UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 29th May 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Mahakaleshwar Temple

Why in News?
The Mahakal Lok corridor, located at Ujjain's Mahakaleshwar temple, recently experienced massive destruction caused by strong winds.
About Mahakaleshwar Temple:
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva.
- Location:
- It is located in the ancient city of Ujjain in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- The temple is situated besides the Rudra Sagar lake.
- It is one of the twelve Jyotirlingams of Lord Shiva.
- Mahakaleshwar idol is Dakshina Mukhi, facing south, unlike all the other Jyotirlingas.
- The temple, which is spread over five levels, sees a huge throng of devotees during the Maha Shivaratri festival.
- Architecture:
- The temple complex comes with a spacious courtyard that is adorned with finest sculptures that are believed to be influenced by Chalukya, Maratha, and Bhumija styles of structural design.
- The foundation and platform are built of stones. Most of the upper structure rests on the strong and well-designed pillars and plasters.
- It is complete with impressive lingam sculptures of Mahakaleshwar.
- The images of Ganesh, Parvati and Karttikeya are installed in the west, north and east of the sanctum sanctorum.
- The temple also houses a tank constructed in the sarvatobhadra style.
What are Jyotirlingas?
- A Jyotirlinga is a shrine where Lord Shiva is worshipped in the form of a Jyotirlingam.
- There are currently 12 main Jyotirlingas in India.
- The 12 Jyotirlinga temples in India take the name of the presiding deity. Each considered a different manifestation of Lord Shiva.
- 12 Jyotirlingas in India are:
- Somnath Jyotirlinga in Gir, Gujarat
- Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga in Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh
- Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh
- Omkareshwar Jyotirlinga in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh
- Baidyanath Jyotirlinga in Deoghar, Jharkhand
- Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga in Maharashtra
- Ramanathaswamy Jyotirlinga in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu
- Nageshwar Jyotirlinga in Dwarka, Gujarat
- Kashi Vishwanath Jyotirlinga in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
- Trimbakeshwar Jyotirlinga in Nasik, Maharashtra
- Kedarnath Jyotirlinga in Rudraprayag, Uttarakhand
- Ghrishneshwar Jyotirlinga in Aurangabad, Maharashtra
Source: The Hindu
Enhancing Agricultural Research and Development for Climate Resilience

Why in News?
Recently the G-7 Summit 2023 held in Japan highlighted the urgent need to address climate change and set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. India has the largest workforce (45.6 per cent in 2021-22) engaged in agriculture amongst G20 countries faces significant challenges. To mitigate the impact and ensure food and nutritional security, policymakers must prioritize agricultural research, development, education, and extension (ARDE).
Importance of ARDE
- ARDE, which stands for Agricultural Research, Development, Education, and Extension, plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges faced by the agriculture sector, particularly in the context of climate change.
- Climate Resilience: Through research and development efforts, scientists and experts can identify crops and varieties that are more tolerant to changing climatic conditions, such as drought, heatwaves, or extreme rainfall. This enables farmers to adapt and minimize the negative impacts of climate change on crop yields and agricultural productivity.
- Resource Efficiency: By focusing on research and innovation, it aims to optimize the use of key resources like water, soil, and energy. This includes the development of precision farming techniques, efficient irrigation systems, soil management practices, and sustainable pest and disease control methods. Such advancements help conserve resources, reduce input costs, and minimize the environmental footprint of agriculture.
- Enhanced Productivity: This involves developing high-yielding crop varieties, improving agronomic practices, and disseminating knowledge and best practices through education and extension programs. By adopting these advancements, farmers can increase their yields, improve crop quality, and contribute to food security and economic growth.
- Sustainable Agriculture: ARDE focuses on reducing reliance on chemical inputs, minimizing soil degradation, preserving biodiversity, and promoting organic farming. Through research and education, it supports the transition towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural systems, ensuring the long-term viability of the sector.
- Innovation and Technology Adoption: By investing in research and development, it facilitates the discovery and dissemination of cutting-edge technologies, such as precision agriculture, genetic engineering, biotechnology, and smart farming solutions. These advancements help farmers improve efficiency, reduce losses, and enhance profitability.
- Knowledge Transfer and Capacity Building: They focus on disseminating research findings, best practices, and agricultural knowledge to farmers, rural communities, and agricultural stakeholders. By strengthening the knowledge base and building capacity, ARDE empowers farmers with the skills and information necessary to make informed decisions and improve their farming practices.
India’s challenges in adapting to climate change
- Vulnerability to Extreme Weather Events: India is highly susceptible to extreme weather events, including cyclones, floods, droughts, and heatwaves. These events can cause significant damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and livelihoods, impacting the overall resilience of communities.
- Water Scarcity and Stress: Climate change exacerbates water scarcity in many regions of India. Changes in rainfall patterns, melting glaciers, and rising temperatures affect water availability for agriculture, domestic use, and industries. This poses challenges for irrigation, drinking water supply, and overall water management.
- Agriculture and Food Security: The agricultural sector is crucial for India’s food security and rural livelihoods. However, climate change poses risks to crop yields, productivity, and quality. Erratic rainfall, increased pests and diseases, and extreme temperature fluctuations can impact crop growth and food production, leading to food security challenges.
- Coastal Vulnerability: India has a long coastline, making it highly vulnerable to sea-level rise, coastal erosion, and storm surges. Coastal regions face threats to infrastructure, settlements, agriculture, and ecosystems. Climate change-induced sea-level rise also increases the risk of saltwater intrusion, affecting freshwater sources and agriculture in coastal areas.
- Health Impacts: Climate change influences the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue, as well as heat-related illnesses. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns can affect the distribution of disease vectors and impact public health systems, particularly in vulnerable communities with limited access to healthcare.
- Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption: Climate change poses risks to India’s rich biodiversity and ecosystems. Habitats, wildlife, and fragile ecosystems like coral reefs and mangroves face threats from changing temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and habitat loss. This can disrupt ecological balance and affect natural resources vital for human well-being.
- Infrastructure Resilience: India’s infrastructure systems, including transportation networks, energy grids, and urban settlements, face challenges in adapting to climate change impacts. Infrastructure vulnerabilities can lead to disruptions in services, increased costs for repairs and maintenance, and hindered economic growth.
- Socio-economic Inequalities: Climate change impacts can exacerbate existing socio-economic inequalities in India. Vulnerable communities, such as small farmers, tribal populations, and marginalized groups, are disproportionately affected by climate risks due to their limited resources, lack of access to information, and inadequate adaptive capacities.
Policy Reforms for Climate Resilience
- National Climate Change Adaptation Strategy: Developing a comprehensive national strategy focused on climate change adaptation is essential. This strategy should identify priority sectors, vulnerable regions, and specific adaptation measures.
- Mainstreaming Climate Considerations: Integrating climate change considerations into sectoral policies and plans is vital. This includes incorporating climate resilience into agriculture, water management, urban planning, infrastructure development, and coastal zone management policies.
- Strengthening Institutional Frameworks: Establishing robust institutional frameworks and coordination mechanisms for climate adaptation is necessary. This includes enhancing the capacity of relevant government departments, local authorities, and institutions to implement adaptation measures effectively.
- Building Climate Information Systems: Developing and strengthening climate information systems includes improving meteorological services, climate monitoring networks, early warning systems, and climate data management. Accessible and reliable climate information helps policymakers, communities, and sectors plan and respond to climate risks effectively.
- Promoting Nature-Based Solutions: Encouraging nature-based solutions can enhance climate resilience. This involves conserving and restoring natural ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and mangroves, which provide crucial ecosystem services. Nature-based solutions contribute to flood control, water regulation, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity conservation, thereby improving resilience to climate change.
Addressing Funding and Allocation Imbalance
- Scaling Up Experiments: To address climate change challenges effectively, increased funding allocation for ARDE is essential. While there has been an increase in total expenditure on ARDE, research intensity (ARDE as a percentage of agri-GDP) has declined. It is crucial to allocate more funds to scale up experiments and innovations in sustainable agriculture.
- Sector-wise Allocation: The current allocation of ARDE shows a skewed distribution towards crop husbandry, neglecting sectors like soil, water conservation, forestry, animal husbandry, dairy development, and fisheries. This imbalance needs correction to promote holistic agricultural research and development.
Conclusion
- As global temperatures rise and climate change impacts intensify, addressing remaining gaps in agricultural research and development becomes imperative. Increased investment in ARDE, realignment of expenditures and policies, and a focus on sustainable farming practices are essential to build climate resilience in India’s agriculture sector. By prioritizing these measures, India can secure food and nutritional security while mitigating the challenges posed by climate change.
Source: DTE
GS-II
Forum Shopping

Why in News?
Chief Justice of India, D.Y.Chandrachud condemned ‘forum shopping’ practise in courts.
About Forum Shopping:
- “Forum shopping” is a term that describes the strategy of some litigants or lawyers who try to find the most favourable court or judge for their case.
- Litigants or lawyers do this by looking at various factors, such as the reputation, law, or procedure of the court or judge, and the likelihood of getting a positive outcome.
- This practice undermines the integrity and impartiality of the judicial system, as well as the merit of judgements of judicial system.
- Moreover, it can also lead to wastage of judicial resources, delay in justice delivery, and inconsistency in legal precedents by resorting such practises to get favourable judgements.
Indian Judiciary on Forum Shopping:
- The concept of forum shopping has not been defined in any Indian statue.
- However, Indian Judiciary through its observation has assisted in streamlining this concept in the country’s legal system.
- The practice of forum shopping is not permitted by Indian law.
- Types of Forum shopping includes;
- Filing multiple lawsuits in different courts on the same or similar issues, hoping that one of them will grant the desired relief.
- Choosing a court or a jurisdiction that has a more lenient or favourable substantive or procedural law for the case.
- Seeking to transfer or remove a case from one court to another for strategic reasons.
- Influencing or bribing judges or court officials to assign a case to a particular judge or bench.
- SC Bench of Justice S. Abdul Nazeer and Justice Krishna Murari in the case of ‘Vijay Kumar Ghai vs. State of W.B- termed forum shopping as a “disreputable practise by the courts” that “has no sanction and paramountcy in law”.
Impacts of forum shopping in Indian Judiciary:
- Creates uncertainty: It creates uncertainty and confusion among litigants and lawyers about the proper jurisdiction and venue for their cases.
- Losses trust: It erodes public confidence and trust in the judiciary, as it creates an impression that justice is not based on merit but on manipulation.
- Conflicting Judgements: Creating conflicting or inconsistent judgments on the same or similar issues, leading to legal uncertainty and chaos.
- Produce favourable judgements in absence of merit: Eroding the credibility and impartiality of the judiciary, as well as the trust and respect of the public and the legal profession.
- Creates venues of corruption: Encouraging forum shopping by other litigants or lawyers creates a vicious cycle of abuse and corruption.
Bench Hunting
- The term “Bench hunting” refers to petitioners managing to get their cases heard by a particular judge or court to ensure a favourable order.
- Recently, based on the 2017 SC ruling in ‘Kamini Jaiswal vs. Union of India’, the court observed that the practise of bench hunting and related unacceptable practises are prevalent to find a court or forum of their choice.
Source: Indian Express
India- Australia Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement

Why in News?
India and Australia signed a migration and mobility pact to open up opportunities for students and business people.
About India- Australia Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement:
- India and Australia signed the Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement.
- Aim: The agreement is aimed at making it easier for students, academics and professionals to live study and work in each other’s countries.
- India has similar mobility agreements with Austria, France, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Finland.
- It will regulate multiple entry visas for professionals and student exchange programs.
- These programs will be reviewed regularly by a Joint Working Group (JWG) to ensure that they are meeting their objectives and delivering the desired outcomes.
Source: Hindustan Times
Menstrual Health in Urban India: Breaking the Taboos
Why in News?
In a recent incident in Maharashtra, a man mistakenly perceived period stains on his sister’s clothes as a sign of a sexual relationship, highlighting the prevalence of misinformation about menstruation in urban India. Despite living in the public domain, girls and women face challenges related to periods due to shame, stigma, and discrimination.
What is Menstruation?
- Menstruation, or period, is normal vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman’s monthly cycle.
- It is a normal process for girls and women who have reached puberty.
- Every month, girl or women’s body prepares for pregnancy.
- If no pregnancy occurs, body gets rid of the lining in the uterus.
- The menstrual blood is partly blood and partly tissue from inside the uterus.
- The length of a period can be different for each person, but usually lasts for 3-7 days.
Barriers to Menstrual Hygiene in Urban Areas
- Lack of Awareness: Low-income groups in urban areas have limited understanding of periods and menstrual health, leading to poor practices and hygiene management.
- Limited Access to Menstrual Products: While period products are more easily available in urban areas, they are often wrapped in paper or black plastic bags, contributing to the associated shame and stigma.
- Inadequate Toilet Facilities: Low-income slums, pavement dwellers, educational institutions, and workplaces lack easily accessible, safe, clean, and convenient toilet facilities.
- Poor Waste Management: Improper disposal of menstrual waste poses health risks to sanitation workers who are forced to sort through waste without proper protection, undermining their health and dignity.
Did you know?
- The menstrual cycle can be affected by external factors such as stress, changes in temperature and altitude, and even exposure to certain chemicals and toxins.
- This can cause changes in the length of the cycle, the intensity of bleeding, and the severity of symptoms.
- There is also a small percentage of women who experience menorrhagia, which is an excessive bleeding during menstruation. This can be caused by hormonal imbalances, fibroids, endometriosis, and other underlying medical conditions.
Actions for Improvement
- Awareness and Education: Continuous efforts should be made to raise awareness about periods, address harmful social norms, and challenge gender stereotypes related to menstruation.
- Availability of Menstrual Products: Reusable and disposable menstrual products should be made more accessible through retail outlets, government schemes, social enterprises, and NGOs, ensuring people have the freedom to choose the products they prefer.
- Female-Friendly Toilets: Initiatives such as ‘She Toilets’ and ‘Pink Toilets’ that provide safe, private, and clean facilities with essential amenities for managing periods should be expanded.
- Menstrual Waste Management: Innovative solutions like providing dustbins and incinerators in female toilets, along with waste segregation initiatives like the ‘Red Dot Campaign’ and ‘PadCare Labs,’ can contribute to proper waste management.
Way ahead: Addressing Remaining Gaps
- Reaching Marginalized Groups: Efforts should be made to reach people living in unregistered slums, pavements, refugee camps, and other vulnerable conditions in urban areas. Outreach programs, community engagement, and partnerships with local organizations can help provide access to accurate information, menstrual products, and improved facilities.
- Worksites Support: Both formal and informal worksites need to cater to the menstrual needs of women who work. This can include providing clean and private toilet facilities, ensuring access to menstrual products, and promoting supportive workplace policies that address menstrual health needs.
- Innovations in Menstrual Waste Management: Continued support for innovative solutions in menstrual waste management is essential. This includes safe and effective methods for disposal, such as incineration or environmentally friendly alternatives, as well as scalable approaches that can be adopted in different urban contexts.
- Engaging Men and Boys: Promoting gender equality and breaking menstrual taboos require engaging men and boys as allies and advocates. Educating them about menstrual health, addressing gender stereotypes, and fostering supportive attitudes can help create an environment of acceptance and inclusion.
- Research and Data Collection: Robust research and data collection on menstrual health in urban areas are crucial for evidence-based interventions and policy formulation. Collecting data on access to facilities, product usage, hygiene practices, and health outcomes can guide targeted efforts and measure progress.
- Strengthening Partnerships: Collaboration among government agencies, NGOs, private sector entities, and community-based organizations is vital for comprehensive and sustainable interventions.
- Education and Awareness: Continuously raising awareness about menstrual health is pivotal. This includes comprehensive menstrual health education in schools, community workshops, and media campaigns to dispel myths, challenge social norms, and promote positive attitudes towards menstruation.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocating for supportive policies at the local, regional, and national levels can help address systemic gaps. This involves advocating for menstrual health as a public health priority, ensuring budget allocations for menstrual health initiatives, and integrating menstrual health into broader policies related to health, education, sanitation, and gender equality.
Conclusion
- As the world observes Menstrual Hygiene Day (28 May), it is essential to recognize menstrual health as vital to personal health, public health, and human rights for all. Urban India must overcome taboos, improve awareness, enhance access to products and facilities, and promote proper waste management. By addressing these issues, we can empower girls and women to navigate public spaces with dignity and ensure their overall well-being.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
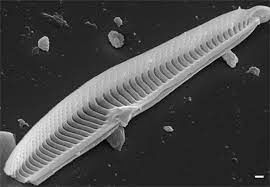
What is Gomphonema rajaguruii?
Why in News?
Researchers at the Pune-based Agharkar Research Institute (ARI) recently discovered a new species named Gomphonema rajaguruii from the northern Western Ghats.
About Gomphonema rajaguruii:
- It is a new freshwater diatom species.
- It was found in a semi-aquatic environment along the wet walls in Maharashtra’s popular hill station, Mahabaleshwar in Satara District.
- It was named after a veteran geo-archaeologist from the city, the late Professor S N Rajaguru.
- It is unique because it shows the characteristics of two genus – Gomphonema and Gomphoneis.
What are Diatoms?
- It is a photosynthetic, single celled organism.
- They are a major group of algae and form one of the most common forms of phytoplankton.
- They are found in almost every aquatic environment including fresh and marine waters.
- Diatoms have cell walls made of silica, Each species has a distinct pattern of tiny holes in the cell wall (frustule) through which they absorb nutrients and get rid of waste.
- Collectively, they are responsible for generating up to 50% of the oxygen produced globally each year.
Source: Indian Express
Amangarh Tiger Reserve

Why in News?
The mutilated carcass of an adult leopard was recently found in the Amangarh Tiger Reserve area.
About Amangarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location:
- It is located in Amangarh in Bijnor district in the state of Uttar Pradesh.
- It is situated in the Terai region and covers an area of around 578 sq km.
- It shares its boundaries with Jim Corbett National Park of Uttarakhand.
- It was originally part of the Jim Corbett National Park, and after the state of Uttarakhand was carved out of Uttar Pradesh, Jim Corbett went to Uttarakhandand Amangarh remained in Uttar Pradesh.
- It was declared a tiger reserve in 2012.
- Flora: The vegetation of the tiger reserve is a combination of grasslands, wetlands and dense forest.
- Fauna:
- Mammals: Tiger, Elephant, Swamp Deer, Sambar, Cheetal, Hog Deer, Kakar, Langur, Sloth Bear, Porcupine, Otter.
- Birds: Hornbill, Red Jungle Fowl, Pea Fowl, Bengal Florican, Fishing Eagle, Serpent Eagle, Osprey, Woodpeckers, Shama, Indian Pitta, Paradise Flycatcher, Orioles, Emerald Dove.
- Reptiles: Monitor Lizard, Turtles, Python, Gangetic Dolphin, Mugger, Gharia etc.
Source: The Print
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|