UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Local Government- Panchayati Raj & Municipality | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Q.1. Consider the following statements: (2025)
I. Panchayats at the intermediate level exist in all States.
II. To be eligible to be a Member of a Panchayat at the intermediate level, a person should attain the age of thirty years.
III. The Chief Minister of a State constitutes a commission to review the financial position of Panchayats at the intermediate levels and to make recommendations regarding the distribution of net proceeds of taxes and duties, leviable by the State, between the State and Panchayats at the intermediate level.
Which of the statements given above are not correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Statement I: Incorrect
The Constitution of India does not mandate the establishment of intermediate-level Panchayats (Panchayat Samitis) in all states. States with a population below 20 lakh are exempt from creating this tier, as per the 73rd Constitutional Amendment. This allows smaller states flexibility in their Panchayati Raj structure.
Statement II: Incorrect
The minimum age for eligibility to become a member of a Panchayat is 21 years, as specified under the Panchayati Raj Acts of various states, aligning with the Representation of the People Act. The claim of a 30-year minimum age is inaccurate.
Statement III: Incorrect
The State Finance Commission is appointed by the Governor of the state, not the Chief Minister, as per Article 243-I of the Indian Constitution. The Governor is responsible for constituting the commission to review the financial position of Panchayats and make recommendations.
Q.2. With reference to the funds under Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme(MPLADS), which of the following statements are correct? (2020-I)
- MPLADS funds must be used to create durable assets like physical infrastructure for health, education etc.,
- A specified portion of each MP’s fund must benefit SC/ST populations
- MPLADS funds are sanctioned on yearly basis and the unused funds cannot be carried forward to the next year.
- The district authority must inspect at least 10% of all works under implementation every year
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
- 15 percent of MPLADS funds are to be utilized for areas inhabited by SC population and 7.5 per cent for areas inhabited by ST population. So, #2 is correct. b eliminated.
- The funds released under the Scheme are nonlapsable, i.e., the entitlement of funds not released in a particular year is carried forward to the subsequent years, subject to eligibility. So, #3 is wrong. Upon reading the official guidelines page 34: District Authority would inspect at least 10% of the works under implementation every year. So, #4 is right answer therefore Answer is d.
Q.3. Consider the following statements: (2016-I)
- The minimum age prescribed for any person to be a member of Panchayat is 25 years.
- A Panchayat reconstituted after premature dissolution continues only for the remainder period.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
First Statement (Incorrect) – The minimum age prescribed for a person to be a member of a Panchayat is 21 years, as per Article 243F of the Indian Constitution. Therefore, the statement that the minimum age is 25 years is incorrect.
Second Statement (Correct) – If a Panchayat is dissolved before completing its full term of five years, the newly reconstituted Panchayat will serve only for the remainder of the original term and not for a fresh five-year term. This is in accordance with Article 243E(4) of the Constitution.
Thus, only Statement 2 is correct, making option (b) the right choice
Q.4. The fundamental object of Panchayati Raj system is to ensure which among the following ? (2015 - I)
- People's participation in development
- Political accountability
- Democratic decentralization
- Financial mobilization
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The fundamental objective of the Panchayati Raj system is to promote democratic decentralization and ensure people's participation in development at the grassroots level.
People's participation in development (Correct) – Panchayati Raj institutions (PRIs) empower local people to take part in decision-making and development planning.
Political accountability (Incorrect) – While PRIs promote governance at the local level, their primary focus is decentralization, not political accountability in the broader sense. Political accountability is more relevant to parliamentary and executive structures.
Democratic decentralization (Correct) – The 73rd Constitutional Amendment (1992) established the three-tier Panchayati Raj system to decentralize power and strengthen local self-governance.
Financial mobilization (Incorrect) – While PRIs do have financial responsibilities (such as taxation powers at the local level), financial mobilization is not the primary objective of the Panchayati Raj system.
Thus, only statements 1 and 3 are correct, making option (c) the right choice.
Q.5. The Government enacted the Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act in 1996. Which one of the following is not identified as its objective? (2013 - I)
(a) To provide self-governance
(b) To recognize traditional rights
(c) To create autonomous regions in tribal areas
(d) To free tribal people from exploitation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The salient feature of the Panchayats (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA) and the modalities worked out to grant rights to tribals in the country are:
- Legislation on Panchayats shall be in conformity with the customary law, social and religious practices and traditional management practices of community resources;
- Habitation or a group of habitations or a hamlet or a group of hamlets comprising a community and managing its affairs in accordance with tradiations and customs; and shall have a separate Gram Sabha.
- Every Gram Sabha to safeguard and preserve the traditions and customs of people, their cultural identity, community resources and the customary mode of dispute resolution.
Q.6. In the areas covered under the Panchayat (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, what is the role/power of Gram Sabha? (2012 - I)
- Gram Sabha has the power to prevent alienation of land in the Scheduled Areas.
- Gram Sabha has the ownership of minor forest produce.
- Recommendation of Gram Sabha is required for granting prospecting licence or mining lease for any mineral in the Scheduled Areas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Recommendation of Gram sabha or Panchayat at the appropriate level shall be mandatory for grant of prospecting licence or mining lease for minor minerals (not for any minerals) in the sheduled areas. Therefore statement 3 is false.
Q.7. The Constitution (Seventy-Third Amendment) Act, 1992, which aims at promoting the Panchayati Raj Institutions in the country, provides for which of the following? (2011 - I)
- Constitution of District Planning Committees.
- State Election Commissions to conduct all panchayat elections.
- Establishment of State Finance Commission.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Seventy-Third Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 provides for the following:
- State Election Commission to conduct Panchayat elections, as mentioned in Article 243K.
- State Finance Commission to review and recommend financial distribution to Panchayati Raj Institutions, as per Article 243I.
However, the District Planning Committees are covered under the Seventy-Fourth Amendment Act, 1992, which deals with urban local bodies and not Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Therefore, only statements two and three are correct.
Q.8. Consider the following statements: (2011 - I)
In India, a Metropolitan Planning Committee:
- is constituted under the provisions of the Constitution of India.
- prepares the draft development plans for metropolitan area.
- has the sole responsibility for implementing Government sponsored schemes in the metropolitan area.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Article 243ZE – Committee on Metropolitan Planning does not have a sole responsibility for implementing Government sponsored schemes in metropolitan area. Metropolitan planning committee is constituted under the provisions of the constitution of India.
According to the constitution of India, every Metropolitan area shall have a Metropolitan planning committee to prepare a draft development plan.
Q.9. If a Panchayat is dissolved, elections are to be held within: (2009)
(a) 1 month
(b) 3 months
(c) 6 months
(d) 1 year
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Duration of Panchayats is five year. Fresh election to constitute a Panchayat shall be completed before the expiry of its term; or in case of dissolution fresh election is to be conducted before the expiry of a period of 6 months from the date of its dissolution.
Q.10. In India, the first Municipal Corporation was set up in which one among the following? (2009)
(a) Calcutta
(b) Madras
(c) Bombay
(d) Delhi
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In 1688, the first Municipal Corporation of India was set up in Madras.
Q.11. Consider the following statements: (2005)
- Part IX of the Constitution of India provisions for Panchyats and was inserted by the Constitution (Amendment) Act, 1992.
- Part IX A of the Constitution of India contains provisions for Municipalities and the Article 243 Q envisages two types of Municipalities a Municipal Council and a Municipal Corporation for every State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments were passed by Parliament in December, 1992. Through these amendments local self-governance was introduced in rural and urban India. The Acts came into force as the constitution (73rd Amendment) Act, 1992 on April 24, 1993 and the constitution (74th Amendment) Act, 1992 on June 1, 1993. These amendments added two new parts to the constitution, namely, 73rd Amendment added part IX titled "The Panchayats" and 74th Amendment added part IXA titled "The Municipalities". The Local bodies-'Panchayats' and 'Municipalities' came under Part IX and IXA of the Constitution after 43 years of India becoming a republic.
Q.12. Assertion (A): The Central Rural Sanitation Programme was launched in 1986 to improve the quality of life of rural people in India.
Reason (R): Rural sanitation is a subject in the Concurrent List in the Constitution of India.
In the context of above two statements, which one of the following is correct? (2004)
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Rural sanitation is not a subject in the Concurrent List. Public Health and Sanitation comes under the State List. Personal and food hygiene have been major cause of many diseases in developing countries. It was in this context that the central Rural Sanitation Programmer (CRSP) was launched in 1986.
Q.13. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: (2000)(a) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
(b) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
(c) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4
(d) A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)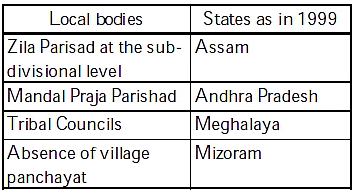
Q.14. A college student desires to get elected to the Municipal Council of his city. The validity of his nomination would depend on the important condition, among others, that: [2000]
(a) he obtains permission from the principal of his college
(b) he is a member of a political party
(c) his name figures in the voters’ list
(d) he files a declaration owing allegiance to the Constitution of India
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Name in the voters list is the important condition.
Q.15. In the new Panchayati Raj Bill enacted in 1993, there are several fresh provisions deviating from the past. Which one of the following is not one such provisions? (1999)
(a) A number of added responsibilities in the area of agriculture, rural development, primary education and social forestry among other
(b) Elections being made mandatory for all posts at the time they are due
(c) A statutory representation for women in the panchayats, upto a third of the strength
(d) Regular remuneration to the panchayat members, so as to ensure their punctuality and accountability
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Provision given in option (d) is not included under 73rd Amendment Act 1993.
Q.16. Panchayat Raj was first introduced in India in October, 1959 in: (1998)
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Kerala
(d) Karnataka
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Panchayati Raj System was first introduced in Nagaur district of Rajasthan on October 2, 1959 followed by Andhra Pradesh in 1959.
Q.17. Which one of the following was not proposed by the 73rdConstitutional Amendment in the area of Panchayati Raj? [1997]
(a) Thirty percent seats in all elected rural local bodies will be reserved for women candidates at all level
(b) The States will constitute their Finance Commissions to allocate resources to Panchayati Raj institutions
(c) The Panchayati Raj functionaries will be disqualified to hold their offices if they have more than two children
(d) The elections will be held in six months time if Panchayati Raj bodies are superceded or dissolved by the State government
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Statement given under option (c) is not mentioned in 73rd amendment act. But this norm is applied in Haryana, Rajasthan, MP, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
Q.18. What is the system of governance in the Panchayati Raj set up? [1996]
(a) Single tier structure of local self government at the village level .
(b) Two tier system of local self government at the village and block levels
(c) Three tier structure of local self government at the village, block and district levels
(d) Four tier system of local self government at the village block, district and in the state levels
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
According to 73rd Amendment Act, three-tier system of Panchayats exists: Village level, District Panchayat at the district level, the intermediate Panchayat which stands between the village and District Panchayats in the States where the population is above 20 Lakhs.
Q.19. Which one of the following is incorrect in respect of Local Government in India? (1995)
(a) According to the Indian Constitution, local government is not an independent tier in the federal system
(b) 33% of the seats in local bodies are reserved for women
(c) Local government finances are to be provided by a Commission
(d) Elections to local bodies are to be determined by a Commission
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
According to 73rd Amendment Act 1993, under Article 243D, not less than 1/3rd i.e. 33% seats should be reserved for women in local bodies.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Local Government- Panchayati Raj & Municipality - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is Panchayati Raj and Municipality? |  |
| 2. How is Panchayati Raj different from Municipality? |  |
| 3. What are the functions of Panchayati Raj institutions? |  |
| 4. How are members of Panchayati Raj and Municipality elected? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of Panchayati Raj and Municipality in local governance? |  |





















