UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Fundamental Rights & Duties | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Note: No Questions was being asked from this topic in the year 2025.
Q.1. Under which of the following Articles of the Constitution of India, has the Supreme Court of India placed the Right to Privacy? (2024)
(a) Article 15
(b) Article 16
(c) Article 19
(d) Article 21
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
- The Supreme Court of India has recognized the Right to Privacy as part of Article 21.
- Article 21 ensures the right to life and personal liberty.
- This important decision was made in the famous case of K.S. Puttaswamy vs. Union of India in 2017.
Q.2. A Writ of Prohibition is an order issued by the Supreme Court or High Courts to: (2024)
(a) a government officer prohibiting him from taking a particular action.
(b) the Parliament/Legislative Assembly to pass a law on Prohibition.
(c) the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
(d) the Government prohibiting it from following an unconstitutional policy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- A writ of prohibition is a legal order issued by the Supreme Court or High Courts.
- This order is directed towards a lower court.
- It stops the lower court from continuing with a case.
- The reason for this prohibition is that the lower court is handling a matter that is beyond its jurisdiction.
Q.3. In essence, what does 'Due Process of Law' mean? (2023)
(a) The principle of natural justice
(b) The procedure established by law
(c) Fair application of law
(d) Equality before law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- The term Due Process of Law means a principle that guarantees fair treatment and safeguards individual rights in legal matters.
- It includes key elements such as:
- The right to notice: Individuals must be informed about legal actions affecting them.
- An opportunity to be heard: People should have the chance to present their case.
- A fair and impartial adjudication: Decisions should be made by an unbiased judge or jury.
- This principle makes sure that the government adheres to established rules and respects the basic rights of individuals.
- In simple terms, Due Process of Law highlights the importance of protecting individual rights and ensuring that laws are applied fairly.
- Therefore, the right answer is (c) Fair application of law.
Q.4. With reference to the writs, issued by the Courts in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
1. Mandamus will not lie against a private organisation unless it is entrusted with a public duty.
2. Mandamus will not lie against a Company even though it may be a Government Company.
3. Any public minded person .can, be a petitioner to move the Court to obtain the writ of Quo Warranto.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is option (c)
- Statement 1: Mandamus is a legal order from the court that tells a public official to do their job, especially if they have not done it or have refused to do it. This order can also be directed at public organizations, companies, lower courts, tribunals, or the government for similar reasons. Typically, it cannot be directed at private individuals unless they have a public responsibility.
- Statement 2: This statement is incorrect. As mentioned earlier, Mandamus can indeed be used against government-owned companies or corporations.
- Statement 3: Quo Warranto is a court order that investigates whether someone's claim to a public office is legal. This writ helps stop someone from illegally taking a public office. Unlike other types of writs, anyone who is interested can request Quo Warranto, not just the person who has been harmed.
Q.5. If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is option (a)
- The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution focuses on how Scheduled Areas are managed and the rights of Scheduled Tribes living in states other than Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- If an area is included in the Fifth Schedule, it is considered that all land in that area is Adivasi land.
- This means that:
- No land can be sold or given to non-Adivasis.
- If non-tribal people currently own land in these areas, any transfer of that land should ensure it returns to the Scheduled Tribes.
Q.6. With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
- State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The provision of Parole is a privilege/concession but not a right of any convicted prisoner. Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- States do have separate prison/parole rules because “prison and persons detained” is a state subject of the 7th schedule. So, statement 2 is correct.
- And, Option (b) is correct.
Q.7. Which one of the following best defines the term ‘State’? (2021)
(a) A community of persons permanently occupying a definite territory independent of external control and possessing an organized government
(b) A politically organized people of a definite territory and possessing an authority to govern them, maintain law and order, protect their natural rights and safeguard their means of sustenance
(c) A number of persons who have been living in a definite territory for a very long time with their own culture, tradition and government
(d) A society permanently living in a definite territory with a central authority, an executive responsible to the central authority and an independent judiciary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In political science, the term “State” has a more specific and definite meaning- “word State means a community or society politically organized under one independent government within a definite territory.
It alone has the prerogative of making laws. The lawmaking power derives from sovereignty, which is the most distinctive characteristic of the State.
Q.8. What is the position of the Right to Property in India? (2021)
(a) Legal right available to citizens only
(b) Legal right available to any person
(c) Fundamental Right available to citizens only
(d) Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Forty Fourth Constitutional Amendment, 1978, deleted Articles 19(1)(f) and 31 from Part III, the chapter on Fundamental Rights in the Constitution. Instead, it inserted Article 300A in a new chapter IV of Part XII of the Constitution, thereby depriving the ‘right to property’ of its ‘fundamental right’ status. Article 300A directs that - Persons not to be deprived of property save by authority of law.—No person shall be deprived of his property save by authority of law.
Q.9. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017? (2019-I)
- Pregnant women are entitled for three months predelivery and three months post-delivery paid leave
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum six creche visits daily
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1,2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
As per the bare act:
- In case of a woman who has two or more children, the maternity benefit will continue to be 12 weeks. If less than two children then she'll get 26 weeks paid leave.
- Every establishment with 50 or more employees to provide crèche facilities within a prescribed distance. The woman will be allowed four visits to the crèche in a day. So #2 is wrong. We are left with Answer C: only 3.
Q.10. Other than the Fundamental Rights, which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflects the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)? (2020-I)
- Preamble
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental Duties
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Preamble to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about dignity of an individual. Preamble of Indian Constitution speaks about “EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity” So #1 is correct.
Article 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about the Right to Work. Similar concept in Article 41 of the Indian Constitution, under the head of DPSPs. Article 29 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about duties. A similar concept that was inserted in the Indian Constitution by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976 under Part IV-A of the Constitution (Article 51A).
Q.11. Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? [2018-I]
(a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution
(b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV
(c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part. III
(d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Supreme Court ruled that "the right to privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 and as a part of the freedoms guaranteed by Part III of the Constitution" so Option c is right.
Let's also look at the wrong options:
- Article 14- Gives the Right to Equality. 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act 1976, is known as mini constitution.
- Article 17- Related to the Abolition of Untouchability. It is part of Right to Equality. Part IV- Directive Principles of State Policy, does not have any mention about the Privacy.
- Article 24- Prohibition of employment of children in factories, et(c) 44th Constitution Amendment- 44th amendment of the Constitution was enacted by the Janata Government mainly to nullify some of the amendments made by the 42nd Amendment Act, 1976.
Q.12. "To uphold and protect the Sovereignty, Unity and Integrity of India" is a provision made in the [2015-I]
(a) Preamble of the Constitution
(b) Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) Fundamental Rights
(d) Fundamental Duties
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The idea behind incorporation of fundamental duties was to remind the citizens of the country that they have certain obligations towards the country and society. The fundamental duties were added to the constitution on the recommendations of the Swaran Singh Committee. There were ten fundamental duties at the time of incorporation but the eleventh was inserted by the 86th Amendment in 2002. To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India is one of the fundamental duty mentioned in the constitution.
Q.13. Which of the following is/are among the Fundamental Duties of citizens laid down in the Indian Constitution? [2012 - I]
- To preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture
- To protect the weaker sections from social injustice
- To develop the scientific temper and spirit of inquiry
- To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
All the statements except 2 regarding the Fundamental Duties of citizens are correct.
Q.14. Under the Constitution of India, which one of the following is not a fundamental duty ? (2011 - I)
(a) To vote in public elections
(b) To develop the scientific temper
(c) To safeguard public property
(d) To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
To vote in public elections is not a fundamental duty.
Q.15. Consider the following statements: [2006]
- Free and compulsory education to the children of 6-14 years age-group by the State by the seventy-sixth Amendment to the Constitution of India.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan seeks to provide computer education even in rural areas.
- Education was included in the Concurrent List by the Forty-second Amendment, 1976 to the Constitution of India’.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Statement 1 is incorrect as this provision was added by 86th Amendment Act (not 76th ).
Q.16. Match List I (Articles of the Constitution of India) with List II (Provision) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: (2004)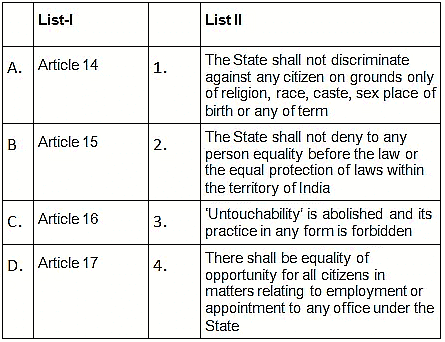 (a) A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
(a) A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
(b) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
(c) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
(d) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
These are Fundamental rights under Part III of the Constitution.
Q.17. Which Article of the Constitution of India says, ‘No child below the age of fourteen years shall the employed to work in any factory or mine or engaged in any other hazardous employment’? (2004)
(a) Article 24
(b) Article 45
(c) Article 330
(d) Article 368
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Article 24 of the constitution states that, no child below the age of fourteen years shall be employed to work in any factory or mine or engaged in any other hazardous employment.
Q.18. Match List-I (Article of Indian Constitution) with List -II (Provisions) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: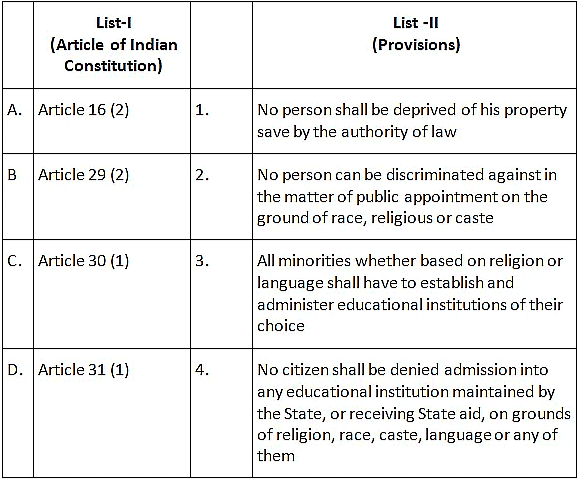 (a) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
(a) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
(b) A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
(c) A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
(d) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
These are Fundamental Rights under Part III of the Constitutionm, runs from Art 14 – 32.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Fundamental Rights & Duties - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the Fundamental Rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. How do Fundamental Duties complement Fundamental Rights in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Article 32 concerning Fundamental Rights? |  |
| 4. Can Fundamental Rights be amended or limited by the Parliament? |  |
| 5. What are the remedies available for the violation of Fundamental Rights? |  |






















