UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 6th August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Gyanvapi Mosque Dispute
Subject: History

Why in News?
The Supreme Court refused to stop the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) survey at the Gyanvapi complex amid the dispute.
Background:-
- The Court disposed of a petition filed by Anjuman Intezamia Masjid Committee challenging Allahabad High court, which permitted the ASI to undertake the survey.
About Gyanvapi Mosque Dispute:-
Historical Background:-
- It is a popular belief that the Gyanvapi Mosque was built in 1669 by the Mughal ruler Aurangzeb by demolishing the ancient Vishweshwar temple.
- Saqib Khan’s book ‘Yasir Alamgiri’, mentions that Aurangzeb had demolished the temple in 1669 by ordering Governor Abul Hassan.
Judicial Intervention:-
- The case of Gyanvapi mosque has been in court since 1991, when three persons, including Pandit Somnath Vyas, a descendant of the priests of the Kashi Vishwanath temple, filed a suit in the court of the civil judge of Varanasi claiming that Aurangzeb had demolished the temple of Lord Vishweshwar and built a mosque on it so that the land should be returned to them.
- In 2021, in the same court in Varanasi, five women filed a petition demanding to worship in the temple of Mother Gauri, accepting which the court constituted a commission to know the present status of the Makeup Gauri Temple.
- In this context, the court asked the commission to give the survey report by video graphing the idol of Makeup Gauri and the Gyanvapi complex.
- This created an uproar, as questions were raised on the impartiality of the court commissioner appointed by the Muslim side for the survey.
Hindu Side arguments:-
- Vijay Shankar Rastogi, appearing for the Hindu side, submitted a map of the entire Gyanvapi complex as evidence in the court, which mentions the temples of Hindu deities around after the entrance of the mosque, as well as the Vishweshwar temple, Gyankoop, the big Nandi and the basement of the Vyas family.
- There has been a controversy over the survey and videography of this basement.
Muslim Side arguments:-
- The Muslim side says that no decision can be given on the dispute under the Religious Places Act of 1991.
- Under Section 3 of the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, it is prohibited to convert a place of worship, even its clause, into a place of worship of a different religious denomination or a different class of the same religious denomination.
- Section 4(2) of the Act states that all litigations, appeals, or other proceedings relating to changing the nature of the place of worship (which were pending till August 15, 1947) shall cease after the enactment of this Act and no fresh action can be taken on such cases.
- However, if the change in the nature of the place of worship has occurred after the cut-off date of August 15, 1947 (after the act came into force ), legal action can be initiated in that case.
- For example The disputed site of Ayodhya (Ram Janmabhoomi-Babri Masjid) was exempted from the Act.
About Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) :-
- Established in 1861.
- Established by: Alexander Cunningham.
- Ministry: Union Ministry of Culture.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- The ASI is the premier organization for the archaeological research and protection of the cultural heritage of the country.
Functions of ASI:-
- It maintains the archaeological sites, ancient monuments, and remains of national importance.
- It regulates all archaeological activities as per the provisions of the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, of 1958.
- It also regulates the Antiquities and Art Treasure Act, of 1972.
Source: AIR
Great Nicobar Island Project
Subject: Geography
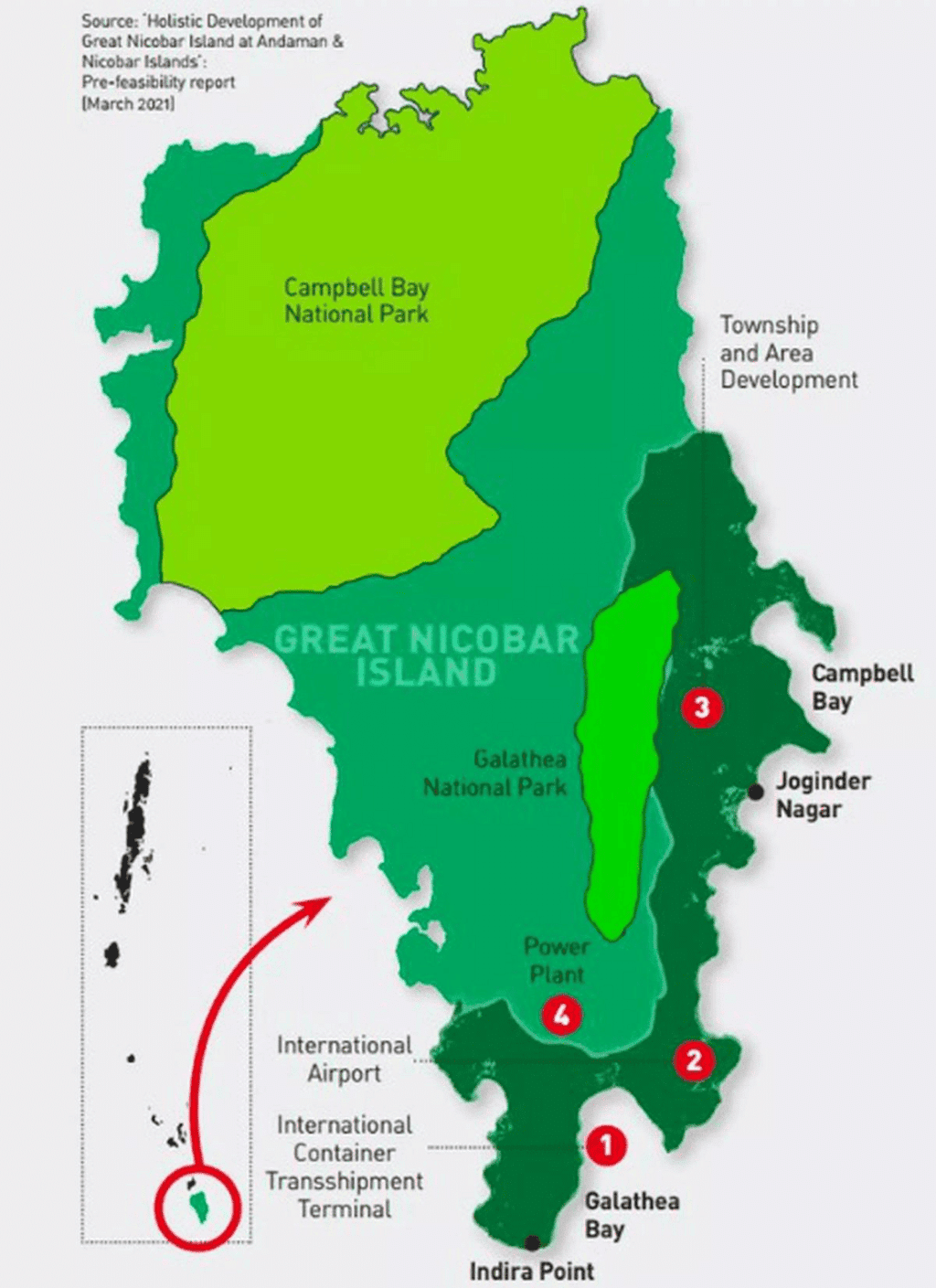
Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change told the Rajya Sabha that an estimated 964,000 trees would be felled for the Great Nicobar Island Project.
About Great Nicobar Island Project:-
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Implementing agency: Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- It is a ₹72,000-crore mega project piloted by NITI Aayog.
- Objective: holistic development of the Great Nicobar Island (GNI).
- The project aims to transform the Great Nicobar Island, in the Bay of Bengal, into a modern, sustainable, and self-sufficient territory.
Components of the plan:-
The plan has four components:-
- A ₹35,000 crore transshipment port at Galathea Bay
- A dual-use military-civil international airport
- A power plant, and
- A township
Benefits of the Projects:-
Economic Benefits:-
- The proposed port will allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment.
- Great Nicobar is equidistant from Colombo to the southwest and Port Klang and Singapore to the southeast, and positioned close to the East-West international shipping corridor, through which a very large part of the world’s shipping trade passes.
- It can potentially become a hub for cargo ships traveling on this route.
Strategic Benefits:-
- Increasing Chinese assertion in the Indian Ocean has added great urgency to this imperative in recent years.
- Great Nicobar is equidistant from Colombo to the southwest and Port Klang and Singapore to the southeast, and positioned close to the East-West international shipping corridor, through which a very large part of the world’s shipping trade passes.
Feasibility Issues:-
- Hinterland Economic Activities: A successful transshipment hub requires viable hinterland economic activities, which may be wishful thinking in Great Nicobar.
- Afforestation and Coral Reef Translocation: The far-field afforestation recommendation and coral reef translocation are questionable compensation methods.
- Tectonic Instability: Great Nicobar Island’s proximity to the Ring of Fire and its history of earthquakes raise concerns about the feasibility of developing an urban port city.
About Great Nicobar:-
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost island of the Nicobar Islands
- The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve harbors a wide spectrum of ecosystems comprising tropical wet evergreen forests, mountain ranges reaching a height of 642 m (Mt. Thullier) above sea level, and coastal plains.
- It is situated in the Bay of Bengal.
- It is the largest island in the Nicobar group of islands.
Source: Down to Earth
GS-II
4 Years after Removal of Article 370: Political Changes and Security Situation in J&K
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Union Territory of J&K has witnessed many firsts in the past four years after removal of its special status under Article 370 in August, 2019.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), the abrogation of Article 370 had paved the way for peace and development in J&K.
Article 370 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 370 is the first article of Part XXI of the Constitution - ‘Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions’.
- It exempts J&K from the application of the Constitution of India (except Article 1 and Article 370 itself) and permits the state to draft its own Constitution.
- It restricts Parliament’s legislative powers in respect of J&K and for extending a central law on subjects included in the Instrument of Accession (IoA), mere “consultation” with the state government is needed.
- IoA was signed by Raja Hari Singh of the then princely state of J&K and Governor General Lord Mountbatten in 1947.
- The IoA gave Parliament the power to legislate in respect of J&K only on Defence, External Affairs and Communications.
- But for extending it to other matters, “concurrence” of the state government is mandatory.
- Article 370 had been described as a tunnel through which the Constitution was applied to J&K.
- By the 1954 order, almost the entire Constitution was extended to J&K including most Constitutional amendments.
Removal of Special Status of J&K:
- Article 370(3) permits deletion of special status of J&K by a Presidential Order.
- Such an order, however, is to be preceded by the concurrence of J&K’s Constituent Assembly.
- Since such an Assembly was dissolved on January 26, 1957, one view is that special status cannot be removed.
- But the other view is that it can be done, only with the concurrence of the State Assembly.
- In 2019, the Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order 2019, issued by the President, withdrew the special status of J&K and extended all provisions of the Indian Constitution to J&K.
- The J&K (Reorganization) Act 2019 bifurcated J&K into two UTs - J&K was an UT with a Legislative Assembly; Ladakh was without an Assembly.
- Recently, the Supreme Court of India began hearing the petitions challenging the 2019 abrogation of Article 370.
Many firsts in the past 4 years in J&K:
- Establishment of all three tiers of Panchayati Raj
- Reservation of seats for Scheduled Tribes (STs) during the delimitation of Assembly constituencies.
- A change in domicile laws to enable people from elsewhere in the country to settle in J&K.
How has been the Security Situation in J&K in the past 4 years?
- No more stone pelting: With the unprecedented numbers of security forces in the Valley, and the harsh action taken by central agencies such as the NIA, incidents of stone throwing have been reduced to virtually zero.
- Incidents of terrorism have witnessed a steep decline: Government data show a decline of 32% in “acts of terrorism” between August 5, 2019 and June 6, 2022, compared with the 10 months preceding the historic decisions.
Political Changes in J&K in the past 4 years:
- District Council elections:
- Elections were held to District Development Councils (DDCs) in all 20 districts of J&K in 2020, raising hopes for a democratic process at the grassroots.
- DDCs in J&K were earlier called District Planning and Development Boards, with members who were nominated by the state government.
- Political realignments:
- Almost all major opposition leaders were either detained or had their movements curtailed after the abrogation of Article 370.
- With political actions by mainstream parties frozen, new outfits emerged, and several leaders changed loyalties. For example, PDP joined hands with NC.
- Delimitation Commission:
- The Centre constituted a 3-member Commission under retired SC judge Justice Ranjana Desai in 2020 to carve out 90 Assembly constituencies, including reserved ones for SCs and STs.
- In its final report in 2022, the commission increased the number of Assembly seats in Jammu division from 37 to 43 and in Kashmir from 46 to 47.
- It also recommended reservation of 9 constituencies for STs, 6 for SCs, and a provision for nomination of two Kashmiri Hindus and a displaced person from PoK.
Challenges that Need to be Addressed in J&K:
- Grassroot democracy is still not a reality: DDC chairpersons have complained that in most cases the development plans are prepared by officials.
- Polls, quotas, and protests:
- The delimitation exercise led to speculation about early Assembly elections. However, there is very little chance of elections being held before next year’s Lok Sabha polls.
- Meanwhile, the Centre’s attempt to include four new groups in the state’s ST list triggered widespread demonstrations from the Gujjars and Bakerwals.
- Targeted killings: A spate of killings of civilians, especially of Kashmiri Hindus and non-Kashmiris in the Valley, has exposed the fragility of the security successes.
- Cross-border terrorism: The targeted killings have been aided by the dropping of small weapons by low-cost drones from across the border, and the engagement of alleged ‘part-time’ militants by handlers in Pakistan.
Source: The Hindu
BharatNet Project | Objectives, Progress & Challenges Associated with It
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved an outlay of Rs 1.39 lakh crore for BharatNet, the government’s project for last-mile connectivity across 6.4 lakh villages in the country.
About BharatNet Project:
- Bharat Net is the world's largest optical fiber-based rural broadband connectivity project.
- It is executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a special purpose organisation under the Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications.
- It is an ambitious rural internet access programme - an initiative by the Union government under its Digital India
Features & Benefits of BharatNet:
- Using optical fibre, the programme is intended to bring broadband internet connectivity to each of the more than 2.5 lakh gram panchayats across the country.
- The government intends to provide a minimum of 100 Mbps bandwidth at each Gram Panchayat so that everyone, especially those in rural India, can access e-services offered by various Central and State Government agencies.
- This covers services such as e-governance, e-learning, e-banking, e-commerce, and e-health.
- As part of BharatNet project, the Centre will also provide last mile connectivity through Wi-Fi and other means and is setting up Wi-Fi hotspots in all gram panchayats.
- The penetration and proliferation of broadband is also expected to increase direct and indirect employment and income generation.
- Under the BharatNet project, the home broadband package will start from Rs 399 a month, giving 30 Mbps unlimited data, bundled with OTT offering, etc.
- In 2016, the DoT approved to implement the project in three phases.
Budget:
- The total budget allocation for the BharatNet project is Rs. 61,000 crore.
- Funds for the BharatNet project are allocated as a whole and not state/Union Territory-wise.
- A lump sum amount is allocated and disbursed from Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) to BBNL for execution of BharatNet project.
- USOF is name for the levies collected by the Centre from telecom companies with a view to ensuring funding and development of communication services in rural and underserved areas.
Phases of Implementation:
- Phase-I:
- 1,00,000 GPs to be covered - under implementation.
- Being executed by 3 CPSUs viz. BSNL, RailTel and PGCIL.
- Targeted to be completed by March 2017.
- Phase-II:
- Balance GPs using optical mix of underground/aerial OFC, radio and satellite to be used.
- To be executed by 3 CPSUs and State Govts. through their Discoms or any other agency.
- Targeted to be completed by December 2018.
- Phase-III:
- Futuristic network with ring topology to be used between districts and blocks and blocks and GPs.
- Targeted to be completed by 2023.
Progress So Far:
- The initial scope of the project was to cover 2.5 lakh gram panchayats in the country with optical fiber by August 2021.
- However, that deadline was missed.
- Around 1.94 lakh villages have been connected at present and rest of the villages are expected to be connected in the next 2.5 years.
- The project progress was affected due to lockdown and movement restrictions due to COVID pandemic.
- In the Union Budget 2022-23, the Government extended the project deadline to 2025.
Challenges Associated with BharatNet Project:
- Slow Pace of Implementation:
- The pace of BharatNet has been slow given that the government has been able to make just 194,000 gram panchayats service ready so far.
- From November 2022 till March this year, about 6,000 gram panchayats have been made service ready.
- PPP Mode of Implementationis yet to take off:
- The first request for proposal (RFP) for implementation of the project, which was floated in July 2021, failed to get any response from private companies.
- The industry had highlighted that some of the terms and conditions of the tender were too onerous for the private players while the revenue sharing model proposed by the government was also unfavourable to them.
- The Government will come out with a revised PPP model for BharatNet project in a couple of months.
News Summary:
- The Union Cabinet approved an additional Rs 1.39 lakh crore for modernising the BharatNet project which involves changing its execution strategy and providing fiber connections to the last mile through Village Level Entrepreneurs.
- With this upgrade, the government is looking to speed up its process in connecting all the remaining villages over the next 2.5 years.
- The Government, under the PPP model, will involve village level entrepreneurs or Udyamis to take the fiber connections to the homes on a 50:50 revenue-sharing basis.
- The cost for taking the infrastructure to the home will be borne by the government.
- The rural entrepreneur will only need to be involved in maintenance and operations of home connections, including addressing consumer complaints related to fiber cuts, etc.
Source: The Hindu
Anusandhan National Research Foundation Bill-2023
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation Bill, 2023 was recently introduced in the Lok Sabha.
About Anusandhan National Research Foundation Bill-2023:
- It aims to set up the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (NRF).
- It will be an apex body to provide high-level strategic direction of scientific research in the country as per recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP).
- It seeks to set up a Rs 50,000-crore fund, with a sizeable contribution from the private sector, to "seed, grow and promote" research and development (R&D) and foster a culture of research and innovation throughout India's universities, colleges, research institutions, and R&D laboratories.
- It seeks to set up different funds:
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation Fund: For the financing of activities under the Act.
- Innovation Fund: For supporting outstanding creativity in the areas supported by the foundation
- Science and Engineering Research Fund: For the continuation of the projects and programmes initiated under the Science and Engineering Research Board Act, 2008.
- One or more special-purpose funds for any specific project or research.
- Functions of NRF:
- NRF will forge collaborations among the industry, academia, and government departments and research institutions and create an interface mechanism for the participation and contribution of industries and state governments in addition to the scientific and line ministries.
- It will focus on creating a policy framework and putting in place regulatory processes that can encourage collaboration and increased spending by the industry on R&D.
- Structure of NRF:
- It will have a governing board consisting of 15 to 25 eminent researchers and professionals headed by the prime minister, who will be the ex-officio president.
- The education minister and the science and technology Minister will be the vice presidents of the NRF.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) will be the administrative department of NRF,
- The proposed foundation will also have an executive council under the principal scientific adviser.
Source: AIR
GS-III
Trachoma
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently announced that Iraq has now eliminated trachoma.
About:
- What is Trachoma? Trachoma is a disease of the eye. It is a neglected tropical disease.
- Cause: Chlamydia trachomatis is the bacterium that causes trachoma.
- Transmission: The infection is transmitted by direct or indirect transfer of eye and nose discharges of infected people, particularly young children who harbour the principal reservoir of infection. These discharges can be spread by particular species of flies.
- Impact/Symptoms: Trachoma is the most common infectious cause of blindness in the world. The eyelashes are being pushed inward into the eye over time as a result. Consequently, it gets rubbed against the eyeball with each blink. Trichiasis is the name of this severe kind of trachoma.
- Prevention and Treatment (SAFE Strategy by WHO): They are easy to treat. Elimination programmes in endemic countries are being implemented using the WHO-recommended SAFE strategy. This consists of:
- Surgery to treat the blinding stage (trachomatous trichiasis),
- Antibiotics to clear the infection, particularly the antibiotic azithromycin,
- Facial cleanliness and
- Environmental improvement, particularly improving access to water and sanitation.
Prevalence / Elimination by Iraq
- Iraq has now joined 17 other countries to eliminate trachoma. Additionally, Iraq is the 50th to receive recognition from the UN office for health for eradicating at least one neglected tropical illness internationally.
- Other countries that have eliminated Trachoma are: Benin, Cambodia, China, Gambia, Ghana, Iran, Laos , Malawi, Mali, Mexico, Morocco, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Togo and Vanuatu.
- Africa is the most affected continent. The disease is still known to be endemic in six countries of the WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region. Although. There has been progress in the number of people in the region requiring antibiotic treatment for ‘trachoma elimination purposes’, which has fallen from 39 million in 2013 to 6.9 million in April 2023.
- The disease thrives especially in crowded living conditions where there are shortages of water, inadequate sanitation and where numerous eye-seeking flies are present.
Source: The Hindu
Voyager Mission
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) recently lost communication with Earth’s longest-running space probe, Voyager 2.
About Voyager 1 and 2
- Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space(the region that lies outside the impact of our Sun’s constant flow of material and magnetic field).
- The first was Voyager 1, sent to space about two weeks after Voyager 2 ( Voyager 1 was launched after Voyager 2).
- The most interesting discoveries made by Voyager 1 included the finding that Io, one of Jupiter’s moons, was geologically active.
- Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 discovered three new moons of Jupiter: Thebe, Metis and Adrastea.
Source: Indian Express
Perucetus colossus (Ancient Peruvian whale)
Subject: Environment

Why in News?
Researchers have identified a gigantic species of extinct whale that may have been heavier than any other creature on Earth.
About Perucetus colossus
- The Perucetus colossus — meaning the colossal whale from Peru —was almost twice that of the largest blue whale and more than three times that estimated for Argentinosaurus, one of the largest dinosaurs ever found.
- Its diet may have consisted of scavenging food or eating up tons of krill and other tiny sea creatures in the water.
- The density of the bones indicates that the whale may have been usually present in shallow, coastal waters like dugongs and manatees (known as Sirenians).
- Dugong (Dugong dugon) also called as ‘Sea Cow’ is one of the four surviving species in the Order Sirenia and it is the only existing species of herbivorous mammal that lives exclusively in the sea including in India.
- Dugongs are protected in India and occur in Gulf of Mannar, PalkBay, Gulf of Kutch and Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Source: Indian Express
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|





















