UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2024: Indian Polity | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Q1: How many Delimitation Commissions have been constituted by the Government of India till December 2023?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Four
Delimitation Commissions are constituted to redraw the boundaries of parliamentary and assembly constituencies based on population changes. As of December 2023, four Delimitation Commissions have been constituted by the Government of India:
- First Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1952 under the Delimitation Commission Act, 1952.
- Second Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1963 under the Delimitation Commission Act, 1962.
- Third Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1973 under the Delimitation Act, 1972.
- Fourth Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 2002 under the Delimitation Act, 2002.
Each commission has been tasked with the responsibility of readjusting constituencies to reflect changes in population, ensuring fair representation in legislative bodies. Thus, the correct answer to the question is (d) Four.
Q2: The Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992 amends the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution to include which of the following languages?
1. Konkani
2. Manipuri
3. Nepali
4. Maithili
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1,2 and 3
The Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992, brought significant changes to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India by adding three languages:
- Konkani: Spoken predominantly in the Konkan region of Goa, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
- Manipuri (Meitei): The official language of Manipur, spoken by the Meitei community.
- Nepali: Widely spoken in Nepal and also by a significant population in India, particularly in the northeastern states.
These languages were included to promote their recognition and usage in official capacities throughout India. This amendment reflected India's commitment to linguistic diversity and cultural inclusivity. Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 1, 2 and 3, as these three languages were added by the Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992.
Q3: Consider the following pairs:
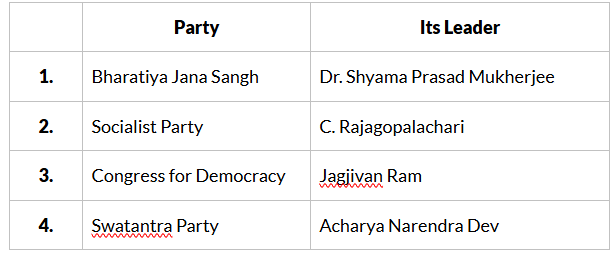
How many of the above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Only two.
Bharatiya Jana Sangh - Dr. Shyama Prasad Mukherjee: This pair is correctly matched. Dr. Shyama Prasad Mukherjee was indeed associated with the Bharatiya Jana Sangh.
Socialist Party - C. Rajagopalachari: This pair is incorrect. C. Rajagopalachari was not associated with the Socialist Party. He was a prominent leader of the Indian National Congress and later founded the Swatantra Party.
Congress for Democracy - Jagjivan Ram: This pair is correct. Jagjivan Ram was associated with the Congress .
Swatantra Party - Acharya Narendra Dev: This pair is incorrect. Acharya Narendra Dev was not associated with the Swatantra Party. He was a prominent socialist leader.
Q4: Which of the following statements are correct about the Constitution of India?
1. Powers of the Municipalities are given in Part IX A of the Constitution.
2. Emergency provisions are given in Part XVIII of the Constitution.
3. Provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution are given in Part XX of the Constitution.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) 1, 2 and 3.
Powers of the Municipalities are given in Part IX A of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part IX A of the Constitution deals with municipalities, providing for their establishment, composition, powers, and responsibilities.
Emergency provisions are given in Part XVIII of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part XVIII of the Constitution (Articles 352 to 360) contains provisions related to emergencies, including national emergency, state emergency (previously termed as President's rule), and financial emergency.
Provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution are given in Part XX of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part XX of the Constitution (Articles 368) deals with the procedure for amending the Constitution of India.
Therefore, all three statements are correct, and the correct answer is (d) 1, 2 and 3.
Q5: Which one of the following statements is correct as per the Constitution of India?
(a) Inter-State trade and commerce is a State subject under the State List.
(b) Inter-State migration is a State subject under the State List.
(c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List.
(d) Corporation tax is a State subject under the State List.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List.
Inter-State trade and commerce: This falls under the Union List, not the State List. It is regulated by the Central Government under Article 301-307 of the Constitution.
Inter-State migration: This is not explicitly mentioned as a subject under either the Union List or the State List. Migration, especially in terms of rights and restrictions, generally falls under laws related to citizenship, which is a Union subject.
Inter-State quarantine: This is indeed a Union subject under the Union List. It relates to public health and is regulated by the Central Government to prevent the spread of diseases between states.
Corporation tax: This is a Union subject under the Union List (specifically under "Taxes on income other than agricultural income"). It is exclusively within the jurisdiction of the Central Government.
Therefore, among the options given, (c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List is the correct statement as per the Constitution of India.
Q6: Under which of the following Articles of the Constitution of India, has the Supreme Court of India placed the Right to Privacy?
(a) Article 15
(b) Article 16
(c) Article 19
(d) Article 21
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Article 21
- Article 15: Prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth.
- Article 16: Provides for equality of opportunity in matters of public employment.
- Article 19: Guarantees certain fundamental rights regarding freedom of speech, assembly, association, etc.
- Article 21: Ensures the protection of life and personal liberty. Over the years, the Supreme Court has interpreted Article 21 expansively to include the Right to Privacy as a fundamental right implicit within the right to life and personal liberty.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Article 21.
Q7: Which of the following statements about the Ethics Committee in the Lok Sabha are correct?
1. Initially it was an ad-hoc Committee.
2. Only a Member of the Lok Sabha can make a complaint relating to unethical conduct of a member of the Lok Sabha.
3. This Committee cannot take up any matter which is sub-judice.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 1 and 3 only
Initially it was an ad-hoc Committee: This statement is correct. The Ethics Committee in the Lok Sabha was initially constituted as an ad-hoc committee to examine matters related to the ethical conduct of members of the Lok Sabha.
Only a Member of the Lok Sabha can make a complaint relating to unethical conduct of a member of the Lok Sabha: This statement is incorrect. While members of the Lok Sabha can certainly raise concerns about unethical conduct, complaints can also be made by citizens or other individuals. It's not limited to only members of the Lok Sabha.
This Committee cannot take up any matter which is sub-judice: This statement is correct. The Ethics Committee generally avoids taking up matters that are already under judicial consideration (sub-judice matters).
Therefore, the correct answer, based on the statements provided, is (c) 1 and 3 only.
Q8: Who was the Provisional President of the Constituent Assembly before Dr. Rajendra Prasad took over?
(a) C. Rajagopalachari
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) T.T. Krishnamachari
(d) Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha
Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha served as the first temporary or provisional President of the Constituent Assembly from 9 December 1946 to 11 December 1946. He was succeeded by Dr. Rajendra Prasad, who then became the President of the Constituent Assembly until its completion and adoption of the Constitution.
Q9: As per Article 368 of the Constitution of India, the Parliament may amend any provision of the Constitution by way of:
1. Addition
2. Variation
3. Repeal
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) 1,2 and 3
According to Article 368 of the Constitution of India, Parliament has the authority to amend any provision of the Constitution by way of:
Addition: Parliament can introduce new provisions into the Constitution.
Variation: Parliament can modify or alter existing provisions of the Constitution.
Repeal: Parliament can remove or annul existing provisions of the Constitution.
These three methods provide Parliament with flexibility in amending the Constitution to adapt to changing circumstances or to correct deficiencies in the legal framework. This constitutional provision underscores the dynamic nature of India's governance structure while maintaining the core principles and framework of the Constitution.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 1, 2 and 3, as all these methods are permissible under Article 368 for amending the Constitution of India.
Q10: Which of the following statements are correct in respect of a Money Bill in the Parliament?
1. Article 109 mentions special procedure in respect of Money Bills.
2. A Money Bill shall not be introduced in the Council of States.
3. The Rajya Sabha can either approve the Bill or suggest changes but cannot reject it.
4. Amendments to a Money Bill suggested by the Rajya Sabha have to be accepted by the Lok Sabha.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 1,2 and 3
Article 109 mentions special procedure in respect of Money Bills: This statement is correct. Article 109 of the Constitution of India specifies the special procedure that must be followed for the introduction and passage of Money Bills in Parliament.
A Money Bill shall not be introduced in the Council of States: This statement is correct. According to Article 110 of the Constitution, a Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha (House of the People), and not in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States).
The Rajya Sabha can either approve the Bill or suggest changes but cannot reject it: This statement is correct. The Rajya Sabha does not have the power to reject a Money Bill. It can only make recommendations for amendments, which the Lok Sabha may or may not accept.
Amendments to a Money Bill suggested by the Rajya Sabha have to be accepted by the Lok Sabha: This statement is incorrect. The Lok Sabha has the discretion to accept or reject any amendments suggested by the Rajya Sabha. However, the Rajya Sabha cannot amend a Money Bill directly; it can only suggest amendments.
Therefore, the correct statements, based on the options provided, are (c) 1, 2 and 3.
Q11. The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. Subsequent to the amendment of NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises which of the following members?
1. Governor of the Constituent State
2. Chief Minister of the Constituent State
3. Three Members to be nominated by the President of India
4. The Home Minister of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1,2 and 3 only
The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. According to the amended provisions of the NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises the following members:
Governor of the Constituent State: The Governors of the North Eastern states are members of the NEC.
Chief Minister of the Constituent State: The Chief Ministers of the North Eastern states are also members of the NEC.
Three Members to be nominated by the President of India: The President of India nominates three members to the NEC.
The Home Minister of India: The Home Minister of India is not a member of the NEC.
Therefore, based on the options provided, the correct answer is (a) 1, 2 and 3 only.
Q12: Consider the following statements regarding ‘Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam’:
1. Provisions will come into effect from the 18th Lok Sabha.
2. This will be in force for 15 years after becoming an Act.
3. There are provisions for the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes Women within the quota reserved for the Scheduled Castes.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Option c is the correct answer.
In September 2023, history was made with Parliament passing the Women’s Reservation Bill called the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam. The bill seeks to reserve one-third of the total number of seats for women in Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and Delhi Assembly. The allocation of reserved seats shall be determined by such authority as prescribed by Parliament.
Statement 1 is incorrect. According to the provisions of the Bill, the reservation is set to be enforced following the publication of a new census and the completion of the delimitation exercise. Furthermore, it’s important to note that for the bill to be fully ratified, it necessitates approval from a minimum of 50% of the states.
Statement 2 is correct. Reservation of seats for women shall cease to exist 15 years after the commencement of this Amendment Act.
Statement 3 is correct. The Bill provides that One-third of the total number of seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes shall be reserved for women of those groups in the Lok Sabha and the legislative assemblies.
Q13: A Writ of Prohibition is an order issued by the Supreme Court or High Courts to:
(a) a government officer prohibiting him from taking a particular action.
(b) the Parliament/Legislative Assembly to pass a law on Prohibition.
(c) the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
(d) the Government prohibiting it from following an unconstitutional policy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
A Writ of Prohibition is a legal remedy issued by a higher court (such as the Supreme Court or High Court) to a lower court or tribunal, instructing them to stop or prohibit further proceedings in a particular case. This writ is typically issued when the lower court is acting beyond its jurisdiction or is conducting proceedings that are legally improper or unlawful.
Key points to remember:
- It is not issued to government officers (option a).
- It does not instruct Parliament or Legislative Assembly to pass a law (option b).
- It is not issued to the government to prohibit unconstitutional policies (option d).
Therefore, option (c) is correct because it accurately describes the purpose and scope of a Writ of Prohibition as it pertains to judicial proceedings in lower courts or tribunals.
Q14: Consider the following statements:
1. It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
2. A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 2 only
It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
- This statement is incorrect. The recognition and declaration of any community as a Scheduled Tribe in a State is not done by the Governor alone. It is actually done by the President of India after consultation with the Governor of the concerned State, as per Article 342(1) of the Constitution of India.
A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
- This statement is correct. The list of Scheduled Tribes varies from State to State. A community recognized as a Scheduled Tribe in one State may not necessarily be recognized as such in another State. Each State has its own list of Scheduled Tribes based on their specific social and demographic considerations.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 2 only.
Q15: With reference to Union Budget, consider the following statements:
1. The Union Finance Minister on behalf of the Prime Minister lays the Annual Financial Statement before both the Houses of Parliament.
2.At the Union level, no demand for a grant be made except on the recommendation of the President of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 2 only
The Union Finance Minister on behalf of the Prime Minister lays the Annual Financial Statement before both the Houses of Parliament.
- This statement is incorrect. It is not the Annual Financial Statement, but rather the Union Budget that is presented by the Union Finance Minister on behalf of the President of India. The Budget includes the Annual Financial Statement, but it is formally presented on behalf of the President, not the Prime Minister.
At the Union level, no demand for a grant can be made except on the recommendation of the President of India.
- This statement is correct. As per Article 113 of the Constitution of India, no demand for a grant can be made except on the recommendation of the President. This ensures that all expenditures from the Consolidated Fund of India are approved through a formal recommendation process.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 2 only.
Q16: With reference to the Speaker of the Lok Sabha, consider the following statements:
While any resolution for the removal of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha is under consideration.
1. He/she shall not preside.
2. He/She shall not have the right to speak.
3. He/She shall not be entitled to vote on the resolution in the first instance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1only
- Statement 1 is correct. The Speaker shall not preside while a resolution for his/her removal is under consideration.
- Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect. The Speaker can speak and vote in the first instance as a member, but not as the presiding officer.
Q17: With reference to the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements:
1. A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses on its dissolution.
2. A bill passed by the Lok Sabha and pending in the Rajya Sabha lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
3. A bill in regard to which the President of India notified his/her intention to summon the Houses to a joint sitting lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 1 and 2
A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses on its dissolution.
- This statement is correct. When the Lok Sabha is dissolved, all bills pending in it (whether introduced or not) lapse and do not carry over to the next Lok Sabha.
A bill passed by the Lok Sabha and pending in the Rajya Sabha lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- This statement is correct. If a bill has been passed by the Lok Sabha but is pending in the Rajya Sabha at the time of dissolution, it lapses and needs to be reintroduced in the new Lok Sabha.
A bill in regard to which the President of India notified his/her intention to summon the Houses to a joint sitting lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- This statement is incorrect. If the President has notified their intention to summon a joint sitting of both Houses for consideration of a bill, the bill does not lapse on dissolution. It can still be taken up in the joint sitting convened after the new Lok Sabha is constituted.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 1 and 2.
Q18: With reference to the Parliament of India, consider the following statements:
1. Prorogation of a House by the President of India does not require the advice of the Council of Ministers.
2. Prorogation of a House is generally done after the House is adjourned sine die but there is no bar to the President of India prorogating the House which is in session.
3. Dissolution of the Lok Sabha is done by the President of India who, save in exceptional circumstances, does so on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 2 and 3
Prorogation of a House by the President of India does not require the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Incorrect. The President acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers in all matters, including prorogation, as per Article 74 of the Constitution.Prorogation of a House is generally done after the House is adjourned sine die, but there is no bar to the President of India prorogating the House which is in session.
Correct. Prorogation usually occurs after adjournment sine die, but the President can prorogue the House while it is in session.Dissolution of the Lok Sabha is done by the President of India who, save in exceptional circumstances, does so on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Correct. The President dissolves the Lok Sabha based on the advice of the Council of Ministers, except in extraordinary situations, such as when the Council loses the majority and is unable to advise.
|
150 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2024: Indian Polity - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key features of the Indian Constitution that are often tested in UPSC Prelims? |  |
| 2. How does the concept of 'Basic Structure' influence the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of emergencies provided in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. How does the structure of the Indian Parliament differ from that of the U.S. Congress? |  |

















