UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 7th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/ Science and Technology
INS Tushil: The Latest Addition to the Indian Navy

Why in News?
The Indian Navy is preparing to commission its newest multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, INS Tushil, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant enhancement of India's naval capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- INS Tushil is the latest frigate in the upgraded Krivak III-class series.
- The ship is part of the Russian-designed Project 1135.6.
- It is the seventh vessel in this series, with two upgraded frigates contracted in 2016.
Additional Details
- Ship's Name and Symbolism: The name Tushil means "protector shield", reflecting the Indian Navy's mission to protect India’s maritime borders.
- Advanced Features: INS Tushil boasts advanced stealth technology that enhances its evasion capabilities against enemy radar.
- Indigenous Technology: The frigate incorporates 26 percent indigenous technology, featuring over 33 systems developed by Indian manufacturers.
- Operational Command: It will be assigned to the Western Fleet under the Western Naval Command, enhancing the 'Sword Arm' of the Indian Navy.
INS Tushil represents a crucial development in the Indian Navy's ongoing modernization efforts, enhancing its operational capabilities and furthering its commitment to safeguarding national interests at sea.
GS2/International Relations
Collapse of France’s Government
Source: Indian Express Why in News?
Why in News?
French Prime Minister Michel Barnier has resigned following a no-confidence vote that united both far-right and leftist lawmakers, leading to the downfall of his government just three months after taking office. This event marks the first time in over 60 years that a French government has fallen due to a no-confidence motion, resulting in a political crisis and making Barnier the shortest-serving Prime Minister in modern French history. His government will now operate in a caretaker capacity until a new government is formed. President Emmanuel Macron is expected to address the nation soon.
Key Takeaways
- The French government fell due to a no-confidence vote.
- Michel Barnier is now the shortest-serving PM in modern history.
- The government will function as a caretaker until a new one is appointed.
Additional Details
- System of Governance: France operates under a semi-presidential system established by the Fifth Republic in 1958, which combines elements of both parliamentary and presidential systems.
- Structure of Parliament:The French Parliament is bicameral, consisting of:
- National Assembly (Assemblée Nationale): The lower house with 577 deputies elected for five years through a two-round majority voting system.
- Senate (Sénat): The upper house, indirectly elected by an electoral college representing local authorities.
- Role of the President: The President is the head of state with significant powers including appointing the Prime Minister, presiding over the Council of Ministers, commanding the armed forces, and calling referenda.
- Role of the Prime Minister: The Prime Minister is responsible for implementing laws and managing domestic policies, accountable to the National Assembly.
- Emergency Budget Provisions: The caretaker government can pass emergency laws to ensure continuity in public sector operations and avoid a shutdown.
The collapse of the French government has ushered in a period of political uncertainty, with concerns about the stability of the government and the approval of the 2025 budget. This situation has caused investor anxiety, leading to increased borrowing costs for France. Additionally, the political upheaval in France poses challenges for the European Union, which is already facing its own political issues.
GS3/Science and Technology
CAR T-Cell Therapy
Source: Nature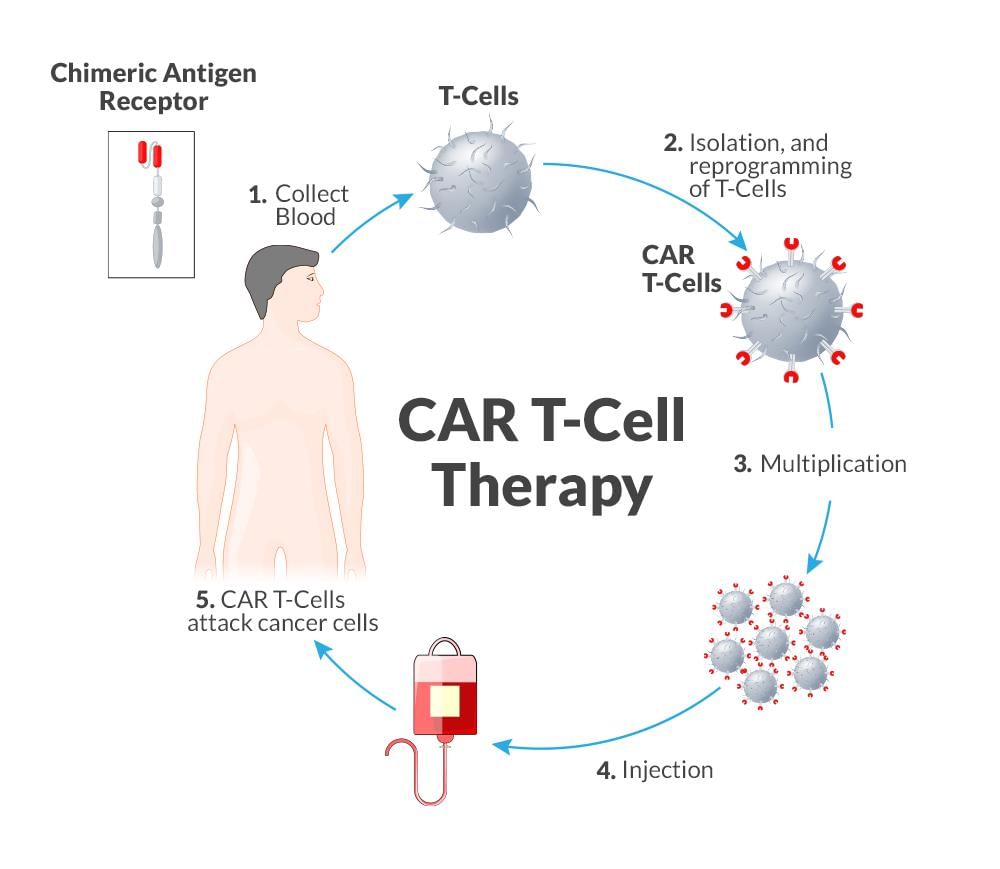 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has been a key supporter of research projects focusing on CAR T-cell therapies for cancers.
Key Takeaways
- Innovative Immunotherapy: CAR T-cell therapy involves genetically modifying T-cells to target cancer cells.
- Targeted Treatment: This therapy specifically targets CD19, a protein found on the surface of B-cells.
- Approval and Trials: Approved by DCGI in March 2021; Phase 1 trials have shown promising results.
Additional Details
- Objective of the Therapy: Aimed at treating blood cancers, especially B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL).
- Implementation: Developed jointly by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT-Bombay) and Tata Memorial Center (TMC), Mumbai, since 2015.
- Future Scope: Phase 2 trials are currently ongoing, with potential for expansion to other cancers such as Multiple Myeloma and Glioblastoma.
- Support: Trials have been supported by academic grants from government agencies and conducted at various hospitals.
CAR T-cell therapy represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment, providing options for patients whose diseases have relapsed or are resistant to conventional therapies.
GS3/Economics
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PMKMY)
Source:PIB
Why in News?
The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare has released state-wise statistics regarding the number of farmers registered under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PMKMY). This scheme recently marked its completion of five successful years since its launch on 12th September 2019.
Key Takeaways
- Top three states with the highest registrations: Haryana (5,74,467), Bihar (3,45,038), and Chhattisgarh (2,02,734).
- Bottom three states/UT with the lowest registrations: Lakshadweep (72), Ladakh (114), and Goa (150).
Additional Details
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Objective: To offer a voluntary, contributory pension scheme for farmers aged 18 to 40 years, ensuring a monthly pension of ₹3,000 after they reach 60 years of age.
- Implementation & Structural Mandate: The scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, with the Pension Fund Manager being the Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) of India.
- State-wise Registration: Farmers are registered and managed by respective state governments in collaboration with LIC, facilitating a structured approach to fund collection and matching contributions.
- Contribution: Farmers are required to contribute between ₹55 and ₹200 per month, based on their age at entry.
- Beneficiaries & Benefits: Farmers aged between 18 and 40 years are eligible for the scheme, with an assured pension of ₹3,000 per month post-60 years, alongside government matching contributions.
- Exclusions: Those who are income taxpayers, members of government pension schemes, or already enrolled in other pension schemes are not eligible for this scheme.
The PMKMY aims to provide financial security for farmers in their old age, thereby enhancing their livelihood sustainability and improving their quality of life.
GS3/Science and Technology
RuTAG Initiative
Source: PIBWhy in News?
The first annual review meeting of the Rural Technology Action Group (RuTAG) 2.0 projects recently took place at the Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST) in Srinagar, Kashmir. This meeting highlights the ongoing efforts and progress of the RuTAG initiative in enhancing rural technology interventions.
Key Takeaways
- RuTAG is an initiative launched by the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India in 2004.
- The initiative focuses on providing Science & Technology support tailored for rural areas.
- RuTAG 2.0 was launched in April 2023, emphasizing commercialization and wider dissemination of technologies.
Additional Details
- Demand-Driven Interventions: RuTAG initiatives are designed to address specific needs at the grassroots level, aiming to bridge technology gaps and enhance existing technologies.
- The initiative provides training, demonstrations, and innovative projects to empower rural communities.
- Focus on Market-Ready Products: RuTAG 2.0 aims to translate innovative ideas into products that can be commercialized, enhancing socio-economic development in rural regions.
The RuTAG initiative represents a significant step towards fostering sustainable development in rural areas by empowering communities through accessible and impactful technology solutions.
GS1/Indian Society
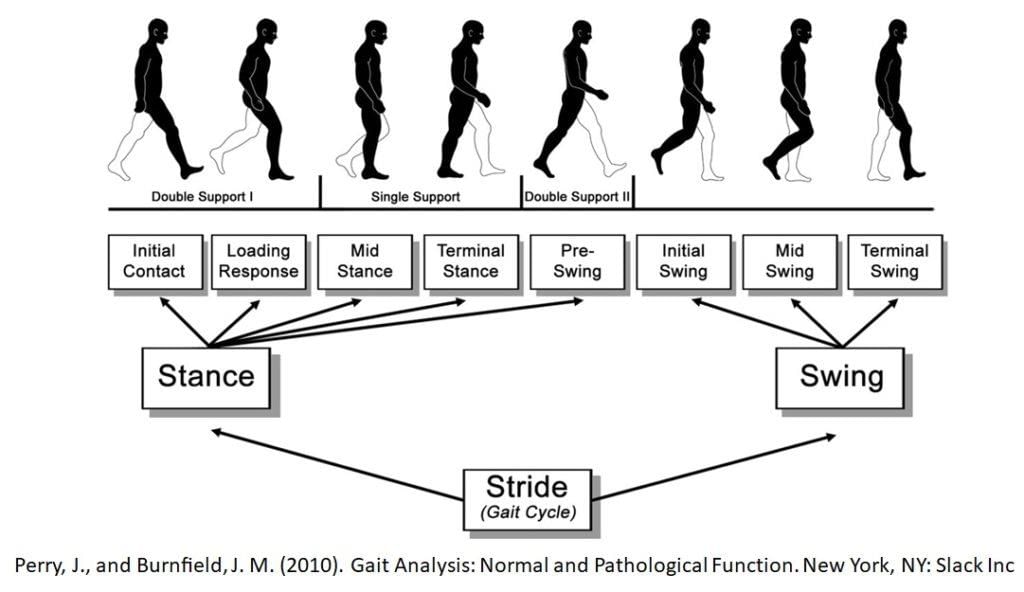
What is Gait Analysis?
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, gait analysis played a crucial role in the arrest of a rapist involved in the case of a 7-month-old in Bengal, highlighting its significance in forensic investigations and medical assessments.
Key Takeaways
- Gait analysis assesses the way an individual moves, particularly while walking or running.
- The main goal is to identify abnormalities in locomotion that could indicate underlying health issues.
Additional Details
- Gait Analysis: It is a comprehensive evaluation of how a person stands and walks, integrating inputs from the visual, somatosensory, and vestibular systems.
- Abnormalities in gait can result in unusual walking patterns, which may stem from diseases or injuries, leading to discomfort in areas like the hips, back, neck, feet, knees, or ankles.
- Gait analysis can help identify sources of pain, diagnose skeletal misalignments, and monitor the progression of conditions such as arthritis or muscular dystrophy.
This analysis not only aids in medical diagnoses but also enhances our understanding of human movement, allowing for better treatment plans and rehabilitation strategies.
GS1/History, Art and Culture
Angami Tribe
Source:Nagaland Tribune
Why in News?
Recently, 1,500 members of the Angami Naga tribe showcased their cultural heritage during a vibrant ceremony at Nagaland's Hornbill Festival, highlighting their unity and strength.
Key Takeaways
- The Angami tribe is one of the prominent Naga tribes, known for its distinct cultural identity.
- They primarily inhabit the Kohima district of Nagaland and have ancestral ties to Myanmar.
Additional Details
- Language: The most widely spoken language among the Angami Nagas is Tenyidie, though they do not possess a script of their own. The Nagamese language, a blend of Assamese, Bengali, Hindi, and Nepali, has become the common spoken language in the region.
- Economy: The Angami Naga tribe primarily engages in agriculture, practicing shifting cultivation, known as Jhum. They are recognized for their terrace wet cultivation and also participate in animal husbandry. A notable aspect of their craftsmanship is their traditional cane and bamboo basketry, with the khophi being a signature utility basket.
- Their society is characterized by a patriarchal and patrilineal structure, and most members have adopted Christianity.
- Festivals: The main festival celebrated by the Angami tribe is Sekrenyi, which reflects their rich cultural traditions.
The Angami tribe's participation in cultural events like the Hornbill Festival not only showcases their vibrant traditions but also reinforces their identity within the diverse tapestry of Naga culture.
GS3/ Science and Technology
National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Health has re-strategized its approach under the 100-Day TB Elimination Campaign, aiming to reduce tuberculosis (TB) cases and mortality through targeted interventions and a comprehensive strategy.
Key Takeaways
- India accounted for 26% of global TB cases and deaths in 2023, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- A National TB Prevalence Survey by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) reported 312 TB cases per lakh population.
- The TB incidence rate decreased by 17.7% from 2015 to 2023.
- TB-related deaths declined by 21.4% in the same period.
Additional Details
- Former Name: Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP)
- Objective: To eliminate tuberculosis (TB) as a public health issue in India by 2025, aligning with PM Modi's target set in 2018.
- Focus Areas:
- Early detection and complete treatment of TB.
- Prevention and strengthening TB care and control services.
- Key Components of NTEP:
- Universal Drug Susceptibility Testing (UDST): Facilitates early detection of drug-resistant TB.
- Free Diagnosis and Treatment: Available for all TB patients across India.
- Nikshay: A case-based web-enabled TB information system for monitoring and managing cases.
- Private Sector Engagement: Involves private healthcare providers to ensure standardized care.
- Objectives under the National Strategic Plan:
- Eliminate TB as a public health problem by 2025.
- Achieve universal access to quality TB care.
- Prevent the emergence of drug-resistant TB through early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Reduce the TB burden via preventive interventions and awareness campaigns.
- Ensure better case management through the Nikshay monitoring system.
- Engage the private sector for standardized and quality TB care.
- Government Initiatives:
- Provision of free diagnosis and treatment for all TB patients.
- Implementation of the Nikshay System for case management.
- Enhanced diagnostic facilities including genetic and molecular tests for early detection.
- Targeted interventions for vulnerable populations, focusing on high-risk groups such as children and marginalized communities.
In summary, the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) represents a comprehensive effort by the Indian government to combat tuberculosis through improved diagnosis, treatment, and engagement with multiple sectors to ensure effective public health interventions.
GS3/Economics
Key Highlights of Recent RBI Announcements
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In a strategic move to enhance liquidity in the financial system, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has reduced the cash reserve ratio (CRR) by 50 basis points (bps) to 4%. This decision comes amidst rising inflation and economic uncertainties.
Key Takeaways
- The CRR has been decreased by 50 bps, resulting in an injection of ₹1.16 lakh crore into the banking system.
- The repo rate has been maintained at 6.5%, remaining unchanged for the 11th consecutive time.
- Inflation forecast for FY2025 has been revised to 4.8%, while GDP growth estimates have been lowered to 6.6%.
- The RBI introduced MuleHunter, an AI-based system to combat digital fraud.
- Interest rate ceilings on Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank (FCNR(B)) deposits have been increased.
- Small Finance Banks (SFBs) can now offer pre-sanctioned credit lines via UPI.
Additional Details
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): This is the percentage of a bank's net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) that must be held as reserves with the RBI. Lowering the CRR increases liquidity in the banking sector, facilitating more lending.
- Repo Rate: The rate at which the RBI lends short-term funds to banks, influencing overall borrowing costs in the economy.
- Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL): This includes total deposits held by a bank minus its liabilities, such as loans and advances.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): A measure that tracks changes in the retail prices of goods and services, serving as an indicator of inflation levels.
- Mule Bank Accounts: These are fraudulent accounts used to transfer illicit funds, often exploiting unsuspecting account holders.
- Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank (FCNR(B)) Deposits: Accounts that allow Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) to deposit earnings in foreign currencies, protecting them from currency fluctuations.
- Alternative Reference Rate (ARR): A benchmark interest rate used to set loan and deposit rates in various currencies globally.
- Basis Points (bps): A unit of measurement equal to 0.01%, where 100 bps equals 1%.
These recent announcements by the RBI reflect an adaptive monetary policy aimed at stabilizing the economy and enhancing financial inclusion. The focus on leveraging technology to combat fraud and the adjustments in deposit interest rates are significant steps towards fostering a more resilient financial framework.
GS2/Polity & Governance
Tackling Case Backlog: The Supreme Court's Approach to Prioritising Cases
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India (SC) is currently confronted with a significant backlog, with more than 82,000 cases pending. In response, Chief Justice of India (CJI) Sanjiv Khanna has initiated reforms aimed at managing this situation, particularly by prioritising Special Leave Petitions (SLPs) for more rapid resolution.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court is working to address a backlog of over 82,000 cases.
- CJI Sanjiv Khanna has introduced reforms to expedite the resolution of Special Leave Petitions (SLPs).
- SLPs allow for appeals against High Court decisions and are subject to the Court's discretion.
Additional Details
- Special Leave Petition (SLP): The SC possesses extraordinary jurisdiction under Article 136 of the Constitution, enabling it to entertain SLPs. SLPs can be filed against any judgment, decree, or order from any court or tribunal in India, barring military tribunals.
- Eligibility and Filing: Any aggrieved party can file an SLP if dissatisfied with a High Court judgment or if a High Court refuses to grant a certificate of appeal. The time limit for filing is 90 days from the judgment date or 60 days from the refusal of a certificate.
- Reforms Under CJI Khanna: CJI Khanna's reforms focus on streamlining SLP processes by reserving specific days for hearing these petitions, thus aiming to reduce case pendency effectively.
- Challenges: While the reforms provide quicker hearings for SLPs (averaging around 1 minute and 33 seconds), they may lead to longer delays for full hearings, which can take over four years.
CJI Khanna's strategy represents a proactive shift towards resolving admission-stage cases rapidly in an effort to mitigate the increasing backlog. Although this approach aims to hasten decisions on SLPs, it raises concerns about the extended delays in long-pending regular hearing matters. The ongoing administrative and judicial reforms of the Supreme Court reflect its commitment to balancing efficiency and justice.
GS3/ Environment and Ecology
What is Little Gull?
Source: Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Little Gull, a bird native to the Eurasian region, has recently been spotted for the first time in the National Capital Region (NCR).
Key Takeaways
- The Little Gull (Hydrocoloeus minutus) is recognized as the smallest species of gull in the world.
- It belongs to the family Laridae and primarily breeds in northern Europe and across the Palearctic.
- This species is migratory, wintering along coasts in western Europe, the Mediterranean, and in smaller numbers in the northeast United States.
Additional Details
- Habitat: The Little Gull can be found in various environments including seacoasts, bays, estuaries, rivers, lakes, ponds, marshes, and flooded fields.
- Physical Features:
- This gull measures approximately 25–30 cm in length, has a wingspan of 61–78 cm, and weighs between 68–162 g.
- In its breeding plumage, it is pale grey with a black hood, dark underwings, and often displays a pinkish flush on the breast.
- During winter, its head turns white with a darker cap and eye-spot.
- It has a thin black bill and dark red legs, and its flight pattern resembles that of a tern.
- Young Little Gulls exhibit black markings on their heads and upper parts, with a distinct "W" pattern across their wings; they take three years to mature.
- IUCN Red List Status: The Little Gull is classified as Least Concern.
The recent sighting of the Little Gull in NCR marks an important observation, contributing to the understanding of its migratory patterns and habitat preferences.
GS1/Social Issues
Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival and Concerns Over Liquor Provision
Source:Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The 25th Hornbill Festival in Nagaland is currently being celebrated amidst discussions regarding the potential relaxation of the 35-year-old Nagaland Liquor Total Prohibition (NLTP) Act of 1989. The state's Tourism Minister has announced that both tourists and stall owners are allowed to consume Indian-made Foreign Liquor (IMFL) at the festival venue in Kisama Heritage Village. This decision has sparked criticism from influential church groups who oppose the availability of alcohol, including traditional rice beer, during the state's largest public gathering. The state government is also contemplating a review of the NLTP Act.
Key Takeaways
- The Hornbill Festival, initiated in 2000, is Nagaland's largest annual public event aimed at promoting tourism and celebrating Naga culture.
- It serves as a platform for the 14 recognized Naga tribes to showcase their unique traditions and practices.
- The festival attracted over 154,000 visitors in 2023, including over 2,100 foreign tourists.
- The ongoing debate around liquor prohibition reflects cultural and political tensions within the state.
Additional Details
- Prohibition Law in Nagaland: Nagaland enforced complete prohibition under the NLTP Act in 1989, largely supported by the Church and the Naga Mothers’ Association (NMA). This law traces its origins to American Baptist influences in the 1870s, which established strict moral codes against alcohol consumption.
- The Hornbill Festival is a rare occasion when the government allows the sale and consumption of Thutse, a local rice beer, highlighting the complex relationship between cultural identity and religious beliefs.
- Despite a majority Christian population, traditional practices related to rice beer remain prevalent.
- Recent discussions in the state assembly have raised concerns about the effectiveness of the prohibition law, citing issues such as spurious alcohol and illegal smuggling.
The government’s consideration to amend the prohibition law faces significant opposition from church authorities, emphasizing the need to balance cultural heritage with contemporary social issues.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 7th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What led to the collapse of France’s government? |  |
| 2. What is the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PMKMY)? |  |
| 3. What is the ecological significance of the Little Gull? |  |
| 4. How does the PMKMY benefit small farmers financially? |  |
| 5. What are the conservation efforts for the Little Gull? |  |
















