UPSC Prelims PYQs: Constitution of India- History, Development & Salient Features | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
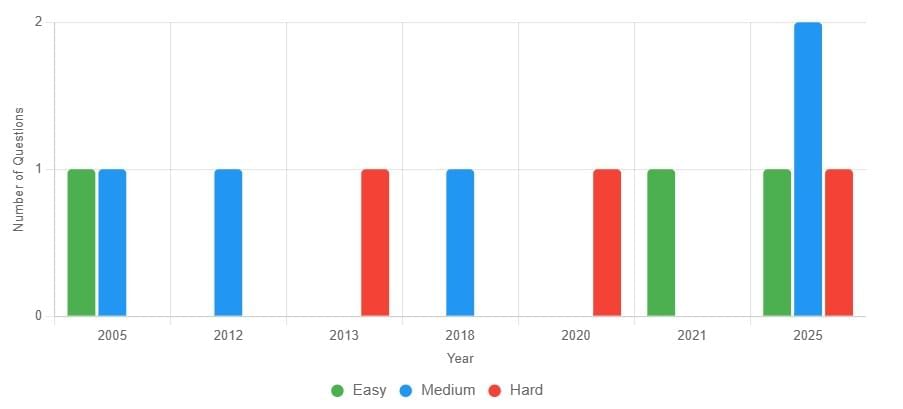
From 2005 to 2025, 11 questions of varying difficulty have been asked: 3 easy (27%), 5 medium (45%), and 3 hard (27%)—emphasis is generally placed on topics such as Indian polity, constitutional provisions, and historical governance structures.
Q.1. With reference to India, consider the following: (2025)
I. The Inter-State Council
II. The National Security Council
III. Zonal Councils
How many of the above were established as per the provisions of the Constitution of India?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Among the listed bodies, only the Inter-State Council is constitutionally established. The others are created through statutory or executive measures.
I. Inter-State Council – Correct
Constituted under Article 263 of the Indian Constitution to promote coordination between the Centre and States.
II. National Security Council – Incorrect
Set up in 1998 via an executive order, not enshrined in the Constitution.
III. Zonal Councils – Incorrect
Formed under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, making them statutory but not constitutional bodies.
Q.2. Consider the following statements: (2025)
Statement I: In India, State Governments have no power for making rules for grant of concessions in respect of extraction of minor minerals even though such minerals are located in their territories.
Statement II: In India, the Central Government has the power to notify minor minerals under the relevant law.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II explains Statement I
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II does not explain Statement I
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is not correct
(d) Statement I is not correct but Statement II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Regarding the regulation of minerals under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act):
Statement I: Incorrect
The regulation of minor minerals primarily falls under the jurisdiction of State Governments, as per the MMDR Act, 1957. States are empowered to frame rules for granting extraction concessions for minor minerals.
Statement II: Correct
The Central Government has the authority to designate and notify which minerals are classified as 'minor minerals' under the MMDR Act, 1957.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect, while Statement II is correct.
Q.3. With reference to the Government of India, consider the following information: (2025)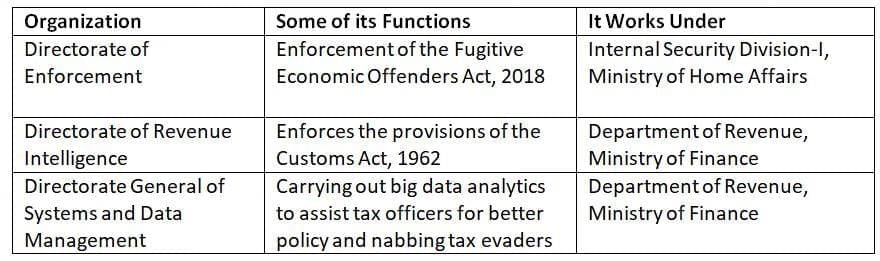
In how many of the above rows is the information correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The following evaluates the accuracy of mappings between investigative bodies, their functions, and their parent ministries or departments.
Row I: Incorrect
The Directorate of Enforcement (ED) implements the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018, but it operates under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, not the Ministry of Home Affairs as incorrectly stated.
Row II: Correct
The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is responsible for enforcing the Customs Act, 1962, and functions under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
Row III: Correct
The Directorate General of Systems and Data Management supports big data analytics for tax enforcement and operates under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
Thus, Rows II and III are correctly mapped, while Row I is incorrect due to the wrong attribution of the parent ministry.
Q.4. Consider the following pairs: (2025)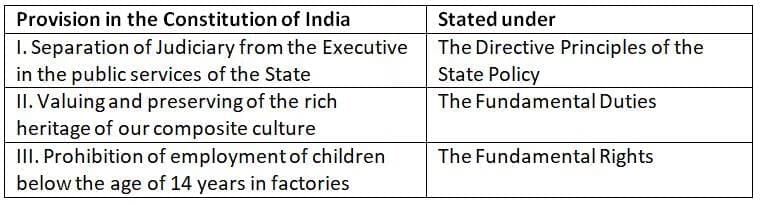
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Each of the following pairs accurately links a constitutional provision to its respective part in the Constitution of India.
Statement I: Directive Principles of State Policy – Correct
Article 50, under the Directive Principles of State Policy, mandates the separation of the judiciary from the executive in the public services of the State to ensure judicial independence.
Statement II: Fundamental Duties – Correct
Article 51A(f), part of the Fundamental Duties, requires citizens to value and preserve the rich heritage of India's composite culture.
Statement III: Fundamental Rights – Correct
Article 24, within the Fundamental Rights, prohibits the employment of children below the age of 14 years in hazardous occupations, such as factories or mines, to safeguard their well-being.
Thus, all three pairs are correctly matched with their respective constitutional provisions.
Q.5. Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character? (2021)
(a) The independence of judiciary is safeguarded.
(b) The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units.
(c) The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties.
(d) The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Key features of federalism:
- There are two or more levels (or tiers) of government.
- Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administration.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution. So the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
- The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of government. Such changes require the consent of both the levels of government.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
- The highest court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers. The most important feature of the federal system adopted by the Indian Constitution is the principle that relations between the States and the centre would be based on cooperation. And for this, Independent Judiciary is the prerequisite. Hence, Option (a) is correct.
- Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial Autonomy..
Q.6. One common agreement between Gandhism and Marxism is (2020-I)
(a) The final goal of a stateless society
(b) Class struggle
(c) Abolition of private property
(d) Economic determinism
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Stateless Society: A society which lacks formal institutions of government.
- Gandhiji is a philosophical anarchist. Anarchist is one who is opposed to every type of state; Gandhian Ramrajya is that it is a self-regulating system where everyone is one’s own ruler.
- Marxism revolves a classless society and stateless society. Karl Marx had predicted that the proletariats will take control of the state and production, the, destroy all class differences and class antagonisms, and finally resulting in the ‘withering Away of the State’. Thus, the end result will be a stateless society.
- Thus, we can inform that both Gandhi & Marx aimed for Stateless society.
Q.7. In the federation established by The Government on India Act of 1935. Residuary Power were given to the (2018-I)
(a) Federal Legislature
(b) Governor General
(c) Provincial Legislature
(d) Provincial Governors
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Residuary powers were in the hands of Governor General.
Q.8. With reference to Indian History, the Members of the Constituent Assembly from the Provinces were (2013 - I)
(a) directly elected by the people of those Provinces
(b) nominated by the Indian National Congress and the Muslim League
(c) elected by the Provincial Legislative Assemblies
(d) selected by the Government for their expertise in constitutional matters
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The members of the constituent Assembly from the provinces were indirectly elected by the members of the provincial assemblies, who themselves were elected on a limited franchise.
Q.9. The distribution of powers between the Centre and the States in the Indian Constitution is based on the Act provided in the (2012 - I)
(a) Morley-Minto Reforms, 1909
(b) Montagu-Chelmsford Act, 1919
(c) Government of India Act, 1935
(d) Indian Independence Act, 1947
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Distribution of power between the Centre and the States in the Indian Constitution is based on the Government of India Act. 1935.
Q.10. Consider the following statements: (2005)
- The Constitution of India has 20 parts.
- There are 390 Articles in the Constitution of India in all.
- Ninth, Tenth, Eleventh and Twelfth Schedules were added to the Constitution of India by the Constitution (Amendment) Acts.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Constitution of India has 24 parts, 12 schedules and more than 444 articles at present. In the original constitution, there were 22 parts, 8 schedules and 395 articles. Ninth Schedule was added by 1st Constitutional Amendment Act, 1951. Tenth Schedule was added by 52nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1985. Eleventh Schedule was added by 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992. Twelfth Schedule was added by 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992
Q.11. Who among the following was the chairman of the Union Constitution Committee of the Constituent Assembly? (2005)
(a) B.R. Ambedkar
(b) J. B. Kripalani
(c) Jawaharalal Nehru
(d) Alladi Krishnaswami Ayyar
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Chairman of different Committees of Constituent Assembly: Union Power Committee – Jawaharlal Nehru, Drafting Committee – B R Ambedkar, Flag Committee – J B Kriplani, Fundamental Rights and Minority Committee – Vallabh Bhai Patel, Provincial Constitution Committee – Vallabh Bhai Patel. Jawaharlal Nehru was the chairman of the Union Constitution Committee.
|
171 videos|999 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Prelims PYQs: Constitution of India- History, Development & Salient Features - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the history of the Constitution of India? |  |
| 2. What are the salient features of the Constitution of India? |  |
| 3. What is the development process of the Constitution of India? |  |
| 4. What are the fundamental rights provided by the Constitution of India? |  |
| 5. What are the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Constitution of India? |  |

















