UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Vedic Period | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
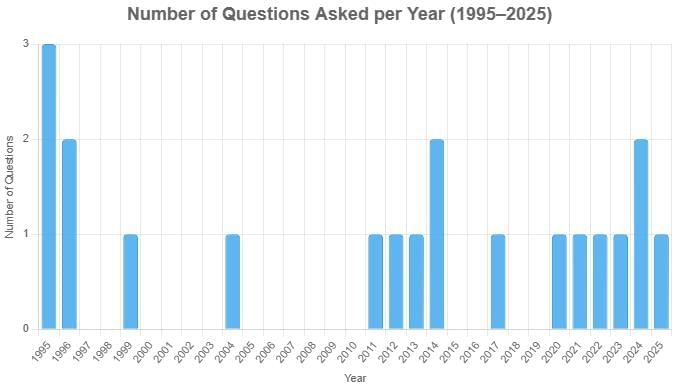
From 1995 to 2025, 20 questions with varying difficulty level have been asked: 6 easy (30%), 10 medium (50%), and 4 hard (20%)— emphasis is generally given on topics such as Vedic literature, Jainism, and cultural practices across different periods.
Q.1. With reference to ancient India (600–322 BC), consider the following pairs: (2025)
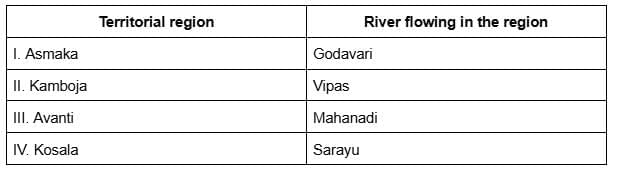
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All the four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
1. Asmaka – Godavari
This is correctly matched. Asmaka was located in the southern part of the Indian subcontinent (present-day Telangana/Maharashtra) and was situated on the banks of the Godavari River.
2. Kamboja – Vipas (Beas)
Incorrect. Kamboja was a north-western region, likely around present-day Afghanistan and parts of Central Asia. The Vipas (modern Beas) river flowed in the Punjab region, not associated with Kamboja.
3. Avanti – Mahanadi
Incorrect. Avanti was located in western Madhya Pradesh, particularly around Ujjain. The major rivers in this region were the Narmada and Shipra. Mahanadi flows in eastern India (Chhattisgarh and Odisha), and thus, this pair is incorrectly matched.
4. Kosala – Sarayu
This is correctly matched. Kosala was located in eastern Uttar Pradesh with its capital at Ayodhya, which lies on the banks of the Sarayu River.
Q.2. Which one of the following is a work attributed to playwright Bhasa? (2024)
(a)Kavyalankara
(b)Natyashastra
(c)Madhyama-vyayoga
(d)Mahabhashya
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Option a is not correct. Kavyalankara is a book about poetry that is linked to the scholar Bhamaha.
- Option b is also incorrect. Natyashastra is an ancient Indian text about the performing arts, which is credited to Bharata Muni.
- Option c is correct. The Madhyama-vyayoga play is one of the thirteen plays that are traditionally associated with Bhasa. It is a one-act play that tells a story from the Mahabharata and focuses on the reunion of the Pandava brothers.
- Option d is incorrect. Mahabhashya is a commentary on Panini’s grammar, and it is attributed to Patanjali.
Q.3. Consider the following statements:
1. There are no parables in Upanishads.
2. Upanishads were composed earlier than the Puranas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2024)
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is (b) 2only
- Statement 1 is not correct. The Upanishads include parables and stories that help explain important philosophical ideas.
- Statement 2 is correct. The Upanishads were written before the Puranas.
Q.4. With reference to ancient Indian History, consider the following pairs: (2023)
| Literary work | Author |
| Devichandragupta | Bilhana |
| Hammira-Mahakavya | Nayachandra Suri |
| Milinda-panha | Nagarjuna |
| Nitivakyamrita | Somadeva Suri |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Devichandragupta – Bilhana
- Correct Author: Devichandragupta is a Sanskrit play created by Vishakhadatta, not Bilhana.
- The play tells the story of the brave actions of Chandragupta, especially his efforts to save his elder brother's wife from the Shaka ruler.
- Therefore, Pair 1 is incorrect.
- Hammira-Mahakavya – Nayachandra Suri
- Correct Author: Hammira-Mahakavya is a 15th-century Sanskrit epic poem written by the Jain scholar Nayachandra Suri.
- This work is a legendary biography of Hammira, a 13th-century king from the Chahamana dynasty.
- Hence, Pair 2 is correct.
- Milinda-panha – Nagarjuna
- Correct Author: Milinda-panha (The Questions of Milinda) is a text featuring conversations between the Buddhist monk Nagasena and King Milinda (also known as Menander I).
- This text was not written by Nagarjuna; it is in the Pali language, and the specific author is not known.
- Thus, Pair 3 is incorrect.
- Nitivakyamrita – Somadeva Suri
- Correct Author: Nitivakyamrita is a work that discusses ethics, politics, and social norms, written in Sanskrit by Somadeva Suri, a well-known Jain monk and scholar.
- This work is composed of verses (shlokas) and offers lessons on various life topics.
- Hence, Pair 4 is correct.
- Summary of Pairs:
- Pairs 2 and 4 are correctly matched.
- Pairs 1 and 3 are incorrect.
- The correct answer is Option 2: Only two.
Q.5. With reference to Indian history, consider the following texts: (2022)
- Nettipakarana
- Parishishtaparvan
- Avadanashataka
- Trishashtilakshana Mahapurana
Which of the above are Jaina texts?
(a)1, 2 and 3
(b)2 and 4 only
(c)1, 3 and 4
(d)2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Nettipakarana is related to Buddhism’s Pali Canon. Hence, option 1 is incorrect.
- The Nettipakaraṇa is a mythological Buddhist scripture, sometimes included in the Khuddaka Nikaya of Theravada Buddhism's Pali Canon.
- The main theme of this text is Buddhist Hermeneutics through a systematization of the Buddha's teachings.
- Parishishtaparvan was written by Hemachandra which describes the establishing Chandragupta’s connections with Jainism. Hence, option 2 is correct.
- According to the Parishishtaparvan, Jayasimha spotted Hemachandra while passing through the streets of his capital.
- The king was impressed with an impromptu verse uttered by the young monk
- Acharya Hemachandra was an Indian Jain scholar, poet, mathematician, and polymath who wrote on grammar, philosophy, prosody, mathematics, and contemporary history.
- Noted as a prodigy by his contemporaries, he gained the title kalikalasarvajna, "the knower of all knowledge in his times".
- The Avadanashataka or “Century of Noble Deeds” is an anthology in Sanskrit which contains some collection of Buddhist narratives compiled from the second to fifth centuries CE. Hence, option 3 is incorrect.
- Trishashthilkshana Mahapurana is a major Jain text composed largely by Acharya Jinasena during the rule of Rashtrakuta. Hence, option 4 is correct.
Q.6. With reference to the history of ancient India, Bhavabhuti, Hastimalla and Kshemeshvara were famous (2021)
(a) Jain monks
(b) Playwrights
(c)Temple architects
(d) Philosophers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Bhavabhuti was a famous Sanskrit playwright who wrote famous plays like Mahaviracharita, Malatimadhava, etc.
- He is believed to be the court poet of King Yashovarman of Kannauj.
Hastimallawrote 8 plays including Vikrant Kaurava and Subhadra Harana.
- He was a noted Kannada poet and playwright in the Hoysala Empire.
Kshemeshvara is also a playwright in the ancient period.
Q.7. With reference to the cultural history of India consider the following pairs: (2020)
- Parivrajaka - Renunciant and Wanderer
- Shramana - Priest with a high status
- Upasaka - Lay follower of Buddhism
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a)1 and 2 only
(b)1 and 3 only
(c)2 and 3 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- During Vedic age, there was a lot of emphasis on rituals and sacrifices. This type of excessive ritualism produced a natural reaction in the form of Sramana religion, which protested against the divine origin of the Vedas and efficacy of the sacrifices.
- Sramanas were recruited from all people irrespective of caste and creed. Their teachers were anti-Vedic and anti-Brahmanic and they challenged Vedic learning and Vedic rituals. So, 2 is wrong. By elimination we are left with correct answer “b”
- Sree Narayana Guru had become a ‘Parivrajaka’ (one who wanders from place to place in quest of Truth), so, #1 is correct.
Q.8.With reference to the difference between the culture of Rigvedic Aryans and Indus Valley people, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- Rigvedic Aryans used the coat of mail and helmet in warfare whereas the people of Indus Valley Civilization did not leave any evidence of using them.
- Rigvedic Aryans knew gold, silver, and copper whereas Indus Valley people knew only copper and iron.
- Rigvedic Aryans had domesticated the horse whereas there is no evidence of Indus Valley people having been aware of this animal.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b)2 and 3 only
(c)1 and 3 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
All the gold jewelry found at Harappan sites was recovered from hoards. So, the second statement is wrong, which eliminated B and D. But then depending on which history book you refer to, Harappans were aware or unaware about the horses. So the experts were divided between option A and options C. UPSC chose ‘C’ as the official answer- meaning Harappans did not know about the horses.
Q.9.The national motto of India, ‘Satyameva Jayate’ inscribed below the Emblem of India is taken from (2014 )
(a)Katha Upanishad
(b)Chandogya Upanishad
(c) Aitareya Upanishad
(d) Mundaka Upanishad
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The words Satyameva Jayate came from Mundaka Upanishad, meaning‘Truth Alone Triumphs’.
Q.10. Which one of the following pairs does not form part of the six systems of Indian Philosophy? (2014)
(a)Mimamsa and Vedanta
(b)Nyaya and Vaisheshika
(c) Lokayata and Kapalika
(d)Sankhya and Yoga
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Lokayata and Kapalika do not form of Six systems of Indian philosophy
Q.11. In the context of the cultural history of India, a pose in dance and dramatics called ‘Tribhanga’ has been a favorite of Indian artists from ancient times till today. Which one of the following statements best describes this pose? (2013 )
(a) One leg is bent and the body is slightly but oppositely curved at the waist and neck
(b)Facial expressions, hand gestures, and make-up are combined to symbolize certain epic or historic characters
(c)Movements of body, face, and hands are used to express oneself or to tell a story
(d) A little smile, a slightly curved waist, and certain hand gestures are emphasized to express the feelings of love or eroticism
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The pose ‘Tribhanga’ is the favorite posture of Lord Krishna. We have often seen Lord Krishna standing in tribhanga posture before his cow ‘Kamdhenu’ or whenever he is playing his flute. He is often called Tribhana Murari.
Q.12. The religion of early Vedic Aryans was primarily of (2012)
(a) Bhakti
(b)image worship and Yajnas
(c)worship of nature and Yajnas
(d)worship of nature and Bhakti
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The early Vedic Aryans indulged in Image Worship and Yajnas.
Q.13. The “Dharma” and “Rita” depict a central idea of the ancient Vedic civilization of India. In this context, consider the following statements : (2011)
- Dharma was a conception of obligations and of the discharge of one’s duties to oneself and to others.
- Rita was the fundamental moral law governing the functioning of the universe and all it contained.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d)Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
‘Rita’ refers to regulation order by nature and was related to the conduct of the Vedic Gods and Humans, somewhere related to the moral and physical law. Statement 2 is correct. ‘Rita’ was later replaced by ‘Dharma’and was a more sophisticated form of principles of law. As per Chanakya, ‘Dharma’ was the promotion of one’s own security, happiness as well as social order.
Q.14. Which one of the following four Vedas contains an account of magical charms and spells? (2004)
(a)Rigveda
(b)Yajurveda
(c)Atharvaveda
(d)Samaveda
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Atharvaveda is a book of magical formulas. It contains charms and spells to ward off evil and disease.
Q.15. The term 'Aryan' denotes: (1999)
(a)an ethnic group
(b) a nomadic people
(c) a speech group
(d)a superior race
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Aryanis in fact a linguistic term indicating a speech group of Indo-European origin and is not an ethnic term.
Q.16. The river most mentioned in early Vedic literature is : (1996)
(a)Sindhu
(b)Sutudri
(c)Sarasvati
(d) Ganga
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Sapta Sindhu plays a prominent part in the hymns of the Rigveda, and consequently in early Vedic religion.
Q.17. According to ancient Indian cosmogonic ideas, the sequential order of the cycle of four aeons (yugas) is: (1996)
(a)Dvapara, Krita, Treta and Kali
(b)Krita, Dvapara, Treta and Kali
(c)Krita, Treta, Dvapara and Kali
(d)Treta, Dvapara, Kali and Krita
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
A complete Yuga starts with the Satya Yuga (Krita), via Treta Yuga and Dvapara Yuga into a Kali Yuga.
Q.18. According to Mimamsa system of philosophy, liberation is possible by means by (1995)
(a)jnana
(b)bhakti
(c)yoga
(d)karma
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Mimansa means investigation or enquiry. The primary enquiry is into the nature of dharma based on close theology of the Vedas. It has two divisions, Purva Mimansa and Uttar Mimansa. The Purva Mimansa explains the Dharma as a"virtue", "morality"or"duty". Dharma is the essentially ritualism, and there is a great significance of the Karma or action in attaining Dharma. Mimansa system of philosophy stresses on the doctrine of "karma". It says that liberation is possible by means of performing "Karma."
Q.19. Who among the following was a Brahmavadini who composed some hymns of the Vedas? (1995)
(a)Lopamudra
(b)Gargi
(c)Leelavati
(d)Savitri
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Other Brahmavadini are Vishwawara, Sikta, Nivavari, Ghosha, and Maitreyi.
Q.20. The word ‘Hindu’ as a reference to the people of Hind (India) was first used by: (1995)
(a)the Greeks
(b)the Romans
(c) the Chinese
(d)the Arabs
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The name of India is a corruption of the word Sindhu. Sindhu is the name of the Indus River, mentioned in the Rigveda. Neighboring Arabs, Iranians uttered 's' as 'h' and called this land Hindu. Greeks pronounced this name as Indus.
|
110 videos|653 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Vedic Period - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the Vedic period in Indian history? |  |
| 2. What were the major social institutions during the Vedic period? |  |
| 3. What were the main occupations and economic activities during the Vedic period? |  |
| 4. What were the religious beliefs and practices during the Vedic period? |  |
| 5. How did the Vedic period contribute to the development of the Indian civilization? |  |

















