UPSC Mains Answer PYQ 2024: Public Administration Paper 1 (Section- B) | Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Section B
Q5: Answer the following questions in about 150 words each: (10 × 5 = 50 Marks)
(a) The Anti-Development Thesis is a critical perspective on the traditional development models. Comment.
Ans: The Anti-Development Thesis is a critique of mainstream development theories that have often emphasized economic growth, modernization, and industrialization as the ultimate goals for societies. Scholars like Ivan Illich and Giorgio Agamben argue that traditional development models, especially those rooted in Western ideals, impose a one-size-fits-all approach to societies, disregarding local cultures, values, and ecosystems.
This perspective contends that development often leads to environmental degradation, social inequality, and cultural erosion, and that the focus on material progress overlooks the well-being and holistic growth of communities. The Anti-Development Thesis advocates for alternative models that emphasize sustainability, community well-being, and cultural integrity over economic growth alone.
In conclusion, while traditional development models prioritize measurable growth indicators, the Anti-Development Thesis challenges these views by highlighting the negative consequences of development on marginalized communities and the environment.
(b) Civil Servants should be allowed only to cast vote or to participate in the electoral process of the country. Examine.
Ans: Civil servants, as neutral public servants, play a key role in the administration of government policies, irrespective of the political party in power. The debate on whether civil servants should participate in elections revolves around maintaining political neutrality and ensuring the effective functioning of the bureaucracy.
On one hand, allowing civil servants to vote upholds their democratic right to participate in the electoral process, similar to other citizens. However, participating in electoral campaigns or public political activities could compromise their impartiality, leading to conflicts of interest and undermining public trust.
In India, the All India Services (Conduct) Rules prohibit civil servants from actively participating in politics, thereby ensuring they remain politically neutral. This prevents situations where political affiliations might influence administrative decisions or hinder governance.
In conclusion, while voting is a basic democratic right, active political participation by civil servants could jeopardize the principle of neutrality, which is crucial for the effective and unbiased functioning of the civil service.
(c) Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to plan and manage project effectively. Discuss.
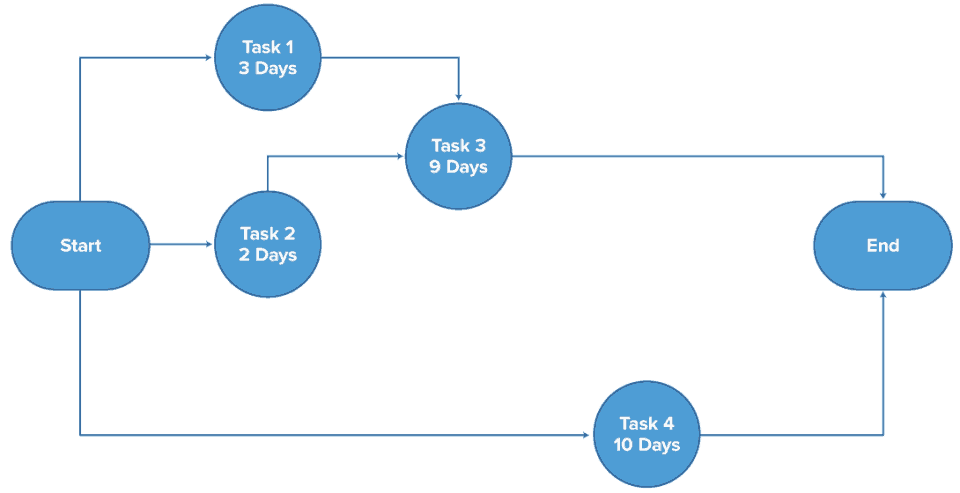
Ans: The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a widely used project management tool that helps in planning, scheduling, and controlling complex projects. It focuses on determining the longest sequence of dependent tasks that must be completed on time for the entire project to be finished. This sequence is called the critical path.
CPM involves the following steps:
- Identify all tasks that need to be completed for the project.
- Determine dependencies between tasks (i.e., which tasks must be completed before others can start).
- Estimate the duration of each task.
- Determine the critical path by calculating the longest path through the project network of tasks.
The key advantage of CPM is that it highlights tasks that are critical to the project’s completion, helping project managers allocate resources efficiently and focus on preventing delays in these tasks. For example, in infrastructure projects like building a bridge, CPM can help track the construction stages to ensure timely completion.
In conclusion, CPM is an essential tool for effective project management, particularly for large-scale projects with multiple interdependent tasks. It helps in resource optimization and timely delivery by focusing on the critical path and managing risks accordingly.
(d) Auditing is not about finding faults, it is about ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial information. Analyse.
Ans: Auditing is a systematic examination of financial records to ensure their accuracy, fairness, and compliance with accounting standards and laws. While many view auditing as a tool for identifying mistakes or fraudulent activities, its primary purpose is to ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial information.
The process of auditing involves assessing the financial statements, verifying transactions, and ensuring that the financial reports reflect the true and fair view of an organization’s financial position. Auditors evaluate the internal controls, risk management practices, and overall financial health, not to find faults, but to confirm that the financial data is reliable for decision-making.
For example, in public sector audits, such as those conducted by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG), the goal is not to point fingers but to ensure that taxpayers' money is spent correctly, and financial records are transparent and accurate.
In conclusion, auditing is not solely about detecting errors or fraud, but it serves as a critical mechanism for ensuring that the financial information provided by organizations is accurate, trustworthy, and complies with the necessary standards.
(e) The study of Public Administration must include its ecology. Discuss.
Ans: The study of Public Administration cannot be isolated from its ecology, which refers to the environmental and social context in which it operates. Public Administration is deeply intertwined with the societal, political, economic, and cultural dynamics that shape governance. Understanding the ecology of Public Administration helps in contextualizing policies, practices, and reforms.
Ecology in Public Administration includes various factors such as:
- Political Environment: Government policies, political ideologies, and party dynamics directly influence how public administration functions. For instance, bureaucratic autonomy might be challenged during political shifts.
- Social Environment: Social issues, inequality, and public demands shape administrative priorities. The rise of movements like Right to Information (RTI) has pushed for greater transparency and accountability in public administration.
- Economic Environment: Economic conditions, fiscal policies, and the resource allocation processes influence how administrative systems function, such as the implementation of welfare schemes like PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana).
- Technological Environment: The advent of digital technology impacts public administration through e-governance initiatives like Aadhaar and Digital India, making governance more transparent and efficient.
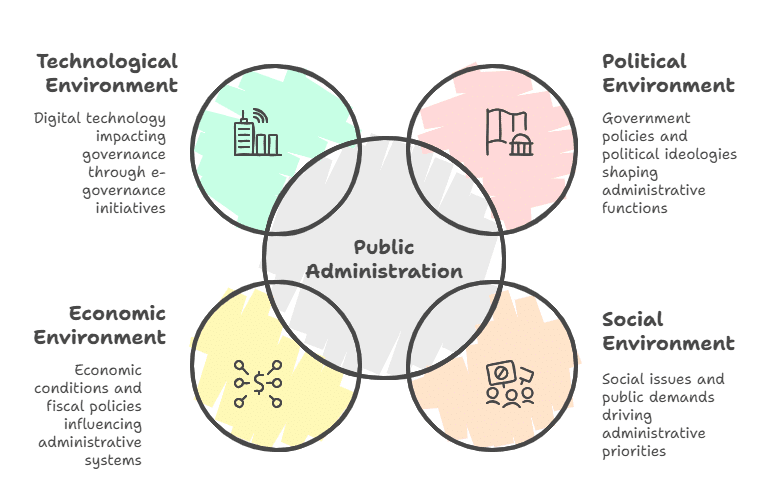
In conclusion, understanding the ecology of Public Administration provides a comprehensive view of how external and internal factors shape administrative actions and outcomes. A nuanced approach that considers these ecological influences ensures that policies and administrative practices are responsive, inclusive, and effective.
Q6:
(a) A trend to adopt innovative practices in administrative ethics is gaining ground for improving public trust in government. Discuss. (20 Marks)
Ans: In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards adopting innovative practices in administrative ethics to enhance transparency, accountability, and public trust in government institutions. Administrative ethics revolves around the values and principles that guide the behavior of public servants, ensuring that their actions align with public interest and moral standards.
Innovative practices in this domain include:
- E-Governance and Digital Transparency: The implementation of platforms such as RTI portals and online grievance redressal systems allows citizens to monitor government actions and holds public servants accountable.
- Ethical Training Programs: Regular workshops and training on ethical behavior and decision-making for civil servants, such as those conducted by the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), help build a culture of integrity.
- Whistleblower Protection: Legislative measures like the Whistleblower Protection Act promote transparency by protecting individuals who report unethical practices in government.
- Citizen Participation: Increasingly, governments are encouraging citizen involvement through mechanisms like public consultations and social audits, as seen in programs like MGNREGA.
Such practices not only curb corruption but also foster a culture of openness and responsibility. In conclusion, innovative practices in administrative ethics are crucial for building public trust, ensuring that the government operates fairly and responsibly.
(b) The future of e-governance is shaped by emerging trends for making government services efficient and accessible. Analyse. (15 Marks)
Ans: E-governance refers to the use of digital tools and technologies by governments to enhance the delivery of services, improve transparency, and ensure accountability. The future of e-governance is increasingly being shaped by emerging trends aimed at making government services more efficient, accessible, and user-friendly.
Key emerging trends include:
- Blockchain Technology: This can be used for secure and transparent record-keeping, particularly in areas like land registration and public financial management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data: AI can help in streamlining administrative processes, improving decision-making, and providing personalized services. Big data can enable governments to analyze trends, predict issues, and offer better-targeted services.
- Mobile Government (m-Government): With the increasing use of smartphones, mobile apps are becoming crucial tools for delivering public services, as seen in initiatives like Aadhaar-linked services.
- Cloud Computing: By centralizing data storage and reducing infrastructure costs, cloud-based solutions improve the speed and accessibility of government services.
- Citizen-Centric Platforms: Governments are increasingly developing platforms that prioritize the needs of citizens, simplifying procedures such as e-filing taxes and digital health records.
In conclusion, the future of e-governance will be shaped by advanced technologies that enhance efficiency, reduce barriers to access, and improve the overall user experience, fostering a more responsive and transparent governance system.
(c) Undoubtedly, social and historical factors play a significant role in shaping administrative system, but side by side, understanding of these influences is essential for designing responsive governance structure. Examine. (15 Marks)
Ans: Social and historical factors have always been integral in shaping administrative systems, influencing how public administration evolves and functions. These factors include cultural values, political traditions, and historical experiences, which affect governance structures, administrative practices, and the relationship between the government and its citizens.
Historical Context: Colonial legacies, for example, have had a lasting impact on administrative structures in post-colonial states. In India, the bureaucratic framework inherited from British colonial rule continues to influence the functioning of civil services today.
Social Context: Social factors such as caste, religion, and socio-economic disparities affect access to services, equity in policy implementation, and the responsiveness of government institutions. For instance, affirmative action policies like reservations have been shaped by India's social structure to address historical inequities.
However, while historical and social factors are significant, understanding these influences is crucial for designing a responsive governance structure. A governance system that acknowledges social dynamics—such as caste-based or regional disparities—can better address the needs of marginalized communities. The design of inclusive policies, such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), acknowledges these factors by focusing on providing financial inclusion to underserved populations.
In conclusion, while social and historical contexts shape administrative systems, recognizing these influences allows policymakers to create governance structures that are not only responsive but also equitable and sustainable in addressing diverse societal needs.
Q7:
(a) Riggs' Prismatic Model has been criticised as overly gloomy and technical complex, but it remains as a useful starting point for Comparative Public Administration research. Analyse. (20 Marks)
Ans: Riggs' Prismatic Model of public administration, developed by Fred W. Riggs, is a framework used to understand the complex dynamics of public administration in developing countries. It draws from the comparative approach to analyze the relationship between traditional and modern elements within an administrative system.
The model is often criticized for being overly gloomy and technically complex. Critics argue that it presents an overly pessimistic view of developing nations' administrative systems, emphasizing the "prismatic" nature of public institutions—where traditional and modern practices are often in conflict. Moreover, its technicality makes it difficult to apply universally, as the model's complexity is seen as a barrier to practical implementation.
However, despite these criticisms, the Prismatic Model remains a valuable starting point for Comparative Public Administration research. It helps researchers analyze the transition of societies from traditional to modern administrative systems, particularly in the context of developing countries where bureaucratic systems often face institutional contradictions and cultural tensions. For example, Riggs' model has been used to analyze the bureaucratic structures in India and Pakistan, where modernization efforts coexist with traditional governance systems.
In conclusion, while Riggs' Prismatic Model may not offer a perfect framework, its focus on the evolving nature of public administration in developing countries and its ability to provoke critical analysis remains useful for comparative studies.
(b) Performance Management and Performance Appraisal are two distinct activities in Public Personnel Administration. Discuss. (15 Marks)
Ans: In Public Personnel Administration, Performance Management and Performance Appraisal are two distinct yet interconnected activities aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of government employees.
Performance Management refers to the continuous process of setting objectives, providing feedback, and ensuring that employees have the resources and support needed to perform their roles effectively. It involves the alignment of individual performance with organizational goals and focuses on employee development. The goal of performance management is to optimize employee performance by providing ongoing support, training, and development opportunities. For example, the Annual Performance Reports (APRs) in India are used to set expectations and track overall performance over time, focusing on long-term growth.
Performance Appraisal, on the other hand, is a formal and periodic evaluation of an employee's work performance, often tied to incentives, promotions, or rewards. It is a more evaluative process, where supervisors assess an employee’s achievements against set criteria. The appraisal typically happens at the end of a performance cycle (e.g., yearly), with feedback given on strengths and areas for improvement. An example of this is the confidential reports used in the Indian Civil Services, which are reviewed periodically to assess the performance of officers.
In conclusion, while performance management focuses on continuous improvement and employee development, performance appraisal is a more formal assessment of an individual’s achievements and contributions. Both activities are essential for optimizing the overall efficiency of public administration.
(c) Balancing State intervention and Market freedom is the need of developing countries. Comment. (15 Marks)
Ans: In developing countries, the need to balance State intervention and market freedom has been a persistent challenge in the pursuit of sustainable development, economic growth, and social equity.
On the one hand, State intervention is essential in ensuring social welfare, poverty alleviation, and addressing market failures. The state plays a crucial role in regulating key sectors such as health, education, and infrastructure, where market forces may not always prioritize the public good. For example, in India, state intervention through schemes like Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) provides a safety net for the rural poor, ensuring employment in times of economic distress.
On the other hand, market freedom fosters competition, innovation, and economic efficiency. Encouraging market-driven growth enables private enterprises to thrive, leading to job creation, investment, and technological advancements. For instance, the liberalization policies in India, starting in the 1990s, opened up various sectors to private players, boosting the country's economic growth.
However, the challenge lies in finding the right balance. Excessive state intervention can stifle entrepreneurship and lead to inefficiencies, while too much market freedom may exacerbate inequality and environmental degradation.
In conclusion, developing countries must strike a balance between state intervention to ensure equity and market freedom to drive growth. This balanced approach can help in achieving both economic development and social justice.
Q8:
(a) Bureaucracy in developing countries faces several challenges and tackling of these will make them more responsive, adaptive and align with development needs. Discuss. (20 Marks)
Ans: Bureaucracy in developing countries plays a crucial role in implementing government policies, but it faces several challenges that can undermine its effectiveness. To address these challenges, reforms are needed to enhance its responsiveness, adaptability, and alignment with development goals.
Challenges:
- Over-centralization: Bureaucracies in many developing countries are often centralized, limiting the autonomy of lower-level officials to respond to local needs. This can lead to inefficiency and delays in decision-making.
- Corruption: Corruption within the bureaucracy hampers the equitable delivery of services and erodes public trust.
- Lack of Capacity: Inadequate training and resources prevent bureaucrats from effectively managing complex development programs.
- Political Interference: Bureaucratic autonomy is often compromised by political influence, leading to policies that are more politically motivated than development-focused.
Tackling these challenges:
- Decentralization: Decentralizing power allows local officials to address region-specific issues more effectively. The Panchayati Raj system in India is an example of decentralization aimed at improving responsiveness.
- Anti-corruption measures: Implementing strict anti-corruption laws and promoting transparency (e.g., Right to Information Act) can improve the integrity of the bureaucracy.
- Capacity-building: Investing in the continuous professional development of civil servants ensures that they have the necessary skills to meet evolving development needs.
- Promoting meritocracy: Ensuring that appointments and promotions are based on merit rather than political connections helps create a more competent and neutral bureaucracy.
In conclusion, addressing these challenges will help create a more responsive, adaptive, and development-oriented bureaucracy that can effectively contribute to the goals of economic and social development.
(b) Modern economists think public debt is an essential means of increasing employment, and element of economic policy, but it also shifts the burden to future generations. Analyse. (15 Marks)
Ans: Modern economists view public debt as a tool that can support economic growth, employment generation, and national development, but it comes with long-term risks that affect future generations.
Positive Aspects of Public Debt:
- Boosting Employment: Public debt can finance infrastructure projects and social welfare programs, which can create jobs and stimulate economic growth. For instance, the New Deal programs in the U.S. during the Great Depression relied heavily on government spending financed by debt to combat high unemployment.
- Economic Stimulus: Public debt, when used strategically, can increase aggregate demand during economic slowdowns. For example, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, governments worldwide used debt to provide fiscal stimulus and support economic recovery.
- Investment in Growth: Debt can finance investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, which lay the foundation for long-term economic growth.
Negative Aspects of Public Debt:
- Future Burden: Excessive debt accumulation shifts the repayment burden to future generations, potentially leading to higher taxes or inflation. This is evident in developed countries like the U.S. and Japan, where national debt levels have raised concerns about fiscal sustainability.
- Debt Servicing Costs: High debt levels lead to increased interest payments, which may crowd out other essential government spending, such as investments in welfare or infrastructure.
- Sovereign Risk: Excessive debt may lead to default risk, as seen in cases like Greece’s debt crisis, where the country faced severe economic consequences due to unsustainable public debt.
In conclusion, while public debt can be an essential policy tool to stimulate employment and growth, it must be managed prudently to avoid creating unsustainable fiscal pressures on future generations.
(c) Unless there is a sound mechanism for policy evaluation, policy formulation process remains redundant. Examine. (15 Marks)
Ans: Policy evaluation is crucial to ensure that government actions meet their intended objectives and contribute to the well-being of society. Without a robust mechanism for evaluating policies, the entire policy formulation process becomes less effective and may fail to achieve its goals.
Importance of Policy Evaluation:
- Feedback and Improvement: Evaluation provides feedback on the effectiveness of policies, enabling policymakers to make necessary adjustments. For instance, the evaluation of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in India has led to changes that improve its implementation and reach.
- Accountability: It ensures that the government remains accountable for its actions, as evaluation helps identify whether resources are being utilized efficiently and whether policies are meeting the needs of the public.
- Informed Decision-Making: By systematically assessing outcomes, governments can make better-informed decisions about which policies to continue, modify, or discontinue. For example, the evaluation of the National Food Security Act (NFSA) helps assess whether food distribution systems are functioning as intended.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluation helps measure the long-term impact of policies on societal welfare, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
Without a sound evaluation mechanism, policies may continue to be implemented without proper understanding of their real-world implications. Feedback loops from regular evaluations ensure that policies remain adaptive to changing conditions.
In conclusion, a well-designed policy evaluation system is vital for refining and improving government policies, ensuring their relevance, efficiency, and overall impact.
|
58 videos|242 docs
|
FAQs on UPSC Mains Answer PYQ 2024: Public Administration Paper 1 (Section- B) - Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What are the key topics covered in the UPSC Public Administration Paper 1? |  |
| 2. How should one prepare for the Public Administration Paper in the UPSC Mains exam? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of Public Administration in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. Can you provide tips for writing effective answers in the Public Administration Paper? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid while preparing for the Public Administration Paper? |  |





















