnings on OTT Platforms
Why in News?
Over-the-top (OTT) streaming platforms must display anti-tobacco warnings similar to those seen in movies screened in theatres and on TV.
- The requirement is based on a Union Health Ministry notification that amends the rules under the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA), 2004.
What is COTPA, 2004?
| Description | |
| Purpose | Regulate production, sale, distribution, and consumption of tobacco products |
| Prohibition of Smoking in Public Places | Smoking prohibited in public areas like offices, restaurants, parks, public transport, etc. |
| Health Warnings on Tobacco Products | Mandatory display of health warnings on cigarette packages and other tobacco products |
| Ban on Advertisement and Promotion | Prohibition on direct and indirect advertising of tobacco products |
| Prohibition on Sale to Minors | Selling tobacco products to individuals below 18 years of age is strictly prohibited |
| Packaging and Labelling Requirements | Health warnings and pictorial representations of harmful effects on cigarette packages |
| Powers of Enforcement | Authorities empowered to enforce the act, conduct inspections, and seize contraband products |
New requirements for Anti-Tobacco Warnings
- Publishers of online curated content displaying tobacco products or their use must show anti-tobacco health spots at the beginning and middle of the program.
- When tobacco products or their use are displayed during the program, an anti-tobacco health warning must be prominently displayed as a static message at the bottom of the screen.
- The warning message should be legible and readable, with black font on a white background.
- The specified warnings are ‘Tobacco causes cancer’ or ‘Tobacco kills.’
- Health spots, warnings, and audio-visual disclaimers should be in the same language as used in the show.
Negative health impacts of tobacco
- Cancer: Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable cancer. It can cause cancer of the lungs, mouth, throat, larynx, pancreas, bladder, kidney, and cervix.
- Respiratory diseases: It may cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It can also worsen asthma symptoms.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Consumption increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Reproductive health: Tobacco use can lead to infertility, premature birth, and low birth weight in babies.
Socio-economic impact
(1) On an individual level:
- Decreased productivity: Smoking-related illnesses can result in absenteeism from work, decreased work performance, and increased medical expenses.
- Decreased life expectancy: Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased life expectancy, which reduces the overall productive years of an individual.
(2) On a societal level:
- Healthcare cost: Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased economic development due to the increased burden of healthcare costs and decreased productivity.
- Increased social expenditure: According to a study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), tobacco-related illnesses cost India about $22.4 billion in healthcare costs and lost productivity annually
Why tobacco isn’t completely banned?
- Revenue loss: The industry contributes a significant amount of tax revenue to the government. Banning tobacco would result in the loss of these tax revenues, which are used for various public welfare programs and initiatives.
- Economic Impact: The tobacco industry provides employment to a large number of people, especially in the agricultural sector, where tobacco farming is prevalent.
- Not a psychotropic substance: While the harmful effects of tobacco are well-documented, banning a legal product entirely requires careful consideration and legal processes.
- Regulatory approach: Instead of a complete ban, the Indian government has adopted a regulatory approach to control tobacco use.
Way forward
- Strengthen tobacco control laws: Review and enhance existing laws to effectively reduce tobacco consumption.
- Conduct public awareness campaigns: Educate the public about the health risks of tobacco use and the benefits of quitting.
- Expand access to tobacco cessation programs: Increase availability of affordable and effective programs to support individuals who want to quit tobacco.
- Implement sin taxes on tobacco products: Increase taxes to discourage consumption, especially among price-sensitive populations.
- Enforce smoke-free environments: Strictly implement smoke-free laws in public places, workplaces, and public transport.
- Support tobacco farmers: Provide alternative livelihood options and assistance for farmers transitioning away from tobacco farming.
- Conduct research and surveillance: Invest in data collection and analysis to inform evidence-based policies and interventions.
- Collaborate with international organizations: Partner with global entities like WHO to leverage expertise and resources in tobacco control.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
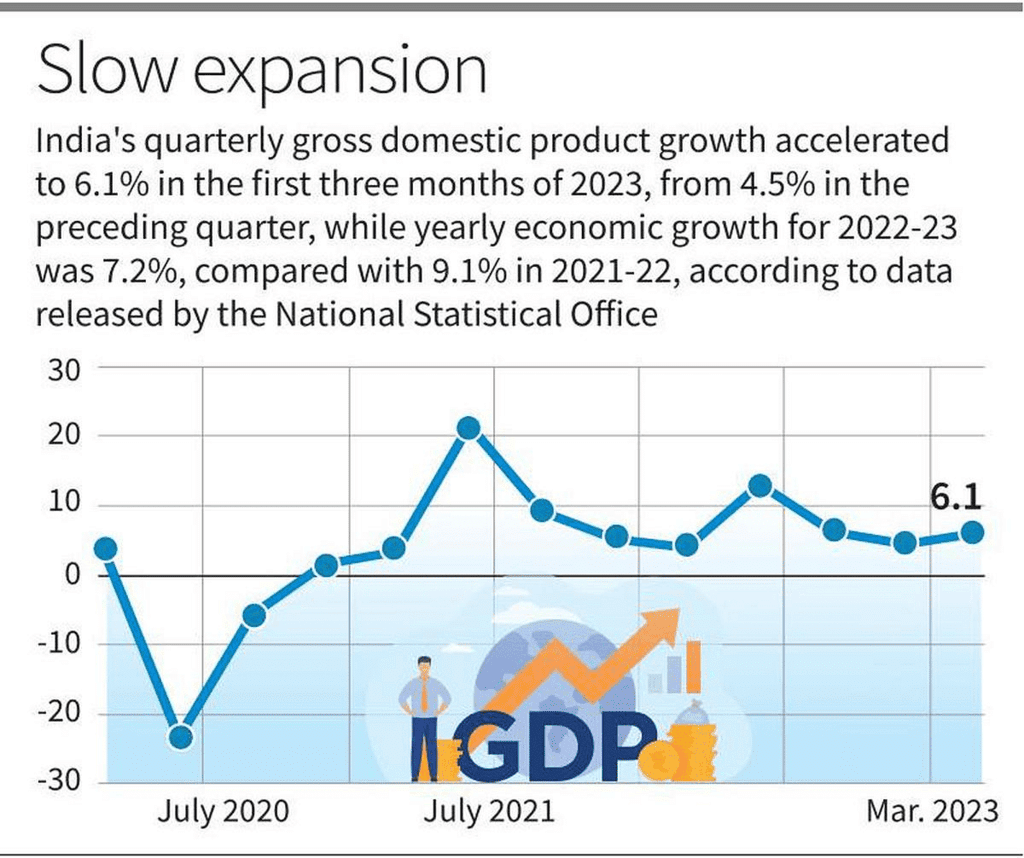
National Income data: India’s GDP expanded 6.1% in 2022-23’s last quarter
Why in News?
According to the provisional national income data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), India’s gross domestic product (GDP) growth accelerated to 6.1% in the January to March 2023 quarter.
- This has lifted the economy’s growth rate in 2022-23 to 7.2% from the 7% estimated earlier.
Key Economic Terminologies:
- GDP and GVA are the two main ways to ascertain the country’s economic performance that measures national income.
- GDP:
- The GDP is a monetary measure of all final products and services (those purchased by the final user) produced in a country over a certain period.
- The GDP accomplishes this by adding total expenditures in the economy, examining who spent how much, thus, measuring the economy's overall "demand."
- 4 key engines of GDP growth: (GDP = C + I + G + NX)
- Consumption (C)/Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE): The biggest engine is consumption demand from private individuals.
- Investment (I)/Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF): The second-biggest engine is the investment demand generated by private sector businesses.
- Government (G)/Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE): The third engine (~11%) is the demand for goods and services generated by the government.
- Net Exports (NX) = Exports minus imports.
- Gross value added (GVA):
- It calculates the same national income from the supply side, by adding up all the value added (value of output minus the value of its intermediary inputs) across different sectors.
- This value added is shared among the primary factors of production, labour and capital.
- By looking at the GVA growth one can understand which sector of the economy is robust and which is struggling.
- How are GDP and GVA related? GDP = (GVA) + (Taxes earned by the government) — (Subsidies provided by the government). If the taxes > subsidies it provides, the GDP will be higher than GVA.
GDP:
- India’s 6.1% GDP growth was the fastest among major economies in the fourth quarter and the prospects look better for this year than they did four months ago.
- GVA:
- It is estimated to have risen 7% in 2022-23, compared to 8.8% in 2021-22, with manufacturing GVA growth sliding to just 1.3% from 11.1% a year ago.
- Economists noted that though several sectors delivered a positive surprise, consumption remained weak and the overall growth pattern remains uneven.
- Agri, services growth:
- The agricultural GVA grew 4%, up from 3.5% in the previous year.
- The financial, real estate and professional services sectors saw their GVA grow 7.1%, compared to 4.7% in 2021-22.
- The GVA of the trade, hotels, transport, and communication sectors, as well as services related to broadcasting grew 14%, marginally faster than in the previous year.
- This means the current economic outcomes are boosted by the farm and services sector.
Takeaways from the Recent Data:
- The 2022-23 GDP growth figures underscored the resilience of the Indian economy amidst global challenges.
- Exports of goods and services accounted for 23.5% of GDP, the highest since 2014-15.
- The private consumption hit the highest level since 2006-07 at 58.5% and gross fixed capital formation is at the highest point (34% of GDP) since 2013-14.
- GVA from the employment-intensive construction sector grew 10% in 2022-23, from 14.8% in 2021-22.
- However, the phenomenon of pent-up demand that lifted services through last year and this fiscal year’s first two months will not be strong, and private sector investment has to pick up.
Source: The Hindu
Lightweight and portable payment system

Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is developing a lightweight and portable payment system designed to operate during catastrophic events.
About Lightweight and portable payment system:
- The RBI has conceptualized this system which it is calling a bunker which is an equivalent of digital payments that can be operated from anywhere by a bare minimum staff in exigencies such as natural calamities or war.
- It is expected to operate on minimalistic hardware and software and would be made active only on a need basis.
- The infrastructure for this system will be independent of the technologies that underlie the existing systems of payments such as UPI, NEFT, and RTGS.
- The system is expected to process transactions that are critical to ensure the stability of the economy, including government and market-related transactions.
- The existing conventional payment systems such as RTGS, NEFT, and UPI are designed to handle large volumes of transactions while ensuring sustained availability.
- As a result, they are dependent on complex wired networks backed by advanced IT infrastructure.
What is NEFT?
- The National Electronic Funds Transfer is an electronic method of transferring money online.
- It enables transferring funds from the account maintained with any bank to any other bank branch, provided the transaction is attempted between the banks that participate in the NEFT payment system.
- The payments made via NEFT are processed and settled half hourly batches and transactions can be performed 24*7.
- Minimum Transfer Value: Rs. 1
- Maximum transfer value: No limit
- Money transfer made through NEFT does not require any additional transaction costs.
What is RTGS?
- It stands for Real-time Gross Settlement, which is a payment mode where the money is transferred from one bank account to the other in real time, without any delay.
- It is mostly used for transactions of high value.
- When using the banking method, RTGS is the fastest possible way to transfer money.
- Transactions made through RTGS are processed on a one-to-one basis and transactions can be performed 24*7.
- Minimum Transfer Value: 2 lakh
- Maximum transfer value: No upper limit is there, but can vary between banks.
Source: Indian Express
Mainstreaming Biodiversity: A Pivotal Step Towards a Sustainable Future

Why in News?
The observance of International Biodiversity Day on May 22 serves as a powerful reminder of the critical role our natural world plays in addressing the climate change crisis and the threat to our future posed by declining biodiversity. Preserving and enhancing biodiversity emerges as a cost-effective approach to sequester carbon dioxide and mitigate climate change.
What is Biodiversity?
- Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms found on Earth, including plants, animals, microorganisms, and their interactions within ecosystems. It encompasses the diversity of species, genetic diversity within species, and the diversity of ecosystems.
- Biodiversity is not limited to specific areas but exists everywhere, from terrestrial habitats like forests, grasslands, and deserts to aquatic environments such as rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- It also includes the diversity of habitats, ecological processes, and the complex web of relationships between organisms and their environment.
- Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to humans. It supports essential ecosystem services, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, soil formation, and water purification.
- Biodiversity also contributes to food security by providing a variety of crops, livestock, and wild foods. Additionally, it plays a vital role in medicine, as many pharmaceuticals are derived from natural sources.
The Decline of Biodiversity: key contributing factors
- Habitat Loss: The conversion of natural habitats into agricultural lands, urban areas, and industrial zones is a primary driver of biodiversity loss. Deforestation, land degradation, and habitat fragmentation disrupt ecosystems and displace numerous species.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events associated with climate change have a profound impact on biodiversity. Species may struggle to adapt or migrate quickly enough, leading to population declines and even extinction.
- Pollution: Pollution, including air and water pollution, poses a severe threat to biodiversity. Chemical contaminants, such as pesticides, herbicides, and industrial pollutants, can accumulate in ecosystems and harm both flora and fauna.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable harvesting of wildlife, overfishing, and illegal wildlife trade put immense pressure on species populations. This overexploitation disrupts ecological balance and can lead to the collapse of ecosystems.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced into new environments can outcompete native species, disrupt ecological interactions, and cause harm to local ecosystems. Invasive species often lack natural predators or controls, allowing them to multiply rapidly.
- Agricultural Practices: Intensive agricultural practices, including the use of chemical inputs, monoculture farming, and the destruction of natural habitats for agriculture, contribute to the loss of biodiversity. This impacts both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
- Disease and Pathogens: The spread of diseases and pathogens, both natural and human-mediated, can have devastating effects on wildlife populations. Diseases can cause mass die-offs and population declines, leading to decreased biodiversity.
- Inadequate Conservation Efforts: Inadequate conservation measures, weak enforcement of protective laws, and insufficient funding for conservation initiatives contribute to the decline of biodiversity. Conservation efforts are often fragmented and not prioritized, further exacerbating the problem.
- Lack of Public Awareness and Engagement: Limited awareness among the general public about the importance of biodiversity and the consequences of its decline hinders collective action. Engaging communities and fostering a sense of responsibility towards biodiversity is crucial for effective conservation.
Reimagining Biodiversity Management: A holistic and inclusive approach
- Multifunctional Landscapes: Moving beyond the traditional focus on forests, biodiversity management should encompass diverse ecosystems such as grasslands, savannas, alpine pastures, and deserts. Recognizing the value of multifunctional landscapes allows for the conservation and sustainable use of various ecological communities.
- Community Engagement: Empowering local communities and indigenous groups in biodiversity management is crucial. Their traditional knowledge, practices, and direct involvement are valuable assets for effective conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. Establishing platforms such as gram sabhas and biodiversity management committees facilitates community participation and decision-making.
- Mainstreaming Biodiversity: Biodiversity considerations should be integrated into all sectors and aspects of society. Development programs, government departments, public and private institutions, and industries should incorporate biodiversity conservation and sustainable practices as core principles.
- Policy and Legal Frameworks: Ensuring effective implementation of regulations, enforcing laws against biodiversity crimes, and revisiting policies that hinder biodiversity protection are key steps. It is also important to support the rights of indigenous communities and local stakeholders through legal mechanisms.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting biodiversity education and raising awareness about its importance among the general public, policymakers, and stakeholders is crucial. This includes integrating biodiversity topics into educational curricula, conducting awareness campaigns, and disseminating information about the benefits of biodiversity conservation.
- Research and Science-Based Approaches: Investing in scientific research, monitoring, and data collection is vital for evidence-based decision-making and effective biodiversity management. This includes studying biodiversity patterns, understanding ecosystem dynamics, and identifying key species and habitats for conservation priorities.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Building partnerships and collaborations among various stakeholders is essential. This includes government agencies, non-governmental organizations, research institutions, local communities, and private sectors. Collaboration fosters knowledge sharing, resource mobilization, and the implementation of joint initiatives for biodiversity conservation.
- Sustainable Financing: Ensuring sustainable financing mechanisms for biodiversity conservation is crucial. This includes exploring innovative funding models, leveraging public-private partnerships, and integrating biodiversity into sustainable development financing frameworks.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating at the global level is necessary to address transboundary biodiversity issues. Sharing best practices, knowledge exchange, and aligning efforts with international conventions and agreements such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) can strengthen biodiversity management.
Our Role as Caretakers: key actions we can take as responsible stewards
- Sustainable Land Use: Promoting sustainable land use practices is essential to minimize habitat loss and degradation. This includes supporting initiatives such as reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable agriculture that maintain ecosystem integrity.
- Responsible Consumption: Making informed choices as consumers can have a significant impact on biodiversity. Supporting sustainable and ethically sourced products, reducing waste, and opting for environmentally friendly practices can reduce the demand for products that harm biodiversity.
- Preservation of Natural Habitats: Protecting and preserving natural habitats, including forests, wetlands, and marine ecosystems, is critical. This involves advocating for the establishment and expansion of protected areas, national parks, and wildlife reserves.
- Sustainable Fisheries: Supporting sustainable fishing practices, such as responsible fishing quotas, implementing fishing regulations, and avoiding overfishing, helps maintain healthy marine ecosystems and protect marine biodiversity.
- Support Conservation Organizations: Contributing to and supporting conservation organizations and initiatives can make a significant difference. Donations, volunteering, and participation in citizen science projects can aid in research, conservation efforts, and advocacy for biodiversity protection.
What is The National Mission on Biodiversity and Human Wellbeing?
- Objective: The mission aims to integrate biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services into various sectors to address critical challenges related to climate change, regenerative agriculture, and ecosystem and public health.
- Enhancing Human Wellbeing: The mission focuses on fostering human well-being by enhancing and conserving biodiversity. It aims to support the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals related to poverty alleviation, nutrition and health, and environmental protection.
- People-Centric Approach: The mission recognizes the importance of active engagement and participation of all citizens in biodiversity conservation and sustainable use. It places people at the center of the mission’s activities.
- Mainstreaming Biodiversity: The mission seeks to embed biodiversity considerations into development-oriented programs of both the public and private sectors. This ensures that biodiversity conservation becomes an integral part of decision-making processes and actions.
- Education and Awareness: The mission aims to create awareness about the importance of biodiversity and foster curiosity about nature. It seeks to instill a sense of responsibility for safeguarding biodiversity in every child and student.
- Nature-Based Solutions: The mission emphasizes the utilization of nature-based solutions to address challenges related to climate change, agriculture, and public health. It recognizes the value of ecosystems and biodiversity in providing sustainable solutions.
- Traditional Knowledge and Community Participation: The mission promotes the integration of traditional knowledge and the active participation of local communities and indigenous groups in biodiversity management. It acknowledges their role in conservation efforts.
- Sustainable Development Goals Alignment: The mission aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, aiming to contribute to poverty alleviation, nutrition and health, and environmental protection.
- Pending Implementation: Although the mission has received preliminary approval from the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Council, it is still in the proposal stage and yet to be fully implemented.
Conclusion
- The mainstreaming of biodiversity represents a significant step toward securing a sustainable future. Recognizing the interconnectedness of all life forms and ecosystems, we must redefine our approach to biodiversity management. The proposed National Mission on Biodiversity and Human Wellbeing provides a roadmap and empowers all citizens to take part in safeguarding our precious natural heritage.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|