UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 30th August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Supreme Court Ruling on ‘Self-Respect’ Marriages
Subject: Society
Why in News?
The recent Supreme Court ruling on ‘self-respect’ marriages under Section 7(A) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 has clarified the legal standing of these marriages.
- The court’s decision has significant implications for the validity and recognition of such unions, particularly in the state of Tamil Nadu.
Self-respect Marriages
- Amendment: The Hindu Marriage (Tamil Nadu Amendment) Act, 1967 introduced Section 7-A into the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955, applicable solely in Tamil Nadu.
- Recognition of ‘Self-Respect’ Marriages: Section 7-A recognizes and legalizes ‘self-respect’ or ‘suyamariyathai’ marriages, allowing them to be solemnized without the need for traditional rituals or priests.
- Ceremony Description: Such marriages are performed in the presence of relatives, friends, or other individuals, with couples declaring each other as spouses in a language understood by them. Exchange of garlands, rings, or tying a ‘thali’ (mangal sutra) is required. Registration remains obligatory.
Legal Controversy
- Madras High Court Ruling (2014): A 2014 Madras High Court ruling declared marriages solemnized by advocates as invalid, asserting that ‘self-respect’ marriages must not be secretive and should be celebrated publicly.
- Current Supreme Court Ruling: The recent Supreme Court ruling, passed by Justices S Ravindra Bhat and Arvind Kumar, overruled the 2014 Madras High Court decision.
Supreme Court’s Interpretation and Decision
- The Supreme Court clarified that there is no blanket ban on advocates solemnizing ‘self-respect’ marriages under Section 7(A) of the Hindu Marriage Act.
- The court held that ‘self-respect’ marriages can indeed be solemnized and recognized, and the 2014 Madras High Court ruling was set aside.
- The ruling was delivered in response to a petition filed by Ilavarasan, who sought recognition of his ‘self-respect’ marriage and the release of his wife from her parents’ custody.
- The Supreme Court’s decision is based on the interpretation of Section 7(A) and its application in the context of ‘self-respect’ marriages.
Precedents and Past Rulings
- In the case of Nagalingam vs. Sivagami (2001), the Supreme Court had already recognized the validity of ‘self-respect’ marriages under Section 7(A) of the Hindu Marriage Act.
- The court emphasized that the presence of a priest is not obligatory for a valid marriage, and parties can enter into a marriage with the participation of relatives, friends, or other individuals.
Conclusion
- The recent Supreme Court ruling has resolved the ambiguity surrounding the legality of ‘self-respect’ marriages solemnized by advocates under Section 7(A) of the Hindu Marriage Act.
- By overturning the previous Madras High Court ruling, the Supreme Court has clarified the validity and recognition of such marriages, ensuring that ‘self-respect’ marriages can be solemnized without the need for traditional rituals or priests in Tamil Nadu.
Source: Indian Express
Taiwan Strait
Subject: Geography
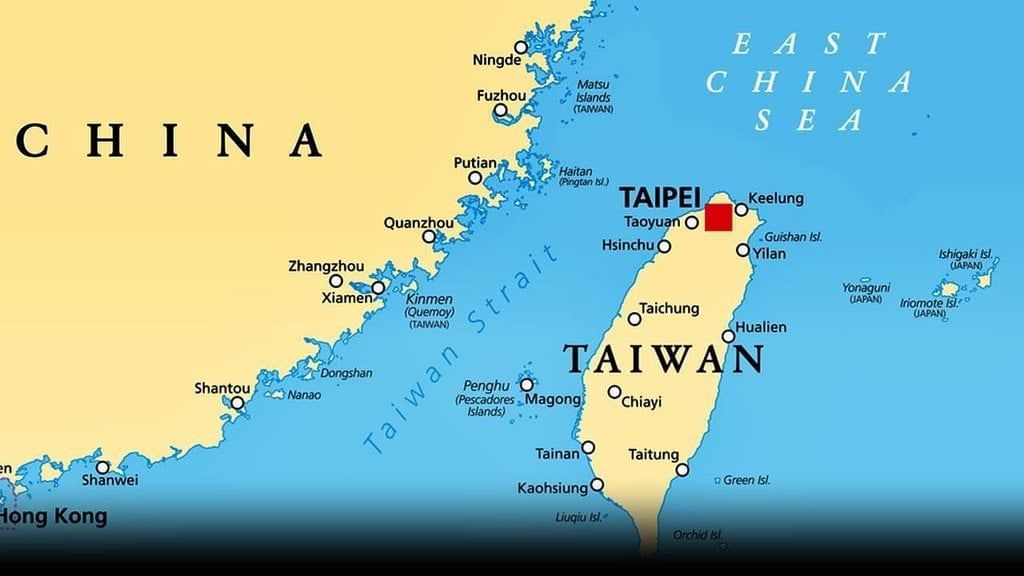
Why in News?
Taiwan recently scrambled its aircraft, naval ships, and land-based missiles after spotting 11 Chinese military aircraft that breached the sensitive median line of the Taiwan Strait.
About Taiwan Strait:
- Taiwan Strait, also called Formosa Strait, is a 180-kilometre-wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental Asia.
- The strait extends from southwest to northeast between the South and East China Seas.
- The narrowest part is 130 km wide.
- It reaches a depth of about 230 feet (70 m) and contains the Pescadores Islands (which are controlled by the government of Taiwan).
- The chief ports are Amoy in mainland China and Kaohsiung in Taiwan.
- The median line of the Taiwan Strait:
- It is the informal dividing line in the Taiwan Strait between the Chinese mainland and Taiwan.
- It came about during the Cold War as a way to try and delineate the two opposing sides and reduce the risk of clashes.
- No agreement or treaty ever solidified its status. But over the decades, it helped keep Taiwan and China's militaries apart.
Key Facts about Taiwan:
- It is an island territory in East Asia, between the East China Sea in the north and the South China Sea in the south.
- The Republic of China (ROC) is the official name of the territory and government of Taiwan.
- Taiwan's main island is located east off the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China, separated by the Taiwan Strait and 370 km (230 mi) north of Luzon Island (Philippines).
- It shares maritime borders with China, Japan and the Philippines.
- Capital: Taipei
- Languages: Spoken languages are Mandarin Chinese (Putonghua; official) and Taiwanese (Taiwanese Hokkien); regional languages are Hakka and Formosan languages.
- Religion: The main religions are Buddhism (35%) and Taoism (33%).
Source: The Print
Nataraja
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
Recently, it was announced that a 28-ft. Nataraja bronze sculpture, from Tamil Nadu would grace the G20 summit venue in New Delhi.
Background:-
- The statue, weighing 19 tonnes, and made of eight metals: gold, silver, lead, copper, tin, mercury, iron, and zinc (Ashtadhatu).
About Nataraja:-
- It is the representation of the Hindu god Shiva during his form as the cosmic dance.
- It is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India.
- It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
Features of the Nataraja:-
- The upper right hand holds the drum: it signifies the sound of creation.
- All creations spring from the great sound of the damru.
- The upper left hand holds the eternal fire: it represents the destruction. Destruction is the precursor and inevitable counterpart of creation.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf.
- The dwarf symbolizes ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of the river Ganges.
- In ornamentation, one ear of Shiva has a male earring while the other has a female.
- This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as
- A snake is wrapped around the arm of Shiva.
- The snake symbolizes the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Evolution of G20: A Catalyst for Global Economic Cooperation
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
The upcoming G20 summit in Delhi marks the culmination of a year-long series of meetings involving heads of state/government from G20 members.
- As a crucial platform for international economic cooperation, the G20 has transformed into a pivotal force in shaping global economic governance.
Origins and Composition of G20
| Origin | Formed in 1999 in response to the financial crises of the late 1990s, with the aim to bring together major economies for international financial stability. |
| Composition | Comprises 19 individual countries: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, UK, US, and the European Union. |
| Purpose | Serves as a platform for major economies to discuss and coordinate on international financial, economic, and social issues. |
| Significance | Represents around 85% of global GDP, 75% of global trade, and covers two-thirds of the world population. |
| Leadership | Operates without a permanent secretariat or staff. Presidency rotates among its members on an annual basis. |
| Current Presidency | India holds the G20 Presidency for the period December 2022 to November 2023. |
Emergence of G20
- Unplanned Emergence: The G20’s formation was not meticulously orchestrated but emerged due to a combination of circumstance and necessity.
- Adapting to Global Dynamics: The decline of the North-South divide and the rise of economically potent nations in the Global South underscored the requirement for a more inclusive and representative global economic forum.
From G22 to G20
- Response to Crisis: The Asian financial crisis in the late 1990s exposed vulnerabilities in the existing global economic governance framework.
- Genesis of G22: The G20’s precursor, the G22, was established in 1998 as a crisis-response mechanism.
- Evolving to G20: Dissatisfaction with the ad hoc nature of the G22 and G33 meetings led to the establishment of the G20 in 1999, aiming for a more structured platform.
Global Economic Crisis of 2008: Catalyst for Change
- The idea of a G20 leaders’ forum was proposed by Canadian Prime Minister Paul Martin in 2005, yet it faced resistance, particularly from the US.
- The global economic crisis of 2008, comparable to the Great Depression, accelerated the establishment of the G20 leaders’ summit.
- Recognizing the complexity and magnitude of the crisis, the G20 emerged as a suitable platform to address and mitigate the crisis’s repercussions.
First G20 Leaders’ Summit
- Washington DC Summit (2008): The inaugural G20 leaders’ summit, titled ‘Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy,’ took place in November 2008.
- Extended Participation: Alongside G20 member nations, heads of institutions including the IMF, World Bank, and UN were invited. Spain and the Netherlands also attended.
Conclusion
- The evolution of the G20, from its spontaneous beginnings to the imminent Delhi summit, epitomizes its role as a responsive mechanism for fostering global economic cooperation.
Source: The Hindu
India needs comprehensive sexuality education
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), 51,863 cases were reported under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act in 2021; of them, 33,348 or 64% were of sexual assault.
- In this context, understanding sexual consent is important not only to learn about violation and abuse, but also to maintain healthy relationships.
About sexual consent:
- It is a mutual agreement between individuals to engage in any form of intimate activity.
- It is essential for maintaining healthy relationships and understanding boundaries.
- Consent can be given, asked for, and withdrawn at any point.
- Many teenagers and young adults in India may not fully understand this concept.
- According to the United Nations, comprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality.
- There is a need for clear language and education in regional languages to discuss and teach about consent and its significance.
Significance of sexual education:
- Rights of Individual and sexuality: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), with comprehensive sexuality education, young people will be better informed of their rights and sexuality, and will be more likely to engage in sexual activity later.
- Sexual consent: Understanding sexual consent is important not only to learn about violation and abuse, but also to maintain healthy relationships.
- Lead to early awareness: The UN global guidance recommends starting comprehensive sexuality education from the age of five along with formal education.
- This means that young children will be taught about their bodies, emotions, the basic principles of consent, and how to deal with violence, bullying or abuse.
- Reducing the intimate partner violence: The ramifications of a comprehensive sexuality education are far-reaching, especially in the matter of intimate partner violence.
- Sexual habits and health: Studies have shown that sexually aware students are most likely to say no to unprotected sex.
- Through sex education, teenagers can be taught the positive and negative sides of sex. They can learn about sexually transmitted disease, teenage unintended pregnancy, and emotional effects of sex.
- Educating women on sex: When women are educated and aware of sexual wellness, they make better reproductive decisions.
- This means lesser teenage pregnancies, child mortality, or sexually transmitted infections.
- The Kerala High Court was informed that awareness about the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act would be included in the curriculum from 2024-25.
- This reflects an effort to integrate relevant legal and awareness components into the education system.
Challenges associated with sexual education in India:
- Data vs reality: The research has found that more than 90% of students think sex education in school curriculum is important. 60% also stated that they had exposure to sex education in school.
- However, only 45% said that they had received appropriate sex education.
- Lack of interest by the State governments: Several State governments and certain sections of society in India have adopted an ostrich-like approach to comprehensive sexuality education.
- The governments that it sexualises children, they have either watered down the existing programmes or withdrawn them on the grounds that they violate “Indian values”.
- Patriarchal in the society: Traditional values are often shaped by patriarchal and hierarchical social structures.
- Mass media often propagates such values and it negatively affects young adults of all genders.
- Lack of teacher’s education: Teachers reported that they lacked the knowledge to talk about diverse topics with the existing programmes along with sexual education.
- Lack of sexual awareness to women and young girls: The victims of poor sexual awareness are primarily women.
- It is women who suffer most because of social taboo, menstrual issues, or unwarranted pregnancies.
- Women also have lower awareness and knowledge around contraception, sex, pregnancy, and reproductive health.
Suggestive measures:
- United Nations (UN) recommends comprehensive sexuality education, which is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality.
- Role of state govts: In India, the responsibility of sexuality education is vested with the State governments.
- Each State has the freedom to develop creative curriculums within the framework suggested by the UNFPA.
- Role of Teachers: NCRB data show that it is necessary for schools to impart comprehensive sexuality education not only to children, but also to parents and caregivers.
- Skill training for teachers: According to the UNESCO 2021 Global Status Report on ‘the journey towards comprehensive sexuality education’, capacity-building of teachers is critical as the curriculum requires non-intuitive participatory pedagogies.
- Educating the parents: The sex education advice for parents is that they educate themselves first.
- They should also let go of their inhibitions and reservations.
- Regional languages to discuss the concept of sexual consent: While the concept of sexual consent is evolving through criminal jurisprudence, the term itself may have been borrowed from English or other Western languages.
- With the non-English language speaking population becoming substantial, an explicit creation of vocabulary in regional languages to discuss the concept of sexual consent and its nuances is urgently required.
A case study from Jharkhand demonstrates the successful mainstreaming of a school-based program, Udaan, which began as an Adolescent Reproductive and Sexual Health initiative and was later integrated into the education department.
Source: The Hindu
Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector PRIP Scheme
Subject: Government Schemes
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma-MedTech sector (PRIP) scheme with an outlay of ₹5,000 crore for five years.
About PRIP Scheme:
- The objective of the PRIP scheme is to transform the Indian Pharma MedTech sector from cost-based competitiveness to innovation-based growth by strengthening the research infrastructure in the country.
- The aim of the scheme is to promote industry-academia linkage for R&D in priority areas to inculcate a culture of quality research and nurture our pool of scientists.
- Rs 5,000 crore will be spent in five years (2024-28) under the PRIP scheme, and companies will be given incentives for research.
- The six focus areas of the scheme are:
- new chemical entities, including biological and phytopharmaceuticals;
- complex generics and biosimilars;
- precision medicines such as gene therapy and stem cells;
- medical devices using artificial intelligence and machine learning;
- orphan drugs;
- anti-microbial resistance;
- It focuses on two components:
- Strengthening research infrastructure through Centres of Excellence (CoE) in the seven existing National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs), Institutes of national importance at a tentative cost of Rs. 700 crore over a period of five years.
- Government engagement with nine established pharmaceutical companies with an outlay of Rs. 125 crores over five years, an aid of Rs. 100 crores to 30 research projects on high-potential products and funding to 125 research projects among startups.
- An Empowered Committee under the chairmanship of CEO, NITI Aayog, with the secretary-level representation of Pharmaceuticals, Health, ICMR, DBT, CSIR, AYUSH and DST, will provide guidance for the implementation of this ambitious scheme by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
BRIGHT STAR-23
Subject: Defence

Why in News?
As per recent reports, thirty-four countries including India will participate in the joint military exercise, BRIGHT STAR-23.
About BRIGHT STAR-23:-
- Date: 31 August to 14 October 2023.
- Venue: Mohammed Naguib Military Base,
- Indian Army contingent comprising 137 personnel will participate in a military exercise.
- It is a multinational tri-services joint military exercise.
- It will be led by US CENTCOM and the Egyptian Army.
- This year 34 countries will participate in the Exercise.
- It will be the largest-ever joint military exercise in West Asia and North Africa region.
- This is the first time that the Indian Armed Force with 549 personnel participated in the exercise.
- During the exercise participating countries will share the best practices to combat emerging unconventional threats and enhance regional partnerships.
- Significance: The exercise will provide a unique opportunity for the Indian Army to share best practices and experiences with other armies aimed at enhancing defense cooperation
Source: AIR
Takahe Bird
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
A large flightless bird named ‘Takahe’, believed to be extinct decades ago, has returned to the forests of New Zealand's South Island.
About Takahe Bird:
- It is hailed as one of the world’s rarest creatures native to New Zealand.
- They have been an intrinsic part of New Zealand's ecosystem since the prehistoric Pleistocene era, as evidenced by fossil remains.
- Their population nosedived during the late 1800s when European settlers came along with their animal companions— stoats, cats, ferrets and rats.
- The birds had been formally declared extinct in 1898. It was rediscovered in 1948 in several remote valleys on New Zealand’s South Island, and their numbers have been steadily growing since then.
- Features:
- They are large, stout birds with vibrant plumage.
- They have predominantly blue feathers on their bodies, green wings, and a large red beak.
- Their legs are pink, and they have a white undertail.
- Size: They grow up to the size of a large hen and can weigh as much as 3kg.
- Breeding: They breed only once a year, raising one to two chicks.
- Lifespan: They live up to 18 years in the wild and 22 years in sanctuaries.
- Diet: They live on a high-fibre diet of starchy leaves and seeds.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|





















