UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 22nd July 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
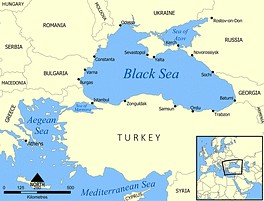
Black Sea
Why in News?
Russia recently warned that ships sailing to Ukraine's Black Sea ports will be seen as potential military targets.
About Black Sea:
- It is a large inland sea located in southeastern Europe.
- Bordering countries: It is bordered by six countries, Ukraine to the north, Russia to the northeast, Georgia to the east, Turkey to the south, Bulgaria to the southwest, and Romania to the west.
- It is connected to the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosporus Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles Strait.
- It covers an area of approximately 436,000 square kilometers (168,000 square miles).
- The Black Sea receives freshwater inflows all around the basin, but the important ones (Danube, Dniepr and Dniestr) discharge into the north-western coastal waters.
- Limited Oxygen Levels:
- The Black Sea's deeper waters have lower levels of oxygen due to its unique geological and hydrological conditions.
- The lack of oxygen in the lower layers creates a distinct environment, and it is one of the world's largest anoxic basins, meaning it has areas with very little dissolved oxygen.
- Islands: It contains several islands, with the largest ones being Snake Island (Ukraine), Giresun Island (Turkey) and St. Ivan Island (Bulgaria).
Source: The Hindu
Heat Index
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Earth Sciences informed that the India Meteorological Department (IMD) has launched the Heat Index on an experimental basis.
About Heat Index:
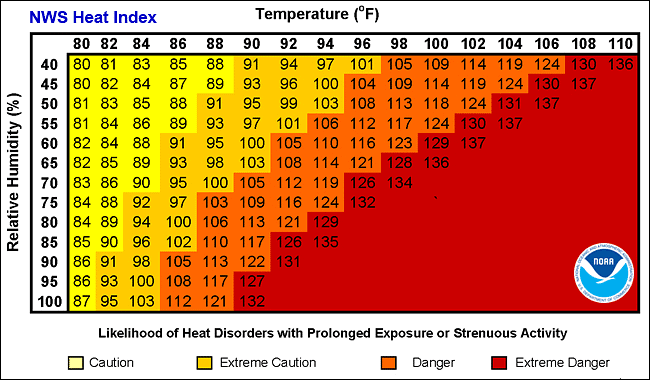
- It provides information about the impact of humidity on the high temperatures and thus provides a feel like temperature for human beings which can be used as an indication for human discomfort.
- It provides guidance towards additional care to be taken by people to reduce discomfort.
- Colour codes used for Experimental Heat Index are as follows:
- Green: Experimental heat Index less than 35 deg C
- Yellow: Experimental heat Index in the range 36-45 deg C
- Orange: Experimental heat Index in the range 46-55 deg C
- Red: Experimental heat Index greater than 55 deg C
- The Heat Index is implemented on experimental basis only across the entire country including the State of Andhra Pradesh.
- At present, heat index is derived using the heat index equation similar to what is used by National Weather Service, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), USA.
Key facts about IMD
- It is the main agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology in India.
- It operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica.
- Regional offices are in Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Nagpur, Guwahati and New Delhi.
- It has the responsibility for forecasting, naming and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Malacca Straits, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Source: PIB
GS-II
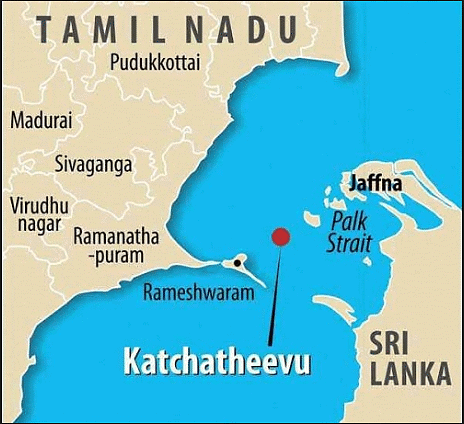
Katchatheevu’s Issue
Why in News?
Tamil Nadu CM Stalin urged the Union government to initiate diplomatic efforts to revisit the agreement transferring the Katchatheevu islet to Sri Lanka.
Major issues with Sri Lanka
- Issue of Katchatheevu:
- The unpopular truth in the entire conflict is accusations about Tamil fishermen entering Sri Lankan waters & the ownership of Katchatheevu Island, where Tamil fishermen had traditional fishing rights for centuries, remains an unresolved issue.
- In 1974, the island was ceded to Sri Lanka after an agreement was signed by Indira Gandhi between the two countries without consulting the Tamil Nadu government.
- The agreement allowed Indian fishermen “access to Katchatheevu for rest, for drying of nests and for the annual St Anthony’s festival” but it did not ensure the traditional fishing rights.
- Proliferation of trawlers in Indian coast:
- Trawlers are mechanised boats with highly exploitative fishing nets unlike most of the poor fishermen on the Sri Lankan coast who use traditional fishing methods.
- The use of mechanised bottom trawlers has become a bone of contention between the fishermen of the two countries.
- The actions of the Tamil Nadu fishermen adversely affect their counterparts in the Northern Province who are also struggling to come to terms with life after the civil war.
- The recent economic crisis in the island nation has only worsened their plight.
- Demarcation of the IMBL:
- The fishermen of Tamil Nadu experience an issue with the lack of fishing areas consequent to the demarcation of the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
- Just as sections of fishermen from the Palk Bay bordering districts of Tamil Nadu continue to transgress the IMBL, cases of many of them getting arrested and their boats being impounded by the Sri Lankan authorities continue.
Problems faced by Indian fishermen
- Indian fishermen face highly restricted access to traditional fishing grounds, increased harassment by the Sri Lankan Navy, and arrests by the Sri Lankan Navy on trespassing charges.
- Restoring the right to fish in the traditional fishing grounds of Palk Bay has always been among the top priorities of the Government of Tamil Nadu.
Suggestions
- Regular patrolling, establishment of communication channels, and installation of warning systems could significantly reduce the incidents of harassment and apprehension.
- Tamil Nadu’s CM has also proposed regular meetings and consultations of the Joint Working Group reconstituted in 2016, which he said would help in building trust, facilitate effective communication and ensure smooth fishing operations.
India - Sri Lanka Relations
- About:
- India and Sri Lanka have a legacy of intellectual, cultural, religious and linguistic interaction and the relationship between the two countries are more than 2500 years old.
- Trade and investment have grown and there is cooperation in the fields of development, education, culture and defence.
- In recent years, significant progress in the implementation of developmental assistance projects for Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs) and disadvantaged sections of the population in Sri Lanka has helped further cement the bonds of friendship.
- The nearly three-decade long armed conflict between Sri Lankan forces and the LTTE came to an end in May 2009.
- During the conflict, India supported the right of the Government of Sri Lanka to act against terrorist forces.
- Commercial Partnership:
- Both countries enjoy a vibrant and growing economic and commercial partnership, which has witnessed considerable expansion over the years.
- In 2020, India was Sri Lanka’s 2nd largest trading partner with the bilateral merchandise trade amounting to about USD 3.6 billion.
- India is also one of the largest contributors to Foreign Direct Investment in Sri Lanka.
- Projects under Lines of Credit:
- 11 Lines of credit (LOC) have been extended to Sri Lanka by the Export-Import Bank of India in the last 15 years.
- Important sectors in which Projects have been executed/ are under execution, under these LOCs include Railway, transport, connectivity, defence, solar.
- A US$ 100 million LoC for undertaking solar projects in Sri Lanka has been signed between the Government of Sri Lanka and EXIM Bank in June 2021.
- People-to-people ties:
- Buddhism is one of the strongest pillars connecting the two nations and civilizations from the time when the Great Indian Emperor Ashoka sent his children Arahat Mahinda and Their Sangamitta to spread the teachings of Lord Buddha at the request of King DevanampiyaTissa of Sri Lanka.
- Human Resource Development:
- India now offers about 710 scholarship slots annually to Sri Lankan students.
- In addition, under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Program, India offers 402 fully-funded slots every year to officials in various Ministries of Government of Sri Lanka and also to other eligible citizens for short term training programs in a wide variety of technical and professional disciplines to enhance skill sets.
- Indian institutes under the ‘Study in India’ Program provide technical expertise across a diverse range of courses and include programs in niche disciplines such as Ayurveda, Yoga, and Buddhist Studies.
- Defence:
- India and Sri Lanka conduct a joint Military exercise named ‘Mitra Shakti’ and a Naval exercise named SLINEX.
- Support during the recent Srilankan crisis:
- Sri Lanka recently faced an acute economic and energy crisis triggered due to a shortage of foreign exchange.
- India has provided a $2.4-bn package of financial assistance in February and March.
- India also appointed experts to assist Sri Lanka’s economic recovery, and for various joint projects.
- India extended a $400-million currency swap and a $500-million credit line for fuel purchases to Sri Lanka earlier this year.
- Since January 2022, India has also signed several key bilateral agreements with Sri Lanka, including the joint development of the Trincomalee Oil Tank Farms, and three major power projects in the north and east, involving the National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) and the Adani Group, apart from the recent pacts on maritime security.
Source: The Hindu
Amended Rules Relating to Retirement Benefits of IAS, IPS, IFOS Pensioners

Why in News?
The Central government has amended All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules 1958 relating to retirement benefits of IAS, IPS (Indian Police Service) and IFos (Indian Forest Service) pensioners.
- The Rules 1958 were amended by the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), to Rules 2023.
- It mainly focuses on retired intelligence or security related organizations.
What are the Changes Made by the 2023 Rule?
- The central government empowers itself to act against IAS, IPS and IFos and withhold or withdraw their pension even without a reference from the state government if they are found guilty of grave misconduct or are convicted of a serious crime.
- The amended rules reiterate that the decision of the Central Government on withholding or withdrawing the pension “shall be final”.
- Rules added ‘grave misconduct’ includes communication or disclosure of any document or information mentioned in the Official Secrets Act and a ‘serious crime’ includes any crime involving an offence under the Official Secrets Act.
- Earlier rule 3(3) in the All-India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958, which stated that the Central government may withhold or withdraw pension or any part of it “on a reference from the State Government concerned.
- Members of intelligence or security-related organizations who have served in such capacities shall not write or publish any writings without obtaining prior clearance from the head of their respective organization.
What will be the Effect of Changed Rules?
- The Centre may not have to wait for a reference from the state government to act against a pensioner found guilty of grave misconduct or convicted of a serious crime by a Court.
- If the state government concerned does not send such references in such cases, the central government may initiate a process of action.
- Expressing and writing in the media and writing books which disclose sensitive information by the officials of security and intelligence organisations will result in action against officials of security and intelligence organisations concerned.
- The proposed amendment would weaken the State’s political control over the bureaucracy.
- It would hobble effective governance and create avoidable legal and administrative disputes. Because amended rules will provide unrestricted power to central govt to act against retired officers.
What is All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958?
- Section 3 of the All-India Services Act. 1951(61 of 1951) empowers the Central Government, after consultation with the Governments of the States concerned, to make such rules.
- They shall apply to all people who retired from the Service on or after the 29th of October 1951.
- They do not apply to those members of the Service who were promoted to the Service from the State Services or were appointed to the Service under the Indian Administrative Service (Extension to States) Scheme or the Indian Police Service
- Nothing contained in these rules shall apply to the people appointed to the service on or after the 1st day of January 2004.
Source: The Hindu
Rule 267 in Rajya Sabha?

Why in News?
Opposition parties in Rajya Sabha recently gave notices under Rule 267 to discuss the Manipur matter.
About Rule 267:
- According to the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Council of States (Rajya Sabha), Rule 267 relates to the suspension of rules.
- It says, “Any member may, with the consent of the Chairman, move that any rule may be suspended in its application to a motion related to the business listed before the Council of that day, and if the motion is carried, the rule in question shall be suspended for the time being; provided further that this rule shall not apply where specific provision already exists for suspension of a rule under a particular chapter of the Rules.”
- Simply put, under Rule 267, Rajya Sabha MPs can submit a written notice to suspend all listed business in the House and discuss an issue of importance that the country is facing.
- A motion under Rule 267 indicates that a matter was serious enough for the House to suspend its normal business to take it up.
- The rule further says, "The Chairman alone has the power to give consent for moving of a motion for suspension of a rule, and it is for the House to decide whether a particular rule should be suspended or not."
- Thus, it is the discretion of the Chairman to decide whether to allow a motion under Rule 267, as it states that “the consent of the Chairman" is required for a member to bring such a motion.
- However, this rule does not apply where specific provisions already exist for the suspension of a rule under a particular chapter of the rules.
- Who can issue Rule 267?
- Any member of the Rajya Sabha can issue a notice to the Chairperson for a discussion on any subject under Rule 267.
- When was Rule 267 last invoked?
- The last time it was used was in November 2016, when the Upper House invoked Rule 267 to discuss demonetisation.
Source: Hindustan Times
GS-III
Why are Tomato Prices Still High?
Why in News?
As per the RBI, High volatility of tomato prices has historically contributed to overall inflation levels in the country.
India’s Tomato Cultivation
- According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, tomato production in the country is concentrated in the States of Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Odisha, and Gujarat, contributing about 50% of total production.
- There are two major crops of tomato annually — kharif (from September) and rabi (between March and August).
- Regions in Maharashtra and Himachal Pradesh are able to grow tomatoes during the monsoon months, and Madanapalle region of Andhra Pradesh alone accounts for tomato cultivation in the entire country.
- As for tomato production, it peaked in 2019-20 at 21.187 million tonnes (MT) and has been declining since. In 2021-22, it dropped to 20.69 MT and 20.62 MT in 2022-23.
What has fuelled the current tomato inflation?
- High rainfall and fungal diseases: The shortage has been attributed to the irregular weather including unseasonable high rainfall which devastated the growing crops and fuelled by a deadly fungal disease.
- High humidity, high soil moisture, cloudiness and temperatures below 24°C are ideal for infection and development of fungal disease in tomatoes.
- Heatwaves and high temperatures in the months of April and May along with delayed monsoon showers in southern India, including Maharashtra led to pest attacks in tomato crops.
- Low commercial realisation, along with the extreme weather conditions , of the tomato for farmers in the months before June as well as last year. As a result, inferior-quality varieties came to markets earlier this year, fetching low prices to farmers.
- The fact that July-August is a lean production period for tomatoes, as it falls between yields, compounded the problem. This led to a crunch in supply.
- Supply chain issues in transporting the tomatoes from areas where it is grown to regions to the regions of scarcity.
- According to the study of Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER), tomato prices have been following a cyclical phenomenon, with the same situation arising every alternate year. The year 2021 also saw prices drop to as low as ₹2-₹3 per kg for farmers. This led to a lot of them cultivating tomatoes in lesser land areas and shifting to other crops, which resulted in a glut.
- For example, many farmers in Karnataka, which is usually responsible for sizable tomato supplies, shifted to different crops like beans owing to the higher prices it fetched last year.
How does a spike in tomato prices affect the Consumer Price Index?
- The Centre has called this sudden and sharp price rise in tomatoes a “seasonal” and temporary issue.
- Policy experts, the RBI and the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) have expressed concerns over this high seasonal price volatility of tomatoes and its impact on the overall Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- According to the study of NABARD, tomatoes are the most volatile out of all the three TOP (tomato, onion, potato) agri-commodities.
What are the ways to control the inflation volatility of tomatoes?
- Improving value and supply chains: Tomatoes are highly perishable. An organised value chain involving a market-focussed collaboration to produce, process and transport in an effective and efficient manner.
- Increasing the processing capacity for tomatoes by creating more processing units and linking tomato value chains. ICRIER suggests processing tomatoes into paste and puree during peak seasons, and using them in the lean season can be a solution.
- Encouraging Farmer Producers Organisations and eliminating middlemen: A 2022 study estimated that farmers get only 32% share of what consumers pay for tomatoes.
Source: The Hindu
Section 69A of IT Act

Why in News?
The Union government has asked Twitter and other social media platforms to take down the video of two Manipur women who paraded naked in pursuance of its powers under Section 69 (A) of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
What is Section 69 (A) of the IT Act?
- It allows the government to issue content-blocking orders to online intermediaries such as Internet Service Providers (ISPs), telecom service providers, web hosting services, search engines, online marketplaces, etc.
- The Section requires the information or content being blocked to be deemed a threat to India’s national security, sovereignty, or public order.
- Both centre and state governments may direct agencies to intercept, monitor or decrypt or cause to be intercepted or monitored or decrypted any information generated, transmitted, received or stored in any computer resource.
- As per rules that govern these blocking orders, any request made by the government is sent to a review committee, which then issues these directions.
What has the Supreme Court said on Section 69 (A)?
- In a landmark 2015 ruling, the Supreme Court in Shreya Singhal vs Union of India struck down Section 66A of the Information Technology Act of 2000, which entailed punishment for sending offensive messages through communication services, etc.
- The plea had also challenged Section 69A of the Information Technology Rules 2009, but the SC held this to be “constitutionally valid”.
- It will be noticed that Section 69A unlike Section 66A is a narrowly drawn provision with several safeguards.
- First, blocking can only be resorted to where the Central Government is satisfied that it is necessary to do so.
- Secondly, such necessity is relatable only to some of the subjects set out in Article 19(2).
- Thirdly, reasons have to be recorded in writing in such blocking order so that they may be assailed in a writ petition under Article 226 of the Constitution.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|