UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 26th April 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Tughlaqabad Fort
Why in News?
Recently, the Delhi High Court directed the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to remove encroachments in the historic Tughlaqabad Fort.
About Tughlaqabad Fort:
- It was built by the Ghiyathu’d-Din Tughluq (1321-25) who belongs to the Tughluq dynasty.
- The fortified city was built in four years on the rocky terrain, as a defence mechanism.
- Features
- It is in two parts, the citadel and palaces along the southern walls forming one unit and the city to the north the other.
- The citadel is still intact, and the walls of palaces can also be discerned.
- The city portion is, however, in extreme ruins, although one may make out the alignment of some of its streets.
- Across the main entrance from the south is Ghiyathu’d-Din’s tomb is located.
- It is faced with red sandstone relieved by marble, and with batter on the exterior, it is enclosed within high walls forming an irregular pentagon.
- Ghiyathu’d-Din’s successor, Muhammad Tughluq (1325-51), added the small fortress of ‘Adilabad on the hill south of Tughluqabad, with which it shares the main characteristics of construction.
Key Facts about the Archaeological Survey of India
- Under the provisions of the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act of 1958 (AMASR Act, 1958), the ASI administers more than 3650 ancient monuments, archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
- It also regulates the Antiquities and Art Treasure Act, of 1972.
- It was established in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham (He also became its first Director-General).
HQ: New Delhi. - Nodal Ministry: It is an attached office to the Ministry of Culture.
Source: The Print
Zero Shadow Day
Why in News?
Recently, Bengaluru experienced a ‘Zero Shadow Day’, when vertical objects appear to cast no shadow.
About Zero Shadow Day:
- What it is? It is a sub-solar point where the sun is directly overhead at a particular latitude.
- When the sun is at the zenith (the highest point in the sky) its rays will be hitting a particular point exactly perpendicular to the surface.
- This will make the shadow of a person exactly under him, making it look like there are no shadows.
When does it occur?
- There are two zero shadow days every year in May and July/August, observed in places that lie between the tropic of Cancer and the tropic of Capricorn.
- One falls during the Uttarayan (when the Sun moves northwards), and the other is during Dakshinayan (when the Sun moves southwards).
- It lasts for a small part of a second, but the effect can be seen for a minute to a minute-and-a-half.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
National Civil Services Day
Why in News?
Recently, National Civil Services Day was commemorated.
About National Civil Services Day:-
- National Civil Services Day is celebrated in India on 21st April.
- This day acts as a reminder for civil servants, working in various departments, of the cause to serve the citizens of the country above all else.
- The government of India celebrates Civil Services Day, every year as an occasion for the civil servants to rededicate themselves to the cause of serving citizens and renew their commitments to public service and excellence in work.
- The reason behind choosing this very date was to commemorate the day when the first Home Minister of Independent India, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, addressed the probationers of Administrative Services Officers in 1947 at Metcalf House, Delhi.
- There he referred to civil servants as the ‘steel frame of India’.
- This meant that civil servants, employed at various levels of the government, act as supporting pillars of the country’s administrative system.
- As part of Civil Services Day, Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration are presented to Districts/Implementing Units for implementation of Priority programmes and innovation categories.
- The theme for this year’s Civil Services Day is ‘Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens and Reaching the Last Mile’.
Source: Indian Express
National Panchayati Raj Day
Why in News?
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj in collaboration with the Government of Madhya Pradesh commemorated National Panchayati Raj Day (NPRD).
Major Highlights of the Day
- The Prime Minister inaugurated an integrated e-GramSwaraj and GeM portal for public procurement at the Panchayat level.
- The integration aims at enabling panchayats to market their goods and services through GeM leveraging the e-GramSwaraj platform.
- The Prime Minister handed over SVAMITVA Property Card to select beneficiaries, symbolizing the attainment of the milestone of 1.25 crore property cards distribution under the SVAMITVA Scheme in the country.
- A dedicated website and Mobile App on “Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav – SAMAAVESHI VIKAS” was launched by Prime Minister.
About National Panchayati Raj Day
- It is celebrated on April 24 every year in India to commemorate the historic day when the Panchayati Raj System was introduced in the country.
- The Panchayati Raj System is a decentralized system of governance in India, where local bodies or Gram Panchayats are given the power to govern themselves and make decisions for the development of their respective areas.
- This system was introduced in 1993 by the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, which aimed at bringing democracy at the grassroots level and empowering people in rural areas.
Historical Linkages
- The Panchayati Raj System has its roots in ancient India, where the village council or Panchayat was the primary unit of governance.
- The system was revived in the early 1950s when the first National Development Council recommended the establishment of a democratic system of governance at the grassroots level.
- However, it was not until 1993 that the Panchayati Raj System was given a constitutional status and made mandatory for all states in India.
Significance
- The Panchayati Raj System has been instrumental in bringing about significant changes in the rural landscape of India.
- It has given people in rural areas a voice and an opportunity to participate in the decision-making process, leading to the overall development of their respective areas. The system has also helped in decentralizing power and reducing corruption at higher levels of government, as decisions are made at the local level.
- The system has been successful in bringing about socio-economic development, promoting social justice, and empowering women in rural areas.
Source: Economic Times
Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP)
Why in News?
The Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) Committee has taken up measures to establish close to 2500 theme-based polling stations across Karnataka.
About Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP):-
- Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation program, better known as SVEEP, is the flagship program of the Election Commission of India.
- It is for voter education, spreading voter awareness and promoting voter literacy in India.
- It is working towards preparing India’s electors and equipping them with basic knowledge related to the electoral process since 2009.
- SVEEP’s primary goal is to build a truly participative democracy in India by encouraging all eligible citizens to vote and make an informed decision during the elections.
- The programme is based on multiple general as well as targeted interventions.
- These are designed according to the socio-economic, cultural and demographic profile of the state as well as the history of electoral participation in previous rounds of elections and learning thereof.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
India’s First Water Body Census
Why in News?
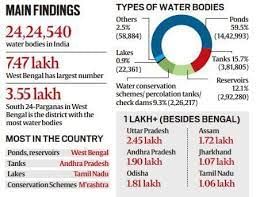
The Ministry of Jal Shakti has recently released the report of India’s first water bodies census.
More about the census
- About:
- India’s first water bodies census contains a comprehensive database of ponds, tanks, lakes, and reservoirs in the country.
- The census was conducted in 2018-19, and enumerated more than 2.4 million water bodies across all states and Union Territories.
- Background:
- The Centre earlier maintained a database of water bodies that were getting central assistance under the scheme of Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of water bodies.
- Recommendation for the census:
- In 2016, a Standing Committee of Parliament pointed to the need to carry out a separate census of water bodies.
- The government then commissioned the first census of water bodies in 2018-19 along with the sixth Minor Irrigation (MI) census.
- Objective of carrying out census:
- The objective was to collect information “on all important aspects of the subject including their size, condition, status of encroachments, use, storage capacity, status of filling up of storage etc.”.
About “Water Bodies”
- What consists of “Water Bodies”?
- First Census Report considers “all natural or man-made units bounded on all sides with some or no masonry work used for storing water for irrigation or other purposes (e.g. industrial, pisciculture, domestic/ drinking, recreation, religious, ground water recharge etc.)” as water bodies.
- According to the census, the water bodies “are usually of various types known by different names like tank, reservoirs, ponds etc.”.
- A structure where water from ice-melt, streams, springs, rain or drainage of water from residential or other areas is accumulated or water is stored by diversion from a stream, nala or river will also be treated as a water body.
- First Census Report considers “all natural or man-made units bounded on all sides with some or no masonry work used for storing water for irrigation or other purposes (e.g. industrial, pisciculture, domestic/ drinking, recreation, religious, ground water recharge etc.)” as water bodies.
- Excluded Water Bodies
- Seven specific types of water bodies were excluded from the count. They were:
- Oceans and lagoons;
- Rivers, streams, springs, waterfalls, canals, etc. which are free flowing, without any bounded storage of water;
- Swimming pools;
- Covered water tanks created for a specific purpose by a family or household for their own consumption;
- A water tank constructed by a factory owner for consumption of water as raw material or consumable;
- Temporary water bodies created by digging for mining, brick kilns, and construction activities, which may get filled during the rainy season; and
- Pucca open water tanks created only for cattle to drink water.
- Seven specific types of water bodies were excluded from the count. They were:
Water bodies Census Data highlights
- Districts with highest number of water bodies:
- As per the report, West Bengal’s South 24 Pargana has been ranked as the district having the highest (3.55 lakh) number of water bodies across the country.
- The district is followed by Andhra Pradesh’s Ananthapur (50,537) and West Bengal’s Howrah (37,301).
- Encroachment of water bodies:
- The census found that 1.6% of enumerated water bodies — 38,496 out of 24,24,540 — had been encroached upon.
- More than 95% of these were in rural areas — which is logical because more than 97% of the water bodies covered by the census were in the rural areas.
- In almost 63% of encroached water bodies, less than a quarter of the area was under encroachment;
- In about 12% water bodies, more than three-quarters of the area was under encroachment.
- Uttar Pradesh accounted for almost 40% (15,301) of water bodies under encroachment, followed by Tamil Nadu (8,366) and Andhra Pradesh (3,920).
- No encroachment was reported from West Bengal, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Chandigarh.
- The census found that 1.6% of enumerated water bodies — 38,496 out of 24,24,540 — had been encroached upon.
Threats faced by water bodies in India
- Increasing temperatures:
- India is witnessing a repeat of 2021 conditions, when temperatures touched 40 degrees Celsius as early as February in some parts of the country.
- Climate Change’s Impact:
- Climate change impacts are about heat — increased and scorching temperatures — and about variable and extreme rain.
- Both have a direct correlation with the water cycle.
- Possibility of El Nino conditions:
- Globe saw the event of triple dip La Niña in the last few years — the Pacific water currents that are known to bring cooler temperatures globally.
- But global warming has offset this cooling effect of La Niña.
- Situation is bound to be worse in El Nino conditions.
- Globe saw the event of triple dip La Niña in the last few years — the Pacific water currents that are known to bring cooler temperatures globally.
- Varying Rain Pattern:
- The number of rainy days in India will further go down, but extreme rainy days will increase.
- This will have a huge impact on India’s plans for water management.
Significance of Water Security for India & way ahead
- To Address Rising Demand:
- With total water demand in India expected to rise by over 70% by 2025, a huge demand-supply gap is expected in the coming years.
- Ensuring Health:
- Poor water quality and lack of adequate access to sanitation are also major causes of disease and poor health.
- Proper access to potable water will minimise health issues and medical expenses.
- Supporting Economy:
- Adequate water security will act as a potentially significant booster on economic growth as it will reduce the costs for water infrastructure.
Source: Indian Express
T-14 Armata battle tank
Why in News?
Russia has recently begun using its new T-14 Armata battle tanks to fire on Ukrainian positions
About T-14 Armata battle tank:
- It is a new Russian Main Battle Tank (MBT).
- It is designed by the Russian Defense Company Uralvagonzavod.
- Features:
- It has an unmanned turret, with crew remotely controlling the armaments from "an isolated armoured capsule located in the front of the hull.
- Maximum Speed: 75 km/h.
- The tank has a maximum range of 500 km on internal fuel.
- It is operated by a crew of 3 men, including a commander, gunner and driver.
- It is one of the most protected MBTs in the world. It has newly-developed composite base armour made of steel, ceramics and other materials.
- The tank is armed with a 2A82 (or 2A82-1M) 125 mm smoothbore gun.
- It is capable of firing gun-launched anti-tank guided missiles in the same manner as ordinary projectiles. These missiles have a range of about 5 km and can also target low-flying helicopters.
Source: The Hindu
Jaitapur Nuclear Power Plant (JNPP)

Why in News?
Recently, the French company Electricite de France (EDF) stated that Nuclear liability issues were not resolved for the Jaitapur project.
About Jaitapur Nuclear Power Plant (JNPP)
- Indo-French cooperation on the ‘peaceful use of nuclear energy’ was signed in 2008, primarily for building the Jaitapur Nuclear Power Plant (JNPP).
- India has announced plans to construct six 1,650 MW nuclear power plants at Jaitapur in Ratnagiri, which could become the nation's largest nuclear power site once completed with a 9,900 MW capacity.
- Importance for India
- Nuclear power is clean and environment friendly, apart from having a huge potential to ensure the country’s long-term energy security on a sustainable basis.
- This project will embody the strong partnership between India and France, a commitment to a low carbon future, and will directly benefit Maharashtra with thousands of local jobs.
- It would provide electricity to seven crore households.
Issues
- The issue is arising from India’s Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act.
- The act is considered excessive by foreign companies, which could be liable to pay hundreds of millions of dollars in the event of a nuclear accident.
- As a result, despite signing civil nuclear deals with a number of countries, including the U.S., France and Japan, the only foreign presence in India is that of Russia in Kudankulam, projects that predate the Law.
- India has ratified the international convention on nuclear energy accident liability, which was perceived as a barrier for foreign companies to invest in the country.
- It is believed that international manufacturers have been reluctant to begin any nuclear project in India because of the country’s domestic liability law which makes all, including equipment suppliers, accountable for any untoward incident.
Suggestions and Way Forward
- In the past, India has taken steps to address the issue of civil nuclear liability.
- It released a list of FAQs on “Civil Nuclear Liability” in February 2015 and also launched the India Nuclear Insurance Pool (INIP) in June that year.
- INIP is an insurance pool to cover the equipment suppliers’ risk of potential liability.
- It released a list of FAQs on “Civil Nuclear Liability” in February 2015 and also launched the India Nuclear Insurance Pool (INIP) in June that year.
- The existing technical, financial, and civil nuclear liability issues need to be resolved at the earliest.
- Other measures to enhance the generation from nuclear power plants in the country.
- Accord of administrative approval and financial sanction of - ten (10) indigenous 700 MW Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) to be set up in fleet mode with the provision of equity support.
- Resolution of issues related to the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (CLND) Act & Creation of the Indian Nuclear Insurance Pool (INIP).
- Amendment of the Atomic Energy Act to enable Joint Ventures of Public Sector Companies to set up nuclear power projects.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|