UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Federal System | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
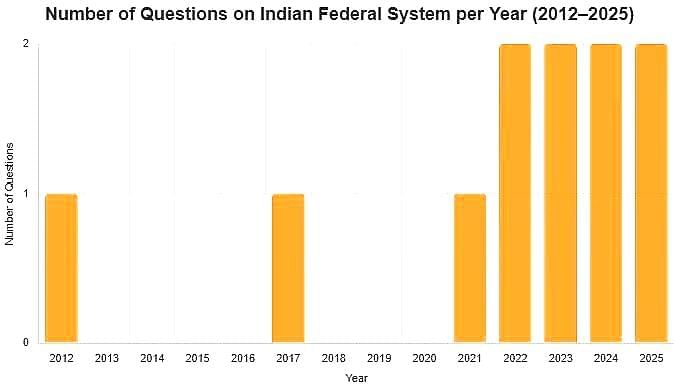
From 2012 to 2025, a collection of 11 questions with varying difficulty level has been asked: 4 easy (36.4%), 5 medium (45.5%), and 2 hard (18.2%)- emphasis is generally on the Indian Federal System, State Government and Features of Federal System.
Q.1. Consider the following statements: (2025)
Statement I: In India, State Governments have no power for making rules for grant of concessions in respect of extraction of minor minerals even though such minerals are located in their territories.
Statement II: In India, the Central Government has the power to notify minor minerals under the relevant law.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement I and II are correct but statement II explains Statement I
(b) Both Statement I and II are correct and statement II does not explain Statement I
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is not correct
(d) Statement I is not correct but Statement II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Statement I: "In India, State Governments have no power for making rules for grant of concessions in respect of extraction of minor minerals even though such minerals are located in their territories."
This statement is not correct.
Under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act), Section 15 clearly provides that State Governments have the power to make rules regarding the grant of mineral concessions for minor minerals. This includes regulation of quarrying, mining leases, royalties, and other related matters for minor minerals within their territory.
Statement II: "In India, the Central Government has the power to notify minor minerals under the relevant law."
This statement is correct.
Under the MMDR Act, the Central Government has the authority to declare certain minerals as "minor minerals" through notification in the Official Gazette. Once a mineral is notified as a minor mineral, the powers of regulation over it are transferred to the State Governments.
Q.2. Consider the following statements regarding Scheduled Areas under the Fifth Schedule of the Indian Constitution: (2025)
I. If an area in a State is declared as a Scheduled Area under the Fifth Schedule, the State Government loses its executive power, and a local body assumes total administration of such areas.
II. The Union Government can take over total administration of such areas under certain circumstances on the recommendation of the Governor.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d) Neither I nor II
Statement I: "If an area in a State is declared as a Scheduled Area under the Fifth Schedule, the State Government loses its executive power, and a local body assumes total administration of such areas."
This statement is incorrect.
- Scheduled Areas under the Fifth Schedule are governed by the State Government, and the Governor has special powers to make regulations for the peace and good governance of such areas.
- The State Government does not lose its executive power; rather, the administration is subject to special provisions, including possible modification of laws and regulations to suit tribal interests.
- Local bodies like Panchayats may have enhanced roles under laws like the PESA Act (1996), but they do not assume total control or replace the State Government.
Statement II: "The Union Government can take over total administration of such areas under certain circumstances on the recommendation of the Governor."
This statement is also incorrect.
- Under the Fifth Schedule, there is no provision for the Union Government to take over total administration of Scheduled Areas.
- The Governor, however, has the power to submit a report to the President regarding the administration of Scheduled Areas, and to make regulations that can override laws of the State Legislature, but that does not lead to a takeover by the Union Government.
Q.3. The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. Subsequent to the amendment of NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises which of the following members? (2024)
1. Governor of the Constituent State
2. Chief Minister of the Constituent State
3. Three Members to be nominated by the President of India
4. The Home Minister of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a)1, 2 and 3 only
(b)1, 3 and 4 only
(c)2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The NEC consists of governors and chief ministers from the states that make up the region, along with three members who are chosen by the President.
- The Union Home Minister serves as the chairman of the NEC by default.
- The Minister of State for the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) is the vice-chairman of the NEC, also by default.
Q.4. Consider the following statements: (2024)
1. It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
2. A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Statement 1 is incorrect. The authority to declare any community as a Scheduled Tribe lies with the President of India, who makes this decision after consulting with the state governor.
- Statement 2 is correct. A community that is recognized as a Scheduled Tribe in one state may not have the same status in another state.
Q.5. Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I: In India, prisons are managed by State Governments with their own rules and regulations for the day-to-day administration of prisons.
Statement-II: In India, prisons are governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 which expressly kept the subject of prisons in the control of Provincial Governments.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c)Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The Prisons Act 1894 is one of the earliest laws in India concerning prisons.
- Statement 1 is true: Prisons are a matter handled by the State as per List-II of the Seventh Schedule in the Constitution. This means that the states have the main duty, authority, and ability to modify the existing laws, rules, and regulations related to prisons.
- This indicates that prisons are run by state governments using their own specific rules and regulations.
- Statement 2 is true: The responsibility for managing and overseeing prisons is solely within the State Governments. This is governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 and the Prison Manuals created by each state.
- Therefore, the Prisons Act 1894 assigned the authority over prisons to the Provincial Governments (or State Governments), which allows them to create their own regulations and rules for prison management.
Q.6. With reference to Finance Bill and Money Bill in the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements: (2023)
1. When the Lok Sabha transmits the Finance Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it can amend or reject the Bill.
2. When the Lok Sabha transmits Money Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot amend or reject the Bill, it can only make recommendations.
3. In the case of disagreement between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, there is no joint sitting for Money Bill, but a joint sitting becomes necessary for the Finance Bill.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a)Only one
(b)Only two
(c)All three
(d)None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Finance Bill is categorized as a Money Bill according to Article 110 of the Constitution.
- A Financial Bill is an ordinary bill that includes both financial and non-financial issues.
Difference Between a Money Bill and a Finance Bill
- A Finance Bill presents the government's plans for:
- Introducing new taxes,
- Changing existing tax structures, or
- Extending current tax structures approved by Parliament.
- This bill is part of the Annual Financial Statement (also known as the Budget) under Article 112.
- The Finance Bill includes a Memorandum that explains its provisions.
- Only the Lok Sabha can introduce the Finance Bill.
- The Rajya Sabha can only suggest changes to the bill.
- The bill must be passed by Parliament within 75 days of its introduction.
- Thus, the first statement about the process is incorrect, while the second statement is correct.
Q.7. If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution focuses on how to manage and oversee Scheduled Areas and the Scheduled Tribes living in states, excluding Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- When an area is included under the Fifth Schedule, it indicates that all the land in that Scheduled Area is considered to be Adivasi land.
- This means that no land should be owned by non-Adivasis, and if any land is currently owned by non-tribal people, it should be returned to the Scheduled Tribes if it is being sold or transferred.
Q.8. Consider the following statements: (2022)
1. The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
2. The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Statement 1 is incorrect: The Constitution of India does not classify the Council of Ministers. Article 74 states that there will be a Council of Ministers led by the Prime Minister. This Council is meant to support and advise the President, who must act according to their guidance while performing his duties.
- Statement 2 is correct: The Constitution (91st Amendment) Act, 2003 changed Article 75. This amendment specifies that the total number of ministers, including the Prime Minister, in the Council of Ministers (COM) cannot exceed 15% of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Q.9. Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character? (2021)
(a) The independence of judiciary is safeguarded
(b) The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units
(c) The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties
(d) The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Key features of federalism:
- There are two or more levels (or tiers) of government.
- Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administration.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution. So the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
- The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of government. Such changes require the consent of both the levels of government.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
- The highest court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers. The most important feature of the federal system adopted by the Indian Constitution is the principle that relations between the States and the centre would be based on cooperation. And for this, Independent Judiciary is the prerequisite. Hence, Option (a) is correct.
- Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial Autonomy.
No questions from this topic has been asked in the year 2020, 2019, 2018.
Q.10. Which one of the following is not a feature of Indian federalism? (2017-I)
(a) There is an independent judiciary in India.
(b) Powers have been clearly divided between the Centre and the States.
(c) The federating units have been given unequal representation in the Rajya Sabha.
(d) It is the result of an agreement among the federating units.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Indian federation is not the result of an agreement among the states unlike the American federation. So, "D" is not the feature of Indian federalism.
No questions from this topic has been asked in the year 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013.
Q.11. Which of the following special powers have been conferred on the Rajya Sabha by the Constitution of India? (2012 - I)
(a) To change the existing territory of a State and to change the name of a State
(b) To pass a resolution empowering the Parliament to make laws in the State List and to create one or more All India Services
(c) To amend the election procedure of the President and to determine the pension of the President after his/her retirement
(d) To determine the functions of the Election Commission and to determine the number of Election Commissioners
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Rajyasabha can pass a resolution empowering the parliament to make laws in the state list and to create one or more All India Services. This is a special power that has been conferred on the Rajya Sabha by the constitution.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Federal System - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the federal system of governance? |  |
| 2. How does the federal system differ from a unitary system? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of a federal system? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of countries with a federal system? |  |
| 5. What role does the Constitution play in a federal system? |  |

















