UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 9th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Sagol Kangjei
Context
Recently Union Home Minister Inaugurated, 122-foot-tall statue of a polo player astride a Manipur Pony in Imphal. It is believed that Sagol Kangjei, the modern-day Polo game originated in Manipur.
About Sagol Kangjei:
- It is a sport indigenous to Manipur, in which players ride horses, specifically the Manipur Ponies, which are referenced in records dating back to the 14th century.
- The sport originated in Manipur and is associated with ancient manuscripts like Kangjeirol.
- Even festivals in Manipur such as Lai Haraoba Festival shows a play sequence in which Maibi (priestess) with a polo stick in hand goes out in search of a bride.
- There are no goalposts in traditional form as the players scores a point by hitting the ball out of the field.
About the Manipur Pony:
- The Manipur Pony is one of five recognised equine breeds of India, and has a powerful cultural significance for Manipuri society.
- The Marjing Polo Complex has been developed as a way to conserve the Manipur Pony.
- One source stated Tibetan ponies as its ancestors while another source stated its origin to be a cross between Mongolian wild horse and Arabian.
- In some manuscripts, it is referred to as Mangal-sa or Mongolian animal.
- In Manipuri mythology, the Manipuri pony was regarded to have descended from “Samadon Ayangba” the winged steed of Lord Margjing, one of the guardian deities of Manipur.
- The 17th Quinquennial Livestock Census 2003 had recorded 1,898 Manipur Ponies;
- The number fell to 1,101 in the 19th Quinquennial Livestock Census in 2012.
- In 2014, it was found difficult to count even 500.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
Arab Spring

Context
K.P. Fabian’s newly launched book, ‘The Arab Spring That Was and Wasn’t’ was seen in the news recently.
About Arab Spring:
- The Arab Spring was a series of pro-democracy uprisings that enveloped several largely Muslim countries, including Tunisia, Morocco, Syria, Libya, Egypt and Bahrain.
- The events in these nations generally began in the spring of 2011, which led to the name.
- However, the political and social impact of these popular uprisings remains significant today, years after many of them ended.
- When protests broke out in Tunisia in late 2010 and spread to other countries, there were hopes that the Arab world was in for massive changes.
- The expectation was that in countries where people rose, such as Tunisia, Egypt, Yemen, Libya, Bahrain and Syria, the old autocracies would be replaced with new democracies.
- But Tunisia is the only country where the revolutionaries outwitted the counter-revolutionaries.
- They overthrew Zine El Abidine Ben Ali’s dictatorship, and the country transitioned to a multi-party democracy.
- But except Tunisia, the country-specific stories of the Arab uprising were tragic.
Source: Indian Express
Sunni Dam Hydro Electric Project
Context
Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently has approved an investment of Rs 2,614 crore for 382 MW Sunni Dam Hydro Electric Project in Shimla and Mandi districts.
About the project:
- It is a run of the river type development proposed to harness the hydel potential of river Satluj.
- It aims to provide various benefits to local suppliers/ local enterprises/MSMEs.
- It is part of the Luhri project, which is designed to comprise three hydropower dams;
- Luhri Stage-I (210 MW),
- Luhri Stage-II (163 MW), and
- Sunni dam (382 MW).
- It will be governed by Indus water Treaty signed between India and Pakistan in 1960.
- This is because the project lies in Satluj basin, which is a part of Indus Basin.
- Its objective to produce as much energy as possible, with minimum cost and fewer negative impacts on the environment.
Benefits of the project:
- It will reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 1.1 Million tons annually
- Encourage entrepreneurship opportunities
- Promote employment and socio-economic development of the region.
- Aid in fulfilling peak electricity demand and the growing energy deficit in the Northern Region.
Source: NewsOnAir
GS-III
Cloud Forest Bond
Context
According to a new report, Cloud Forest Assets Financing is a Valuable Nature-Based Solution released by Earth Security – a global nature-based asset management advisory firm.
- The report is aimed at three stakeholders – national governments, non-profits and communities.
About cloud forests:
- Cloud Forests are montane rainforests
- They refer to the vegetation of tropical mountainous regions where there is heavy rainfall and persistent condensation resulting from the cooling of the moisture being pushed upwards by the mountains.
- They are usually characterized by a persistent, frequent and seasonal low-lying layer of mist and cloud cover usually at the canopy level.
- Cloud forests are rare since the exceptional conditions that create these forests are only found in tropical areas with tall mountains.
- Due to their unique characteristics, cloud forests are usually found along the sides of the mountains at elevations of between 3000 and 10000 feet but as low as 1650 feet in the Tropics between coordinates 23°N and 23°S.
- Only 1% of the global woodlands are considered as cloud forests following a decline from 11% in the 1970s due to interferences by human activities and global warming.
- Just 25 countries hold 90 per cent of the world’s cloud forests
- These twenty-five countries are Indonesia, Tanzania, Democratic Republic of Congo, Colombia, Peru, Venezuela, Mexico, Papua New Guinea, Brazil, Ethiopia, Ecuador, Cameroon, Bolivia, China, Laos, Kenya, Malaysia, Angola, Uganda, Madagascar, Philippines, Gabon, Vietnam, Republic of Congo and Myanmar.
Significance:
- Their hydrological function is of existential value to millions of people living downstream.
- They capture moisture from the air, providing fresh and clean water to people and industries below.
- These 25 countries have around 979 hydropower dams and around half of them use water from the cloud forest.
- The total value of hydroelectricity that currently depends on cloud-affected forests across these 25 countries is estimated to be $118 billion over 10 years. This will increase to $246 billion when new hydropower plants that are being developed become operational.
Cloud forest bonds:
- Cloud Forest Bond will incentivise governments to protect their cloud forests — forests that are on top tropical mountains, largely shrouded in mist.
- Cloud forest bonds will provide governments with financial actors like philanthropy, public finance and private investment to capture the economic value of the ecosystem services of the cloud forests.
- Such a tool will encourage carbon storage and provide funding to set up sovereign-level carbon finance schemes as well as payments for ecosystem services
- The report proposes to mobilise financing for cloud forest protection through payments schemes under which hydropower projects and other industrial water users benefiting from cloud forests pay for this service.
- While these investments must conform to rigorous social and environmental impact safeguards, ensuring the protection of these forests upstream should be included as a risk management priority for investors, project developers and policy-makers.
- The Cloud Forest Bonds will allow the developing countries to improve their debt position and fund the creation of new, long-term income streams from services provided by nature.
- These bonds can be in the form of new bond issuances, debt-swaps and results-based financing instruments, which are matched to the circumstances of each of the twenty-five countries.
- Forest protection is highest where land ownership rights of indigenous peoples and local communities are fully recognised and exercised – by providing a fair share of the benefits from forest carbon and water revenues
- A Cloud Forest 25 (CF25) Investment Initiative to establish a collective of all 25 countries that have high cloud forest to accelerate the international application of market templates and aggregate the blended finance and data needed to achieve solutions at scale.
Source: DTE
Dwarf boa
Context
A new species of dwarf boa has been discovered in the upper Amazon basin, reported a paper published in the journal European Journal of Taxonomy.
Dwarf Boa:
- The snake from the Tropidophiidae family was found in the cloud forest in northeastern Ecuador and was up to 20 centimetres long.
- Tropidophis cacuangoae can be identified from other reptiles in the same genus based on its external features and bone structure.
- Its colouring is primarily light brown with darker brown or black blotches — similar to a boa constrictor.
- The species inhabits eastern tropical piedmont and lower evergreen montane forests in the Amazon tropical rainforest biome
- It is suspected to be an Ecuadorian endemic.
- Both specimens were found within 50 kilometres of each other — Colonso Chalupas national reserve and in the private Sumak Kawsay park.
- The species is unusual for having a “vestigial pelvis”, which is characteristic of primitive snakes.
- This could be evidence that snakes descended from lizards that lost their limbs over millions of years.
- The snake’s name honours Dolores Cacuango, an early 20th-century pioneer in the fight for indigenous and farmers’ rights in Ecuador.
- The discovery of T cacuangoae demonstrates that small and cryptic vertebrates can undergo large periods of time without being detected.
- The discovery of this new species highlights a critical need to accelerate research in remote areas where information gaps remain but are suspected of harbouring high biodiversity and are severely threatened by human impacts
Source: DTE
Over-application of fertilisers in India: How to correct the worsening nutrient imbalance?
Context
According to the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers, urea and di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) sales have increased recently, regardless of the rise or fall in the global fertiliser prices.
- Global fertiliser prices skyrocketed in the run-up to and after Russia's invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, but have since dropped significantly.
- The fertiliser industry in India:
- Fertilisers (organic/inorganic) are substances that provide one or more of the chemicals required for plant growth.
- As per industry experts, out of the 16 elements necessary for plant growth, 9 elements are required in large quantities (major elements = primary and secondary), while the other 7 are needed in smaller amounts (minor elements).
- Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are known as primary plant nutrients;
- Calcium, magnesium and sulphur, as secondary nutrients;
- Iron, manganese, copper, zinc, boron, molybdenum and chlorine as trace elements or micro-nutrients.
- The primary objective of fertiliser industry is to ensure the inflow of both primary and secondary elements as are necessary for crop production in the desired quantities.
- However, the sharp increase in the overall fertiliser requirement in the country during the last 5 years, have resulted in soil nutrient imbalances.
- Inorganic or Chemical Fertiliser:
- These fertilisers are usually derived from chemical compounds like potassium chloride, ammonium phosphates and ammonium nitrate.
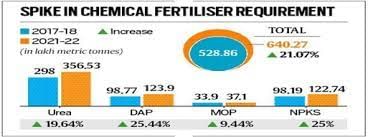
- The requirement of 4 most used chemical fertilisers (Urea, DAP, MOP - Muriate of potash, NPKS - Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium), in the country increased by 21% in 2021-22 in comparison to 2017-18.
- Urea has 46% nitrogen (N), while DAP contains 46% phosphorus (P) plus 18% N and MOP has 60% potassium (K).
- Reasons for increased urea and DAP consumption:
- High subsidy on urea, DAP is a less expensive alternative.
- Thus, price determines the choice of fertilisers, rather than NPKS or other macro and micro nutrients in the fertiliser.
- Easing global prices of fertilisers - The opportunity for India:
- To significantly improve overall availability: This will reduce imports of both finished fertilisers and inputs for domestic manufacture.
- Reduction in the Centre’s fertiliser subsidy outgo: For 2022-23, the government had budgeted Rs 105,222.32 crore for 2022-23.
- However, the actual outgo could touch Rs 230,000 crore, over and above the Rs 153,658.11 crore spent in the previous fiscal.
- Assuming no new geopolitics-induced supply shocks and the government not allowing retail prices to farmers to rise, one can expect the subsidy bill to be within Rs 140,000-150,000 crore in the fiscal beginning April 2023.
- Some initiatives to promote balanced fertilizer use in India:
- Nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) regime (since 2010) in fertilisers: This is to discourage farmers from applying too much urea, DAP and MOP, by moving away from product-specific subsidy, to one where the government fixed a per-kg NBS rate for each nutrient (N, P, K and S).
- Coating of urea with neem oil compulsory from 2015-16: This to check illegal diversion of the heavily-subsidised fertiliser for non-agricultural uses, including by plywood, dye, cattle feed and synthetic milk makers.
- Neem oil also acted as a mild nitrification inhibitor, allowing a more gradual release of nitrogen - increasing nitrogen use efficiency.
- The challenges towards promoting balanced fertilizer use in India:
- Imbalanced application: Since 2017-18, urea consumption has risen and the consumption of NPKS complexes in 2019-20 was lower than in 2011-12.
- Crop yields would suffer if the current NPK ratio (of 13:5:1) was used instead of the ideal 4:2:1.
- Worsening of nutrition imbalances: Consumption of both urea and DAP has shot up, on the other hand, sales of NPKS complexes and MOP have plunged.
- Because of the lack of a complete nutrient-mix, it will have a negative impact on plant and human health.
- Imbalanced application: Since 2017-18, urea consumption has risen and the consumption of NPKS complexes in 2019-20 was lower than in 2011-12.
- The road ahead to prevent DAP becoming the next urea:
- Restrict DAP use to rice and wheat. All other crops can meet their P requirement through NPKS complexes.
- Raise single sulphur phosphate’s (SSP) acceptance by permitting sale only in granular, not powdered, form. SSP powder is prone to adulteration with gypsum or clay.
- The ultimate aim should be to cap urea, DAP and MOP consumption.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 9th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of daily current affairs in the UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 3. What are the frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. How can one effectively prepare for the General Studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. What are some recommended sources to stay updated with daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |




















