UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 7th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I / Geography
Key Facts about Black Sea
Source: First Post
Why in News?
Ukraine's exploding drone boats seem to be targeting smaller, high-speed vessels in the Black Sea following Russia's withdrawal of larger warships after a series of destructive attacks.
About Black Sea:
- The Black Sea is a vast inland sea situated at the southeastern edge of Europe.
- Bordering countries include Ukraine to the north, Russia to the northeast, Georgia to the east, Turkey to the south, and Bulgaria and Romania to the west.
- Russia boasts the longest coastline on the Black Sea at 2,300 km, followed by Turkey (1,329 km) and Ukraine (1,282 km). The Crimean Peninsula extends into the sea from the north.
- It is linked to the Aegean Sea (a branch of the Mediterranean Sea) through the Bosporus Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles Strait, and to the Sea of Azov via the Kerch Strait.
- Originating from tectonic shifts in Asia Minor that separated the Caspian basin from the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea gradually became isolated; its salinity is now less than half that of the world's oceans.
- The Black Sea receives freshwater inflows from all sides of the basin and serves as a confluence for numerous rivers like the Danube, Southern Bug, Dnieper, Rioni, and Dniester.
- It stands as the largest meromictic basin globally, indicating rare water exchange between its lower and upper layers. It also ranks among the world's largest anoxic basins with regions having minimal dissolved oxygen.
- Several islands dot the Black Sea, with notable ones including Snake Island (Ukraine), Giresun Island (Turkey), and St. Ivan Island (Bulgaria).
Key Facts about Venus
Subject: Geography
Source: Telegraph India

Why in News?
A team of US scientists has demonstrated through computer simulations that Venus' lack of water is due to hydrogen chemistry in its atmosphere.
About Venus
- Venus is the second planet from the Sun and the sixth largest in our solar system.
- Despite being closer to the Sun than Venus, Mercury, receiving four times more solar energy, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system.
- The planet's atmosphere exhibits an intensified greenhouse effect, leading to extreme temperatures of 880 degrees Fahrenheit (471 degrees Celsius) that can even melt lead.
- Venus and Earth share many similarities, including size, mass, density, composition, and gravity, with Venus being slightly smaller at around 80% of Earth's mass.
Composition
- Venus is a terrestrial planet with an interior comprising a central iron core and a rocky mantle akin to Earth's composition.
- The planet's atmosphere consists mainly of carbon dioxide (96%) and nitrogen (3.5%), with traces of other gases like carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, water vapor, argon, and helium making up the rest.
- Unique features of Venus include its lack of moons, retrograde rotation (opposite to most planets), and an exceptionally slow rotation period of 243 Earth days on its axis.
- A complete orbit around the Sun takes Venus 225 Earth days, resulting in a day on Venus being slightly longer than a Venusian year.
- Venus stands out in the night sky due to its highly reflective clouds, appearing as a bright white object and being one of the most prominent natural celestial bodies.
GS-II
Custodial Death
Subject: Polity and Governance
Source: ET Legal World

Why in News?
The Supreme Court has emphasized the necessity of adopting a “more rigorous approach” when considering bail applications from police officers charged in cases of custodial deaths.
- Custodial death pertains to a demise transpiring when an individual is under the supervision of law enforcement authorities or a correctional institution.
- It can result from various factors like the application of excessive force, negligence, or mistreatment by the officials.
- As per the Law Commission of India, any offense committed by a public servant against a detained individual in custody constitutes custodial violence.
Constitutional Framework Related to Custodial Death
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to life and personal liberty, encompassing protection from torture and other forms of inhuman treatment.
- Article 20 safeguards accused persons, citizens, foreigners, or legal entities like corporations, from arbitrary or excessive punishment through provisions such as No ex-post-facto law, No double jeopardy, and No self-incrimination.
- In the case of Selvi v. State of Karnataka, the court ruled against conducting narco-analysis, polygraph, and brain-mapping tests on individuals without their consent.
Legal Protections Associated with Custodial Death
- Section 24 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 stipulates that any confessions obtained from the accused under duress by investigating agencies are inadmissible in court.
- Sections 330 and 331 of the Indian Penal Code criminalize causing hurt or grievous hurt to extract confessions.
- Amendments to Section 41 of the Criminal Procedure Code in 2009 introduced safeguards ensuring transparent arrests, reasonable grounds, documentation, and legal representation.
International Conventions Against Custodial Torture
- International Human Rights Law and the United Nations Charter advocate for the humane treatment of prisoners and protection against torture and disappearances.
- The Nelson Mandela Rules of 2015 emphasize dignified treatment of prisoners and the prevention of torture.
- The United Nations Convention Against Torture (UNCAT) aims to prevent cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment globally.
Way Forward to Combat Custodial Torture
- Implementing comprehensive legislation explicitly outlawing custodial torture, as directed by the Supreme Court in the Prakash Singh Case 2006.
- Conducting prompt and impartial investigations into allegations of custodial torture.
- Enhancing police training programs to focus on respecting human rights.
- Promoting accountability, professionalism, and empathy within law enforcement agencies.
- Establishing oversight mechanisms to effectively monitor and address instances of custodial torture.
- Empowering Civil Society and Human Rights Organizations to advocate for custodial torture victims.
- Expanding the mandate of the National Human Rights Commission to investigate human rights violations by armed forces and extending its jurisdiction.
- Providing support and legal aid to victims and their families.
- Collaborating with international human rights bodies for justice and redress.
The Question of Article 31C
Subject: Polity and GovernanceSource: Indian Express

Why in News?
During a recent Supreme Court hearing on the government's authority to acquire and redistribute private property, a nine-judge Constitution Bench led by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud raised a significant query with "radical constitutional consequence": the existence of Article 31C.
Background
The Bench emphasized the necessity of determining whether Article 31C remains valid post the Minerva Mills decision to prevent "constitutional uncertainty."
Key Takeaways
- Article 31C safeguards laws formulated to ensure the equitable distribution of community resources for the common good (Article 39(b)), preventing the concentration of wealth and means of production to the common detriment (Article 39(c)).
- Article 39 of the Constitution outlines directive principles of state policy, serving as guiding principles for legislation but not directly enforceable in courts.
- According to Article 31C, specific directive principles (Articles 39(b) and 39(c)) are immune to challenges based on the right to equality (Article 14) or rights under Article 19 (freedom of speech, right to assemble peacefully, etc).
- The introduction of Article 31C occurred through The Constitution (Twenty-fifth) Amendment Act, 1971.
- In the Kesavananda Bharati case (1973), the 25th amendment faced scrutiny, leading to a crucial ruling on the Constitution's "basic structure."
- The court invalidated a segment of Article 31C that prevented laws from being contested in court for failing to adhere to specified policies.
- The Constitution (Forty-second) Amendment Act, passed in 1976, broadened the shield of Article 31C to encompass principles in Part IV of the Constitution, safeguarding all directive principles from challenges under Articles 14 and 19.
- The amendment aimed to prioritize directive principles over fundamental rights to facilitate socio-economic reforms.
- In the Minerva Mills v. Union of India case (1980), the Supreme Court annulled certain clauses of the 42nd amendment, underscoring limits on Parliament's power to amend the Constitution.
- The ruling sparked a dilemma for the court: did striking down part of the 25th amendment nullify Article 31C entirely, or did it reinstate the protected status of Articles 39(b) and (c) post the Kesavananda Bharati judgment?
The Challenge and Necessity of 'Balanced' use of Fertilisers
Subject: Agriculture
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
The fiscal year ending March 2024 witnessed a record urea consumption of 35.8 million tonnes, marking a 16.9% increase from the levels in 2013-14.
Background on Fertiliser Regulation:
- In January, the government imposed pricing controls on various fertilisers like DAP and MOP, which are supported under nutrient-based subsidy schemes.
Impact of Neem Coating on Urea:
- Neem coating of urea, initiated in May 2015, aimed to curb illegal diversion of subsidised urea and enhance nitrogen use efficiency.
- Neem oil not only prevented misuse but also facilitated a gradual nitrogen release, thereby reducing the number of urea bags per acre.
Importance of Balanced Fertilisation:
- Encouraging balanced fertilisation involves discouraging excessive application of primary nutrients like urea, DAP, and MOP.
- It entails providing primary, secondary, and micro nutrients in appropriate proportions based on soil type and crop requirements.
Challenges in Fertiliser Pricing:
- Ensuring a proper price hierarchy among non-urea fertilisers, with DAP priced highest and MOP lowest, poses a significant challenge.
- India's heavy dependence on fertiliser imports and fluctuating global prices contribute to pricing complexities.
Opportunities for Improvement:
- The cooling of international prices presents an opportunity for the government to rationalise fertiliser prices and enhance balanced plant nutrition.
- Potential strategies include bringing urea under nutrient-based subsidy schemes and adjusting subsidy rates on other nutrients.
Concerns over Urea Consumption:
- Two primary concerns include high levels of urea imports and inefficient Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crop production.
- Approximately 65% of the nitrogen applied through urea remains unutilised by plants, leading to environmental losses.
GS-III
DRIP PRICING
Subject: Economy
Source: Hindustan Times

Why in News?
The Centre recently issued a warning about "drip pricing," emphasizing the potential for consumers to encounter unexpected "hidden charges."
Background:
- The Department of Consumer Affairs has urged consumers to seek assistance from NCH 1915 or via WhatsApp at 8800001915 for concerns related to 'drip pricing'.
About DRIP PRICING
- Drip pricing is a pricing strategy employed by companies where they initially showcase only a portion of a product's price, known as the "headline price."
- As the customer progresses through the purchasing process, additional charges are gradually unveiled.
- This approach can result in unexpected "hidden charges" that catch consumers off guard.
Key Points
- Initial Advertisement: Companies might promote a base price that excludes essential fees like booking, service, or credit card charges.
- Incremental Disclosure: Additional expenses, which could be obligatory, are revealed one by one or "dripped" to the buyer during the purchase phase.
- Common Usage: This tactic is commonly observed in the hospitality and travel sectors, as well as in other online payment scenarios.
- Consumer Impact: It can complicate comparison shopping and lead to frustration among consumers who anticipate knowing the total cost upfront.
- Example: An airline ticket advertised without incorporating baggage fees exemplifies a form of drip pricing.
Choline
Subject: Science and Technology
Source: Medical News Net

Why in News?
Researchers have recently found that choline, a vital nutrient, enters the brain through a protein known as FLVCR2.
About Choline:
- Choline is crucial for various bodily functions, aiding in cellular growth and metabolism. It comes in both water-soluble and fat-soluble forms, with different absorption mechanisms based on its form.
- The body can synthesize limited choline in the liver, but dietary intake is essential due to inadequate endogenous production.
- Rich sources of choline include meat, fish, dairy, eggs, as well as several fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Functions:
- Cell Structure: Choline is a component of phospholipids like lecithin, critical for cell membrane structure in all plant and animal cells.
- Methyl Group Source: It provides methyl groups (―CH3) necessary for various metabolic processes.
- Liver Health: Choline aids in cholesterol clearance from the liver, preventing fat and cholesterol buildup linked to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Healthy Nervous System:
- Essential for acetylcholine production, a key neurotransmitter vital for memory, muscle movement, and regulating heart rate.
- Plays roles in gene expression modulation, cell signaling, lipid metabolism, brain development, and supporting beneficial gut bacteria.
Consequences of Choline Deficiency:
- Choline deficiency can lead to health issues such as cardiovascular disease and muscular damage due to its crucial roles in various bodily functions.
India VIX
Subject: Economy
Source: Money Control
Why in News?
Recently, India VIX surged by 15% on May 6 to 16.58, leading experts to advise caution against large leveraged positions.
What is India VIX?
- India VIX is an index that acts as a gauge of market expectations regarding volatility in the short term. It is also referred to as the fear index.
- Volatility indicates the speed and extent of changes in stock prices or index values.
- The movement in the VIX index reflects the overall market's anticipation of volatility in the next 30 days. A surge in the VIX value suggests that the market foresees increased volatility in the near future.
- The VIX index was originally developed by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 1993 based on the S&P 500 index prices. It has since become a widely recognized measure of volatility in the U.S. equity markets.
- The India VIX was introduced with a similar objective in 2010, utilizing the computation methodology of CBOE but adjusted to suit the Indian markets.
- India VIX is computed by the National Stock Exchange and exhibits a strong negative correlation with Nifty. When India VIX decreases, Nifty tends to rise, and vice versa.
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Subject: Science and Technology
Source: The Hindu
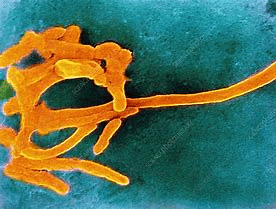
Why in News?
In a recent study, researchers have identified a unique subtype of Fusobacterium nucleatum that is more prevalent in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors.
About Fusobacterium nucleatum:
- Fusobacteria are Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli with species-specific habitats in the human mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and other areas.
- It has traditionally been viewed as an opportunistic pathogen due to its frequent presence in anaerobic samples from patients with various infections.
Highlights of the research:
- The researchers initially studied the genomes of different types of F. nucleatum from colorectal tumors and individuals without cancer.
- Among its various subspecies, only one, known as nucleatum animalis (or Fna), was consistently present in tumor samples.
- Further genetic analyses indicated that Fna could be subdivided into two distinct groups.
- While both groups were equally prevalent in the mouth, only one group, termed Fna C2, was significantly abundant in colorectal tumor samples.
- Fna C2 exhibited higher acid resistance, potentially facilitating its direct passage from the mouth to the intestines through the stomach.
- Additionally, Fna C2 could conceal itself within specific tumor cells, evading the immune system. Moreover, it could utilize nutrients present in the gastrointestinal tract, distinct from those in the mouth.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 7th May 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Black Sea in terms of geography and geopolitics? |  |
| 2. How does Venus differ from Earth in terms of its atmosphere and surface conditions? |  |
| 3. What are the key issues surrounding custodial deaths and how can they be prevented? |  |
| 4. How does Article 31C impact the balance between fundamental rights and directive principles of state policy in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. Why is there a need for a balanced use of fertilizers in agriculture, and what are the challenges associated with achieving this balance? |  |





















