UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS 2/International Relations
India’s Strategic Focus on West Africa

Why in News?
India continues to play a significant role as one of Nigeria's key partners in West Africa, despite China's growing influence in financing and infrastructure development. This highlights India's enduring commitment to the region.
Key Takeaways
- India aims to strengthen its strategic partnership with Nigeria, the largest economy and democracy in Africa.
- Focus on enhancing security cooperation to combat terrorism, piracy, and drug trafficking.
- India positions itself as a development partner through concessional loans and capacity-building initiatives.
- Both countries aspire to amplify their voices in international forums as leaders of the Global South.
Additional Details
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: India seeks to enhance its strategic partnership with Nigeria, which is expected to influence broader regional dynamics in West Africa.
- Focus on Security Cooperation: India aims to bolster security partnerships, including defense collaboration and joint counterterrorism operations against groups like Boko Haram.
- Development Partnerships: India provides concessional loans and capacity-building programs to support Nigeria’s socio-economic growth.
- Diversifying Trade Relations: India intends to revitalize trade with Nigeria by negotiating trade agreements such as the Economic Cooperation Agreement (ECA) and the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT).
- Sectoral Collaboration: Key focus areas include defense, energy, technology, health, and education, leveraging India’s expertise for mutual growth.
- Geopolitical Competition: India's efforts are challenged by China's significant presence in Nigeria, complicating its position as a key partner.
- Economic Fluctuations: The decline in trade between India and Nigeria indicates vulnerabilities due to global oil market shifts.
- Political Instability: Nigeria's unpredictable political landscape poses risks for long-term investments and initiatives.
- Capacity Constraints: Local capacity limitations in Nigeria can hinder the effectiveness of India's developmental assistance.
To move forward, India must deepen strategic collaboration with West African nations, focusing on defense and security partnerships while diversifying trade and enhancing cooperation in key sectors. Additionally, expanding developmental assistance and tailoring initiatives to address local needs will be critical for fostering stability and mutual growth in the region.
GS3/Enviro & Biodiversity
Nilphamari Narrow-Mouthed Frog

Why in News?
A recent study has brought attention to the Nilphamari narrow-mouthed frog (Microhyla nilphamariensis), an endemic species that is increasingly threatened by habitat degradation and changes in land use, particularly within agroforestry settings such as orchards and paddy fields.
Key Takeaways
- The Nilphamari narrow-mouthed frog is a species of narrow-mouthed frog.
- This species is characterized by its small size, narrow triangular mouth, and minimal webbing between its toes.
- It displays a light brown dorsal coloration with a distinctive dark brown diamond-shaped marking.
- Currently, it is not listed by the IUCN or CITES.
Additional Details
- Geographical Location: The Nilphamari narrow-mouthed frog is found across several regions including Bangladesh, India, Nepal, and northern Pakistan.
- Habitat Preferences: This frog thrives in moist environments such as grassy areas near temporary pools.
- Challenges: The species faces significant threats from habitat loss and agricultural land use changes, especially in agroforestry regions.
In summary, the Nilphamari narrow-mouthed frog is a unique species that plays a vital role in its ecosystem. However, ongoing environmental changes pose serious risks to its survival, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts.
GS3/Economics
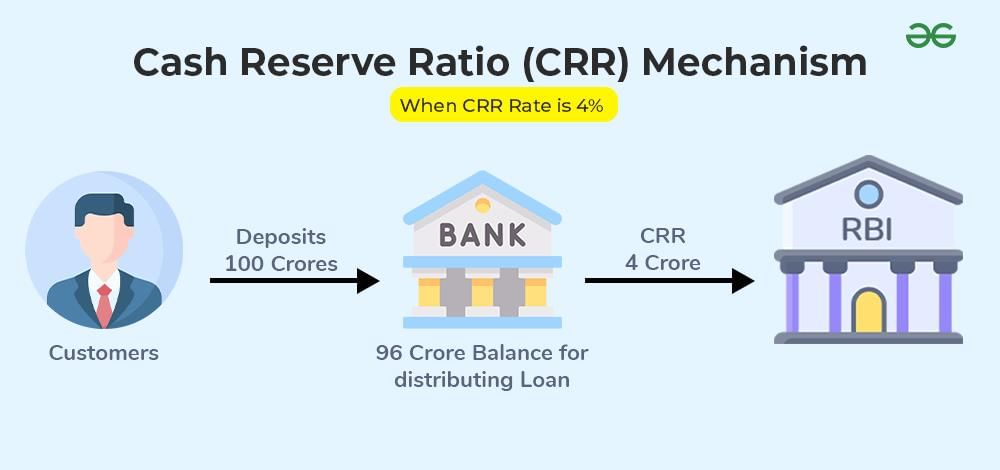
What is Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has initiated a three-day monetary policy review, leading to speculation about a possible cut in the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) to alleviate liquidity pressures in the banking system.
Key Takeaways
- CRR Definition: The Cash Reserve Ratio is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be maintained as liquid cash with the RBI.
- Current Rate: The CRR is currently set at 4.5%.
- Function: CRR is used by the RBI as a monetary policy tool to manage inflation and monitor excessive lending by banks.
- Impact on Banks: Banks do not earn interest on the CRR amount held with the RBI.
CRR Requirements for Different Types of Banks
- Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs): This category includes Public Sector Banks (PSBs), Private Sector Banks (PVBs), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Payments Banks, and various Co-operative Banks.
- Non-Scheduled Co-operative Banks & Local Area Banks: These banks must maintain CRR either with themselves or with the RBI.
Restrictions on CRR Funds
- Banks cannot lend the funds held as CRR to corporates or individual borrowers.
- The money maintained as CRR cannot be used for investment purposes by the banks.
- No interest is earned on the funds maintained as CRR by banks with the RBI.
Incremental CRR (I-CRR)
- Introduced temporarily on August 10, 2023, to absorb surplus liquidity in the banking system.
- Banks were required to maintain a 10% I-CRR increase in their Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) between May 19, 2023, and July 28, 2023.
- The I-CRR was implemented from August 12, 2023, during periods of excess liquidity in the financial system.
Impacts of Declining CRR on the Economy
Positive Impacts:
- Increased Bank Liquidity: A reduction in CRR allows banks to have more funds available, enhancing credit availability and promoting investment and consumption.
- Stimulus for Economic Growth: With increased lending capacity, businesses can access loans more easily, stimulating economic activity and growth across various sectors.
- Lower Interest Rates: Enhanced liquidity may lead banks to lower interest rates on loans, making credit more affordable and encouraging investment and consumer spending.
Negative Impacts:
- Potential Inflationary Risks: Increased lending and spending can elevate demand, which, if not matched by supply, may lead to inflationary pressures in the economy.
- Asset Bubbles: Excess liquidity can result in overvalued assets, such as stocks or real estate, posing risks of unsustainable price increases and market instability.
Previous Year Question (PYQ)
[2010] When the Reserve Bank of India announces an increase of the Cash Reserve Ratio, what does it mean?
(a) The commercial banks will have less money to lend
(b) The Reserve Bank of India will have less money to lend
(c) The Union Government will have less money to lend
(d) The commercial banks will have more money to lend
Understanding the Cash Reserve Ratio is crucial for grasping how the RBI manages liquidity in the economy and its implications for banking operations and the overall economic environment.
GS3/Environment
What is Homo juluensis?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Researchers have recently identified a new species of ancient humans named Homo juluensis, which translates to "big head." This designation stems from the discovery of a notably large skull in China, shedding light on the diversity of ancient human species.
Key Takeaways
- Time Period: Homo juluensis lived approximately 300,000 years ago.
- Geographic Range: This species inhabited eastern Asia in small groups.
- Extinction: They are believed to have disappeared around 50,000 years ago.
- Relation to Other Species: Includes connections to groups such as the Denisovans, whose histories are still being studied.
Additional Details
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils attributed to Homo juluensis, primarily consisting of facial and jaw remains, display dental characteristics similar to those of Neanderthals.
- Brain Size: Initial measurements suggest that their braincases were up to 30% larger than those of Homo sapiens.
- Behavior: Homo juluensis is thought to have hunted wild horses in small groups and created stone tools, potentially processing animal hides for survival.
This discovery emphasizes the complexity of human evolution and highlights the need for further research into ancient human relatives, such as Neanderthals, who were an extinct relative of modern humans found across Europe and into Central and Southwest Asia. Current genetic evidence suggests that Neanderthal and modern human lineages diverged at least 500,000 years ago, and despite their extinction, Neanderthal genes remain present in modern human DNA.
GS3/Environmental Sustainability
SVAGRIHA Rating Achieved by Kalughat Intermodal Terminal

Why in News?
The Intermodal Terminal (IMT) at Kalughat in Bihar, developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India, has been awarded a prestigious five-star SVAGRIHA rating by the GRIHA Council. This recognition highlights the terminal's commitment to sustainable building practices and environmental stewardship.
Key Takeaways
- The SVAGRIHA rating stands for Simple Versatile Affordable GRIHA.
- It promotes the concept of green buildings and sustainability under the Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA).
- The rating system is applicable to small standalone buildings with a built-up area of less than 2500 sq.m.
- It consists of 14 criteria organized into 5 broad sub-groups.
- The rating is awarded on a 1–5 star scale.
Additional Details
- Rating Criteria:The 14 criteria are categorized into five main sub-groups:
- Architecture & Energy
- Water & Waste
- Materials
- Landscape
- Lifestyle
- Projects must achieve points from each sub-group, with a total of 50 points possible.
- The rating system is designed to be a user-friendly online tool that evaluates projects against SVAGRIHA standards.
The Kalughat Intermodal Terminal's five-star rating reflects its innovative use of recyclable materials such as fiber, recyclable glass, and sustainable sanitary fixtures. This initiative is part of a broader strategy by the Inland Waterways Authority of India to enhance the capacity of National Waterway 1 on the River Ganga while prioritizing environmental sustainability.
GS2/Polity & Governance
Is the Caste Census a Useful Exercise?
Why in News?
The discussion surrounding the implementation of a caste census in India has intensified. Advocates argue that it can effectively determine caste populations, which is essential for equitable allocation of resources, reservations, and policy benefits. Nevertheless, historical precedents and present-day complexities indicate that significant challenges may hinder the execution of such a census.
Key Takeaways
- The first detailed caste census was conducted in 1871-72, revealing inconsistent classifications.
- Historical censuses have shown inaccuracies due to varying community identities across regions.
- Challenges include caste mobility, enumerator bias, and data accuracy issues.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: The caste census has roots in the colonial era, starting with the 1871-72 Census, which highlighted arbitrary classifications. The 1931 Census recorded 4,147 castes but faced issues with community identity claims.
- Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) 2011: This census recorded 46.7 lakh caste categories, but also noted 8.2 crore acknowledged errors, showcasing the complexities involved in caste classification.
- Challenges in Conducting a Caste Census: Issues such as caste mobility can lead to misclassification where individuals may identify with higher or lower castes for social or economic advantages. Additionally, enumerator bias can affect data collection accuracy.
- Proportional Representation: The notion of proportional representation in reservations has been criticized for being impractical, given the vast number of castes in India and the implications for recruitment processes.
- Implications of a Caste Census: While a caste census may support equitable resource distribution, it risks deepening social divisions and could exclude smaller castes, countering the intended goal of inclusivity.
In conclusion, although the concept of a caste census aims at achieving social equity, historical and contemporary evidence underscores significant challenges related to its implementation, data reliability, and fairness. Alternative strategies that focus on socio-economic development and inclusivity, without aggravating caste divisions, may provide more viable solutions.
GS3/Environment
Trouessartia thalassina and Proterothrix sibilla
Why in News?
Recently, a research team from Romania has made a significant discovery in the subtropical forests of Meghalaya, identifying two new species of feather mites: Trouessartia thalassina and Proterothrix sibilla.
Key Takeaways
- The newly identified mites are associated with two bird species: the Verditer Flycatcher (Eumyias thalassinus) and the Small Niltava (Niltava macgrigoriae).
- Trouessartia thalassina features semi-ovate terminal lamellae and lanceolate setae in males, while females have non-sclerotized lacunae.
- The name thalassina is derived from the sea-green color of the Verditer Flycatcher.
- Proterothrix sibilla, part of the wolffi species group, is recognized for its larger size and distinctive male genitalia.
Additional Details
- Feather Mites: These are microscopic arachnids that live on bird feathers, feeding on oils, skin flakes, and organic debris. They typically have a symbiotic relationship with birds, aiding in feather cleanliness and health.
- However, under stressful conditions, feather mites can turn parasitic, leading to irritation and potential feather damage.
- Feather mites are found globally and are transmitted between birds through close contact, particularly during nesting periods.
This discovery not only enhances our understanding of biodiversity in Meghalaya but also highlights the ecological roles of feather mites in avian health.
GS1/ Indian Society
Tikhir Tribe
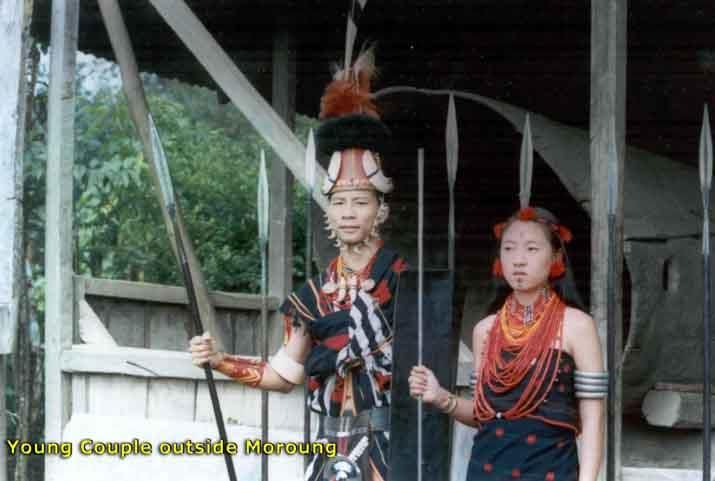 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Tikhir tribe of Nagaland has made history by conducting its inaugural Log Drum Pulling Ceremony during the ongoing 25th Hornbill Festival 2024, marking a significant cultural milestone for the community.
Key Takeaways
- The Tikhir tribe is one of the indigenous Naga tribes located in Nagaland and parts of neighboring states, including Myanmar.
- They communicate using the Naga Yimchungru language, which belongs to the Tibeto-Burman language family.
- Historically, the Tikhir were known as headhunters, with a man's prestige linked to the number of enemies he had killed.
- Headhunting practices were abolished, with the last recorded incident occurring in the 1960s.
Additional Details
- Beliefs and Religion: The majority of the Tikhir converted to Christianity due to the influence of Christian missionaries, although many still practice elements of traditional folk religion.
- Tsonglaknyi Festival: This is the principal festival of the Tikhir, celebrated annually from October 9th to 12th, focusing on the sanctification of their Shield.
- The Tikhir community primarily sustains itself through agriculture and hunting.
The Log Drum Pulling Ceremony not only highlights the rich cultural heritage of the Tikhir tribe but also represents their ongoing traditions and community spirit, fostering a sense of identity and continuity within the tribe.
GS1/History and Art & Culture
Maha Kumbh Mela, 2025
Why in News?
The 2025 Maha Kumbh Mela is scheduled to occur in Prayagraj from January 13 to February 26, marking a significant event in the Hindu calendar.
Key Takeaways
- The Maha Kumbh Mela is a major Hindu pilgrimage that occurs every twelve years, attracting millions of devotees.
- It is held at four key locations in India, with the largest gathering taking place in Prayagraj.
Additional Details
- Types of Kumbh Mela:
- Regular Kumbh Mela: Celebrated every 12 years at one of the four designated locations.
- Purna Kumbh Mela: Occurs when the full 12-year cycle is completed.
- Ardh Kumbh Mela: Takes place every 6 years in Prayagraj, representing half of the full Kumbh Mela.
- Locations:The Kumbh Mela rotates among four cities:
- Haridwar: Located on the banks of the Ganges.
- Prayagraj: The confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Sarasvati river.
- Ujjain: Situated on the banks of the Shipra River.
- Nashik: Found on the banks of the Godavari River.
- Key Rituals:
- Shahi Snan (Royal Bath): A significant ritual where pilgrims participate in processions and bathe in the holy rivers.
- Worship and Prayers: Pilgrims engage in prayers, attend spiritual discourses, and perform fire rituals along the riverbanks.
- Religious Processions: Various processions involving saints, gurus, and devotees occur throughout the festival.
- Community Prayers and Spiritual Discourses: Religious leaders conduct teachings for the gathered devotees.
- Significance and Features:
- Spiritual Significance: Recognized as a sacred event in Hinduism, aimed at spiritual cleansing, salvation, and liberation (Moksha).
- Cultural Unity: A celebration of India's unity and diversity, bringing together millions from around the globe.
- Mass Gathering: Kumbh Mela holds the Guinness World Record for the largest peaceful gathering, with approximately 120 million attendees in 2019.
- Pilgrimage Tourism: The event significantly boosts local and national economies through the influx of pilgrims.
- UNESCO Recognition: In 2017, Kumbh Mela was recognized as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO.
The Maha Kumbh Mela is not just a religious event but a remarkable cultural phenomenon that embodies the spirit of unity, devotion, and rich traditions of India.
GS3/Economics
Why Some PLI Schemes Are in the Slow Lane?
Why in News?
As of June 2024, six out of the fourteen Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes in India, including textiles, solar modules, IT hardware, automobiles, advanced chemical cells (ACC), and specialty steel, are experiencing slow implementation. Understanding the reasons behind this sluggish progress is crucial for optimizing these initiatives.
Key Takeaways
- Stringent eligibility criteria limit participation.
- Challenges in establishing domestic manufacturing bases.
- Difficulty in accessing critical resources hampers production.
- Heavy reliance on imports affects self-sufficiency.
- Slow disbursement of funds has delayed projects.
Additional Details
- Stringent Eligibility Norms: Many industries find the eligibility requirements too strict, which prevents numerous companies from accessing the incentives offered by PLI schemes.
- Initial Setup Challenges: Industries, particularly in solar modules and ACC, face significant hurdles in establishing manufacturing facilities. This process can take between one-and-a-half to three years, thereby delaying job creation.
- Access to Resources: Companies struggle with obtaining essential resources, such as machinery from China and skilled technicians, which constrains their ability to scale up production effectively.
- Market Dependency: Certain sectors remain dependent on imports and have not transitioned to self-sufficient manufacturing, hindering their growth under the PLI framework.
- Slow Disbursement of Funds: The initial years of the PLI schemes saw minimal funds disbursed, with only a small fraction being paid out in the first two years, affecting project timelines.
Sector-Specific Slowdowns
- Textiles: High competition and stringent norms have limited participation and slowed growth in this sector.
- Solar Modules: Despite being critical for renewable energy, the establishment of manufacturing capacities has been delayed. By June 2024, India had a solar module manufacturing capacity of 77.2 GW, but only 7.6 GW for solar cells, leading to supply shortages.
- Automobiles: Initial setup challenges and fluctuating market conditions are hindering the sector, with rising raw material costs and shifts towards electric vehicles complicating the landscape for traditional automakers.
- Advanced Chemical Cells (ACC): This sector faces long commissioning periods and requires substantial investment, contributing to slower growth.
- IT Hardware: Though funding has recently increased, this sector still lags in implementation compared to more successful areas like mobile manufacturing.
Way Forward
- Revising Eligibility Criteria: Simplifying these criteria can encourage more companies, especially smaller firms, to engage and benefit from the PLI schemes.
- Increasing Support for Supply Chains: Strengthening supply chains is essential. The government could provide additional support to smaller suppliers that are vital for scaling production.
- Streamlining Resource Access: Making it easier for companies to access necessary machinery and skilled labor can help improve production rates and reduce import dependency.
- Regular Reviews and Adjustments: Continuous performance monitoring of sectors can help identify issues quickly and enable timely interventions.
- Encouraging Ancillary Industries: Fostering the development of ancillary industries can create additional jobs and enhance local manufacturing capabilities.
Addressing the challenges faced by PLI schemes will be vital for enhancing their effectiveness and ensuring that India can achieve its manufacturing and employment goals. Regular assessments and targeted support measures are necessary to facilitate faster implementation and broader participation.
GS3/Economy
Mohan Bhagwat’s Three-Child Plan: Why Concern About India’s Falling Fertility Rate is Misplaced
Why in News?
Concerns surrounding India's declining fertility rates have ignited extensive debates, touching on issues such as potential labor shortages and political representation. This necessitates a thorough examination of these worries, the suggested solutions, and the effective strategies to tackle India's demographic and socioeconomic challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Demographic narratives in India have shifted from fears of overpopulation to concerns over falling fertility rates.
- Higher fertility rates may exacerbate existing inequalities in resource-limited regions.
- Southern states with lower fertility rates face political and funding concerns due to their demographic shifts.
- Economic growth should not solely rely on increased population but rather on improved infrastructure and education.
Additional Details
- Overpopulation Concerns: India’s population is projected to exceed 1.6 billion by 2060, placing immense pressure on resources and services, especially in economically disadvantaged states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- Encouraging higher fertility rates in struggling regions risks worsening poverty and unemployment.
- Regional Disparities: States such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu have successfully reduced fertility rates due to education and healthcare improvements, making demographic reversal unlikely.
- Societal factors heavily influence family size, with couples often considering financial stability and quality of life over political slogans.
- Political representation fears in southern states should lead to reforms in funding and representation rather than competitive population growth strategies.
- Economic Risks: Overemphasis on population growth without adequate support could strain education, healthcare, and housing, potentially leading to a larger unskilled workforce.
- Historical examples from countries like Germany and Singapore show that managing labor shortages can be achieved through migration and skill development rather than increasing fertility rates.
In conclusion, India's demographic transition presents challenges that require strategic policies rather than simplistic calls for increased fertility. By focusing on healthcare, education, and skill development, India can turn demographic changes into opportunities for sustainable growth.
GS3/Economics
Windfall Gains Tax on Oil Production, Diesel-Petrol Export Removed
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The government has officially withdrawn the windfall gains tax on domestic crude oil production and the export of fuels such as diesel, petrol, and aviation turbine fuel (ATF). This decision comes after a period of global energy turmoil and aims to stabilize the domestic fuel market.
Key Takeaways
- The windfall gains tax was introduced 30 months ago to address rising fuel prices due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Withdrawal of the tax reflects current stability in the global oil market.
- Domestic fuel availability has improved significantly, prompting the government's decision.
Additional Details
- Windfall Tax: This tax targets profits gained unexpectedly from external events, such as the surge in oil prices due to geopolitical conflicts. These profits are seen as unearned and are taxed retrospectively, beyond normal tax rates.
- Rationale Behind Levying This Tax: The windfall tax was enacted to redistribute unexpected gains benefiting producers while consumers faced high prices, fund social welfare schemes, and serve as a supplementary revenue stream for the government.
- Criticism: Critics argue that windfall taxes create market uncertainty and discourage investment due to their retrospective nature. There are also concerns about the fairness of taxing only large companies.
- The windfall gains tax was initially introduced on July 1, 2022, during a surge in crude oil prices, aimed at managing domestic fuel availability amidst global crises.
The withdrawal of the windfall gains tax signals confidence in market stability and reflects the government's response to improved domestic conditions and reduced international fuel prices. The decision is expected to encourage investment in the oil sector and enhance production capabilities.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is India's strategic focus on West Africa? |  |
| 2. Why is West Africa important for India's foreign policy? |  |
| 3. How does India plan to enhance its economic ties with West Africa? |  |
| 4. What are the key areas of collaboration between India and West African countries? |  |
| 5. What challenges does India face in its engagement with West Africa? |  |
















