UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
How Röntgen accidentally discovered x-rays & changed the world
Source: The Indian Express
Why in the News?
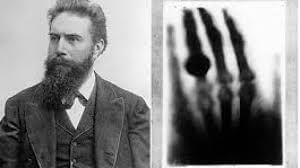
On the evening of November 8, 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen was conducting experiments in his laboratory at the University of Würzburg in Germany when he made an unusual discovery. While experimenting with cathode rays in a glass vacuum tube, Röntgen noticed a fluorescent screen glowing at a distance, despite being too far to be affected by the rays he was studying. Intrigued by this unexpected glow, he wondered if this mysterious ray could penetrate organic materials, so he experimented by photographing his wife’s hand, capturing her bones and ring. This was the world’s first recorded X-ray image of the human body. Röntgen documented his findings in an article titled “On a new kind of rays,” in 1895 which was published by introducing “X-rays” to the scientific community.
About
- Revolution in Diagnostic Medicine: X-rays quickly became integral to medical diagnostics, allowing physicians to view the internal structures of the human body without the need for invasive surgery. This advancement was particularly significant in fields like orthopedics and internal medicine.
- Surgical Advancements: By February 1896, British physician Major John Hall-Edwards utilized X-rays to assist in surgical procedures. Within a short span, military applications emerged using X-rays to locate bullet wounds and diagnose fractures, marking a significant development in trauma care.
- Development of Radiology: Röntgen’s discovery laid the groundwork for the field of radiology, leading to further innovations such as CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and other essential imaging technologies in modern medicine.
- Radiation Safety and Awareness: Initially, the use of X-rays was widespread, even for non-medical purposes (like fitting shoes), with little understanding of the potential health risks. It was only after early reports of radiation burns and subsequent research in the early 20th century that the dangers of radiation exposure became recognized, prompting the establishment of safety protocols.
- Ongoing Safety Protocols: Today, radiation safety is a fundamental aspect of radiology practices. Advances in technology and regulatory standards have significantly reduced exposure risks, ensuring that X-rays remain safe for both patients and healthcare professionals while continuing to provide essential health benefits.
- Public Health and Preventive Care: The ability to detect diseases, fractures, and internal injuries non-invasively has been crucial for preventive healthcare, enabling early diagnosis and treatment. This capability has greatly improved patient survival rates and overall quality of care, establishing diagnostic imaging as a vital component of modern public health.
- Limited X-ray Equipment: Rural Community Health Centres (CHCs) in India often face a shortage of X-ray machines, with only 68% of available units operational, primarily due to high operational costs and a lack of trained technicians.
- Maintenance and Operational Delays: Even when X-ray machines are available, many remain non-functional due to delays in installation and inadequate maintenance, as imaging services are not prioritized in CHC guidelines.
- Access and Specialist Shortages: Patients in rural areas often travel long distances to access imaging services, compounded by a concentration of radiologists in urban settings, which limits timely diagnostic interpretations.
- Strengthen Infrastructure and Access: Enhance the availability and functionality of X-ray machines in rural areas by improving maintenance, and invest in portable and mobile X-ray units to provide diagnostic services directly to underserved communities.
- Telemedicine and Remote Diagnostics: Expand telemedicine platforms like ‘XraySetu’, which allows healthcare workers in rural regions to share X-ray images for remote analysis by radiologists, thereby improving diagnostic capabilities without necessitating long-distance travel for patients.
GS2/Governance
Competition Commission of India
Source: The Economic Times

Why in news?
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has indicated that prominent food delivery platforms in India are violating antitrust and competition regulations by favoring specific restaurants on their services.
About
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory authority established in March 2009 under the Competition Act of 2002.
- Its primary objective is to foster and maintain fair competition within the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and enhancing consumer welfare.
- Key priorities include eliminating practices that negatively impact competition, promoting sustained competition, safeguarding consumer interests, and ensuring freedom of trade in Indian markets.
Mandate
- The CCI is tasked with enforcing the provisions of the Competition Act, 2002, which prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by businesses.
- It regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that may adversely affect competition, requiring certain deals to receive CCI approval prior to completion.
- The Commission monitors large enterprises to prevent them from abusing their dominant status, such as controlling supply chains, imposing inflated purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that could jeopardize smaller businesses.
Composition
- The CCI consists of a quasi-judicial body comprising one chairperson and six additional members.
- All members are appointed by the Central Government of India.
Headquarters
- The headquarters of the Competition Commission of India is located in New Delhi.
GS2/Polity
Test for Determining Minority Educational Institution (MEI) Status
Source: The Indian Express

Why in News?
A 7-judge bench of the Supreme Court, in a narrow 4:3 majority decision, has set aside a 1967 ruling from a 5-judge bench regarding the status of Aligarh Muslim University (AMU) as a minority institution. The Supreme Court has established comprehensive criteria for evaluating the minority character of educational institutions, which will guide a regular bench in resolving the long-standing debate surrounding AMU's status.
Background of the AMU Minority Status Case
- AMU, originally established as the Muhammadan Anglo-Oriental (MAO) College in 1877, transitioned into a university in 1920 through legislation.
- The government contended that this legislative transformation altered its minority status, leading to significant legal disputes.
- The Azeez Basha case in 1967 ruled that AMU was not formed by the Muslim community but rather by a central legislative act, thus disqualifying it from being recognized as a minority institution under Article 30 of the Constitution.
- Subsequent developments included an amendment in 1981 stating that AMU was established for the educational upliftment of the Muslim community, and the introduction of a 50% reservation for Muslims in medical postgraduate courses in 2005.
- In 2006, the Allahabad High Court annulled the 1981 amendment and the reservation policy, reaffirming AMU's non-minority status.
- The Supreme Court referred the matter to a larger bench in 2019, leading to the recent judgement.
Constitutional Protections and Benefits of MEIs
- Article 30(1) guarantees minorities the right to establish and manage educational institutions.
- Article 15(5) provides minority institutions with special privileges, including autonomy in admissions and hiring practices, as well as exemption from quotas for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- Benefits of minority status allow institutions to reserve up to 50% of seats for minority students, promoting cultural and linguistic diversity.
SC’s Criteria for Determining MEI Status
- The Supreme Court has outlined several criteria for determining the minority status of educational institutions:
- The primary objective of the institution should be to preserve minority languages and cultures.
- Minority institutions can include non-minority students without losing their minority status.
- Providing secular education does not negate their minority character.
- Government-funded institutions cannot mandate religious instruction, and those fully funded by the state cannot provide it.
Two-Fold Test to Establish Minority Status
The Supreme Court has proposed a two-step test to evaluate whether an institution possesses minority character:
- Establishment: Courts must assess the origins and purposes behind the institution's creation, determining the extent of community involvement in its establishment.
- Evidence for establishment may include documentation such as letters, funding records, and communications that confirm the institution’s primary aim was to benefit the minority community.
- Administration: While minority educational institutions are not required to appoint exclusively minority individuals to administrative positions, their administrative structure should reflect minority interests.
- For institutions established before 1950, courts must evaluate whether their administration upheld minority interests as of the Constitution's adoption.
Implications of SC Determining MEI Status Test
- This decision confers administrative autonomy, which is significant for institutions like St. Stephen's College, currently involved in legal disputes with Delhi University regarding administrative appointments.
- The ruling reignites discussions surrounding the minority status of Jamia Millia Islamia (JMI), with implications for JMI’s case closely tied to AMU’s legal standing.
- Legal representatives for JMI indicate that the Supreme Court's ruling on AMU's status will likely influence similar principles applied to JMI.
Conclusion
- The Supreme Court's ruling brings AMU closer to potentially securing its minority status by clarifying the criteria for minority character as defined in Article 30.
- However, the ultimate determination of AMU's status will require further judicial review.
- This landmark ruling establishes a significant precedent for minority educational institutions, safeguarding minority rights within India's educational landscape while ensuring adherence to constitutional guidelines.
GS3/Environment
Cyanobacteria
Source: Lives on Earth
Why in News?
Researchers have discovered a mutant form of cyanobacteria, named Chonkus, which has the potential to combat climate change.
About Cyanobacteria
- Cyanobacteria, commonly referred to as blue-green algae, are microscopic organisms that exist in a variety of water environments.
- These single-celled organisms thrive in freshwater, brackish water (a mix of salt and fresh water), and marine settings.
- They utilize sunlight to produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- In conditions that are warm and rich in nutrients—particularly phosphorus and nitrogen—cyanobacteria can reproduce rapidly, leading to blooms that cover the surface of the water.
- Such blooms typically occur in warm, slow-moving waters enriched by nutrients from agricultural runoff or septic system discharges.
- Cyanobacteria require nutrients to survive, and while blooms can happen at any season, they are most prevalent during late summer or early fall.
Key Facts About Chonkus
- The mutant cyanobacteria Chonkus was found in the shallow, sunlit waters around Italy’s Vulcano Island.
- This location is significant due to the presence of volcanic gas-rich groundwater that seeps into the ocean.
- Chonkus has a remarkable ability to absorb a significantly greater amount of carbon dioxide compared to typical cyanobacteria found in ocean waters.
Conclusion
The discovery of Chonkus represents an exciting advancement in the search for natural solutions to mitigate climate change effects.
GS3/Environment
Taking stock of the International Solar Alliance
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
India, in collaboration with France, founded the International Solar Alliance (ISA) during the 2015 Paris Climate Conference to foster solar energy use, especially in developing nations. This initiative positioned India at the forefront of global clean energy leadership. Since its inception, the ISA has expanded to include over 110 member countries. However, its success in enhancing solar energy adoption in developing regions has been limited.
Background - Global Solar Energy Imbalance and the Role of the ISA
- Solar energy is crucial for the global transition to sustainable energy necessary to mitigate climate change, being the fastest-growing renewable source and the least expensive in sunny areas.
- Forecasts suggest that solar capacity must significantly increase to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Deployment of solar energy is uneven globally; for instance, China alone contributes 43% of the world’s solar capacity, while the top 10 countries account for over 95% of installations.
- Africa, where most of the 745 million people without electricity reside, sees less than 2% of new solar installations.
- Moreover, over 80% of solar manufacturing is concentrated in China, hindering rapid expansion in smaller markets. The ISA was established to address and rectify this disparity.
About
- The ISA operates as a treaty-based intergovernmental organization.
- It was conceived as a coalition of countries rich in solar resources, primarily those situated between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, to meet their unique energy needs.
- Jointly launched by India and France during COP 21 (held in Paris) in 2015, the Paris Declaration established the ISA.
- The organization aims to create a global market system that harnesses solar power and promotes clean energy solutions.
Headquarters
- The ISA is headquartered in Gurugram, India.
Objective
- The primary goal of the ISA is to collectively address significant challenges to scaling solar energy according to the needs of its member countries.
- To achieve this, the ISA aims to facilitate future solar generation, storage, and technology advancements, targeting to mobilize over USD 1000 billion by 2030.
Performance of ISA
- Designed primarily as a facilitator, the ISA does not directly develop solar projects.
- It seeks to assist countries in overcoming financial, technological, and regulatory obstacles to enhance solar energy deployment, especially in regions with limited energy access.
- Despite nearly nine years since its establishment, the ISA has witnessed limited impact, with no operational projects to date.
- The first ISA-supported project, a 60 MW solar plant in Cuba, remains in development, with other countries in Africa and Latin America also preparing similar initiatives.
ISA's Limited Impact Amid Global Solar Growth Concentration
- Even with a global surge in solar energy, marked by an average capacity increase of 20% annually over the past five years and a 30% rise in 2023 alone, the ISA has struggled to promote widespread deployment.
- According to the ISA's World Solar Market Report 2024, China represented 62% (216 GW) of the 345 GW of new solar capacity added in 2023.
- More than 80% of solar investments are concentrated in developed nations, China, and large developing countries like India, limiting the ISA's projected impact on smaller or less developed markets.
- The ISA has concentrated efforts on addressing significant entry barriers in smaller developing nations, particularly in Africa, where there is a lack of experience with large-scale solar projects and local developers.
- Foreign investments require stable policies and regulatory frameworks, which the ISA is working to establish in collaboration with governments and local institutions.
- Key initiatives include developing regulatory frameworks, drafting power purchase agreements, and setting up STAR (Solar Technology and Applications Resource) centers to enhance local expertise.
- The ISA has set a target to deploy 1,000 GW of solar power and attract $1 trillion in investments by 2030.
- Beyond promoting solar energy, the ISA serves as a strategic initiative for India’s outreach to the Global South, with a strong emphasis on Africa.
- Although it is an intergovernmental organization, the ISA is widely perceived as an Indian initiative, given its headquarters in New Delhi, Indian financial backing, and Indian leadership of its general assembly, which will continue until at least 2026.
- Prime Minister Modi has emphasized ISA’s role as a symbol of India’s leadership in supporting the Global South.
- Nevertheless, the ISA's impact has been constrained by factors such as underfunding, staffing shortages, and difficulties in generating interest in solar energy among energy-deprived nations.
- This underutilization hampers India's ambitions to lead and represent these countries on the global stage.
GS3/Science and Technology
Sagarmala Parikrama
Source: SSB Crack

Why in News?
Recently, an autonomous surface vessel built by Sagar Defence Engineering completed a 1,500-km voyage from Mumbai to Thoothukudi without human intervention.
About
- Sagarmala Parikrama's journey was virtually inaugurated by the Union Defence Minister on October 29 during the Swavlamban event.
- The initiative is backed by the Indian Navy’s Naval Innovation and Indigenisation Organisation (NIIO), Technology Development Acceleration Cell (TDAC), and Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX).
- This project aligns with global advancements in autonomous surface and underwater systems, showcasing transformative applications in both military and civilian domains.
- This pioneering journey underscores India’s expanding capabilities in autonomous maritime technology, marking a crucial milestone in the development of advanced unmanned systems for national security.
Applications
- The initiative sets a precedent for future utilization of autonomous vessels in essential sea routes, coastal monitoring, and anti-piracy missions.
- This technology enhances the operational scope of the Indian Navy.
Key facts about the Naval Innovation and Indigenisation Organisation
- This organization is structured in a three-tiered manner and was established by the Defence Ministry.
- The Naval Technology Acceleration Council (N-TAC) combines innovation and indigenisation, providing top-level directives.
- A working group under the N-TAC is tasked with executing various projects.
- The Technology Development Acceleration Cell (TDAC) has also been formed to expedite the incorporation of emerging disruptive technologies.
GS2/International Relations
Key facts about Zambia
Source: Intrepid Travel

Why in News?
Recently, India-Zambia held the 6th Session of the Joint Permanent Commission in Lusaka.
About Zambia
- Zambia is a landlocked nation located in south-central Africa.
- The country lies on a high plateau and derives its name from the Zambezi River, which flows through most of its territory.
Bordering Countries
- To the north, Zambia shares a border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- To the south, it is bordered by Zimbabwe and Botswana.
- Tanzania is located to the northeast of Zambia.
- Malawi lies to the west, while Mozambique is found to the southeast.
- Angola is situated to the west of Zambia, and Namibia is to the southwest.
Economy
- The economy of Zambia is primarily reliant on mining, especially copper extraction.
- The majority of the Zambian population communicates using Bantu languages from the Niger-Congo language family.
Major Waterfall
- Victoria Falls, located on the Zambezi River, is one of the most famous waterfalls in the world.
Lake Kariba
- Zambia is home to Lake Kariba, recognized as the largest artificial reservoir globally by volume, formed by the construction of the Kariba Dam on the Zambezi River.
Capital City
- The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka.
GS2/Polity
Bibek Debroy Committee on Reforms in Indian Railways
Source: TOI

Why in news?
The Bibek Debroy Committee was established in 2014 with the objective of proposing comprehensive reforms to enhance the operational efficiency, financial viability, and competitiveness of Indian Railways. The committee, led by a prominent economist, published its influential report in 2015, which identified various challenges within Indian Railways and suggested extensive reforms across various domains.
Introduction (About Bibek Debroy Committee)
- The Bibek Debroy Committee was formed to recommend sweeping reforms for Indian Railways.
- Its focus was on improving operational efficiency and financial sustainability.
- The committee highlighted problems in decision-making, financial management, human resources, and the need for liberalization.
Key Recommendations of the Committee
Empowerment of Railway Officers
- The committee advocated for enhanced decision-making authority for field officers, especially General Managers (GMs) and Divisional Railway Managers (DRMs).
- As a result, GMs and DRMs were given more autonomy to make independent decisions and manage divisions effectively.
Establishment of an Independent Regulator
- A key recommendation was the creation of an independent regulatory body to ensure fair competition and oversee pricing.
- The Rail Development Authority (RDA) was established in 2017 to provide guidance on service pricing and encourage competition.
Liberalization of Indian Railways
- The committee proposed allowing private operators to enhance competition and improve service efficiency.
- Despite this, full implementation faced challenges due to opposition from unions and political entities.
- Currently, private participation is limited to select Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects, mainly in freight services.
Redesignation of Railway Board Chairman as CEO
- The committee recommended that the Railway Board Chairman be designated as Chief Executive Officer (CEO) to streamline decision-making processes.
- This change was enacted in 2020, transitioning the Board into a more corporate-style entity.
Offloading Non-Core Services
- The committee suggested that Indian Railways should focus on its primary function of train operations while outsourcing non-core services.
- This would allow for better operational focus and efficiency.
Reforms in Accounting System
- A significant overhaul of the accounting system was recommended, moving from cash-based to accrual-based accounting.
- This change aims to enhance transparency and financial reporting.
Safety Measures and Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK)
- In response to safety recommendations, the Ministry of Railways established the RRSK in 2017 with a fund of ₹1 lakh crore for safety upgrades.
- In the 2022-23 budget, the government allocated an additional ₹45,000 crore for this initiative.
Integration of Advanced Technology
- The committee recommended the adoption of advanced technologies to modernize railway operations, including high-speed train initiatives and safety systems.
- The establishment of Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya aims to enhance skill development in rail technology.
Implementation Status
Out of the 40 recommendations made by the committee
- 19 recommendations were fully accepted, including the redesignation of the Railway Board Chairman as CEO and accounting reforms.
- 7 recommendations were partially accepted, such as the empowerment of DRMs.
- 14 recommendations were rejected primarily due to opposition from unions or political factors, especially concerning liberalization.
Conclusion
- The recommendations of the Bibek Debroy Committee have laid a crucial foundation for the modernization and financial sustainability of Indian Railways.
- While significant progress has been made with various structural changes and safety initiatives, several challenges still hinder full implementation of all recommendations.
- The journey towards a completely modernized Indian Railways continues to evolve with ongoing efforts and reforms.
GS2/International Relations
Places in News: Loaita Island
Source: TOI

Why in the news?
Philippine forces conducted combat exercises in the South China Sea to practice retaking the disputed waters.
About
- Loaita Island, also referred to as Kota Island, spans an area of 6.45 hectares.
- It ranks as the 10th largest among the naturally occurring Spratly Islands.
- The island is administered by the Philippines as part of Kalayaan, Palawan.
- China, Taiwan, and Vietnam also lay claim to Loaita Island.
- Loaita Island is adjacent to the Loaita Bank, which comprises shoals and reefs.
- The western side of the island features calcarenite outcrops that are visible during low tide.
- The island's vegetation includes mangrove bushes, coconut palms, and various small trees.
- A sovereignty stele was erected on Loaita Island by South Vietnam on May 22, 1963, asserting its claim.
- The Philippines has maintained a military presence on the island since 1968.
- Minimal structures exist on the island, primarily serving as shelters for stationed soldiers.
What is the South China Sea Dispute?
- The South China Sea dispute involves territorial claims and sovereignty over maritime areas, particularly the Paracel and Spratly islands.
- Multiple countries, including China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Malaysia, and Brunei, have overlapping claims in this region.
- In addition to the islands, there are numerous rocky outcrops, atolls, sandbanks, and reefs, such as the Scarborough Shoal.
- China asserts the largest claim over the area, which is outlined by the "nine-dash line" that extends hundreds of miles from Hainan province.
- Beijing argues that its rights to the region date back centuries when the Paracel and Spratly islands were considered integral to Chinese territory.
GS3/Environment
Horn of Africa
Source: Over 65 Million People Food Insecure In Horn Of Africa: UN And IGAD Report
Why in News?
At least 65 million individuals in the Horn of Africa are facing food insecurity, as highlighted by a joint report released today by the United Nations and the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), which is a regional bloc in East Africa.
About
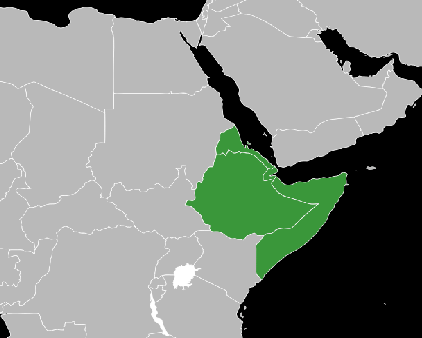
- The Horn of Africa is the easternmost part of the African continent.
- It includes the nations of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region is also referred to as the Somali peninsula.
- The landscape features diverse areas such as:
- The highlands of the Ethiopian Plateau
- The arid Ogaden Desert
- The coastal regions of Eritrea and Somalia
- It is inhabited by various ethnic groups, including the Amhara, Tigray, Oromo, and Somali peoples.
Coastal Line
- The coastlines of the Horn of Africa are bordered by the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden, and the Indian Ocean.
- This region has historically maintained contact with the Arabian Peninsula and southwestern Asia.
- The Horn of Africa is divided from the Arabian Peninsula by the Bab el-Mandeb Strait, which serves as the connection between the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden.
Challenges Faced
- The Horn of Africa is currently grappling with significant food insecurity.
- This situation has been exacerbated by various factors, including:
- The impacts of climate change
- Ongoing conflicts
- Key public health challenges in the region include malnutrition and outbreaks of cholera.
GS1/History & Culture
Bidar Fort
Source: The Economic Times

Why in News?
The Karnataka Waqf Board has identified 17 monuments within the historic Bidar Fort as its own property. These include the 16-Khamba Mosque (Sixteen Pillar Mosque) and 14 tombs of Bahmani rulers and their family members, including Ahmed Shah-IV and Allauddin Hassan Khan, among others.
About Bidar Fort
- Location: Bidar City on the northern plateau of Karnataka, India.
- Historical Significance: The fort has a history spanning over 500 years, beginning with the Western Chalukya dynasty.
- Capital: Sultan Ahmed Shah Wali of the Bahmani dynasty established Bidar as his capital in 1430 and transformed it into a formidable citadel.
Architectural Features
- Material: Constructed from trap rock, with stone and mortar used for the walls.
- Design Elements: Notable for Islamic and Persian architectural features.
- Entrances: The fort has seven main entrances.
- Bastions: Contains 37 octagonal bastions equipped with metal-shielded cannons.
- Structures: Includes mosques, mahals, and over 30 Islamic monuments.
- Entrance Gate: Features a lofty dome painted in vibrant colors.
About the Bahmani Kingdom
- Foundation: The Bahmani Kingdom was founded in 1347 when Ala-ud-din Hassan Bahman Shah revolted against Muhammad Bin Tughlaq of the Delhi Sultanate.
- Significance: This marked the establishment of the first independent Islamic kingdom in South India.
- Territory: The kingdom encompassed regions that are now part of Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Capital Shift: Initially established in Gulbarga (Ahsanabad), the capital was later moved to Bidar.
- Sultans: The kingdom had a total of 14 sultans, with notable rulers including Alauddin Bahman Shah, Muhammad Shah I, and Firoz Shah.
- Key Statesman: Mahmud Gawan served as Prime Minister for 23 years (1458-1481) and played a crucial role in expanding the kingdom's territories, including reclaiming Goa from the Vijayanagar Empire.
- Decline: The Bahmani Kingdom's decline began around 1518 following the defeat of its last ruler by Krishnadeva Raya of the Vijayanagar Empire, leading to the end of Bahmani rule in the region.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 9th November 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. How did Röntgen accidentally discover X-rays? |  |
| 2. What impact did the discovery of X-rays have on medicine? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of X-rays beyond medicine? |  |
| 4. What safety concerns are associated with X-ray usage? |  |
| 5. How did the discovery of X-rays change the field of physics? |  |





















