UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 3rd August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Kuril Islands
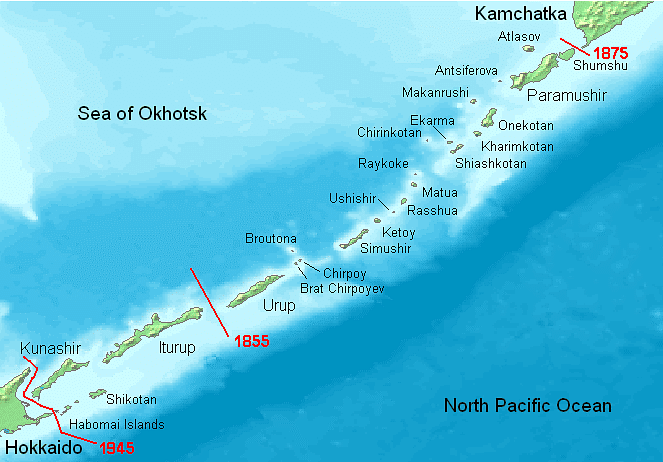
Why in News?
In Japan, conservative voices are hinting that Russian and Ukraine war could give Japan a chance to take control of disputed Kuril Islands.
About Kuril Islands:
- These are a set of four islands situated between the Sea of Okhotsk and the Pacific Ocean near the north of Japan's northernmost prefecture, Hokkaido.
- Japan refers to them as Northern territories, Russia calls them the Kuril Islands and South Korea named them as Dokdo islands.
- These are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire belt and have over 100 volcanoes, of which 35 are said to be active volcanoes along with hot springs.
- Both Russia and Japan claim sovereignty over them though the islands have been under Russian control since the end of World War II.
- The Soviet Union had seized the islands at the end of World War II and by 1949 had expelled its Japanese residents.
- Tokyo claims that the disputed islands have been part of Japan since the early 19th century.
What lies behind the dispute?
- According to Tokyo, Japan’s sovereignty over the islands is confirmed by several treaties like the Shimoda Treaty of 1855, the 1875 Treaty for the exchange of Sakhalin for the Kuril Islands (Treaty of St. Petersburg), and the Portsmouth Treaty of 1905 signed after the Russo-Japanese war of 1904-05 which Japan had won.
- Russia, on the other hand, claims the Yalta Agreement (1945) and the Potsdam Declaration (1945) as proof of its sovereignty and argues that the San Francisco Treaty of 1951 is legal evidence that Japan had acknowledged Russian sovereignty over the islands. Under Article 2 of the treaty, Japan had “renounced all right, title and claim to the Kuril Islands.”
Source: Indian Express
Anna Bhau Sathe
 Image caption
Image caption
 Image caption
Image caption
Why in News?
Bharat Rashtra Samithi (BRS) founder president and Telangana Chief Minister K. Chandrasekhar Rao has demanded Anna Bhau Sathe be conferred with Bharat Ratna
About Anna Bhau Sathe
- Tukaram Bhaurao Sathe later came to be known as Annabhau Sathe was born in a Dalit family on August 1, 1920 in Maharashtra’s Wategaon village in Satara district.
- He belonged to the Matang community among Dalits.
- He was a social reformer, writer and folk poet of Maharashtra.
- He is also known as a pioneer of dalit literature
- He was influenced by the communist ideology and is often known as the ‘Maxim Gorky of Maharashtra’, having been inspired by the Russian writer-activist’s work, as well as the Russian Revolution.
- Contributions: He decided to bring awareness among the masses against Brahmanism which imposed untouchability and virtually compelled the deprived lot to take recourse to criminal and military occupation against the British Government.
- He used his art and poetic genius in educating the masses.
- He formed Dalit Yuvak Sangh, a cultural group and started writing poems on workers’ protests, agitations.
- The group used to perform in front of the mill gates.
- In 1943, he along with Amar Sheikh and Datta Gavhankar, formed the Lal Bawta Kala Pathak.
- The group toured across Maharashtra presenting programmes on caste atrocities, class conflict, and workers’ rights.
- In 1943, he was part of the process that led to the formation of the Indian People's Theatre Association (IPTA).
- He became its national president in 1949.
- He played a vital role in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement.
- Literary Contributions: In 1939, he wrote his first ballad ‘Spanish Povada’.
- Several of his works like ‘Aklechi Goshta,’ ‘Stalingradacha Povada,’ ‘Mazi Maina Gavavar Rahili,’ ‘Jag Badal Ghaluni Ghav’ were popular across the state.
- His ‘Bangalchi Hak’ (Bengal’s Call) on the Bengal famine was translated into Bengali and later presented at London’s Royal Theatre.
- He dedicated his most famous novel Fakira to Dr Ambedkar.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
WHO recognition to Single-pill strategy to beat Cardiovascular diseases

Why in News?
Recently, the WHO included three fixed dose combinations of cardiovascular medicines or polypills on its revised Model Lists of Essential Medicines (EML) 2023 for use in primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
About
- The polypill is not a new drug but a drug delivery mechanism, which improves medication adherence (because it is a single pill) and saves money by preventing hospitalisations.
- The WHO Expert Committee on Selection and Use of Essential Medicines noted that the use of the polypill is associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular events, including fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction and stroke, and the need for revascularization in primary and secondary prevention settings.
Significance
- The polypill is not a new drug but a drug delivery mechanism, which improves medication adherence (because it is a single pill) and saves money by preventing hospitalisations.
- The polypill is thus an important low-cost public health intervention which can prevent over millions of cardiovascular events and deaths every year.
- It is a simple treatment that can be administered with very little monitoring to a majority of people, with backup from physicians.
Fixed-Dose Combination (FDCs)
- A fixed-dose combination or FDC drug contains two or more active ingredients in a fixed dosage ratio.
Advantages of FDSs
- They reduce the pill burden by reducing the number of pills to be taken by the patients.
- They are believed to have higher efficacy compared to higher doses of monotherapy.
- They are overall cost effective and have the least side effects.
Disadvantages of FDSs
- If an adverse drug reaction occurs from using an FDC, it becomes difficult to identify the active ingredient responsible for causing the reaction.
- Scientists face challenges in the development stages of multi-drug formulations such as compatibility issues among active ingredients and excipients affecting solubility and dissolution.
- If one drug is contraindicated for a patient, the whole FDC cannot be prescribed.
Source: The Hindu
WHO Report on Tobacco Control

Why in News?
Bengaluru finds special mention in a World Health Organisation (WHO) report on tobacco control measures released recently.
Findings of the report:
- Hundreds of enforcement drives, putting up ‘No Smoking’ signs, and creating awareness about the effects of smoking and second-hand smoke resulted in a 27% reduction in smoking in public places in the Bengaluru city.
- Across the world, there are 300 million fewer smokers today,with the prevalence of smoking declining from 22.8% in 2007 to 17% in 2021.
- In the 15 years since the MPOWER measures were first introduced, 71% of the entire population remain protected by at least one of the measures. This has increased from just 5% of the population in 2008.
- With a focus on second-hand smoking, the report says that almost 40% countries now have completely smoke-free indoor public spaces.
- Report said, progress so far is being undermined by the tobacco industry’s aggressive promotion of E-cigarettes as a safer alternative to cigarettes. Young people, including those who never previously smoked, are a particular target.
Why is it important to curb second-hand smoke?
- Of the estimated 8.7 million tobacco-related deaths each year, 1.3 million are of non-smokers exposed to second-hand smoke, the report says quoting the Global Burden of Disease 2019.
- The report adds that severe asthma, respiratory tract infections, and sudden infant death syndrome are more common among children exposed to second-hand smoke.
- The report focuses on controlling second-hand smoking by creating smoke-free public areas and also de-normalising the act of smoking in the society.
How does India fare?
- When it comes to India, the report states that the country has the highest level of achievement (among the top 10 countries) when it comes to putting health warning labels(85%) on tobacco products and providing tobacco dependence treatment.
- The cigarette packets in the country also carry a toll-free number for a quit-line and have also banned the sale of e-cigarettes, and banned smoking in healthcare facilities and educational institutions.
What further measures are needed?
- Implementing warnings on OTT platform content when actors are seen using tobacco products. This would make India the first country in the world to do so.
- There is a need to ban the loose sale of cigarettes through amendment to the law on tobacco control. Many college students buy one or two cigarettes instead of the whole pack. This means they are not exposed to the health warning and quit-line at all.
Source: Indian Express
Article 370: As hearings begins on Article 370, question of temporary provision

Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India began hearing the constitutional challenge to the 2019 abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution which granted special status to Jammu and Kashmir.
What is Article 370 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 370 is the first article of Part XXI of the Constitution - ‘Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions’.
- It exempts J&K from the application of the Constitution of India (except Article 1 and Article 370 itself) and permits the state to draft its own Constitution.
- It restricts Parliament’s legislative powers in respect of J&K and for extending a central law on subjects included in the Instrument of Accession (IoA), mere “consultation” with the state government is needed.
- IoA was signed by Raja Hari Singh of the then princely state of J&K and Governor General Lord Mountbatten in 1947.
- The IoA gave Parliament the power to legislate in respect of J&K only on Defence, External Affairs and Communications.
- But for extending it to other matters, “concurrence” of the state government is mandatory.
- Article 370 had been described as a tunnel through which the Constitution was applied to J&K.
- By the 1954 order, almost the entire Constitution was extended to J&K including most Constitutional amendments.
Can Article 370 be Deleted?
- Article 370(3) permits deletion by a Presidential Order. Such an order, however, is to be preceded by the concurrence of J&K’s Constituent Assembly.
- Since such an Assembly was dissolved on January 26, 1957, one view is it cannot be deleted anymore.
- But the other view is that it can be done, but only with the concurrence of the State Assembly.
- In 2019, the Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order 2019, issued by the President, withdrew the special status of J&K and extended all provisions of the Indian Constitution to J&K.
- The J&K (Reorganisation) Act 2019 bifurcated J&K into two UTs - J&K was an UT with a Legislative Assembly; Ladakh was without an Assembly.
Why is Removal of Special Status of J&K being Challenged in the SC?
- Legal arguments against removal:
- The SC will examine whether it is unconstitutional or violates the basic structure of the Constitution.
- Article 370 is not only part of the Constitution but also part of federalism, which is basic structure. Accordingly, the court has upheld successive Presidential Orders under Article 370.
- In Sampat Prakash (1969) the SC refused to accept Article 370 as temporary and said “Article 370 has never ceased to be operative”. Thus, it is a permanent provision.
- The Delhi HC in Kumari Vijayalaksmi (2017) too rejected a petition that said Article 370 is temporary and its continuation is a fraud on the Constitution.
- Legal arguments for removal:
- Article 35A was not passed as per the amending process given in Article 368, but was inserted on the recommendation of J&K’s Constituent Assembly through a Presidential Order.
- Article 35A empowers the J&K legislature to define the state’s permanent residents and their special rights and privileges.
- Since Article 35A predates basic structure theory of 1973, as per Waman Rao (1981), it cannot be tested on the touchstone of basic structure.
Arguments Presented during the Ongoing SC Hearings wrt Article 370:
- A temporary provision: Since the Article itself [370(3)] provides for the process through which it can be declared inoperative, it is a temporary provision.
- Permanence of Article 370:
- While the Constitution of India came into force in 1950, the Constituent Assembly of J&K came into being only in 1951.
- Yet, Article 370(3) makes a reference to the “Constituent Assembly of the State.”
- Any change to the relationship between the State of J&K and the Indian Union could only be brought about on the recommendation of the Constituent Assembly of the State.
- Once the Constituent Assembly ceased to exist (1951-1957), the Article became a permanent feature of the Constitution.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Adopt WHO-standard good manufacturing practices- Govt sets deadline for pharmas

Why in News?
The government has set a deadline for mandatory implementation of the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in India pharmaceutical industries.
- GMP are a set of quality management and regulatory guidelines.
- These are designed to ensure the consistent production of safe, high-quality products, especially in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, cosmetics etc., where product quality and safety are critical.
- The primary goal of GMP is to minimize risks that can arise from errors, contamination, or deviations during the manufacturing process.
- In India, GMP were revised in 2018, bringing them on par with World Health Organisation (WHO) standards.
- This was after the incidents of several countries reporting deaths allegedly linked to contaminated India-manufactured drugs.
Pharmaceutical industry in India: Notable achievements
- The Indian Pharmaceuticals industry plays a prominent role in the global pharmaceuticals industry.
- India ranks 3rd worldwide for production by volume and 14th by value.
- India is the largest provider of generic medicines globally, occupying a 20% share in global supply by volume.
- The pharmaceutical industry in India offers 60,000 generic brands across 60 therapeutic categories.
- It is the leading vaccine manufacturer globally.60% of the world’s vaccines comes from India.
Industry scenario
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- 100% FDI in the Pharmaceutical sector is allowed under the automatic route for greenfield pharmaceuticals.
- 100% FDI in the pharmaceutical sector is allowed in brownfield pharmaceuticals; wherein 74% is allowed under the automatic route and thereafter through the government approval route.
- Market Size
- The pharmaceutical industry in India is currently valued at $50 bn. It is expected to reach $65 bn by 2024 and to $120 bn by 2030.
- Export
- India is a major exporter of Pharmaceuticals, with over 200+ countries served by Indian pharma exports.
- India supplies over 50% of Africa’s requirement for generics, ~40% of generic demand in the US and ~25% of all medicine in the UK.
- For the period 2021-22, export of drugs and pharma products stood at $24.6 bn compared to $24.44 bn as of 2020-21.
- The Indian pharma industry witnessed exponential growth of 103% during 2014-22 from $11.6 bn to $24.6 bn.
- Support by the govt
- The Indian pharmaceuticals market is supported by the following Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes.
- PLIs are aimed to boost domestic manufacturing capacity, including high-value products across the global supply chain.
News Summary: Adopt WHO-standard good manufacturing practices- Govt sets deadline for pharmas
Instructions given by the government
- Deadlines set
- Companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore will have to implement the revised GMP within six months.
- However, medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore will have to implement it within a year.
- Those who do not comply with the direction will face suspension of licence and/ or penalty.
- Introduction of a GMP-related computerised system
- The companies will also have to introduce a GMP-related computerised system.
- These computer programmes will be designed to automatically record all the steps followed and checks done, which will ensure all the processes are followed.
- Carry out stability studies as per the climate conditions
- The companies will also have to carry out stability studies as per the climate conditions.
- At present, most companies store their samples under recommended conditions and test for various parameters from time to time.
- Now, they will have to keep the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Requirement for companies involved supplying medicines to domestic/foreign markets
- Currently, companies exporting medicines to other countries already have to be WHO-GMP certified.
- However, those manufacturing medicines for the domestic market can be granted permission if they meet the requirements listed in Schedule M of rules under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- Among other things, this lists the specifications of the manufacturing units, processes that need to be followed, and equipment needed.
Significance of this step
- For better quality control
- Currently, 2,000 of the 10,500 manufacturing units in the country have been found to be compliant with the global WHO-GMP standards.
- Now, all will have to implement the revised GMP, ensuring quality medicines for the domestic market and abroad.
- Risk-based inspection had pointed out found several deficiencies
- Recently, a risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units and 14 testing labs found several deficiencies.
- This included absence of testing of raw materials before use, absence of quality failure investigation of its products, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas.
- The recent instructions by the government would lead to at least 11 specific changes in the manufacturing process on the ground.
- This includes introduction of a pharmaceutical quality system, quality risk management, product quality review, and validation of equipment.
- India’s image as the pharmacy of the world
- Indian pharma industry is facing a credibility crisis.
- The WHO, in October 2022, said that the deaths of dozens of children in Gambia and Uzbekistan were due to contaminated cough syrups manufactured by Indian drugmakers.
- In February 2023, blindness, severe eye infections and a death in the US were linked to India-made eye drops.
- In this context, the recent instructions would help restore India’s image as the pharmacy of the world.
- Indian pharma industry is facing a credibility crisis.
Source: The Hindu
Geographical Indication (GI) Tags to Seven Products
Seven products from across India including four from Rajasthan were given the Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Geographical Indications Registry in Chennai.
About the products
- The Jalesar Dhatu Shilp (metal craft) : At Jalesar in Etah district in Uttar Pradesh, which was the capital of Magadha King Jarasandha, over 1,200 small units are engaged in making Jalesar Dhatu Shilp.
- This place is known for making decorative metal craft as well as brassware.
- Goa Mankurad mango: The Portuguese named the mango as Malcorada meaning poor coloured and with time this word transformed to ‘Mankurad’ aamo.
- Aamo means mango in Konkani language.
- Goan Bebinca: For the Goan Bebinca: Bebinca is a type of pudding and a traditional Indo-Portuguese dessert.
- It is also known as the Queen of Goan desserts.
- Udaipur Koftgari metal craft : the Udaipur Koftgari metal craftsmen practices the ancient art of Koftgari used in making ornamental weaponry.
- The weapons are exquisitely ornamented by a complicated process of etching of design, heating and then cooling intertwined with the process of embedding gold and silver wire into the metal, pressing and flattening it to a smooth surface using moonstone and finally polishing.
- Bikaner Kashidakari craft : Kashidakari work is done majorly on objects associated with marriage, especially gift items, and makes use of mirror work.
- Jodhpur Bandhej craft : The Jodhpur bandhej craft is the Rajasthani art of tying and dyeing. It is the art of printing varied patterns on fabrics using the tie and dye method.
- Bikaner Usta Kala craft : It is also known as gold nakashi work or gold manauti work, due to the prominence of golden colour in an actual manner developed by gold in the previous period.
- Due to this, the craft has longevity.
Geographical Indication (GI)
- It is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- In order to function as a GI, a sign must identify a product as originating in a given place.
- Typically, such a name conveys an assurance of quality and distinctiveness which is essentially attributable to the fact of its origin in that defined geographical locality, region or country.
- Geographical indications are typically used for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial products.
Governing rules
- Geographical Indications are covered as a component of intellectual property rights (IPRs) under the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property.
- At the International level, GI is governed by the World Trade Organisation’s (WTO’s) Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- In India, Geographical Indications registration is administered by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 which came into force with effect from September 2003. The first product in India to be accorded with GI tag was Darjeeling tea in the year 2004-05.
- The registration of a geographical indication is valid for a period of 10 years.
- It can be renewed from time to time for a further period of 10 years each.
- The registration of a geographical indication is valid for a period of 10 years.
Benefits of GI Tags
- Legal protection to the products
- Prevents unauthorised use of GI tag products by others
- It helps consumers to get quality products of desired traits and is assured of authenticity
- Promotes the economic prosperity of producers of GI tag goods by enhancing their demand in national and international markets
- A geographical indication right facilitates those who have the right to use the indication to prohibit its usage by a third party whose product does not conform to the applicable standards.
- However, a protected GI does not permit the holder to forbid someone from making a product using the same approaches as those set out in the standards for that indication.
Source: The Hindu
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|

















