UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 23rd February 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Child Marriage in India

Why in News?
Activists working on ground suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic combined with poverty may have worsened the phenomenon of child marriage in India.
About Child marriage:
- Child marriage can be described as a formal marriage or an informal union entered into by an individual before attaining the prescribed eligible age.
- The legally prescribed marriageable age in some jurisdictions is below 18 years, including India.
Child marriage in India:
- Child marriage prevalence is generally defined as the percentage of women 20-24 years old who were married or in union before age 18.
- India is estimated to have over 24 million child brides.
- According to the National Family Health Survey, 40% of the world’s 60 million child marriages take place in India.
- According to the International Centre for Research on Women, India has the 14th highest rate of child marriage in the world,
- Eight States have a higher prevalence of child marriage than the national average —
- West Bengal, Bihar and Tripura top the list with more than 40% of women aged 20-24 years married below 18, according to NFHS data.
- In Kerala, women who got married before the age of 18 stood at 6.3% in 2019-20, from 7.6% in 2015-16.
Reasons for child marriage in India:
- Customs and Traditions: Traditions like dowry put a lot of stress on the family because the parents have to give a lot of money, jewellery, land etc. for their daughter to get married.
- Generally the amount of dowry rises with age of the girl, so families prefer to marry their girls young.
- Poverty: Poor Families ‘sell’ their children through marriage to pay off debts or to get out of the cycle of poverty.
- Child marriage makes families poorer because young girls who get married won’t be educated or skilled enough to do well in the workforce.
- “Protecting” the Girl’s Sexuality: In some cultures, marrying a girl young is thought to “protect” the girl’s sexuality and the family’s honour.
- Security: Parents often marry their daughters off young to “secure” a good future for them.
- Abuse, rape, and other crimes against girls, as well as extreme poverty, can make parents turn to child marriage as a way to protect their daughters.
- Laxity in Implementation of Laws: Laws are not implemented stringently. In many cases the ages of the bride and groom aren’t checked at the time of registration of marriage.
- Many child marriages aren’t even registered.
- Discrimination based on gender: Child marriage is a manifestation of discrimination against girls and women.
- According to a UNICEF report on ‘Child Marriage and the Law’, “The discrimination often manifests itself in the form of domestic violence, marital rape, and deprivation of food, lack of access to information, education, healthcare, and general impediments to mobility”.
Harmful impacts of Child Marriage:
Child Rights Issues:
- Children who are forced to get married young lose their rights including the right to an education, the right to be safe from physical and mental violence, injury, or abuse, among others.
Health Issues:
- According to NFHS-5, prevalence of child stunting is 35.5% in 2019-21.
- Premature Pregnancy: Most young brides don’t know much about contraception and don’t have easy access to reproductive health services.
- They get pregnant at a younger age and have more than one child before their mind and bodies are ready.
- Maternal Mortality: Girls under 15 are five times more likely to die during childbirth or pregnancy. The leading cause of death for girls ages 15 to 19 around the world is pregnancy-related deaths.
- Infant Mortality: Babies born to mothers younger than 20 have almost 75% higher death rates than babies born to mothers older than 20 years. The children who do make it are more likely to be born pre-mature and with a low birth weight.
Illiteracy:
- Child brides are often taken out of school and not allowed to get further education.
- Research shows that child marriage and pregnancy are the biggest factors that keep girls from going to school.
Intergenerational Cycle of Poverty:
- Child marriage negatively affects the economy and can lead to an intergenerational cycle of poverty.
- Girls and boys married as children more likely lack the skills, knowledge and job prospects needed to lift their families out of poverty.
- Early marriage leads girls to have children earlier and more children over their lifetime, increasing economic burden on the household.
Teen Widows:
- In a society that allows child marriages, it is not unusual to find widows and divorcees under the age of 18.
Laws and Policies to prevent child marriages:
- The Child Marriage Restraint Act of 1929: It is also known as the Sarda Act. It was a law enacted to restrain the practices of Child Marriage.
- Its main goal was to eliminate the evils placed on young girls who could not handle the stress of married life and to avoid early deaths.
- This act defined a male child as 21 years or younger and a female child as 18 years or younger.
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act of 2006: Under this act, the marriageable age for a male is prescribed as 21 years and that of a female is 18 years.
- Child Marriage is prohibited in India as per the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006.
- Hindu Marriage Act, 1956: Under Hindu Marriage Act, there are no certain provisions for punishing the parents or people who solemnized the marriage.
- A girl can get the marriage annulled only if she wants to get married before attaining the age of fifteen years and she challenges the marriage before turning eighteen.
- Muslim Personal Law: Under the Muslim Laws, there is no bar to child marriage. The couple after marriage has an “option of puberty” known as Khayar-ul-bulugh in which they can repudiate the marriage after attaining the age of puberty.
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012: which aim at protecting children from violation of human and other rights.
- A parliamentary standing committee is weighing the pros and cons of raising the age of marriage for women to 21, which has been cleared by the Union Cabinet.
Way forward:
- The solution lies in empowering girls, creating proper public infrastructure and addressing societal norms.
- It should be ensured that Child Protection Committees and Child Marriage Prohibition officers are doing the job and community support groups should be activated.
- Such efforts can lead to Child Marriage Free Villages like in Odisha which now has over 12,000 such villages.
- Local gram panchayat members should be oriented to spread awareness on child marriage, not only that it is illegal to get a child married off before 18, but also the dangers to the child’s health and her offspring.
- There has been a rise in child marriages during the pandemic, but many have been prevented as well.
Source: The Hindu
What is Open pit mining?

Why in News?
An open pit mine recently collapsed in China's northern Inner Mongolia region, killing at least two people and leaving more than 50 missing.
About Open pit mining:
- What is it? Open-pit mining, also known as opencast mining, is a surface mining technique that extracts minerals from an open pit in the ground.
- It is the most common method used worldwide for mineral mining and does not require extractive methods or
- It is an appropriate extraction method when mineral or ore deposits are found relatively close to the earth's surface, which is overlain by relatively thin vegetation, topsoil, and rock (collectively called overburden).
- It uses a series of level surfaces or benches to reach the deposit, forming an open pit that looks similar to an inverted pyramid.
- Open-pit mines undergo constant expansion until all mineral resources are exhausted.
- Most of the world's annual output of copper, gold, and iron ore is from open-pit mining
- Other commodities produced from open-pit mining include diamonds, molybdenum, manganese, lead and zinc, uranium, and a variety of industrial minerals, such as borates, talc , etc.
- Open-pit mining has higher productivity, lower operating costs, and is relatively safer than other mining methods.
- Environmental effects of open pit mining:
- It consumes enormous amounts of water;
- heavily pollute water and air;
- disfigures landscapes;
- permanently destroys habitat;
- the pit area retains elevated risks of erosion and flooding even after pits are exhausted.
Source: Indian Express
Keeladi Excavation

Why in News?
The excavations in the Keeladi region since 2015 prove that an urban civilisation existed in Tamil Nadu in the Sangam age.
About Keeladi Excavation:
- Keeladi excavation site is a Sangam period settlement that is being excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India and the Tamil Nadu Archaeology Department.
- The settlement lies on the bank of the Vaigai River. This is a large-scale excavation carried out in Tamil Nadu after the Adichanallur archaeological site.
- This site is estimated to be from the period between the 5th century BCE and the 3rd century CE.
Key facts about the Sangam period
- The word ‘Sangam’ is the Tamil form of the Sanskrit word Sangha which means a group of persons or an association.
- This sangama was an academy of poets who flourished in three different periods and different places under the patronage of the Pandyan kings.
- The Sangam literature, which was largely consolidated from the third Sangam, sheds light on people's living conditions at the start of the Christian era.
- It gives information about the secular matter relating to public and social activities like government, war charity, trade, worship, agriculture, etc.
- Sangam literature consists of the earliest Tamil works (Tolkappiyam), the ten poems (Pattupattu), the eight anthologies (Ettutogai) and the eighteen minor works (Padinenkilkanakku), and the three epics.
Source: PIB
GS-II
Special Category Status
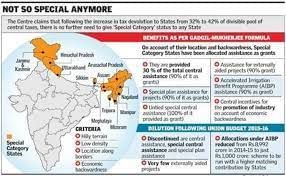
Why in News?
Recently , the Union Finance Minister announced that the Centre will not consider the demands for “special category status “ for any states
About Special Category Status :
- It is a classification given by the Centre to assist development of states that face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages.
- Under this, the Central government extends financial assistance to states that are at a comparative disadvantage against others.
- There is no provision of SCS in the Constitution of India.
- The concept emerged in 1969 with the approval of the Gadgil formula in the Fifth Finance Commission in 1969.
The parameters required for Special Category Status:
- Must be economically backward with poor infrastructure.
- The states must be located in hilly and challenging terrain.
- They should have low population density and significant tribal population.
- Should be strategically situated along the borders of neighboring countries.
- First SCS was accorded in 1969 to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland.
- The 14th Finance Commission has done away with the ‘special category status’ for states, except for the North-eastern and three hill states.
- Presently, eleven states have the Special Category Status in the country including Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Uttarakhand, and Telangana.
Benefits to States with SCS:
- The Centre pays 90% of the funds required in a centrally-sponsored scheme to special category status states as against 60% or 75% in case of other states, while the remaining funds are provided by the state governments.
- Preferential treatment in getting central funds.
- 30 percent of the Centre’s gross budget also goes to special category states.
- Unspent money does not lapse and is carried forward.
- Significant concessions are provided to these states in excise and customs duties, income tax and corporate tax.
- These states can avail the benefit of debt-swapping and debt relief schemes.
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
The New START Treaty

Why in News?
Days before the first anniversary of the beginning of the war in Ukraine, President Vladimir Putin announced in an address to his nation that Russia is suspending its participation in the New START, the last remaining major military agreement with the United States.
Details:
- Putin said the fact that the US wants to inspect Russia’s military facilities — a requirement under the treaty — while at the same time saying openly that its goal is Russia’s strategic defeat, was the “theatre of the absurd”.
What is the New START?
- The name START comes from the original “Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty”, known as START-I, which was signed between the US and the erstwhile USSR in 1991, and came into force in 1994.
- START-I, which capped the numbers of nuclear warheads and intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) that each side could deploy at 6,000 and 1,600 respectively, lapsed in 2009, and was replaced first by the Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (SORT, also known as the Treaty of Moscow), and then by the New START treaty.
- The New START, officially, the “Treaty between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms”, entered into force on February 5, 2011, and placed new verifiable limits on intercontinental-range nuclear weapons.
- The two countries had to meet the treaty’s central limits on strategic offensive arms by February 5, 2018, and to then stay within those limits for the period the treaty remained in force.
- The US and Russia subsequently agreed to extend the treaty through February 4, 2026.
What limits did the New START impose on the two countries?
- 700 deployed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), deployed submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and deployed heavy bombers equipped for nuclear armaments;
- 1,550 nuclear warheads on deployed ICBMs, deployed SLBMs, and deployed heavy bombers equipped for nuclear armaments (each such heavy bomber is counted as one warhead toward this limit);
- 800 deployed and non-deployed ICBM launchers, SLBM launchers, and heavy bombers equipped for nuclear armaments.
Compliance:
- Detailed procedures for the implementation and verification of the central limits, and all treaty obligations, are part of the treaty terms.
- The treaty provides for 18 on-site inspections per year for US and Russian inspection teams.
- Type One inspections focus on sites with deployed and non-deployed strategic systems (up to 10 per year), and Type Two inspections focus on sites with only non-deployed strategic systems (up to 8 per year).
- Since the New START Treaty’s entry into force, as of February 1, 2023, the two parties have conducted 328 on-site inspections, exchanged 25,311 notifications, held 19 meetings of the Bilateral Consultative Commission, and held 42 biannual data exchanges on strategic offensive arms subject to the treaty.
Status of compliance:
- US said that Russia was not complying with the New START, only remaining nuclear arms control treaty between the two countries, jeopardizing a source of stability in their relationship.
- Russia’s refusal to facilitate inspection activities prevents the United States from exercising important rights under the treaty.
- Russia has also failed to comply with the New START treaty obligation to convene a session of the bilateral consultative commission in accordance with the treaty-mandated timeline.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
Why in News?
The IEPFA is seeking applications from young students and scholars for its short-term internship programme which began recently.
About IEPFA:
- IEPF is a statutory body under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, established under the Companies Act 2013.
- It administers the Investor Education and Protection Fund.
- IEPF Authority has undertaken a proactive approach to achieve its mandate of promoting investor education, awareness and protection.
- Its objective is to promote Investor Education, Awareness, and Protection.
- The Amounts credited to IEPF are maintained under the Consolidated Fund of India (Article 266 of the Constitution).
- Composition:
- Secretary Ministry of Corporate Affairs is the Chairperson of the Authority.
- The Joint Secretary Ministry of Corporate Affairs is the Chief Executive Officer of the Authority.
- The Authority is entrusted with the responsibility of administration of the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF), make refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc. to investors and to promote awareness among investors.
- The Authority has taken a 360 degree approach to sensitize stakeholders to include household investors, housewives, professionals, etc. across the country in rural and urban areas through direct investor awareness programmes, media campaign and engaging with other stakeholders with the common goal.
- In the urban and semi-urban areas the Authority organizes investor awareness programmes in association with the Institute of charted Accountants of India, Institute of Cost Accountants of India and Institute of Company Secretaries of India.
- In the rural areas the programmes are organised in collaboration with CSC e-governance Services Private Limited through the Common Service Centre (CSC’s) located in villages.
- Multilingual Information, Education and Communication booklets and films have been developed for creating awareness.
- A Joint Awareness campaign has been launched in association with Reserve Bank of India, Securities and Exchange Board of India & Department of Consumer Affairs.
The IEPF is to be utilized for :
- The refund of unclaimed dividends , matured deposits, debentures , application money due for refund and interest thereon.
- Promotion of investor’s education, awareness and protection.
- Distribution of any disgorged amount among eligible and identifiable applicants for shares or debentures , shareholders, debenture-holders or depositors who have suffered loss due to wrong actions by any one person , in accordance with the ordered made by the court which had ordered disgorgement.
SOURCE: PIB
Phosphor-Gypsum

Why in News?
The National Highways Authority of India along with the Department of Fertilizers, and the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers is going to take up field trials on NHAI projects for use of Phosphor-Gypsum in National Highway construction.
About Phosphor-Gypsum:
- Phosphorus is a mineral critical to all life on Earth. As a requirement of all biological beings, it is a cornerstone of nutrition for plants, animals, and people.
- Phosphogypsum is a waste by-product from the processing of phosphate rock in plants producing phosphoric acid and phosphate fertilizers, such as superphosphate.
- It is used in agriculture for soil amendment or as fertilizer, as well as in the brick and cement industry, and road construction.
Key facts about NHAI
- It was constituted by an Act of Parliament in 1988under the administrative control of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- NHAI has been set up as a Central Authority to develop, maintain and manage the National Highwaysentrusted to it by the Government of India.
- The Authority consists of a full-time Chairman and not more than five full-time Members and four part-time Members who are appointed by the Central Government.
Source: PIB
APJ Abdul Kalam SLV

Why in News?
India’s first hybrid rocket launched from Tamil Nadu’s Pattipulam.
About APJ Abdul Kalam SLV:
- Martin Foundation in association with Dr APJ Abdul Kalam International Foundation and Space Zone India completed the project known as Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Satellite Launch Vehicle Mission 2023.
- It is India’s first hybrid sounding rocket by private players .
- The reusable rocket was made by the selected top 100 students, while the rest made the satellite.
About Hybrid Rocket:
- is a type of rocket engine that combines features of both liquid-fueled and solid-fueled rockets. In a hybrid rocket, a solid fuel is burned in combination with a liquid or gaseous oxidizer to produce thrust.
- The solid fuel in a hybrid rocket is typically made of a polymer, such as hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB), which is cast into a cylindrical shape and placed inside the rocket motor.
- They are generally simpler and less expensive to manufacture than liquid rockets.
- They are also safer than both liquid and solid rockets
SOURCE :THE HINDU
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 23rd February 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What are the daily current affairs and why are they important for UPSC preparation? |  |
| 3. How can I effectively prepare for the UPSC exam using daily current affairs? |  |
| 4. What are Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) and why are they useful for UPSC preparation? |  |
| 5. How can I find frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to UPSC current affairs? |  |

















