UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd July 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Water Mission

Why in News?
Recently, the government’s ambitious ‘Har Ghar Jal’ initiative to provide all rural households in India with potable water connections by 2024 under its flagship Jal Jeevan Mission will likely to fall short of its target, as per the survey reports.
About the Jal Jeevan Mission:
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) was launched in 2019 and is planned to have Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) installed in every rural household, supplying each household with 55 litres of water per person per day.
- It comes under the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Jal Shakti Ministry.
- The fund ratio shared between the Centre and the State:
- for Himalayan (Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh) and the North-Eastern States is 90:10;
- for Union-Territories, it is 100:0; and
- For the rest of the states, it is 50:50.
- It is mainly concentrated on areas such as substantial information, education, and communication, focused on a community-based approach.
- This mission will also concentrate on source sustainability measures, such as recharge and reuse through greywater management, water conservation, and rainwater harvesting.
- As per the survey reports, Only 5% of the total, about one crore households out of nearly 19.5 crore households where work hasn’t even begun, are targeted under the scheme.
- There is a system of ‘certification’ wherein the gram panchayats in a village which district and block level authorities report as fully connected call a quorum, and upload a video attesting to the veracity of the claim.
- There are two mechanisms for independent verification:
- Independent audit agency that conducts a survey by preparing a representative sample and interviewing respondents on whether the installed water connections are actually delivering water to their satisfaction.
- National WASH (Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene) experts who appraise a section of villages on the quality of services provided.
- Only 58,357 villages have been so ‘certified’ of the nearly 1,68,000 villages that are reported as ‘Har Ghar Jal’ where all houses have tap water, suggesting that the gap between reported and verified connections is wide.
- States like Punjab (99.9%), Himachal Pradesh (97.2%), and Bihar (96%) are nearing to fulfil the Har Ghar Jal motto.
- The broad objectives of the Mission are:
- To provide FHTC to every rural household.
- To prioritise provision of FHTCs in quality affected areas, villages in drought prone and desert areas, Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) villages, etc.
- To provide functional tap connections to Schools, Anganwadi centres, GP buildings, Health centres, wellness centres and community buildings.
- To monitor functionality of tap connections.
- To promote and ensure voluntary ownership among local community by way of contribution in cash, kind, and/ or labour and voluntary labour (shramdaan),
- To assist in ensuring sustainability of water supply system, i.e., water source, water supply infrastructure, and funds for regular O&M.
- To empower and develop human resources in the sector such that the demands of construction, plumbing, electrical, water quality management, water treatment, catchment protection, O&M, etc. are taken care of in short and long term.
- To bring awareness to the various aspects and significance of safe drinking water and involvement of stakeholders in manner that makes water everyone's business.
Source: The Hindu
Mahalanobis's Approach: Addressing India's Big Data and AI Challenges

Why in News?
India celebrated National Statistics Day on June 29th, commemorating the birthday of Prof. Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis, renowned as the 'Plan Man' of India.
- As India grapples with the challenges of Big Data and the transformative power of artificial intelligence (AI), reflecting on Mahalanobis's approach can offer insights into addressing these issues effectively.
What Insights Does Mahalanobis's Approach Provide for Tackling India's Big Data and AI Challenges?
- Regulating AI and Mahalanobis's Influence:
- As AI poses challenges such as job displacement, spread of disinformation and other ethical concers, there is a global push for its regulation.
- Mahalanobis's introduction of built-in cross-checks in his surveys, inspired by Kautilya's Arthashastra, demonstrates his foresight in ensuring data integrity.
- Mahalanobis's approach reminds us of the importance of rigorous data preprocessing, ensuring fairness and transparency in AI algorithms.
- For instance, when deploying AI in hiring processes, it is crucial to assess and mitigate biases to ensure equal opportunities for all candidates.
- Mahalanobis's approach emphasizes the need to confront and address such challenges to build responsible and inclusive AI systems.
- Integration of Multiple Data Sources:
- Mahalanobis advocated for integrating diverse data sources to capture a holistic view of the economy and society.
- In the context of Big Data and AI, this implies incorporating various data streams, including structured and unstructured data, social media feeds, satellite imagery, and sensor data.
- Such integration can facilitate comprehensive analysis and enable innovative applications.
- For example, in agriculture, combining meteorological data, satellite imagery, and farmer-generated data can provide valuable insights on crop health, pest outbreaks, and optimal irrigation practices.
- This approach enables the development of AI-driven solutions like precision agriculture, improving crop yields and farmers' livelihoods.
- Importance of Statistical Models:
- Mahalanobis stressed the importance of statistical models to derive meaningful inferences and predictions.
- In the era of Big Data and AI, advanced machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling techniques play a pivotal role in analyzing vast datasets.
- These models can be employed in various domains, such as healthcare, finance, and urban planning.
- For instance, by applying predictive models to healthcare data, policymakers can identify population health trends, forecast disease outbreaks, and allocate resources effectively.
- This approach facilitates evidence-based decision-making and proactive interventions.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
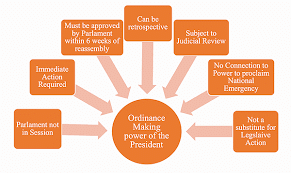
What is the Ordinance making power of the President?
Why in News?
The Delhi government recently urged the Supreme Court to quash the National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Ordinance, 2023.
About Ordinance making power of the President:
- Article 123 of the Indian Constitution grants the President of India certain Lawmaking powers, i.e., to Promulgate Ordinances when either of the two Houses of the Parliament is not in session, which makes it impossible for a single House to pass and enact a law.
- These Ordinances have the same effect as an Act of Parliament.
- Ordinances may relate to any subject that the Parliament has the power to make law, and would be having the same limitations.
- The Ordinances may have a retrospective effect and may modify or repeal any act of Parliament or other ordinances. It may be used to amend a tax law, but it can never amend the Constitution.
- The President may withdraw an ordinance at any time. However, he exercises his power with the consent of the Council of Ministers headed by the President.
- Following limitations exist on the Ordinance making power,
- Legislature is not in session: The President can only promulgate an Ordinance when either of the two Houses of Parliament is not in session.
- Immediate action is required: The President cannot promulgate an Ordinance unless he is satisfied that there are circumstances that require taking ‘immediate action’.
- Parliament should approve: Ordinances must be approved by Parliament within six weeks of reassembling or they shall cease to operate. The same will cease to operate if disapproved by either House.
- In various judicial pronouncements, the Supreme Court has held that the President’s Ordinance making power is not beyond the scope of judicial review.
Source: The Hindu
Demand of Horizontal Reservation for transgender community
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government stated that it would be difficult to provide “additional reservations” to transgender persons in education and public employment.
Background
- Trans persons in India have been fighting for the right to horizontal reservation for a long time.
- The demand for reservation has been raised by many prominent Dalit, Bahujan, Adivasi activists and trans persons as well, such as Grace Banu, Living Smile Vidya and Disha Pinky Shaikh.
What are horizontal reservations?
- Horizontal reservation is an intersectional approach that is provided for within each vertical reservation category.
- For example, a Dalit woman can access vertical reservation under the SC category, whereas through horizontal reservation she will be able to access reservations for women as well — both of which equally influence the person’s social location.
Demand to secure horizontal reservation for trans people
- It has to do with the need for mandating provisions for a community that has been marginalised for long in society and recognising the different aspects making up their social identity
- A study conducted by the National Human Rights Commission revealed that in 2017, only 6 percent of transgender people were formally employed.
- Informal work that a significant portion of the community currently engages in, like begging and sex work, have been criminalised in India under various Acts and laws.
- But trans persons are often employed in such work for reasons related to both ritual and survival.
- In this regard, the NALSA verdict has largely been interpreted as directing reservations for transgender people in the OBC category.
- This perhaps stems from the bench identifying the community as “a socially and educationally backward class”. So far, no implementation has happened even to that end.
- Transgender persons have filed several petitions of late in the Delhi HC, Madras HC, Rajasthan HC, etc., asking for horizontal reservation in education and jobs.
Observations of court’s
- In the National Legal Services Authority of India (NALSA) v Union of India (2014) case, the Supreme Court ruled that transgender persons have a right to reservation, owing to the fact that they “are a socially and educationally backward class”.
- Highlights of judgement : SC directed the Centre and the State Governments to take steps to treat them [transgender persons] as socially and educationally backward classes of citizens and extend all kinds of reservation in cases of admission in educational institutions and for public appointments.”
- The NALSA judgement entitles trans persons to reservations on constitutional grounds. It does not, however, mention the nature of reservations – whether they are to be vertical or horizontal.
Other related developments
- In 2015, Rajya Sabha DMK MP Tiruchi Siva presented the Rights of Transgender Persons Bill.
- This Private Member’s Bill, in line with the NALSA judgment, had provisions for reservation for trans persons — in the public and private sector.
- The Bill was rejected in the Lok Sabha.
- The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2016 was introduced by the Centre. It had no provision for reservations.
- In 2018, a parliamentary standing committee under the Ministry of Social Justice was set up.
- The committee, again in line with the NALSA judgment, recommended reservations for transgender persons.
- Yet, the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 did not have any mention of reservation — vertical or horizontal.
- Alternatively, the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, included in its purview the right of disabled persons to accrue horizontal reservation.
- Since this Act has been implemented, horizontal reservation for disabled people is now ensured under the Central government.
- In 2015, the Tamil Nadu government decided to categorise “transgender or eunuch (thirunangai or aravani)”, that is, only transwomen under the Most Backward Classes (MBC) category.
- After Sangama v State of Karnataka, Karnataka became the first and only state to offer one per cent horizontal reservation to transgender persons in 2021.
- In April 2023, transgender persons were included in the OBC category in Madhya Pradesh.
Government's stand
- Since the NALSA judgement, there has been no direction from the Central government on delivering on the right to reservation for trans persons.
- Even as the clamour for horizontal reservation for transgender people in government jobs and education grows across India, the Union government said that there was no separate policy under consideration to provide jobs to transgender people in government organisations.
Source: IE
GS-III
Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR)
Why in News?
An adult tiger was recently killed in Satpura Tiger Reserve, allegedly by poachers who carried away its head.
About Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Location:
- It is located in the Hoshangabad district of Madhya Pradesh.
- It is located in the Satpura ranges of the Central Indian Landscape.
- It lies south of the river Narmada.
- Satpura, basically meaning "Seven Folds", forms a watershed between Narmada and Tapti Rivers.
- Corridor: It has corridor connectivity with Pench National Park.
- The habitat is also an important testimony to human evolution as it houses more than 50 rock shelters which are almost 1500 to 10,000 years old.
- Geological formations include the Deccan trap series, Gondwanas and Metamorphic rocks.
- Vegetation: Southern tropical moist deciduous forest, Southern tropical dry deciduous forest, Tropical riparian fringing forest, southern tropical thorn forest, central Indian sun tropical hill forest, Dry and moist grassland.
- Flora:
- It has a variety of flora typical of the Central Indian Highlands. These include teak, bamboo, Indian Ebony, various acacias, wild mango, Indian gooseberry, satinwood etc.
- Twenty-six species of the Himalayan region and 42 species of Nilgiri areas are found. Hence STR is also known as the northern extremity of the Western Ghats.
- Fauna: Tiger is the charismatic species along with other mammals like Gaur, Sambhar, Chital, besides co predators, birds, reptiles and fishes.
Source: The Print
LIGO Detectors
Why in News?
Recently, Scientists have found evidence to suggest that the universe is replete with low-frequency gravitational waves – ripples in the fabric of space-time, predicted by Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity more than 100 years ago.
About Gravitational Waves:
- Gravitational waves were first detected in 2015 using an experiment involving Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory (LIGO) detectors.
- But those waves were of high frequency and believed to have been produced by the merger of two relatively small black holes that took place about 1.3 billion years ago.
- Scientists have been looking for low-frequency gravitational waves for decades. They believed that such ripples are perpetually rolling through space like background noise.
- Pairs of supermassive black holes, sitting at the centre of galaxies, merge across the universe, generating gravitational waves. This breakthrough provides enough data to suggest that there is a gravitational wave background which exists in our universe.
- To discover low-frequency gravitational waves, scientists used entirely different technologies that were carried out by radio astronomers representing five different international teams, including Indian Pulsar Timing Array (InPTA).
- The researchers used six large radio telescopes around the world, including the one in Pune, to study objects called pulsars, distant rapidly-rotating neutron stars that emit pulses of radiation, observed from the Earth as bright flashes of light.
- These bursts take place at exact intervals, and therefore scientists use pulsars as ‘cosmic clocks.
- After examining 25 pulsars over 15 years, Scientists have proposed that the observed inconsistencies were due to deformities caused in space-time by gravitational waves. These irregularities showed consistent effects of the presence of gravitational waves.
About LIGO:
- LIGO is an international network of laboratories that detect the ripples (gravitational waves) in space-time produced by the movement of large celestial objects like stars and planets.
- These ripples were first postulated in Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity, which encapsulates our current understanding of how gravitation works.
- The LIGO detectors are sensitive to distance changes that are several orders of magnitude smaller than the length of a proton.
- The experiment works by releasing light rays simultaneously in both chambers. Usually, the light should return at the same time in both chambers.
- However, if a gravitational wave passes through, one chamber elongates while the other squishes, resulting in a phase difference in the returning light rays. Detecting this phase difference confirms the presence of a gravitational wave.
What is Space-time?
- In Special Theory of Relativity, Einstein proposed that space and time don’t exist as independent entities, combining the three dimensions (height, width and depth) of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum, known as space-time.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|



















