UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 7th March 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Black Sea
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Ukraine said on Tuesday that its forces destroyed a Russian military patrol ship in the Black Sea near annexed Crimea, the latest naval attack on Moscow’s fleet in the key waterway.
Geographical Location
- The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea located between Europe and Asia.
- It lies east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia.
- It is bordered by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine.
Connectivity and Water Sources
- The Black Sea is fed by major rivers such as the Danube, Dnieper, and Dniester.
- The Bosporus strait links it to the Sea of Marmara, which is connected to the Aegean Sea through the Dardanelles strait.
- To the north, it is connected to the Sea of Azov via the Kerch Strait.
Water Dynamics
- Although there is a net outflow of water through the Turkish Straits, water flows in both directions simultaneously.
- Denser, saltier water from the Aegean Sea flows into the Black Sea beneath the lighter, fresher water flowing out.
- This phenomenon results in the formation of a deep, anoxic layer in the Black Sea.
Significance of the Anoxic Layer
- The anoxic layer in the Black Sea is responsible for preserving ancient shipwrecks.
- Due to the lack of oxygen in this layer, organic material does not decompose, leading to the remarkable preservation of submerged artifacts.
Source: NDTV
Rupa Tarakasi
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?:
The renowned silver filigree craft of Cuttack city in Odisha has recently been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Rupa Tarakasi:
- Description: Rupa Tarakasi is a highly intricate form of silver craftsmanship.
- Location: This art form has been practiced for centuries in Cuttack, Odisha, known as the silver city.
- Historical Significance: Its origins can be traced back to as early as the 12th century and flourished with support from the Mughal rulers.
- Production Process:
- Silver bricks are meticulously converted into delicate wires or foils, which are then crafted into intricate silver filigree designs.
- The filigree is fashioned using a combination of silver alloys and other metals like copper, zinc, cadmium, and tin.
- Artisans: The skilled craftsmen engaged in this art are referred to as "Rupa Banias" or "Roupyakaras" in the local Odia language.
- Products: This craftsmanship extends to producing a diverse range of items, including jewelry for Odissi dancers, decorative pieces, accessories, as well as religious and cultural artifacts.
Source:- Telegraph India
International Centre of Excellence for Dams
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
The Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) signed a Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) with the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore for the establishment of an International Centre of Excellence for Dams (ICED).
About International Centre of Excellence for Dams
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti recently collaborated with the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, to establish the International Centre of Excellence for Dams (ICED).
- This center serves as a technological support unit for the Ministry, offering specialized assistance in investigations, modeling, research, innovation, and technical services for dam owners in India and abroad.
- The Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) between the MoJS and IISc will be effective for ten years or until the completion of the Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP) Phase-II and III Scheme, whichever comes first.
- ICED's primary focus is on enhancing dam safety, addressing emerging challenges through scientific research, and providing solutions to ensure the safety and stability of dams.
- Additionally, ICED will provide area-specific academic courses, training programs, workshops, applied research, and technology transfers related to dam safety.
- Funding: The Ministry of Jal Shakti has allocated a grant of 118.05 crore rupees for the construction, modernization, and operational setup of ICED.
- ICED will conduct research in two core areas:
- Advanced construction and rehabilitation materials, and material testing for dams
- Comprehensive (multi-hazard) risk assessment of dams
- ICED at IISc Bangalore is the second International Centre established for Dam Safety, with the first center set up at IIT Roorkee following the signing of a similar MoA in February 2023.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Article 371 (A-J)
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
In the backdrop of protests across Ladakh, the Centre is mulling granting Article 371-like protection to the Union Territory.
Background:
- Ladakh witnessed massive protests demanding statehood, legislature and inclusion in the Sixth Schedule, apart from concerns about environmental degradation due to possible industrialisation.
About Article 371 (A-J):
- Article 371 of the Constitution includes special provisions for 11 states, including six of the Northeast.
- Articles 369 through 392 (including some that have been removed) appear in Part XXI of the Constitution, titled ‘Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions’.
- Article 370 dealt with Temporary Provisions with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir.It was repealed in 2019; Articles 371, 371A, 371B, 371C, 371D, 371E, 371F, 371G, 371H, and 371J define special provisions with regard to another state (or states).Articles 370 and 371 were part of the Constitution at the time of its commencement on January 26, 1950; Articles 371A through 371J were incorporated subsequently.
- Article 371 has provisions for Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Article 371A (13th Amendment Act, 1962), Nagaland: This provision was inserted after a 16-point agreement between the Centre and the Naga People’s Convention in 1960, which led to the creation of Nagaland in 1963. Parliament cannot legislate in matters of Naga religion or social practices, Naga customary law and procedure, administration of civil and criminal justice involving decisions according to Naga customary law, and ownership and transfer of land without concurrence of the state Assembly.
- Article 371B (22nd Amendment Act, 1969) has provisions for Assam; Article 371C (27th Amendment Act, 1971) has provisions for Manipur.
- Article 371D & E – has provision for Andhra Pradesh.
- Article 371F (36th Amendment Act, 1975) has provision for Sikkim; Article 371G (53rd Amendment Act, 1986) has provision for Mizoram, Article 371H (55th Amendment Act, 1986) has provision for Arunachal Pradesh.
- Article 371I deals with Goa, but it does not include any provision that can be deemed ‘special’.
- Article 371J (98th Amendment Act, 2012) has provision for Karnataka.
Examples/details of provisions for some northeast states:
- Article 371G (53rd Amendment Act, 1986), Mizoram: Parliament cannot make laws on “religious or social practices of the Mizos, Mizo customary law and procedure, administration of civil and criminal justice involving decisions according to Mizo customary law, ownership and transfer of land unless the Assembly so decides”.
- Article 371A (13th Amendment Act, 1962), Nagaland : Parliament cannot legislate in matters of Naga religion or social practices, Naga customary law and procedure, administration of civil and criminal justice involving decisions according to Naga customary law, and ownership and transfer of land without concurrence of the state Assembly.
Source: Indian Express
Dying Declaration
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently held that the conviction of the accused can be sustained solely based on the dying declaration if the declaration made by the victim inspires the confidence of the court and proves to be trustworthy.
- Understanding Dying Declaration:- A Dying Declaration is a statement made by a deceased person and is governed by Section 32(1) of the Indian Evidence Act 1872. It typically pertains to the cause of the declarant's death and is admissible in both civil and criminal proceedings.
- Format of Dying Declaration:- There is no specific format required for a dying declaration. It can be oral, written, through gestures, a thumb impression, or in a question-and-answer form. The statement should clearly communicate the person's intentions.
- Recording the Dying Declaration:- While a magistrate's recording is preferred, the Supreme Court allows anyone, including public servants or doctors in hospitals, to record a dying declaration. Magistrates often use a question-and-answer format for accuracy.
- Evidentiary Value of Dying Declaration:- A dying declaration carries significant legal weight and can be the sole basis for a conviction without additional evidence. However, the court must ensure the statement was not coerced, and the deceased was of sound mind and capable of identifying the assailants.
Source: Live Law
GS-III
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Subject: Environment and Ecology
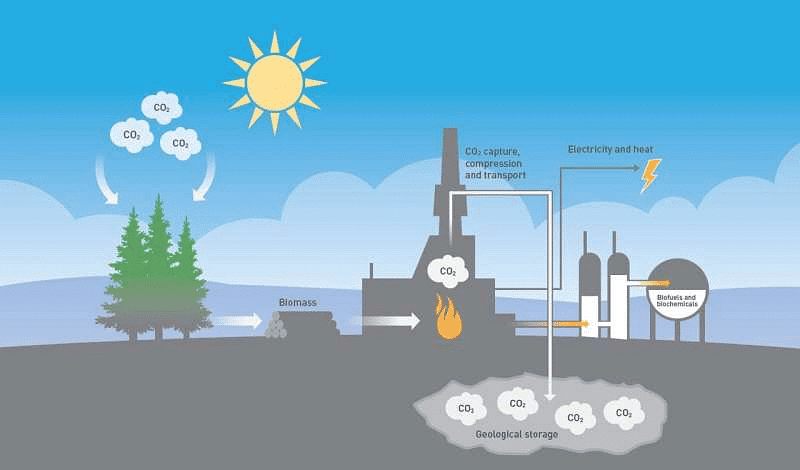
Why in News?
In a significant shift from its previous stance, Germany, a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, has decided to permit industries to capture their carbon emissions and store them underground at offshore sites.
Background on CCS
- Germany, a major greenhouse gas emitter, now allows industries to capture and store carbon emissions underground at offshore locations.
- Germany aims for carbon neutrality by 2045 but faces challenges in reducing emissions from sectors like cement production.
- CCS is viewed as a temporary solution until more sustainable innovations are developed.
About Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- CCS is a critical tool in combating climate change.
- It involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants.
- Unlike carbon dioxide removal (CDR), which takes CO2 out of the atmosphere, CCS stops CO2 from escaping initially.
- The primary goal of CCS is to prevent a substantial amount of CO2 from entering the atmosphere, thus mitigating global warming effects.
Benefits of CCS
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- CCS captures CO2 emissions from industries and power plants, preventing them from being released into the atmosphere.
- By storing CO2 underground, CCS helps lower the overall greenhouse gas concentration.
- Preserving Fossil Fuel Use:
- CCS enables the continued use of fossil fuels while reducing their environmental impact.
- It acts as a transition towards cleaner energy sources by cutting emissions from existing fossil fuel infrastructure.
- Industrial Applications:
- CCS can be applied to sectors like cement production, steel manufacturing, and chemical industries.
- These industries emit significant CO2 amounts, and CCS provides a means to tackle their emissions.
- Creating Carbon Sinks:
- Underground storage sites serve as carbon sinks, storing CO2 away from the atmosphere permanently.
- Well-managed storage sites can trap emissions for extended periods, even centuries.
- Transitioning to Clean Energy:
- CCS offers a strategy for transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- It offers a buffer for renewable technologies to develop and become economically viable.
Source: Economic Times
India's First Under-River Metro Tunnel
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated a metro train service in Kolkata, marking the opening of India's inaugural under-river metro tunnel.
About India's First Under-River Metro Tunnel
- Part of Kolkata Metro's East-West Corridor, this tunnel passes beneath the Hooghly River, connecting Howrah Maidan to Esplanade. The Howrah Maidan station, situated 32 meters below ground level, stands as the deepest metro station in India.
Key Facts about River Hooghly
- Overview:- The Hooghly River, also referred to as the Bhagirathi-Hoogly and Kati-Ganga Rivers, serves as one of West Bengal's prominent rivers. It represents a distributary of the Ganges River.
- Course:- Originating in Murshidabad, the Hooghly River emerges as a split from the Ganga, with the Padma river flowing through Bangladesh. The Hooghly courses west and southward, reaching the Rupnarayan estuary before ultimately emptying into the Bay of Bengal through a 32-kilometer-wide estuary.
- Water Source:- Primarily fed by the Farakka Feeder Canal rather than natural sources, the Hooghly River benefits from water diversion via the Farakka Barrage. This diversion, near Tildanga in the Malda district, ensures a steady water supply even during dry periods.
- Contributing Rivers:- The Hooghly receives water from rivers like Haldi, Ajay, Damodar, and Rupnarayan in its lower reaches. Notable cities along the Hooghly River include Jiaganj, Azimganj, Murshidabad, and Baharampur.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 7th March 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of Article 371 (A-J) in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. What is a Dying Declaration and how is it used in legal proceedings? |  |
| 3. What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology and how does it work? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of India's First Under-River Metro Tunnel? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the International Centre of Excellence for Dams in the field of dam construction and management? |  |
















