UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 29, 2022 | Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT PDF Download
GS-I
Lala Lajpat Rai

Context
Recently, the Prime Minister paid tribute to Lala Lajpat Rai on his Jayanti.
- Lala Lajpat Rai’s birth anniversary is celebrated on 28th of january every year.
About Lala Lajpat Rai
- He was born on 28th January, 1865 in a small village named Dhudike in Punjab’s Ferozepur district
- Lala Lajpat Rai was one of the greatest freedom fighters of India.
- He was also called ‘Punjab Kesari’ and 'Lion of Punjab'.
- He studied law at the Government College, Lahore.
- Was influenced by Swami Dayananda Saraswati and joined the Arya Samaj in Lahore.
- He believed that the ideals in Hinduism combined with nationalism will lead to the establishment of a secular state.
- Along with Bipin Chandra Pal and Bal Gangadhar Tilak, he formed the Lal-Bal-Pal trio of extremist leaders.
- He was also involved with the Hindu Mahasabha.
- He fought against untouchability.
About his Contributions
- Political
- He joined the Indian National Congress (INC) and participated in many political agitations in Punjab.
- For his political agitation, he was deported to Burma without trial in 1907 but returned after a few months because of lack of evidence.
- He was opposed to the partition of Bengal.
- He founded the Home Rule League of America in 1917 in New York. In the US, he worked to get moral support for the Indian independence movement from the international community.
- He was also elected President of the All India Trade Union Congress.
- He supported the non-cooperation movement of Gandhi at the Nagpur session of the Congress in 1920.
- He protested against the Rowlatt Act and the Jallianwala Bagh massacre that followed.
- He was elected deputy leader of the Central Legislative Assembly in 1926.
- In 1928, he moved a resolution in the assembly refusing cooperation with the Simon Commission since the Commission had no Indian members.
- Social
- He founded Hindu Relief movement in 1897 to provide help to the famine -stricken people and thus prevent them falling into the clutches of the missionaries.
- He founded the Servants of People Society in 1921.
- Literary
- His important literary works include Young India, England’s Debt to India, Evolution of Japan, India’s Will to Freedom, Message of the Bhagavad Gita, Political Future of India, Problem of National Education in India, The Depressed Glasses, and the travelogue ‘United States of America’.
- Institutional
- He founded several institutions and organizations such as Hisar Bar Council, Hisar Arya Samaj, Hisar Congress, National DAV Managing Committee.
- He was the editor of the Arya Gazette, which he had founded.
- He co-founded the Punjab National Bank in 1894.
About his Death
- In 1928, he was leading a silent protest against the Simon Commission in Lahore when he was brutally lathi-charged by Superintendent of Police, James Scott.
- He died of injuries sustained a few weeks later.
Padma Awards 2022

Context
General Bipin Rawat, first Chief of Defence Staff who died in an air crash recently, and former Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Kalyan Singh who headed the State during the Babri Masjid demolition were conferred with Padma Vibushan posthumously on the eve of the Republic Day (73rd).
- Padma Vibhushan, part of the Padma series, is the second-highest civilian award.
About Padma Awards 2022
- Background
- The Padma Awards are announced annually on Republic Day (26th January).
- Instituted in 1954, it is one of the highest civilian honours of India.
- Objective
- To recognize achievements in all fields of activities or disciplines where an element of public service is involved.
- Categories
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Padma Vibhushan (for exceptional and distinguished service),
- Padma Bhushan (distinguished service of higher-order) and
- Padma Shri (distinguished service).
- Padma Vibhushan is highest in the hierarchy of Padma Awards followed by Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri.
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Disciplines
- The Awards are given in various disciplines/ fields of activities, viz.- art, social work, public affairs, science and engineering, trade and industry, medicine, literature and education, sports, civil service etc.
- Selection Process
- Padma Awards Committee: The Awards are conferred on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee, which is constituted by the Prime Minister every year.
- Awarded by President: The awards are presented by the President of India usually in the month of March/April every year.
About Bharat Ratna
- Bharat Ratna is the highest civilian award in the country.
- It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service/performance of the highest order in any field of human endeavour.
- It is treated on a different footing from Padma Award. The recommendations for Bharat Ratna are made by the Prime Minister to the President of India.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of three in a particular year.
GS-II
Worries over the electoral bond scheme go beyond its unconstitutionality

Context
Ever since its introduction, the electoral bond scheme has envenomed the democratic process, by destroying altogether any notion of transparency in political funding.
Issue of anonymity in electoral bond
- The electoral bond scheme is designed to allow an individual, or any “artificial juridical person”, including body corporates, to purchase bonds issued by the State Bank of India during notified periods of time.
- These instruments are issued in the form of promissory notes, and in denominations ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹1 crore.
- Once purchased, the buyer can donate the bond to any political party of their choice and the party can then encash it on demand.
Supreme Court’s opinion
- The Supreme Court has allowed the scheme to continue unabated and has denied an interim stay on its operation.
- In one such provisional order, the Court asserted that the bonds were not, in fact, anonymous.
- According to the Court, since both the purchase and the encashment of bonds are made through banking channels, all it would take for a person to glean the identity of a donor was for her to look through every corporation’s financial statement — these records, the Court said, ought to be available with the Registrar of Companies.
- What the order ignored was that there is no attendant obligation on political parties to provide details to the public on each donation received by them through electoral bonds.
- Companies are also under no obligation to disclose the name of the party to whom they made the donation.
Violation of voter’s right
- The Supreme Court has consistently held that voters have a right to freely express themselves during an election and that they are entitled to all pieces of information that give purpose and vigour to this right.
- Surely, to participate in the electoral process in a meaningful manner and to choose one’s votes carefully, a citizen must know the identity of those backing the candidates.
Electoral bond does not eliminate the role of black money in funding elections
- As affidavits filed by the Election Commission of India in the Supreme Court have demonstrated, the scheme, if anything, augments the potential role of black money in elections.
- It does so by, among other things, removing existing barriers against shell entities and dying concerns from donating to political parties.
- Moreover, even if the bonds were meant to eliminate the presence of unaccounted currency, it is difficult to see what nexus the decision to provide complete anonymity of the donor bears to this objective.
- It is for this reason that the Reserve Bank of India reportedly advised the Government against the scheme’s introduction.
Conclusion
The worries over the electoral bond scheme, however, go beyond its patent unconstitutionality. This is because in allowing anonymity it befouls the basis of our democracy and prevents our elections from being truly free and fair.
States must decide on SC/ST quota in promotions: Supreme Court

Context
The Supreme Court has refused to lay down the criteria for determining the inadequacy of representation for granting reservation in promotions for Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe candidates in government jobs.
What did the court held?
- The court stuck firm by the decisions of its Constitution Benches in the Jarnail Singh and M. Nagaraj case that the question of adequate representation of SC/ST communities ought to be left to the respective States to determine.
- It held ‘cadre’, and not class or group or the entire service, as the unit for the purpose of collection of quantifiable data for giving promotion quotas.
Why such decision?
- Determination of inadequate representation depends upon myriad factors of states which this Court cannot envisage.
- Laying down of criteria for determining the inadequacy of representation would result in curtailing the discretion given to the State governments.
What was the case?
- The Union government has been pressing for reservation in promotion proportionate to the population of SCs and STs as per a 1995 judgment by the top court in the RK Sabharwal case.
- It wants it to be left open to the Centre and states to decide on promotional avenues for SCs and STs.
- It claims that the condition regarding the collection of quantifiable data to show the inadequacy of representation of SCs/STs is “vague”.
- Advocates representing the general category have contended that the reservation cannot be for an indefinite period and that it must stop as soon as the upper ceiling has been reached.
- Further, they have emphasized that reservation in promotion should be cadre-based only after quantifiable data is collected and the creamy layer has been excluded.
Defying the need for quantifiable data
- Attorney General sought to convince the court that the roster system, based on the proportionate population of SCs/STs, has been working quite well in all government departments.
- The condition of collecting quantifiable data on inadequacy of representation of SCs/STs may not be required at all.
- He urged that there is no need to verify any further or collect quantifiable data after the roster system.
What is the Nagraj Case?
- Article 16(4A) of Indian Constitution allows reservations to SCs and STs in promotions, as long as the government believes that they are not adequately represented in government services.
- In 2006, a Constitution bench’s ruling in the M Nagaraj case made it incumbent upon the state to collect quantifiable data showing inadequacy of representation in public employment.
- This was to be done in addition to maintaining overall administrative efficiency.
Related amendments
- 77th Amendment: It introduced Clause 4A to the Constitution, empowering the state to make provisions for reservation in matters of promotion to SC/ST employees if the state feels they are not adequately represented.
- 81st Amendment: It introduced Clause 4B, which says unfilled SC/ST quota of a particular year, when carried forward to the next year, will be treated separately and not clubbed with the regular vacancies of that year to find out whether the total quota has breached the 50% limit set by the Supreme Court.
- 82nd Amendment: It inserted a proviso at the end of Article 335 to enable the state to make any provision for SC/STs “for relaxation in qualifying marks in any examination or lowering the standards of evaluation, for reservation in matters of promotion to any class or classes of services or posts in connection with the affairs of the Union or of a State”.
- 85th Amendment: It said reservation in the promotion can be applied with consequential seniority for the SC/ST employee.
Why such demand for quotas in promotion?
- The Attorney General has said that it is tough for a member of the SC/ST to reach the ‘Group A’ category jobs.
- The time has come for the apex court to firm up and draw the basis for reservation in promotions for SC/ST candidates to fill up vacancies in top jobs.
- The Bench referred to records filed before it to note that there was low representation of SC/ST category in Group A jobs.
- Instead of improving the situation in the Group A ranks, the court said, efforts are on to ensure adequate representation in Groups B and C.
- This was not fair, it remarked.
Statehood Day of Himachal Pradesh
Context
Recently, the Prime Minister of India greeted people of Himachal Pradesh (H.P.) on its statehood day (25th Janurary).
History During British Rule
- The British territories in the hill came under British Crown after Queen Victoria’s proclamation of 1858.
- The states of Chamba, Mandi and Bilaspur made good progress in many fields during British rule.
- During the first World War (1914-18), virtually all rulers of the hill states remained loyal and contributed to the British war effort both in the form of men and materials.
History During Post-Independence Period
The history of present day Himachal Pradesh in the post-independence era has been outlined below:
- The Chief Commissioner’s province of H.P. came into being on 15th April, 1948.
- H.P. became a part C state (under Part VII) on 26th January, 1950 with the implementation of the Constitution of India.
- Bilaspur was merged with Himachal Pradesh on 1st July, 1954.
- After recommendation of the State Reorganisation Commission, Himachal Pradesh became Union Territory on 1st November, 1956.
- Kangra and most of the other hill areas of Punjab were merged with H.P. on 1st November, 1966 though its status remained that of a Union Territory.
- On 18th December, 1970 the State of Himachal Pradesh Act was passed by Parliament and the new state came into being on 25th January, 1971. Thus H.P. emerged as the eighteenth state of the Indian Union.
- Himachal Pradesh has come a long way since then. It has seen a number of full-fledged governments which have led the state towards economic self-reliance.
State Reorganisation Commission
- Having achieved India’s independence from British rule, reorganization of more than 500 princely states into effective provincial units was one of the biggest tasks.
- In pursuance of the same, S. K. Dhar commission (1948) and JVP Committee (1948) advocated for reorganization of states based on geographical contiguity, administrative convenience, financial self-reliance and potential for development.
- However, with the sudden death of Potti Srirammalu following hunger strike in demand for Andhra state created a volatile situation.
- The Fazl Ali Commission (1953) was set up and its recommendation for reorganization of state based on linguistic criteria (other criteria were also included) was accepted.
GS-III
What is Pollution-Under-Control (PUC) Certificate?
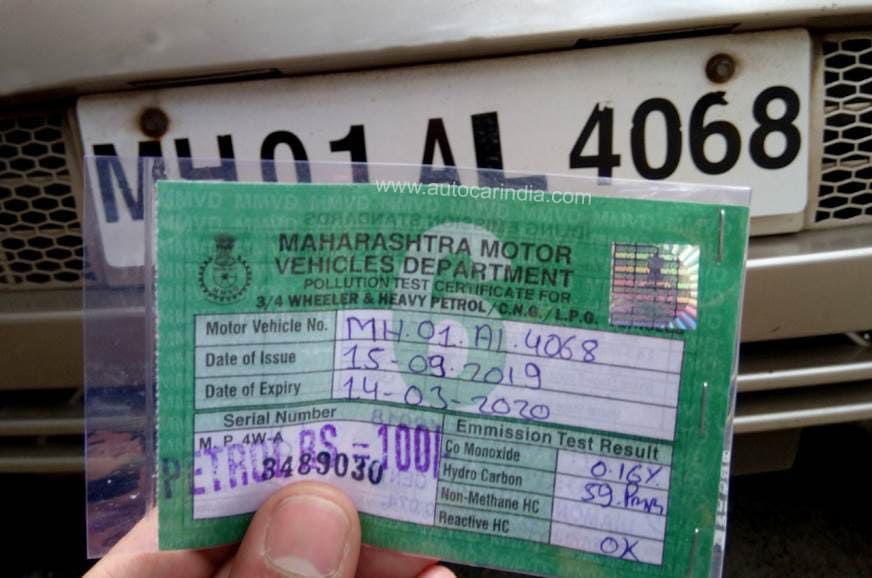
Context
Delhi govt will soon make PUC certificate mandatory for fuel at filling stations.
About PUC Certificate
- The PUC certificate is a document that any person driving a motor vehicle can be asked to produce by a police officer in uniform authorized by the state government.
- These issue certificates if a vehicle is found complying with the prescribed emission norms.
- Since the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019 came into force, PUC certificate has been made mandatory.
- A PUC certificate contains information such as the vehicle’s license plate number, PUC test reading, date on which the PUC test was conducted and the expiry date.
How is a pollution control check carried out?
- The computerized model for pollution check was developed by the Society of Indian Automobile manufacturers.
- A gas analyzer is connected to a computer, to which a camera and a printer are attached.
- The gas analyzer records the emission value and sends it to the computer directly, while the camera captures the license plate of the vehicle.
- Subsequently, a certificate may be issued if the emission values are within the limits.
Fines for non-compliance
- The test costs between Rs 60 and Rs 100.
- The validity of the test is one year for BS-IV vehicles and three months for others.
- The fine for PUC violations has now gone up to Rs 10,000; it used to be Rs 1,000 for the first offence and Rs 2,000 for subsequent violations before the amendments came into force.
US Federal Reserve & Indian Market

Context
Recently, the US Federal Reserve (central bank of US) has signalled a possible hike in interest rates. This has led to a nervous reaction in Indian markets.
- Rate hikes by the Federal Reserve affects not only the US economy, but also shapes the macroeconomic outlook and exerts a certain degree of influence on the monetary policies in other emerging economies.
Co-relation of Federal Reserve & Indian Markets
- Emerging economies such as India tend to have higher inflation and higher interest rates than those in developed countries such as the US and many of the (primarily Western) European nations.
- As a result, financial institutions, particularly Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) would want to borrow money in the US at low interest rates in dollar terms and then invest that money in government bonds of emerging countries such as India in local currency terms to earn a higher rate of interest.
- When the US Federal raises its domestic interest rates, the difference between the interest rates of the two countries decreases.
- This makes India less attractive for the currency carry trade, consequently, some of the money may be expected to move out of the Indian markets and flow back to the US.
- A currency carry trade is a strategy whereby a high-yielding currency funds the trade with a low-yielding currency.
- Therefore decreasing the value of India’s currency against the US dollar.
Impact of Increased Interest Rates on India
- On Equity Market
- Bond yields will rise due to growing dollar shortage in the global market.
- Previously, in India, the debt and equity markets witnessed outflows of over Rs 40,000 crore rupees, due to the strengthening dollar and uncertainties perpetrated by the trade war between the US, China, European Union, and other major nations.
- On Export and Forex
- India being one of the largest crude oil importers of the world.
- A weaker rupee vis-à-vis a dollar results in more expensive imports of crude oil that may put cost-driven inflationary push across the whole economy and especially in those sectors that are highly sensitive to crude oil price movements.
- India’s exports on the other hand, notably IT and IT-enabled services – will benefit to some extent from a stronger dollar with respect to the rupee.
- However, the same benefit may not fully accrue to exporters due to strong competition in the export market.
Fly Ash Management and Utilisation Mission

Context
Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) directed the constitution of a ‘Fly Ash Management and Utilisation Mission.
About Fly Ash Management and Utilisation Mission
- The order by the NGT takes note of the ‘unscientific handling and storage’ of the fly ash by coal thermal power stations.
- For example, the draining of industrial effluents and fly ash in the Rihand Reservoir.
- The Fly Ash Management and Utilisation Mission, besides monitoring the disposal of annual stock of unutilised fly ash, will also see how 1,670 million tonnes of legacy (accumulated) fly ash could be utilized in the least hazardous manner and how all safety measures could be taken by the power plants.
- The Mission will hold its first meeting within one month to assess the fly ash management situation in coal power plants and to prepare action plans to build road maps for ash utilisation by individual plants.
- These meetings shall be conducted each month, for a year.
Aim: To ‘coordinate and monitor issues relating to the handling and disposal of fly ash and associated issues.’
Head & Nodal Agency
- The Mission is to be jointly headed by the secretaries of the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC), Union Ministry of Coal and Power, keeping on board chief secretaries of respective states where the mission is being implemented.
- The secretary of MoEF&CC will be the nodal agency for coordination and compliance.
Different from Fly Ash Notification 2021
- Fly Ash Notification 2021 was issued under the Environment (Protection) Act 1986.
- Prohibiting dumping and disposal of fly ash discharged from coal or lignite based thermal power plants on land or into water bodies, the Centre has made it mandatory for such plants to ensure 100% utilization of ash in an eco-friendly manner, and introduced for the first time a penalty regime for non-compliance based on 'polluter pays' principle.
- Under new rules, the non-compliant power plants will be imposed with an environmental compensation of Rs 1,000 per tonne on unutilised ash during the end of every financial year.
- The amount, collected by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) from the thermal power plants, will be used towards the safe disposal of the unutilised ash. It may also be utilised for advancing research on use of ash including ash based products.
- In cases where fly ash is being used in various activities, power plants will have to deliver fly ash at project sites free of cost.
- The power plant may, however, charge for ash cost and transportation as per mutually agreed terms, in case it is able to dispose of the ash through other means.
- The new fly ash notification of December 2021, has made provision for the ‘enforcement, monitoring, audit and reporting’ of the progress of fly ash utilisation and implementation by coal thermal power plants and user agencies.
- The Notification holds the CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCB) / Pollution Control Committees (PCC) responsible for monitoring the effective implementation of mandates under it.
- However, along with these statutory regulators, the Mission also extends the responsibility of fly ash management to the chief secretaries of the states.
- The Notification mandates the individual thermal power plant to upload monthly information regarding ash generation and utilisation on its web portal.
- The Mission as directed by the NGT, on the other hand, will make the roadmaps and progress in fly ash utilisation available for all thermal power plants and their clusters, on the MoEF&CC website on a quarterly basis for the knowledge of all stakeholders.
|
844 docs|613 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 29, 2022 - Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT
| 1. What are the three general studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of daily current affairs in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What is the role of frequently asked questions (FAQs) in UPSC preparation? |  |
| 4. How can candidates ensure that their FAQs are most likely to be searched by others? |  |
| 5. What is the recommended language to use for FAQs related to UPSC exam articles? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CLAT exam
|

|

















