UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4 August 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Defence & Security
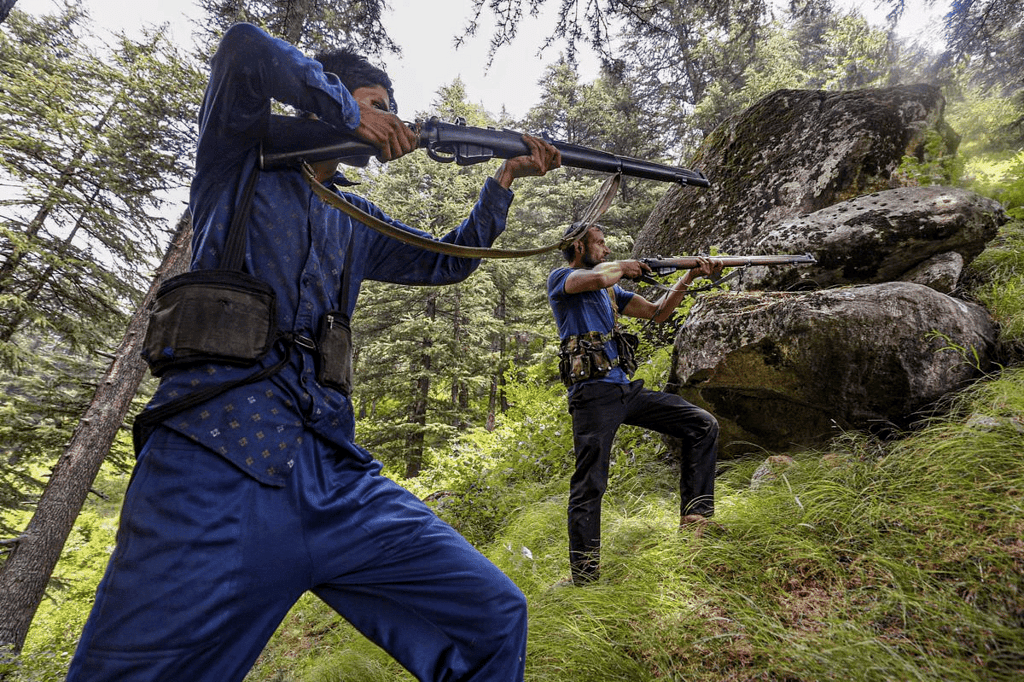
Village Defence Guards provided with sophisticated weapons
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
Recently, Union Minister Jitendra Singh announced that Village Defence Guards (VDGs) in the Jammu region have been equipped with sophisticated weapons to address rising terror incidents.
- Representing the Udhampur constituency, which has seen increased terror activities since 2021, he was speaking at the “Empowering Youth for Viksit Bharat” program in Kathua district.
- He emphasized breaking the nexus between terrorists and drug dealers and noted that defense forces and law enforcement agencies have updated their strategies to combat terrorism more effectively.
Statistics
- Since 2021, the Jammu region has experienced 31 terror incidents, resulting in the deaths of 47 security forces and 19 civilians, along with 48 terrorists killed.
- In contrast, the Kashmir Valley has reported 263 terror incidents, with 68 security forces and 75 civilians killed, and 417 terrorists neutralized.
- While the number of incidents in Jammu is significantly lower than in the Valley, the increased frequency and targeted nature of attacks on pilgrims and security forces in Jammu are particularly concerning.
Background
- The militancy that began in Kashmir in the early 1990s had spread to the adjoining Doda district by mid-1990s.
- The demand for arming the civilian population first rose after the massacre of 13 people in Kishtwar in 1993.
- As the killings increased, prompting the migration of Hindus from villages to nearby towns, the Home Ministry in 1995 decided to set up the VDCs.
About
- VDGs, formerly known as Village Defence Committees (VDCs), are community-based security groups established in the Jammu and Kashmir region.
- Initiated in 1995, the program was aimed at providing local defense against terrorist activities, especially targeting vulnerable communities.
Purpose
- The primary purpose of VDGs is to enhance local security by providing immediate defense against terrorist threats.
- They play a crucial role in supporting formal law enforcement agencies, gathering intelligence, and maintaining peace in their respective areas.
Composition
- Law enforcement agencies will form groups of armed civilians from the "more vulnerable areas".
- Each group will have no more than 15 members and will be designated as Village Defence Guards (VDGs).
- Members are typically volunteers from the community, including ex-servicemen, able-bodied youth, and other civilians who undergo basic training in self-defense and weapon handling.
Control
- The VDGs will function under the direction of the SP/SSP of the district concerned.
Key Functions
- Surveillance and Patrolling: VDGs conduct regular patrols and monitor suspicious activities, acting as the first line of defense against terrorist infiltrations.
- Intelligence Gathering: They collect and share vital information with security forces, aiding in preemptive actions against potential threats.
- Community Mobilization: By involving local residents, VDGs foster a sense of responsibility and vigilance within the community.
Contribution of VDCs in the past
- During the peak of militancy in most parts of Jammu division, the VDCs played a significant role in combating militancy.
- They were the most-feared armed groups among militants in areas where poor road networks delayed the arrival of security forces.
- The villagers, well-versed with the local topography, averted many militant attacks and helped in their capture and killings.
Challenges
- Resource Constraints: VDGs often face limitations in terms of financial and logistical support, affecting their operational efficiency.
- Security Risks: Members of VDGs are at a high risk of being targeted by terrorists due to their active role in local defense.
- Accountability Issues: There have been past allegations of misuse of power by VDG members, including crimes such as abduction and rape, which led to a temporary discontinuation of the program.
Current status
- The VDGs are being revived and strengthened since 2022 in response to the rising incidents of terror in the Jammu region.
- Recent initiatives have included the provision of sophisticated weapons and enhanced training to better equip these groups to handle the evolving security challenges.
GS3/Economy
International Conference of Agricultural Economists
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
The triennial conference organized by the International Association of Agricultural Economists is being held from 02 to 07 August 2024 and is taking place in India after 65 years.
About ICAE (Purpose, Members, Impact, Frequency, etc.
- The International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE) is a prestigious event organized by the IAAE.
- This conference gathers experts, researchers, policymakers, and practitioners from around the world to discuss critical issues and advancements in agricultural economics.
- The ICAE aims to facilitate the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and innovations in the field of agricultural economics.
- It addresses global challenges related to agriculture, food security, rural development, and sustainability.
Participants
- The conference attracts a diverse group of attendees, including academics, researchers, government officials, industry professionals, and representatives from international organizations.
- It serves as a platform for networking and collaboration among these stakeholders.
Sessions and Topics
- The ICAE features a wide range of sessions, including keynote addresses, plenary sessions, panel discussions, and paper presentations.
- Topics covered include agricultural policy, market dynamics, trade, environmental impacts, technological advancements, and rural development.
Global Impact
- The conference plays a significant role in shaping agricultural policies and practices worldwide by providing evidence-based insights and recommendations.
- It promotes the application of economic principles to improve agricultural productivity, sustainability, and food security.
Frequency and Location
- The ICAE is held every three years in different locations around the world, emphasizing its global scope and reach.
International Conference of Agricultural Economists 2024
- The triennial conference organized by the International Association of Agricultural Economists (ICAE) is being held in India from August 2 to 7, 2024, marking its return to the country after 65 years.
- The theme for this year's conference is "Transformation Towards Sustainable Agri-Food Systems," focusing on sustainable agriculture amidst global challenges such as climate change, resource degradation, rising production costs, and conflicts.
- The conference will highlight India's proactive approach to global agricultural challenges and showcase its advancements in agricultural research and policy.
- It provides a platform for young researchers and leading professionals to present their work, network with global peers, and strengthen partnerships between research institutes and universities.
- The event aims to influence policymaking on national and global scales and exhibit India's progress in digital agriculture and sustainable agri-food systems.
- Approximately 1,000 delegates from 75 countries are participating in the conference.
Key Highlights of PM Modi's Speec
- PM Modi welcomed delegates from 75 countries on behalf of millions of Indian farmers, highlighting India's deep agricultural roots.
- He emphasized the longevity and scientific basis of ancient Indian agricultural practices and their relevance today.
- He highlighted India's diverse agro-climatic zones and the significance of this diversity for global food security.
- He noted India's transformation from a food-insecure nation to a major global producer of various agricultural products.
- He stressed the importance of sustainable and climate-resilient farming practices, including natural farming and the development of climate-resilient crop varieties.
- He reiterated India's commitment to global welfare and the sharing of agricultural innovations and experiences with the global community.
- He discussed initiatives like Soil Health Cards, solar farming, e-NAM, and PM Kisan Samman Nidhi to modernize Indian agriculture.
- He highlighted the use of digital technology for real-time crop surveys, land digitization, and promoting drone use in farming.
- He also acknowledged the seriousness of the nutrition challenge along with water scarcity and climate change. He presented Shri Anna, Millet as a solution given the superfood's quality of 'minimum water and maximum production'.
- PM Modi expressed India's willingness to share India's millet basket with the world and mentioned the last year being celebrated as the International Year of Millets.
- He expressed confidence in the conference fostering learning and collaboration towards sustainable agri-food systems.
GS3/Environment
How to Reduce Landslide Risks
Source: The Hindu
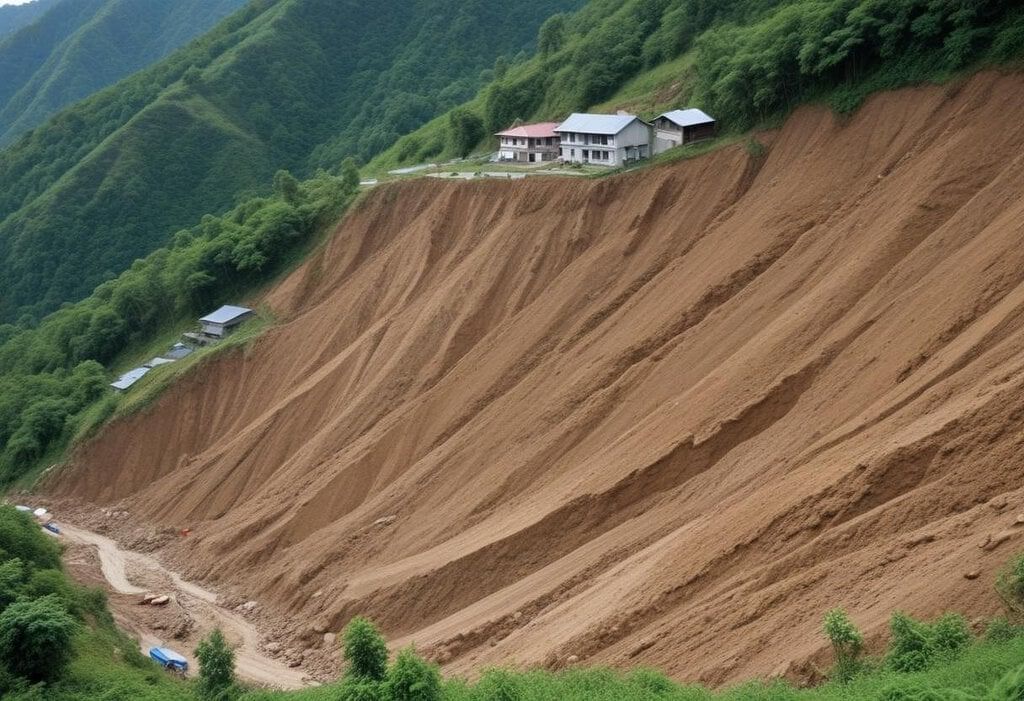

Why in News?
Massive landslides hit the district of Wayanad in northern Kerala, triggering large-scale death (toll stands at 215) and destruction and the number of missing people indicate that the real toll will be higher.
Possible Causes of Landslide in Wayanad
Natural:
- According to the Geological Survey of India (GSI), almost half of Kerala's land area is prone to landslides.
- The heavy rainfall in the region and the slope of the Western Ghats mean that 31.54% of the Wayanad district is highly susceptible to landslides.
Anthropogenic:
- Increasing construction activities:
- The Wayanad region has become a tourist hotspot, with homestays and monsoon tourism being the latest trends.
- The construction of resorts, artificial lakes and quarrying activities in the eco-sensitive zones (ESZ) have exacerbated the danger of a landslide.
Changes in crop patterns:
- Land use changes have occurred starting with the British-era tea plantations. In Wayanad, there has been a 62% reduction in forest cover between 1950 and 2018, coupled with a 1,800% increase in the area under plantation.
- Such monocropping leads to a loosening of the topsoil that was once held in place by the roots of a forest.
Climate change:
- Climate change has played an indirect role, leading to changes in rainfall patterns in the State. The warming of the Arabian Sea is allowing the formation of deep cloud systems, leading to extremely heavy rainfall over a shorter period. Heavy rainfalls cause run-offs that can lead to landslides.
Issues with landslide warnings:
- The IMD issues warnings for heavy rainfall (in a colour-coded system) and the week before the landslides, the alert was largely yellow, which does not call for action.
- The GSI has been designated the nodal agency for landslide studies, and has been given the responsibility of evolving an early warning system and protocols for landslide risk reduction. However, this is still in the experimental stage and will take four or five more years to be ready for public use, a senior GSI official said.
Landslides Prevention Techniques/ Measures
Banning/ regulating construction activities in ESZ:
- For example, the Gadgil panel report of 2011 recommended that the entire region of the Western Ghats, spanning 1,29,000 square km across six States, be declared an ESZ.
Upgrading institutional capacities and coordination:
- For example, IMD must use new technologies for accurate weather predictions.
Engineering solutions:
- Slope stabilisation: It involves adding structural elements to the slope to increase its stability.
- Grading and terracing: It involves modifying the slope's shape and gradient to reduce the risk of landslides.
- Soil reinforcement: It involves adding materials to the slope to increase its strength and stability.
Natural solutions:
- Vegetation control: Planting trees, shrubs, or grasses can help stabilise the soil, absorb excess water, and reduce erosion.
- Mulching: Mulch is a layer of organic or inorganic material applied to the soil surface. It helps retain moisture, prevent erosion, and stabilise the slope.
- Bioengineering techniques: They combine the use of plants and engineering principles to stabilise slopes.
- Water management: It slows down the flow of water, allowing it to infiltrate the soil gradually.
Early warning systems and monitoring for landslides:
- They provide timely information and alerts, allowing individuals and communities to take necessary actions to mitigate the impacts of landslides.
Emergency preparedness for landslides:
- Despite preventive measures, landslides can still occur. Being prepared and knowing how to respond during a landslide event is crucial for minimising the risks.
GS3/Economy
Highest-ever organ transplants in India
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
According to the annual report of the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO), in 2023, India achieved a record 18,378 organ transplants, with 10% going to foreign nationals.
- As per this report, 2023 saw highest-ever organ transplants in India. With this, India ranked third in the world in organ transplant and second in corneal transplant in 2023.
Regulatory frameworks guiding the organ transplantation in Indi
- NOTTO is a national level organization set up under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It functions as apex centre for all India activities of coordination and networking for:
- procurement and distribution of organs and tissues; and
- registry of Organs and Tissues Donation and Transplantation in country.
Legislation
- In 1994, The Transplantation of Human Organs Act (THOA) was promulgated by the government of India.
- Transplantation of Human Organs Rules followed in 1995 and were last amended in 2014, increasing the scope of donation and including tissues for transplantation.
- The act made commercialization of organs a punishable offence and legalized the concept of brain death in India allowing deceased donation by obtaining organs from brain stem dead person.
Institution
- National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) is a national level organization set up under Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Besides laying down policy guidelines and protocols for various functions, it coordinates all the activities associated with organ donation at national level.
Organ transplant rules
- In February 2023 the govt modified national organ transplantation guidelines.
- The new guidelines have done away with the 65-year age limit for registration of patients seeking organs from a deceased donor.
- There was no age cap for living donor transplants, where family members donate organs like kidneys and livers.
- However, people over the age of 65 years couldn’t register to receive organs from deceased donors as per guidelines of NOTTO.
- It has asked states to remove the domicile criterion for registering those seeking organs from deceased donor for transplant procedures. Now the needy person can go to any state of the country and register for getting organ and also get the transplant done.
- The patient will be allotted a unique ID by NOTTO on registering. This will get carried forward even if the patient changes multiple hospitals in different States.
- Noting that some states have been charging fees ranging between Rs 5,000 to 10,000 for registering such patients, this guideline has asked them not to charge money.
Steps for developing a uniform organ transport polic
- To develop a uniform organ transport policy for the country, consultations were held with seven ministries coordinated by NITI Aayog.
- Standard Operative Procedures have been drafted, which prescribe that:
- every concerned ministry will have a nodal officer
- State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (SOTTO) will coordinate with a nodal officer to facilitate organ transport.
Key Highlights of the report
- Status of organ transplants recorded in a year
- Organ transplants recorded in a year have more than tripled in the last decade, with kidney transplants accounting for a majority of them.
- In 2023, a total of 18,378 transplants were carried out in India, which ranks third in the world in organ transplant and second in corneal transplant.
- The total number of transplants comprising, both transplants from living donors and those from deceased donors, in the country was recorded at 4,990 in 2013.
- Milestones achieved in deceased organ donations
- India achieved another milestone in 2023 -- more than 1,000 deceased organ donations in a year for the first time, breaching its record from last year.
- The number of deceased-donor transplants has increased from 837 in 2013 to 2,935 in 2023.
- Trend in organ donation based on gender
- Among living donors, the number of females (9,784) was almost double the number of males (5,651) in 2023.
- However, among deceased donors, males outnumbered females at 844 compared to 255.
- Among the recipients, 30% were women.
- Organ transplants to foreign nationals in India
- There were 1,851 organ transplants to foreign nationals in the country and Delhi-NCR accounted for nearly 78% of these.
- Foreigners are allocated organs from deceased donors only when there are no Indian patients at the state, regional, or national level who matches.
- There were allegations of irregularities in approval for transplants in foreign nationals reported from Delhi and Rajasthan.
- There were allegations of Myanmar nationals "purchasing" kidneys from poor people in their country and getting the surgeries done at Delhi hospital.
- Organ donation rate
- The organ donation rate in our country still continues to be less than 1 per million population.
- There is need to encourage organ donation from deceased individuals to meet the growing demand for organs.
- This is important because more people are suffering from severe organ failure due to the rise in non-communicable and lifestyle diseases.
GS3/ Economy
Bhartiya Beej Sahkari Samiti Limited (BBSSL)
Source: PIB

Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Cooperation, informed Rajya Sabha about Bhartiya Beej Sahkari Samiti Limited (BBSSL).
About Bhartiya Beej Sahkari Samiti Limited (BBSSL):
- Objective: It was set up under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) Act, 2002.
- It is promoted by IFFCO, KRIBHCO, NAFED, National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), and NCDC.
- The initial paid up capital of BBSSL is Rs. 250 Cr with contribution of Rs. 50 Cr each by the five promoters and authorized share capital is Rs. 500 Cr.
- Functions:
- It will undertake production, procurement & distribution of quality seeds under a single brand through a network of cooperatives to improve crop yield and develop a system for preservation and promotion of indigenous natural seeds.
- It will help in increasing the seed replacement rate, and varietal replacement rate by ensuring the role of farmers in production of certified seeds.
- This society will focus on production, testing, certification, procurement, processing, storage, branding, labelling and packaging of two generations of seeds i.e. foundation and certified through Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) by leveraging various schemes and policies of different ministries of Government of India.
- Nodal agency: Ministry of Cooperation.
GS3/Science and Technology
Metal-air batteries
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Researchers from CSIR-CMERI, Durgapur synthesised a cathode material which can be used as catalyst in Metal-air batteries.
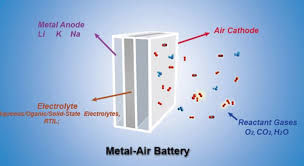
About Metal-air batteries:
- It is an energy storage system based on electrochemical charge/discharge reactions that occur between a positive “Air Electrode” (cathode) and a negative “Metal Electrode” (anode).
- The negative electrode is typically made of metals such as Li, Zn, Al, Fe, or Na, while the positive usually contains some form of porous carbon material and a catalyst.
Advantages :
- These batteries have higher energy density than a lithium-ion battery.
- Accessibility: Metal-air batteries use readily available metals in India, making them more accessible than lithium-ion batteries.
- Cost-Effective: Producing these batteries locally reduces imports.
- Environment-Friendly: Metal-air batteries are recyclable, offering a safer alternative to lithium-ion batteries that pose environmental hazards.
- Lightweight: Metals like aluminum are lightweight and can provide comparable or even higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries, making them an attractive choice.
- Applications: Due to their high scalability and energy density, M-Air batteries can be used in a large variety of applications:
- It is used in large-scale stationary energy storage applications.
- Transportation
- Renewable generation
[Question: 0]
GS3/Environment
Fin Whale
Source: NDTV

Why in News?
Recently, Japan has expanded its commercial whaling to include fin whales, a decision criticised by Australia’s government.
About Fin whale:
- Second-largest animal species on the planet, second only to the blue whale.
- Gets its name from an easy-to-spot fin on its back, near its tail.
- Fastest swimming of the large whales, known as the greyhound of the seas.
Distribution:
- Fin whales inhabit the temperate and polar zones of all major oceans and open seas and, less commonly, in tropical oceans and seas.
- Some populations are migratory, moving into colder waters during the spring and summer months to feed. In autumn, they return to temperate or tropical oceans.
Features
- They have a distinct ridge along their back behind the dorsal fin, which gives it the nickname "razorback."
- Fin whales have a very unusual feature: the lower right jaw is bright white and the lower left jaw is black.
- Lifespan: They can live for 80 to Qu 90 years and females are slightly longer than males.
Conservation status
- IUCN: Vulnerable
|
38 videos|5283 docs|1116 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4 August 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the weapons provided to the Village Defence Guards for their security? |  |
| 2. What was the theme of the International Conference of Agricultural Economists? |  |
| 3. How can landslide risks be reduced according to the article? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the highest-ever organ transplants in India? |  |
| 5. What is the focus of research on Metal-air batteries? |  |
















