UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 3 August 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Schemes implemented by the WCD Ministry clubbed into 3 Verticals
Source: PIB

Why in news?
For better implementation and efficient monitoring, all schemes implemented by the Ministry for the betterment of children have been consolidated into 3 verticals: Saksham Anganwadi, Poshan 2.0, Mission Shakti, and Mission Vatsalya. These verticals aim to improve nutrition and health indicators, ensure safety and empowerment of women, and provide protection and welfare for children in difficult circumstances.
Scheme Details:
Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0 (Mission Poshan 2.0)
- Nutrition Support: For POSHAN and Adolescent Girls.
- Early Childhood Care and Education: Targeting children aged 3-6 years.
- Anganwadi Infrastructure: Upgrading and modernizing Saksham Anganwadis.
- Key Features
- Fortified rice supplied to Anganwadi Centres to meet micronutrient requirements and control anemia among children.
- Emphasis on the use of millets for Hot Cooked Meals at least once a week.
- Take Home Ration (THR) at Anganwadi centers.
Mission Shakti
- Sambal: Focuses on the safety and security of women.
- Includes schemes like One Stop Centres (OSC), Women Helpline (181-WHL), Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP).
- Samarthya: Aims at the empowerment of women.
- Encompasses schemes like Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY), Ujjwala, Swadhar Greh (renamed as Shakti Sadan), Working Women Hostel (renamed as Sakhi Niwas), National Hub for Empowerment of Women (NHEW), National Creche Scheme (renamed as Palna).
Mission Vatsalya
- Objective: To provide better outreach and protection for children in need of care in a mission mode.
- Goals
- Support and sustain children in difficult circumstances.
- Develop context-based solutions for the holistic development of children from varied backgrounds.
- Encourage innovative solutions through green field projects.
- Facilitate convergent action by gap funding if required.
PYQ:
[2016] Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’?
(a)To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
(b)To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
(c)To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
(d)To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
GS3/Economy
Women Entrepreneurship Program (WEP)
Source: PIB

Why in news?
Recently, the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) introduced the Women Entrepreneurship Program (WEP) to empower women entrepreneurs and boost economic growth.
About Women Entrepreneurship Program
- WEP is crafted to tackle the unique hurdles faced by women when initiating and expanding businesses.
- Its goal is to empower around 25 lakh women in India by equipping them with necessary skills, knowledge, and resources.
- In collaboration with Britannia Industries Limited, this initiative emphasizes creating an inclusive environment for female entrepreneurs.
Program Phases
- Phase 1: NSDC, with NIESBUD's backing, will provide free online self-learning entrepreneurship courses through the Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH), covering topics like entrepreneurial skills, finance basics, and digital skills.
- Phase 2: NSDC will offer robust incubation support to 10,000 selected candidates across 100 business models. Their products will be showcased on platforms like UdhyamKart and Britannia's digital ecosystem.
About National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
- Establishment: NSDC was formed on July 31, 2008, as a non-profit public limited company under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Unique Model: Operating as a Public Private Partnership (PPP) under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
GS3/Economy
Nirbhaya Fund
Source: AIR

Why in news?
Under the Nirbhaya Fund, up to the financial year 2023-24, a total amount of Rs. 7212.85 Crore has been allocated. Since the inception of the Nirbhaya Fund, approximately Rs. 5,000 crore has been released and utilized by various Ministries and Departments. This amount represents nearly 76% of the total allocation.
About Nirbhaya Fund
- Establishment: The Nirbhaya Fund was established by the Government of India in 2013, following the tragic 2012 Delhi gang rape incident.
- Nature: It is a non-lapsable corpus fund.
- Purpose: The fund aims to support initiatives that enhance the safety and security of women in India.
- Initial Corpus: It was announced with an initial corpus of Rs. 1,000 crore in the 2013 Union Budget.
Administration
- Managing Body: The fund is administered by the Department of Economic Affairs under the Ministry of Finance.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) is the nodal Ministry to appraise/recommend proposals and schemes to be funded under Nirbhaya Fund. An empowered committee was set up for appraising and recommending proposals.
- Responsibilities: MWCD further has the responsibility to review and monitor the progress of sanctioned schemes in conjunction with the line Ministries/Departments.
Key Initiatives and Projects
- One Stop Centres (OSCs): Also known as "Sakhi Centres," these provide integrated support and assistance to women affected by violence, including medical aid, police assistance, legal aid, and counseling.
- Safe City Projects: Implemented in various cities to enhance women's safety through better infrastructure, increased police presence, and technology-based solutions like CCTV surveillance.
- Emergency Response Support System (ERSS): A pan-India single emergency number (112) for all kinds of emergencies, including those related to women's safety.
GS3/Environment
Conservation and Protection of Western Ghats
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
The Union Environment Ministry (MoEFCC) has issued a draft notification to declare the Western Ghats an ecologically sensitive area (ESA). The ESA includes villages in Wayanad (Kerala), where a devastating series of landslides on July 30 killed at least 210 people, with hundreds more still missing.
About Western Ghats:
- It is a mountain range (in a stretch of 1,600 Km) parallel to the western coast of the Indian peninsula.
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the 36 biodiversity hotspots in the world.
- These are home to high mountain forests, which have been severely fragmented due to human activities, especially clear-felling for tea, coffee, and teak plantations.
Conservation efforts:
- In 2010, MoEFCC appointed the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), to be chaired by ecologist Dr Madhav Gadgil. It was formed to study the impact of population pressure, climate change, and development activities on the Western Ghats.
- Recommendations of the WGEEP: Designate the entire region as an Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA) and classify 64% of the Western Ghats into Ecologically Sensitive Zones called ESZ 1, ESZ 2, and ESZ 3.
- Almost all developmental activities like mining, construction of thermal power plants, and dams were to stop along with the decommissioning of similar projects that have completed their shelf life in ESZ 1.
- The report suggested a bottom-to-top approach and the establishment of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority to manage the ecology of the region and to ensure its sustainable development.
Resistance to the implementation of the WGEEP’s recommendations:
- Stakeholder states resisted the Gadgil panel recommendations amid fears of hindrance to development and loss of livelihood.
- In 2012, MoEFCC constituted a High-Level Working Group on Western Ghats under former ISRO chief Dr K Kasturirangan, to formulate a report to replace WGEEP.
Recommendations of the Kasturirangan-led panel:
- It notified only 37% (against 64% by Gadgil commission) of the area as ecologically sensitive.
- It also split the Western Ghats into cultural (human settlements) and natural (non-human settlements) regions. It was suggested that cultural lands be designated as an ESA.
Status of implementation of above recommendations:
- In 2017, MoEFCC demarcated an area of 56,825 sq Km in the Western Ghats as ESA as opposed to the 59,940 sq Km recommended by the Kasturirangan committee.
- Kerala has 9,993 sq km; Karnataka 20,668 sq km, Tamil Nadu 6,914 sq km; Maharashtra 17,340 sq km; Goa 1,461 sq km and Gujarat 449 sq km.
The Sixth Draft Western Ghats Notification:
- Background: The latest draft notification has been reissued because the previous draft (issued in July 2022) expired, and may have been prompted by recent devastating landslides in Wayanad district. This comes 13 years after the first such demarcation was recommended by a panel led by eminent ecologist Madhav Gadgil in 2011.
- Since then, the proposed protected area has shrunk from the original 75% recommendation to the current 37%.
About the draft notification:
- The proposal for the ESA classification covers six states and 59,940 square kilometres of the Western Ghats or roughly 37% of the range.
- It states that all new and expansion projects of building and construction with a built-up area of 20,000 square metres and above, and all new and expansion townships and area development projects with an area of 50 hectares and above or with a built-up area of 150,000 square metres and above shall be prohibited.
Impact of the latest draft:
- If finalized, the notification would impose a complete ban on mining, quarrying, sand mining, thermal power plants, and polluting industries in the designated areas.
- It would also prohibit new construction projects and township developments above certain thresholds.
- Additionally, hydropower projects and less polluting industries would be regulated, and a monitoring mechanism would be established.
Challenges Towards Conserving Western Ghats:
- The outcome of this long-standing environmental protection effort remains uncertain, with conservation needs clashing with the developmental aspirations in one of India’s most ecologically significant regions.
- As the draft notification now stands, it is up to the Western Ghats state governments to accept or reject the proposal.
- Despite its six iterations, the draft notification is yet to become law, as all six affected States have objected to specific places that have been included in the ESA regions.
- The dominant sentiment in Kerala was that this notification would subsume agricultural plantations, curtail the State’s hydro-electricity plans, and would lead to a migration crisis given the State’s high population density.
GS2/Polity
Sub-Classification of SC, ST
Source: Times of India

Why in news?
In a significant ruling, a seven-judge panel of the Supreme Court on August 1 has reshaped the functioning of the Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) reservation system. The Chief Justice of India-led Bench has allowed states to establish sub-classifications within the SC and ST groups to offer broader protections, including sub-quotas, to the most marginalized communities within these categories.
Background:
- Previously, in the case of E V Chinnaiah v State of Andhra Pradesh in 2004, the Supreme Court adjudged that the SC/ST list constitutes a 'homogeneous group' and should not be further divided or sub-classified.
Key takeaways:
- Article 341 of the Constitution empowers the President to designate as SC various 'castes, races, or tribes' that have faced untouchability. SC groups collectively receive 15% reservation in education and public employment.
- Over time, certain groups within the SC list have been inadequately represented compared to others, leading states to explore extending more safeguards to these groups. However, such attempts have encountered legal challenges.
- In 1975, Punjab issued a notification granting primary preference in SC reservations to the Balmiki and Mazhabi Sikh communities. This move was contested following the 2004 E V Chinnaiah ruling, which invalidated a similar law in Andhra Pradesh.
- E V Chinnaiah judgment: The court opined that any efforts to differentiate within the SC list would essentially amount to tampering with it, a power not vested in states by the Constitution. Article 341 exclusively authorizes the President to make such a notification, and Parliament to make additions or deletions to the list. The court also highlighted that sub-categorizing b violates the right to equality under Article 14.
- In 2006, the Punjab & Haryana High Court annulled Punjab's 1975 notification in Dr. Kishan Pal v State of Punjab.
- Despite this, Punjab reintroduced the primary preference in the Punjab Scheduled Caste and Backward Classes (Reservation in Services) Act, 2006. This Act was challenged, ultimately leading to its rejection by the High Court in 2010, followed by an appeal to the Supreme Court. In 2014, the case was referred to a five-judge Constitution Bench to deliberate on whether the E V Chinnaiah decision necessitated reconsideration.
- In 2020, the Constitution Bench in Davinder Singh v State of Punjab determined that the 2004 E V Chinnaiah ruling merited reevaluation, acknowledging that SCs are not a homogeneous group and that disparities exist within SCs, STs, and socially and educationally backward classes. Given that this Bench, like in E V Chinnaiah, comprised five judges, a seven-judge Bench addressed the issue in February 2024.
Key issues before the Bench included:
- Are all castes in the SC list to be treated uniformly?
- Can states make modifications or sub-classifications to the Presidential list?
- What criteria should be employed for sub-classification?
- Does the concept of the creamy layer apply to Scheduled Castes?
In conclusion, the Supreme Court's ruling demonstrates a nuanced stance on SC reservations, acknowledging internal disparities within SCs and empowering states to address them with suitable measures supported by evidence.
GS3/Environment
Why the Odisha government will Plant Palm Trees to Combat Lightning Strikes
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
In July, the Odisha government approved a proposal to plant 1.9 million palm trees to mitigate deaths caused by lightning strikes, which were declared a state-specific disaster in 2015.
How many people have lost their lives to lightning in Odisha?
Over the last 11 years, a total of 3,790 people have lost their lives due to lightning strikes in Odisha. In the previous three fiscal years, 791 fatalities were reported, indicating an increasing frequency of lightning strikes. On September 2, 2023, Odisha recorded 61,000 lightning strikes in a two-hour period, resulting in the deaths of at least 12 people.
Why are Lightning strikes of particular concern in Odisha?
- Odisha is located in a tropical zone and experiences a hot, dry climate that creates ideal conditions for lightning strikes.
- The state has the highest number of cloud-to-ground lightning strikes in eastern and central India.
- The Annual Lightning Report 2023-2024 indicates a significant concentration of lightning activity in this region.
- Research indicates that climate change exacerbates lightning activity, with a 10% increase in lightning occurrences for every degree Celsius of warming.
- This is particularly relevant in Odisha, where climatic factors contribute to frequent lightning events.
- With 96% of lightning strikes occurring in rural areas, the most affected populations include farmers and daily wage earners who work outdoors, making them particularly vulnerable during peak agricultural seasons.
How can Odisha defend Itself against lightning strikes?
- Planting Palm Trees: The Odisha government has approved a proposal to plant 19 lakh palm trees as a natural defense against lightning strikes. Palm trees are considered effective conductors of lightning due to their height and moisture content, which can absorb lightning and mitigate its impact on the ground.
- Financial Commitment: The state has allocated Rs 7 crore for the palm tree plantation initiative and has banned the felling of existing palm trees to enhance this strategy.
- Public Awareness and Early Warning Systems: While the state has implemented early warning systems to forecast lightning strikes, experts emphasize the need for widespread public education on safety measures during lightning events.
Concerns:
Experts have raised concerns about the effectiveness of palm trees as a long-term solution, noting that it takes 15 to 20 years for them to reach a height where they can effectively mitigate lightning strikes.
- Preparation and Awareness: The Local government should educate the communities about lightning safety and the risks associated with thunderstorms.
- Seek Shelter: During a thunderstorm, individuals should seek shelter in a fully enclosed building or a hard-topped metal vehicle. Open vehicles and structures such as metal sheds or under-construction buildings are unsafe.
- Avoid Trees: Taking shelter under trees is discouraged, as they can attract lightning. If in a wooded area, find the shortest trees for shelter.
- Crouching Position: If no shelter is available, crouch down with heels touching and head between the knees to minimize height and reduce risk.
- 30-30 Rule: After seeing lightning, start counting to 30. If you hear thunder before reaching 30, go indoors. This rule helps assess the distance of the storm.
Way forward:
- Installation of Lightning Rods and Conductors: The government should invest in the widespread installation of lightning rods and conductors in rural and vulnerable areas. These devices can provide immediate protection to critical infrastructure, homes, and open fields where farmers and workers are most at risk.
- Advanced Early Warning Systems: Need to enhance the existing early warning systems with more accurate, real-time data and ensure these warnings are disseminated quickly through multiple channels, including mobile alerts, community announcements, and local radio.
Main PYQ:
Explain the mechanism and occurrence of cloudburst in the context of the Indian subcontinent. Discuss two recent examples. (2022)
GS3/Economy
Indo-pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
Source: AIR

Why in news?
India has been chosen as the Vice-Chair of the Supply Chain Council within the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), with the USA as the Chair. This decision positions India to significantly contribute to bolstering supply chain resilience in the Indo-Pacific area.
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) represents a strategic roadmap designed to foster economic integration, connectivity, and collaboration among nations situated in the Indo-Pacific region.
- It envisions a comprehensive and inclusive strategy to leverage the economic potential of the area while promoting stability, growth, and mutual prosperity.
- Launched by U.S. President Joe Biden on May 23, 2022.
- The IPEF is structured around four core pillars:
- Trade: Focuses on boosting trade relations and facilitating economic transactions.
- Supply Chains: Aims to enhance supply chain resilience and coordination.
- Clean Economy: Seeks to advance sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
- Fair Economy: Works towards fostering fairness, competitiveness, and inclusivity among member economies.
GS3/ Science and Technology
Legionnaires' disease
Source: Times of India
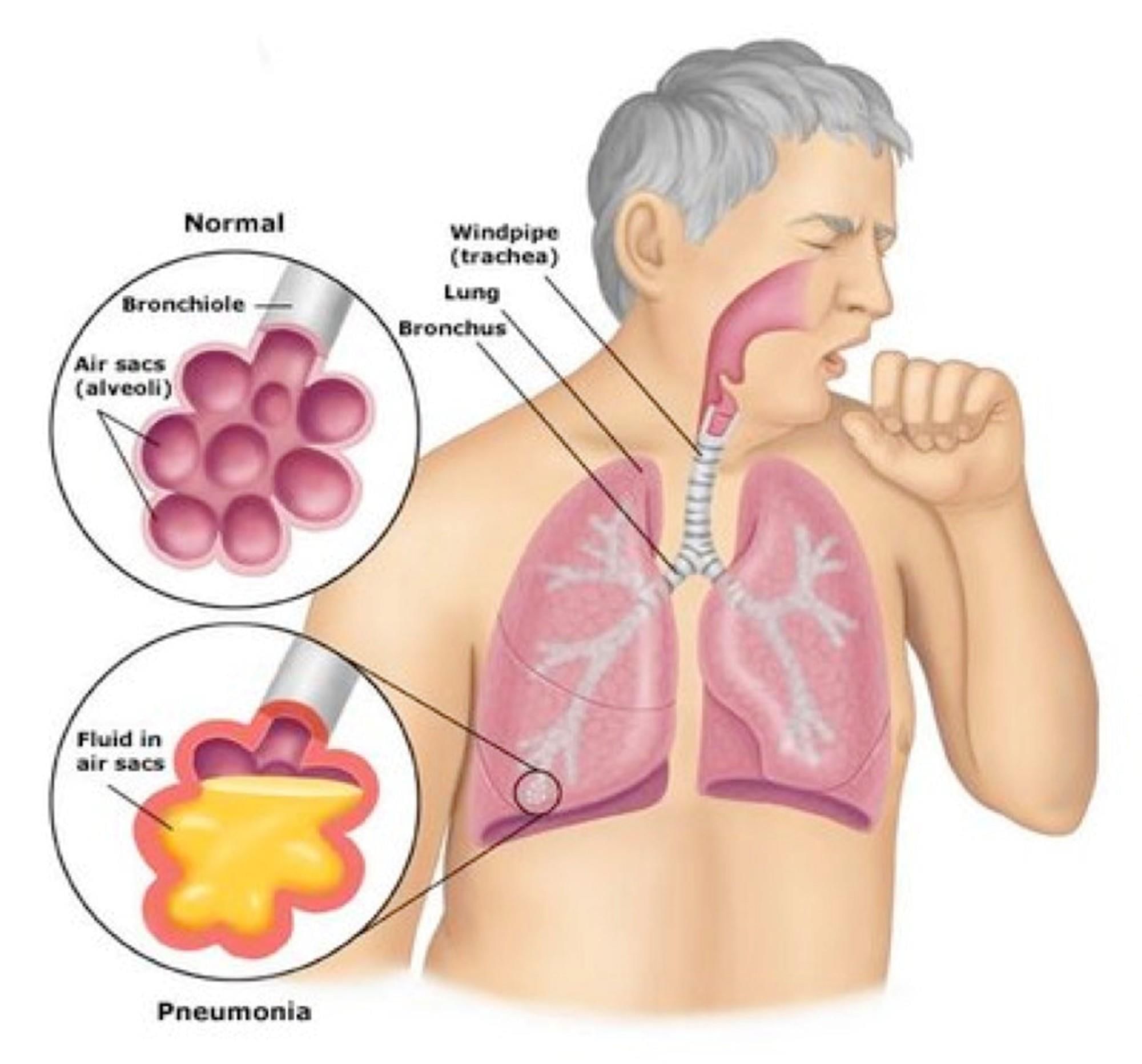
Why in News?
About Legionnaires' disease:Australia's Victoria has recorded 71 confirmed cases of legionnaires' disease and a woman died from the disease.
- It is caused by the Legionella bacteria, which can only be found in natural bodies of water such as lakes and hot springs.
- It is a severe form of pneumonia — lung inflammation usually caused by infection. It's caused by a bacterium known as legionella.
- This bacterium is found in lakes and ponds, but they can also develop in tanks and other water systems.
- Transmission: The most common form of transmission of Legionella is inhalation of contaminated aerosols from contaminated water.
- It is not contagious, meaning it is not spread from person-to-person.
- Symptoms: The main symptoms are fever, chills, headache, malaise and muscle pain (myalgia).
- Treatment: Treatments exist, but there is no vaccine currently available for Legionnaires’ disease.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 3 August 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. Why is the Odisha government planting palm trees to combat lightning strikes? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Women Entrepreneurship Program (WEP) implemented by the WCD Ministry? |  |
| 3. How does the Nirbhaya Fund contribute to enhancing women's safety and security in India? |  |
| 4. What is the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) and how does it benefit countries in the region? |  |
| 5. How does the Conservation and Protection of Western Ghats scheme contribute to environmental sustainability and biodiversity conservation? |  |





















