UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 8th March 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
One Nation One Challan

Why in News?
The Gujarat government recently told the High Court, that it was in the process of setting up virtual traffic courts in the state under the ‘One Nation One Challan’ initiative.
About One Nation One Challan :
- One Nation, One Challan is an initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
Objective :
- to bring all related agencies, such as the traffic police and the Regional Transport Office (RTO), on one platform, to enable the seamless collection of challans as well as data transfer.
- involves the detection of traffic violations through the CCTV network
- involves getting the registration number of the erring vehicle from applications like VAHAN (detecting the vehicle’s ownership details) and SARATHI (compilation of driving licenses).
- An e-challan is then generated with the relevant penalty amount and sent to the mobile number linked with the vehicle.
About VAHAN (detecting the vehicle’s ownership details) :
- VAHAN is a software that enables the processes at RTO/DTO/MLO/SDM involving Vehicle Registration, Fitness, Taxes, Permits & Enforcement to get computerized.
- The State Transport Department is governed by both Central Motor Vehicle Regulation (CMVR) and state-specific Motor Vehicle Regulation (State MVR).
VAHAN Services:
- Vehicle Registration.
- Permit
- Taxes
- Fitness
- Enforcement
About Virtual traffic courts:
- If a challan amount is not paid within 90 days, it will be automatically forwarded to a virtual court and proceedings will begin.
- The accused will receive a summons on their mobile phone.
- The virtual court aims to eliminate the physical presence of litigants.
- The accused can search for their case on the virtual court’s website and pay the fine.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
World Meteorological Organisation (WMO)

Why in News?
The World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has recently come up with a new Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure that aims to provide better ways of measuring planet-warming pollution and help inform policy choices.
About World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN).
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was founded in 1873.
- Established in 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the UN for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology and related geophysical sciences.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Currently it has a membership of 187 countries.
- Governance Structure:
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress, which consists of representatives of all members. It meets at least every four years to set general policy and adopt regulations.
- A 36-member Executive Council meets annually and implements policy.
- The Secretariat, headed by a secretary-generalappointed by the congress for a four-year term, serves as the administrative centre of the organization.
- Six regional associationsaddress problems peculiar to their regions.
- Eight technical commissions.
- Major Programmes:
- World Weather Watch: A system of satellites and telecommunication networks connecting land and sea sites for monitoring weather conditions.
- World Climate Programme: It monitors climate change, including global warming.
- Atmospheric Research and Environment Programme: Designed to promote research on issues such as ozone depletion.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Scrub typhus
Why in News?
Recent studies reported that combination therapy can save more lives in Scrub typhus.
About Scrub typhus :
- Scrub typhus is also known as bush typhus.
- It is a disease caused by a bacteria called Orientia tsutsugamushi.
- Scrub typhus is spread to people through bites of infected chiggers (larval mites).
- The most common symptoms of scrub typhus include fever, headache, body aches, and sometimes rash. .
- No vaccine is available to prevent scrub typhus.
About Doxycycline :
- Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in the treatment of some bacterial and parasitic infections such as bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis.
Source: THE HINDU
Sea horses
Why in News?
Recent reports show that ‘Hippocampus kelloggi’ or sea horse, could be migrating toward coastal Odisha due to fishing pressures.
About Sea horses :
- A seahorse is any of 46 species of small marine fish in the genus Hippocampus.
Characteristic feature :
- Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse,
- They also feature segmented bony armor, an upright posture, and a curled prehensile tail.
Habitat and Distribution across India :
- Seahorses are mainly found in shallow tropical and temperate saltwater throughout the world, from about 45°S to 45°N.
- They live in sheltered areas such as seagrass beds, estuaries, coral reefs, and mangroves.
- Seahorses range in size from 1.5 to 35.5 cm.
- They are named for their equine appearance, with bent necks and long-snouted heads, and distinctive trunks and tails.
- The species are distributed along the coasts of eight States and five Union Territories from Gujarat to Odisha, apart from Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Conservation status :
- IUCN status : Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix II
Source: THE HINDU
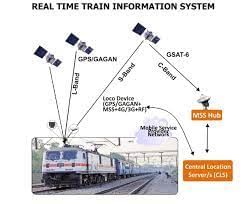
What is the Real Time Train Information System (RTIS) project?
Why in News?
The Indian Railways is collaborating with Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) under the Real Time Train Information System (RTIS) project.
About Real Time Train Information System (RTIS) project:
- RTIS devices that use satellite imagery are being installed on the trains to automatically acquire its “movement timing at the stations, including that of arrival and departure or run-through”.
- These timings get automatically plotted on the control chart of those trains in the Control Office Application (COA) system.
- The project is executed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- RTIS is developed in collaboration with ISRO. ISRO has launched GSAT satellites that have GAGAN payloads for tracking the movement of trains.
- Applications of RTIS:
- RTIS gives mid-section updates with a periodicity of 30 seconds.
- The Train Control can now track the location and speed of RTIS-enabled locomotives/train more closely, without any manual intervention.
- It allows passengers to get the real-time location or train running status of a train on their smartphone.
Source: The Hindu
Nallamala Forest
Why in News?
Nallamala forest is witnessing frequent forest fires due to rising temperatures, where the day temperature is almost touching 40 degrees Celsius.
About Nallamala Forest:
- It is one of the largest stretches of undisturbed forest in South India, apart from the Western Ghats.
- Location:
- It is spread over five districts in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- It is located in Nallamala Hills, which is a part of the Eastern Ghats.
- It lies south of the Krishna river.
- The forest has a good tiger population, and a part of the forest belongs to the Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, the largest tiger reserve in the country.
- Climate:
- It has a warm to hot climate throughout the year, with summer especially hot and winters mostly cool and dry.
- It gets most of its rain during the South West monsoon.
- Vegetation: Tropical dry deciduous.
- Flora: It harbors endemic species like Andrographis nallamalayana, Eriolaena lushingtonii, Crotalaria madurensis var, Dicliptera beddomei and premna hamitonii.
- Fauna: It is home to as many as 700 species of animals besides tigers, leopards, such as black buck, wild hog, peacock, pangolin, Indian Python and King Cobras and several rare bird species.
Source: Indian Express
Cybercrime in India
Why in News?
‘Cyber Warrior’ Teams and Help Desks to Combat Rising Cybercrime in Visakhapatnam.
- During the year 2022, Visakhapatnam had reported as many as 610 cybercrime cases, as against 316 during the year 2021, which is almost a 93% increase.
About Cyber Warriors:
- As part of the initiative, around 70 police personnel, including around 20 sub-inspectors and several ASIs will be undergoing virtual and offline training on various aspects of cybercrime.
- The cyber warriors team will be headed by a Sub-Inspector and staff.
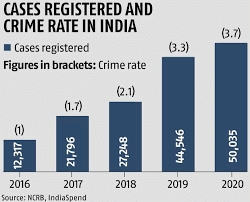
Cybercrime in India as per NCRB Report:
- India reported nearly 52,974 cybercrime incidents in 2021 which was an increase of nearly 6% from 2020.
- Telangana was the state with the highest number of cybercrime cases, accounting for more than 19% of the total.
- Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka saw a decrease in the number of cybercrime cases by 20% and 24%, respectively.
- The main challenges in prosecuting cybercrime cases are jurisdictional issues and difficulty in obtaining electronic logs from foreign service providers.
- Bengaluru had the highest number of cybercrime cases, but there has been a decline in cases over the past three years.
- Fraud was the most common motive for committing cybercrime, accounting for nearly 61% of cases.
- Karnataka recorded the highest number of cybercrimes against women in 2021, with 2,243 cases.
- The police pendency percentage in cybercrime cases improved from 3% in 2020 to 56.4% in 2021.
- The conviction ratio for cybercrime cases remains poor, and the charge-sheeting rate declined from 5% in 2020 to 33.8% in 2021.
- The court pendency percentage remained high, with 81.4% of total cases in trial in 2021 remaining. pending at the end of the year.
Challenges of cybercrime:
- Lack of Awareness: Many people in India are still not aware of the risks associated with cybercrime, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
- Rapidly Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape: Cybercrime is evolving at a rapid pace, with new threats emerging regularly. It is challenging for law enforcement agencies to keep up with these developments.
- Low Cybersecurity Awareness: A large number of individuals and organizations in India lack basic cybersecurity awareness, making them easy targets for cybercriminals.
- Increasing Use of Technology: With the widespread adoption of technology in India, more people are becoming vulnerable to cybercrime, making it even more challenging to combat.
- Lack of Cybercrime Laws: India has outdated cybercrime laws that are not in line with current threats. There is a need for updated laws to be enacted to combat the ever-changing cybercrime landscape.
- Limited Cybersecurity Infrastructure: India’s cybersecurity infrastructure is still developing, and many organizations do not have adequate security measures in place to protect their networks and data.
Need for controlling cybercrimes in India:
- Increasing Digitalization: With the growing digitalization of India, more people are using online services and technology, which has led to an increase in cybercrime incidents.
- National Security: Cybercrime can have severe consequences for national security, as it can compromise sensitive information and infrastructure, leading to potential political instability.
- Personal Privacy: Cybercrime can violate personal privacy, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other forms of cyberstalking.
- Economic Impact: Cybercrime has a significant economic impact on India, with losses amounting to billions of dollars annually. The country is also losing out on potential investments due to concerns about cybersecurity.
- Digital India Initiative: The Indian government’s Digital India initiative aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. However, cybercrime can hinder the initiative’s progress and undermine public trust in digital technologies.
- Cyber Security Jobs: With the growing importance of cybersecurity, there is a need for skilled professionals in the field, creating job opportunities in India.
Government Initiatives To Tackle Cyber Crime in India:
- Banning of unsafe apps: India had banned apps that posed a threat to security.
- India had banned many apps (mostly of Chinese origin), which were found to be unsafe for usage by Indian citizens.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): It operates as the national agency for tackling the country’s cybersecurity, and has helped in lowering the rate of cyber-attacks on government networks.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C):
- To act as a nodal point in the fight against cybercrime
- To prevent misuse of cyber space for furthering the cause of extremist and terrorist groups
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC):
- It is a central government establishment, formed to protect critical information of India, which has an enormous impact on national security, economic growth, or public healthcare.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: Cyber Swachhta Kendra helps users to analyse and keep their systems free of various viruses, bots/ malware, Trojans, etc.
- Launched in early 2017.
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat: It was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in 2018 with an aim to
- spread awareness about cybercrime and
- building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- The Cyber Warrior Police Force: It was organised on the lines of the Central Armed Police Force in 2018.
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (Amended in 2008): It is the main law for dealing with cybercrime and digital commerce in India.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) was created under Section 70A of IT Act 2000 to protect Cyberinfrastructure.
Way Forward:
Cybercrime is a crucial issue in India due to its economic, national security, and personal privacy implications. It is necessary to take proactive steps to combat cybercrime and create a safe and secure digital environment in the country. Therefore, Cyber warriors are significant especially when India ranks fifth globally in terms of the number of incidents reported.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 8th March 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of UPSC in India? |  |
| 2. What are the subjects covered under the GS-II and GS-III papers of the UPSC examination? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for the UPSC examination effectively? |  |
| 4. What are some common challenges faced by aspirants during the UPSC examination preparation? |  |
| 5. What are the career prospects after clearing the UPSC examination? |  |