UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 30th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
World Asteroid Day

Why in News?
World Asteroid Day is observed on June 30 every year.
About World Asteroid Day:
- It is observed on June 30 every year.
- The day aims to raise awareness about asteroid impact hazards and crisis communication actions in case of a credible asteroid threat to planet Earth.
- The day also aims to educate people about the latest and upcoming asteroid research and technology through numerous events and activities held by organisations across the globe.
- History:
- The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) passed a resolution in December 2016, designating June 30 as International Asteroid Day.
- The UNGA adopted the resolution based on the proposal made by the Association of Space Explorers, endorsed by the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS).
- The date was chosen to commemorate the anniversary of the Tunguska asteroid’s impact over Siberia on June 30, 1908.
Tunguska Event:
- It is considered the biggest asteroid impact in recorded history when an asteroid exploded a few kilometers above the Tunguska region of central Siberia.
- It flattened more than 80 million trees in seconds, over an area spanning nearly 800 square miles (2,000 square kilometers) — but left no crater.
What is an Asteroid?
- Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the sun.
- Although asteroids orbit the sun like planets, they are much smaller than planets.
- They are leftovers from the formation of our solar system.
- From being as small as 10 meters across to as huge as 530 km in diameter, asteroids have varied sizes.
Source: Indian Express
Padma Awards

Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs announced that the online nominations for Padma Awards 2024 would be open till 15th September 2023.
About Padma Awards:-
- The Padma Award are one of the highest civilian honours of India.
- Instituted:1954.
- Objective: to recognize achievements in all fields of activities or disciplines where an element of public service is involved.
- Presented by: President of India.
- Time period: March/April every year.
- It is announced every year on the occasion of Republic Day.
- There was a brief interruption(s) during the years: 1978 and 1979 and 1993 to 1997.
- The Awards are given in three categories:-
- Padma Vibhushan: for exceptional and distinguished service.
- Padma Bhushan: for distinguished service of higher order.
- Padma Shri: for distinguished service.
Historical Background:–
- 1954: The Government of India instituted two civilian awards-Bharat Ratna & Padma Vibhushan.
- Padma Vibhushan had three classes namely Pahela Varg, Dusra Varg and Tisra Varg.
- 1955: These were renamed as Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri.
Eligibility:-
- All persons without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex are eligible for these awards.
- Exclusion: Government servants including those working with PSUs, except doctors and scientists, are not eligible for these Awards.
- The award seeks to recognize works of distinction and is given for distinguished and exceptional achievements/service in all fields of activities/disciplines:-
- Art: includes Music, Painting, Sculpture, Photography, Cinema, Theatre etc.
- Social work: includes social service, charitable service, contribution to community projects etc.
- Public Affairs: includes Law, Public Life, Politics etc.
- Science & Engineering: includes Space Engineering, Nuclear Science, Information Technology, Research & Development in Science & its allied subjects etc.
- Trade & Industry: includes Banking, Economic Activities, Management, Promotion of Tourism, Business etc.
- Medicine: includes medical research, distinction/specialization in Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Siddha, Allopathy, Naturopathy etc.
- Literature & Education: includes Journalism, Teaching, Book composing, Literature, Poetry, Promotion of education, Promotion of literacy, Education Reforms etc.
- Civil Service: includes distinction/excellence in administration etc. by Government Servants
- Sports: includes popular Sports, Athletics, Adventure, Mountaineering, promotion of sports, Yoga etc.
- Others: fields not covered above and may include propagation of Indian Culture, protection of Human Rights, Wild Life protection/conservation etc.
Decoration:-
- The awardees are presented a Sanad (certificate) signed by the President and a medallion.
- The recipients are also given a small replica of the medallion, which they can wear during any ceremonial/State functions etc.
Selection Process:-
- The nomination process is open to the public.
- Even self-nomination can be made.
- The Padma Awards are conferred on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee.
- Padma Awards Committee: It is constituted by the Prime Minister every year.
- It is headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
- Other members: Home Secretary, Secretary to the President and four to six eminent persons as members.
- Approval: The recommendations of the committee are submitted to the Prime Minister and the President of India for approval.
Special Features of Padma Awards:-
- The total number of awards to be given in a year (excluding posthumous awards and to NRI/foreigners/OCIs) should not be more than 120.
- The award does not amount to a title and cannot be used as a suffix or prefix to the awardees’ name.
- The award is normally not conferred posthumously.
- However, in highly deserving cases, the Government could consider giving an award posthumously.
Source: AIR
GS-II
What is the Intergovernmental Negotiations framework (IGN)?

Why in News?
President of the 77th session of the United Nations General Assembly recently said the first segments of the UN Intergovernmental Negotiations framework (IGN) meetings are now webcast and a dedicated website on Security Council reform has been established.
About Intergovernmental Negotiations Framework (IGN):
- IGN is a group of nation-states working within the UN to further reform the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- Composition: The IGN is composed of several different international organizations, namely:
- The African Union;
- The G4 nations (India, along with Brazil, Japan and Germany are pressing for a permanent seat in the reformed UNSC);
- The Uniting for Consensus Group (UfC), also known as the "Coffee Club";
- The L.69 Group of Developing Countries;
- The Arab League; and
- The Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
- Each group represents a different set of positions vis-a-vis reforming the UNSC.
- The group's conversations are considered "informal" in nature due to the lack of single text and thus, UNGA rules of procedure don't apply.
- But in 2015, a framework document was agreed when it comes to the reform, which can be the basis for future talks.
What is the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)?
- The United Nations Charter established six main organs of the United Nations, including the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- UNSC has the primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- Under the UN Charter, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council decisions.
- The Security Council has a permanent residence at the United Nations Headquarters in New York City.
- Powers:
- Establishment of peacekeeping operations.
- Establishment of international sanctions.
- Authorization of military action through Security Council resolutions.
- Members:
- The U.N. Charter provides for 15 members on the UNSC:
- 5 permanent members known as P5, including United Kingdom, China, France, Russia and the US. They have veto power over decisions of the UNSC.
- 10 non-permanent members. Each year the 193-member General Assembly elects five non-permanent members for a two-year term at the UNSC.
Source: Indian Express
Manila and New Delhi: A 21st Century Partnership

Why in News?
The year 2022 brought about a significant turning point for the world as Covid-19-related restrictions were gradually lifted, ushering in a renewed focus on international trade, commerce, and strategic partnerships. Against this backdrop, the Philippines and India have reinvigorated their cooperation after almost three years, aiming to strengthen bilateral ties and foster economic resurgence in the post-pandemic era.
Economic promise and growth trajectory of India and Philippines
- India’s Economic Promise and Growth Trajectory:
- Projected Third-Largest Economy: India is projected to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2027. This forecast highlights the country’s immense economic potential and growth prospects.
- Fastest-Growing Large Economy: India has consistently maintained an impressive average GDP growth of 5.5 percent over the past decade. This growth rate positions India as the fastest-growing among the large economies globally.
- Investment Opportunities: India’s growing economy offers numerous investment opportunities across various sectors, attracting both domestic and foreign investors seeking to capitalize on its vibrant market and expanding consumer base.
- Emerging Middle Class: India’s rising middle class presents a significant consumer market, driving consumption and fueling economic growth. The expanding middle class creates opportunities for businesses and stimulates economic development.
- Philippines’ Economic Promise and Growth Trajectory:
- Upper-Middle-Income Status: The Philippines is on the threshold of achieving upper-middle-income status, which signifies significant progress in its economic development and per capita income.
- Trillion-Dollar Economy by 2033: The Philippines aims to become a trillion-dollar economy by 2033, reflecting its ambitious goals for economic growth and prosperity.
- Poverty Reduction and Socio-Economic Agenda: President Ferdinand R Marcos Jr’s socio-economic agenda focuses on reducing poverty and fostering sustainable economic growth. This agenda sets the stage for inclusive development and resilience in key sectors such as agriculture, energy, and infrastructure.
- Empowerment and Inclusion: The Philippines places emphasis on empowering its population and fostering greater inclusion. By ensuring that the benefits of economic growth reach all segments of society, the country aims to create a more equitable and prosperous nation.
The prospects for expanding trade and economic cooperation between the Philippines and India
- Innovation and New Technologies: Both countries have vibrant innovation ecosystems and a growing focus on technological advancements. Collaborative efforts in research and development, knowledge sharing, and technology transfer can lead to the creation of innovative solutions and products. This cooperation can enhance productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness in various sectors.
- Clean Energy and Renewable Technologies: India has emerged as a global leader in renewable energy, particularly in the development of wind and solar power. The Philippines has also made substantial investments in renewable energy technologies. Leveraging India’s expertise and experience, there is scope for collaboration in clean energy projects, including the adoption of advanced renewable technologies, sharing best practices, and promoting sustainable energy solutions.
- Digital Infrastructure and Connectivity: India’s “Digital India” initiative and the Philippines’ efforts to strengthen its digital infrastructure provide opportunities for collaboration. This can involve sharing knowledge, experiences, and technologies in digitalization, e-governance, cybersecurity, and data management. Strengthening digital connectivity can facilitate trade, e-commerce, and digital services between the two countries.
- Defense and Security Cooperation: There is potential for deeper cooperation in defense and security between the Philippines and India. The signing of contracts for defense procurement, such as the Philippines’ procurement of India’s BrahMos Shore-based Anti-Ship Missile System, signifies the beginning of such collaborations. Both countries can further explore joint exercises, defense industry partnerships, and information-sharing mechanisms to enhance their defense capabilities and address common security challenges.
- Regional Economic Integration: The Philippines and India’s engagements within the framework of ASEAN, coupled with India’s “Act East Policy,” provide avenues for regional economic integration. Strengthening economic ties, promoting trade facilitation measures, and improving connectivity within the ASEAN-India network can enhance regional trade and investment flows. Collaboration in infrastructure development, logistics, and trade facilitation can further deepen economic integration.
- People-to-People Exchanges: Enhancing people-to-people exchanges, including tourism, cultural interactions, and educational cooperation, can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of each other’s countries. This can contribute to building stronger economic and social ties between the Philippines and India.
Opportunities for regional cooperation in the Indo-Pacific
- Economic Integration: Strengthening economic integration within the Indo-Pacific region is essential for creating a robust and interconnected economic ecosystem. The Philippines and India can play active roles in promoting and participating in initiatives such as the ASEAN Economic Community, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), and other regional economic forums.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure Development: Collaborative efforts in developing infrastructure, such as ports, roads, railways, and digital connectivity, can enhance regional connectivity and support economic growth. The Philippines and India can engage in infrastructure projects, joint investments, and partnerships to promote seamless connectivity within the region.
- Maritime Security and Freedom of Navigation: Ensuring maritime security and upholding freedom of navigation in the Indo-Pacific is essential for trade, economic activities, and regional stability. Collaborative initiatives for maritime domain awareness, joint exercises, information-sharing mechanisms, and adherence to international law, including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), can strengthen regional security and stability. The Philippines and India can actively participate in regional security frameworks, such as the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) and the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS), to address common maritime challenges.
- Sustainable Development and Climate Change: Collaborative efforts in promoting sustainable development practices, sharing best practices in climate change adaptation and mitigation, and supporting initiatives for renewable energy and environmental conservation can contribute to the region’s long-term resilience. The Philippines and India can engage in knowledge sharing, capacity-building programs, and joint initiatives to address these challenges collectively.
- People-to-People Exchanges and Cultural Cooperation: The Philippines and India can promote tourism, cultural exchanges, educational scholarships, and academic collaborations to deepen connections and promote mutual understanding among the diverse nations in the region.
- Rules-based Order and Multilateralism: Upholding the principles of a rules-based order and inclusive multilateralism is crucial for regional stability and cooperation. The Philippines and India, as advocates for the rule of law, can actively engage in regional multilateral platforms such as the East Asia Summit (EAS), ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF), and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) to shape regional norms, promote dialogue, and address regional challenges collectively.
Conclusion
- As the Philippines-India Joint Commission on Bilateral Cooperation convenes for its fifth iteration in New Delhi, the two nations look forward to meaningful exchanges that will set a firm course for a stronger partnership. Building upon their nearly 75 years of diplomatic ties and shared values as democratic Asian republics, the Philippines and India are poised to reinforce bilateral relations and leverage their common interests to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the post-pandemic era.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
National Research Foundation

Why in News?
Recently, the government has decided to bring the National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill, 2023 to strengthen the research ecosystem in the country.
Background:-
- The Bill approved by the Union Cabinet will pave the way to establish National Research Foundation (NRF).
- The Bill will repeal the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) established by an act of Parliament in 2008 and subsume it into NRF.
- It will seed, grow and promote research and development and foster a culture of research and innovation throughout India’s universities, colleges, and research institutions.
About National Research Foundation:-
- It is an apex body to promote, fund and mentor scientific research in higher education institutions.
- Initial budget of Rs 50,000 crore for over a five-year period between 2023 and 2028.
- The NRF would also provide fellowships for post-doctoral research, the funding for which is not available right now.
Objective:-
- Cultivating the culture of research in universities and colleges.
- Facilitating research in universities across the country.
Historical Background:-
- The proposal for an NRF was first floated in the public domain by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2019, during his address to the Indian Science Congress.
- The NRF found a second mention on January 20 of that year during a joint session of Parliament.
- Later, it was mentioned in the Finance Minister’s speech during the Budget Session in July 2019.
- The creation of NRF was also one of the key recommendations of the National Education Policy 2020.
- 2023: the Union Cabinet approved the National Research Foundation(NRF),2023 bill to establish NRF.
Administration of NRF:-
- The NRF would be administratively housed in the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- It would have a 16-member governing board.
- Of these two members from DST, five from industry, one from humanities and six experts would be selected depending on the nature of the project being evaluated.
Structure of NRF:-
- Prime Minister will be the ex-officio president of the board and the Minister of Science and Technology and the Minister of Education will be the ex-officio vice presidents.
- The NRF’s functioning will be governed by an executive council chaired by the Principal Scientific Advisor to the government of India.
Funding for NRF:-
- Of the Rs 50,000 crore estimated funding over the next five years, Rs 36,000 crore would come from the industry.
- Scientific research projects under the NRF would be funded by the DST and industry on a 50:50 basis.
- The Department of Science and Technology’s main funding body, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) will be absorbed in the NRF.
- SERB: it was set up in 2008.
- It is responsible for funding science and technology start-ups, setting up incubators and funding science-related projects in central and state universities.
Function of NRF:-
- The NRF will forge collaborations among the industry, academia, government departments and research institutions.
- It will create an interface mechanism for the participation and contribution of industries and state governments in addition to the scientific and line ministries.
SOURCE: AIR
Time-of-Day Tariff
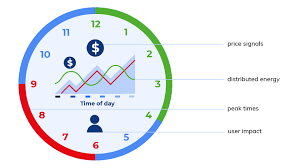
Why in News?
The Ministry of Power has recently introduced Time-of-Day (ToD) tariff for electricity, which will be implemented next year for commercial users and in 2025 for home users.
- This article aims to explain what ToD tariff is, how it impacts consumers, and why it is important for the power sector.
What is Time-of-Day Tariff?
- Amendments: The government has made amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules 2020, introducing ToD tariff and rationalizing smart meters.
- Tariff structure: Under ToD tariff, electricity charges will vary based on the time of day. The current flat rate system will be replaced. During daytime, the tariff may decrease by up to 20%, benefiting consumers. Conversely, during night-time, the tariff will increase by the same amount.
- Benefits for consumers: ToD tariff allows consumers to regulate and manage their electricity consumption and control their bills. It gives them the flexibility to take advantage of lower tariffs during off-peak hours.
Impact on electricity bills
- Impact on different households: For small working couples who primarily use electricity at night, their bills are likely to increase. However, other households can offset the nighttime spike by shifting some of their electricity usage to daytime hours.
- Power consumption patterns: Power consumption typically peaks in the morning when schools and offices open, in the late afternoon when children return home, and in the early evening when air conditioners and heaters are in high demand. ToD tariff aims to discourage excessive power consumption during these peak hours.
Power guzzling appliances
- Identifying power-consuming appliances: Appliances such as air conditioners, coolers, refrigerators, heaters, and geysers are the major contributors to electricity consumption in households. Other significant power-consuming appliances include washing machines, dishwashers, and microwaves.
- Energy-efficient alternatives: It is worth noting that energy-efficient versions of most electrical appliances are available in the market, which can help reduce overall electricity consumption.
Readiness of infrastructure
- Requirement of smart meters: To implement ToD tariff, smart meters are necessary. These meters automate the meter-reading process and provide accurate cost estimation, minimizing wastage. They send consumption information to power distribution companies every 15 minutes, which is crucial for calculating ToD charges.
- Status of smart meter installation: Currently, over 6.5 million smart meters have been installed in the country, with a target of reaching 250 million by 2026. Approximately 230 million smart meters have been sanctioned so far.
Benefits for the power sector
- Improved billing efficiency: ToD tariff and smart metering can enhance billing efficiency and reduce transmission and distribution losses.
- Differential tariff for renewable power: As the share of renewable power increases, it needs to be blended with coal-based power, requiring differential tariff structures. ToD tariff can facilitate this blending effectively.
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and ToD tariff: With the expected surge in EV adoption, ToD tariff can encourage consumers to charge their vehicles during off-peak hours, reducing the strain on the power grid.
- Flexibility for discoms: ToD tariff provides flexibility for loss-making distribution companies (discoms) to revise tariffs, addressing their financial challenges.
Source : The Hindu
PM-PRANAM Scheme gets cabinet nod

Why in News?
The union cabinet has given its approval to PM-PRANAM scheme, which aims to promote the usage of alternative fertilizers and balanced utilization of chemical fertilizers.
- This scheme, announced in the budget for 2023-24, reflects the government’s commitment to sustainable agricultural practices and the conservation of natural resources.
What is PM-PRANAM Scheme?
- PM-PRANAM stands for Prime Minister Promotion of Alternate Nutrients for Agriculture Management Yojana.
- The scheme was proposed during the National Conference on Agriculture for Rabi Campaign in September 2022.
- Its objective is to reduce the subsidy burden on chemical fertilizers by promoting the use of alternative fertilizers.
Notable features of the scheme
- Incentivizing States and UTs: The scheme incentivizes states and Union Territories to promote the usage of alternative fertilizers and achieve a balanced use of chemical fertilizers. States that demonstrate significant savings in funds due to reduced chemical fertilizer usage receive grants as incentives.
- Subsidy Savings Allocation: Around 50% of the subsidy savings resulting from reduced chemical fertilizer consumption will be allocated as a grant to the state that exhibits the highest savings. This encourages states to actively participate in the adoption of alternative fertilizers.
- Creation of Assets: A significant portion (70%) of the granted funds will be utilized for creating assets associated with the technological integration of alternate fertilizers. This includes establishing production units at the village, block, and district levels, facilitating local production and availability of alternative fertilizers.
- Recognition and Incentives for Farmers: The remaining 30% of the granted funds will be utilized to incentivize and recognize farmers and other village entities for their contributions to reducing fertilizer usage. This recognizes their efforts in adopting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Environmentally Friendly Farming Practices: The scheme aims to promote environmentally friendly farming practices by encouraging the adoption of alternative fertilizers. This reduces the dependency on chemical fertilizers, which in turn contributes to environmental conservation and sustainability.
- Long-term Soil Health and Agricultural Ecosystems: By promoting a balanced use of fertilizers, the scheme ensures the long-term health and fertility of agricultural ecosystems. It emphasizes sustainable agricultural practices that preserve soil health and protect natural resources.
- Technological Integration: The scheme supports the integration of technology into agriculture for the production and utilization of alternative fertilizers. This includes the establishment of production units at the grassroots level, encouraging local production and accessibility of alternative fertilizers.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|





















