UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 26th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund

Context
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) crosses Rs.30,000 crore mark of capital mobilisation for projects in agriculture sector for creation of post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets
What is Agriculture Infrastructure Fund?
- About:
- AIF is a financing facility launched in July 2020.
- It aims to provide all-around financial support to the farmers, agri-entrepreneurs, farmer groups like Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) etc. and many others to create post-harvest management infrastructure and build community farming assets throughout the country.
- Features:
- AIF provides support of 3% interest subvention, credit guarantee support through Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) scheme for loan of up to Rs. 2 crore and facility of convergence with other Central and State Government schemes.
- AIF is helping in reducing post-harvest losses by creating and modernising agriculture infrastructure, which includes primary processing centres for vegetables, hi-tech hubs for rental of agricultural machinery.
- Management:
- The fund will be managed and monitored through an online Management Information System (MIS) platform. It will enable all the qualified entities to apply for loans under the Fund.
- The National, State and District level monitoring committees will be set up to ensure real-time monitoring and effective feed-back.
What is Post Harvest Management?
- About:
- Post-harvest management refers to the activities and techniques used to preserve and protect crops after they have been harvested.
- This includes activities such as cleaning, sorting, grading, packaging, storage, and transportation.
- The goal of post-harvest management is to maintain the quality and safety of the crops, as well as to extend their shelf life, so that they can be sold and consumed at a later time.
- Challenges:
- Lack of Convenient Access to Credit: A convenient line of credit is not available to small and marginal farms. As per the NABARD 2018 survey, farmers with smaller plot sizes took a greater share of loans from the non-institutional lenders than did farmers with larger plot sizes (> 2 hectares).
- This indicates that more small and marginal farmers rely on (expensive) informal sources of credit than large ones.
- Stubble Burning: The problem of ‘on-farm’ burning or stubble burning is intensifying in recent years due to shortage of human labour, high cost of removing the crop residue from the field and mechanised harvesting of crops, contributing majorly to air pollution in Northern India.
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks: More than 30% of the produce from farm gate is lost due to inadequate cold chain infrastructure.
- The NITI Aayog cited a study that estimated annual post-harvest losses close to Rs 90,000 crore.
- Lack of all-weather roads and connectivity make supply erratic.
- Lack of Convenient Access to Credit: A convenient line of credit is not available to small and marginal farms. As per the NABARD 2018 survey, farmers with smaller plot sizes took a greater share of loans from the non-institutional lenders than did farmers with larger plot sizes (> 2 hectares).
How can India Harvest Rich Returns from Agriculture?
- Integrating Traditional and Frontier Technologies: Rainwater harvesting and recycling of organic waste for plant nutrient, pest management, etc., are examples of traditional technologies that can be used to complement frontier technologies like tissue culture, genetic engineering, to achieve higher productivity.
- Upgrading Agricultural Surplus Management: An infrastructure upgrade and development program are needed for post-harvest handling, seed, fertiliser and agrochemical quality regulation.
- Additionally, it is necessary to promote grading and standardisation of procurement centres.
- Harvesting Rich Returns Through Market Integration: There is a need to streamline domestic markets and put in place the infrastructure and institutions to connect local markets with national and global markets.
- To facilitate smooth integration between domestic and world markets, and to manage trade liberalisation more effectively, India needs a nodal institution that can monitor world and domestic price movements closely and take timely and appropriate measures to avoid major shocks.
Source: PIB
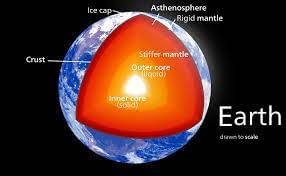
What is the Inner Core of the Earth?
Context
A recent study says that the inner core of Earth seems to have stopped spinning in the same direction as the rest of the planet.
About the Inner core of the Earth:
- It is the innermost layer of the Earth.
- Structure:
- It is a solid metallic ball made mainly of iron.
- The inner core is solid due to the pressure caused by the weight put on it by the Earth’s other top layers.
- It is distinct from the outer core, which is a liquid.
- Radius:
- The inner core has an average radius of 1220 km.
- The boundary between the inner and outer cores is located at approximately 5150 km below the surface of the Earth.
- This boundary is called the Lehman Seismic Discontinuity.
- Temperature: Inner core temperatures reach extraordinary levels, estimated to be between 7,200–8,500ºF (4,000–4,700ºC).
- Properties:
- It is predicted to have very high thermal and electrical conductivity.
- The inner core generates its own magnetic field and spins a bit faster than the rest of the planet.
What are the three layers of Earth?
- The earth is made up of three different layers: the crust, the mantle and the core.
- The crust: This is the outside layer of the earth and is made of solid rock, mostly basalt and granite.
- The mantle: It lies below the crust and is up to 2900 km thick. It consists of hot, dense, iron and magnesium-rich solid rock.
- The core: It is the center of the earth and is made up of two parts: the liquid outer core and solid inner core. The outer core is made of nickel, iron and molten rock.
GS-II
BharOS
Context
Recently, BharOS, an indigenous mobile operating system was developed by JandK Operations Private Limited, a non-profit organization incubated at IIT Madras and funded by the Department of Science and Technology.
Key Features of BharOS
- BharOS is a mobile operating system similar to Android or iOS; it is based on an AOSP (Android Open Source Project) operating system and does not use any Google apps or services.
- It would support Native Over The Air (NOTA) updates as well as No Default Apps (NDA).
- It has a minimalistic home screen with the Indian flag, a list of app categories, and a selection of apps that have passed the OS's trust and security standards.
- It will employ the Private App Store Services (PASS) system to examine and curate apps that are safe for users.
- These systems enable smartphone users to interact with their devices and access their features while also ensuring their safety.
- Current status: The current version of BharOS includes third-party apps such as DuckDuckGo and Signal by default.
What is Native Over The Air (NOTA)?
- Security updates and bug fixes will be automatically installed rather than users having to check for updates and implement them on their own
What is the No Default Apps setting? :
- Users do not have to keep or use pre-installed apps in this mobile operating system.
Source: PIB
SC removes magistrate-nod rider to prepare ‘living will’
Context
The Supreme Court has removed the condition that managed a magistrate’s approval for withdrawal or withholding of life support to a terminally ill person.
What is the Concept of Euthanasia?
- Euthanasia is defined as the hastening of death of a patient to prevent further sufferings.
- Active Euthanasia –
- Active euthanasia refers to the physician deliberate act, usually the administration of lethal drugs, to end an incurably or terminally ill patient’s life.
- There are three types of active euthanasia, in relation to giving consent for euthanasia, namely:
- Voluntary euthanasia – at patient request,
- Nonvoluntary – without patient consent,
- Involuntary euthanasia – patient is not in a position to give consent.
- Passive Euthanasia –
- Passive euthanasia refers to withholding or withdrawing treatment which is necessary for maintaining life.
What is ‘Living Will’?
- The “living will” is a person’s right to issue advance directive on the course of his/her treatment, including withdrawal of life support, should such a situation arise.
- However, there is no way a living will provision can be made fool-proof requiring no intervention of the doctor or immediate decisionmakers around a person.
Is Euthanasia Legal in India?
- A five-judge bench of the Supreme Court in Common Cause vs Union of India (2018) recognised a person’s right to die with dignity.
- It said that a terminally ill person can opt for passive euthanasia and execute a living will to refuse medical treatment.
- The Court permitted an individual to draft a living will specifying that she or he will not be put on life support if they slip into an incurable coma.
- The Court recognised the right to die with dignity as a fundamental right and an aspect of Article 21 (Right to Life).
- Is Active Euthanasia Legal?
- In India, active euthanasia is a crime.
- Section 309 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) deals with the attempt to commit suicide and Section 306 of the IPC deals with abetment of suicide – both actions are punishable.
- Only those who are brain dead can be taken off life support with the help of family members.
News Summary:
- The Supreme Court has modified its order in the 2018 judgement on passive euthanasia.
- With the modified order, the Court aims to make the procedure of removal of (or withholding) life support from terminally ill patients less cumbersome for the patients, their families and the doctors by limiting the role played by government officials.
Supreme Court’s Order:
- Firstly, the requirement of setting up two medical boards – one primary and other review – to examine the medical condition of the patient has been retained.
- However, the Court has done away with the rule mandating that the district collector set up the review board.
- The Court said both boards will be constituted by the hospital and there would be one nominee doctor of the district medical officer in the review board.
- The medical board must take a decision on such cases preferably within 48 hours.
- The Court has also made the process of making a “Living Will” simplified.
- While the earlier rule stipulated that a living will had to be made in the presence of two attesting witnesses and countersigned by the jurisdictional Judicial Magistrate of First Class (JMFC).
- The new order says such a will can be attested by notary or a gazetted rank officer.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Skyglow

Context
Recently, a new study has found that non-natural light had increased the brightness of Skyglow, by 9.2-10% every year between 2011 and 2022 with significant ecological, health and cultural implications.
- Researchers have analyzed a global database of what the dimmest star visible from a particular location is; the database had more than 51,000 entries submitted by citizen scientists.
What is Skyglow?
- The Skyglow, is an omnipresent sheet of light across the night sky in and around cities that can block all but the very brightest stars from view.
- The brightening of the night sky over inhabited areas because of streetlights, security floodlights and outdoor ornamental lights cause the Skyglow.
- This light floods directly into the eyes of the Nocturnal (active at night) and also into the skies and misleads their path.
- 'Skyglow' is one of the components of light pollution.
What is the Scenario of Skyglow?
- Global
- The Skyglow had brightened around 6.5% over Europe, 10.4% over North America, and 7.7% over the rest of the world.
- The finding is significant because it disagrees with satellite-based data, which has indicated that the rate of increase has been around 2% per year.
- The discrepancy is probably the result of the satellites being unable to ‘sense’ blue light emitted by LEDs and to study light that is emitted parallel to the ground.
- India:
- A 2016 study reported that 19.5% of India’s population – the lowest fraction among G20 countries – experiences a level of skyglow that would at least keep the Milky Way galaxy out of sight and at most render “dark adaptation for human eyes” impossible.
- The effects include stimulating the cone cells in human eyes, which is possible only when an environment is considered to be well-lit.
- A 2017 study reported that between 2012 and 2016, India’s lit area increased by 1.07-1.09% and the average radiance of “stably lit areas” – e.g., excluding wildfires – increased by 1.05-1.07%.
What are the Implications of Skyglow?
- Wastes Energy and Money:
- Lighting that emits too much light or shines when and where it’s not needed is wasteful. Wasting energy has huge economic and environmental consequences.
- Disrupting the Ecosystem and Wildlife:
- Plants and animals depend on Earth’s daily cycle of light and dark rhythm to govern life-sustaining behaviors such as reproduction, nourishment, sleep and protection from predators.
- Scientific evidence suggests that artificial light at night has negative and deadly effects on many creatures including amphibians, birds, mammals, insects and plants.
- Ex: Lit beaches deter sea turtles from coming ashore to nest. Skyglow keeps trees from sensing seasonal variations.
- Clownfish eggs don’t hatch when exposed to artificial light at night, killing the offspring.
- Harming Human Health:
- Like most life on Earth, humans adhere to a Circadian Rhythm — our biological clock — a sleep-wake pattern governed by the day-night cycle. Artificial light at night can disrupt that cycle.
- A small 2009 review concluded that circadian disruption – which altered melatonin levels can cause – increased the risk of breast cancer among night-shift workers by 40%.
- The erasure of the night sky acts to erase Indigenous connection to the stars, acting as a form of ongoing cultural and ecological genocide.
What can be the Solutions?
- The researchers recommend light sources casting light at an angle below the plane of the horizon, capping the emissions of these sources and calibrating their output according to the total brightness at the spot being lit.
- Where lights cannot be turned off, they can be shielded so that they do not shed light into the surrounding environment and sky.
- The International Dark-Skies Association has certified more than 130 ‘International Dark Sky Places’, where artificial lighting has been adjusted to reduce skyglow and light trespass. However, nearly all are in developed countries in the northern hemisphere.
- Less-developed regions are often both species-rich and, currently, less light-polluted, presenting an opportunity to invest in lighting solutions before animals there are seriously affected.
Source: The Hindu
Risk of Moving from Fossils to Clean Energy
Context
Recently, a study published in the Global Environmental Change journal, which states that India’s financial sector is highly exposed to the risks of the economy transitioning from being largely dependent on fossil fuel to clean energy.
What are the Findings?
- Transition can Negatively Impact:
- India’s financial sector is highly exposed to the activities related to fossil fuels and any transition from fossil fuel to clean energy will have a negative impact on this sector.
- 60% of lending to the mining sector is for oil and gas extraction.
- 20% of manufacturing sector debt is for petroleum refining and related industries.
- Electricity production is the largest source of carbon emissions, accounting for 5.2% of outstanding credit.
- Shortage of Experts:
- There is a shortage of experts in India’s financial institutions who have the expertise to appropriately advise the institutions on transition from fossil fuel to clean energy.
- Only four of the ten major financial institutions surveyed collect information on environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks and these firms do not systematically incorporate that data into financial planning.
- Less Capacity to respond to Shocks and Stresses:
- High-carbon industries - power generation, chemicals, iron and steel, and aviation-account for 10% of outstanding debt to Indian financial institutions.
- However, these industries are also heavily indebted, and therefore have less financial capacity to respond to shocks and stresses.
- This will further expose India’s financial sector to the risk associated with the transition.
- More Polluting and More Expensive Energy Supply:
- The financial decisions of Indian banks and institutional investors are locking the country into a more polluting, more expensive energy supply.
- For example, only 17.5% of bank lending to the power sector has been to pure-play renewables.
- Consequently, India has much higher electricity from carbon-sources than the world average.
- Coal currently accounts for 44% of India’s primary energy sources and 70% of its power(electricity).
- The country’s coal-fired power plants have an average age of 13 years and India has 91,000 MW of new proposed coal capacity in the works, second only to China.
- According to the Draft National Electricity Plan 2022, coal’s share in the electricity generation mix will decrease to 50% by 2030.
- Potential:
- The current lending and investment patterns reveal that India’s financial sector is heavily exposed to potential transition risks.
- However, the other side of risks is the tremendous opportunity to move finance towards sustainable assets and activities.
- In 2021, India committed to reach net-zero emissions by 2070.
- India has also announced plans to source half of its electricity needs (50%) from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- This will require financing to the order of at least a trillion dollars to meet these commitments.
Source: The Hindu
What is the Light Tank Zorawar?
Context
According to a recent report, DRDO-L&T developed Zorawar Light Tank that is under fabrication and will be “rolled out” soon.
About Light Tank Zorawar:
- It is an indigenously designed and developed Light Tank.
- Developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with Larsen & Toubro Limited.
- Features:
- It is designed to operate in varying terrain from high altitude areas and marginal terrains to island territories.
- It will be highly transportable for rapid deployment to meet any operational situation.
- It will be equipped with all the modern technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Drone Integration, a high degree of situational awareness, and amphibious operation capability.
- It will weigh less than 25 tonnes with a high power-to-weight ratio as well as superior firepower and protection.
Who was Zorawar?
- He was a military general — Zorawar Singh Kahluria, and had served under Jammu’s Raja Gulab Singh in the 19th Century.
- He is honoured for his conquests in the Himalayas including Ladakh, Tibet, Baltistan and Skardu.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 26th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What are the three stages of the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What is the syllabus for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare for the UPSC exam effectively? |  |
| 5. How many attempts are allowed for the UPSC exam? |  |




















