Unit Test (Solutions): Heredity | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
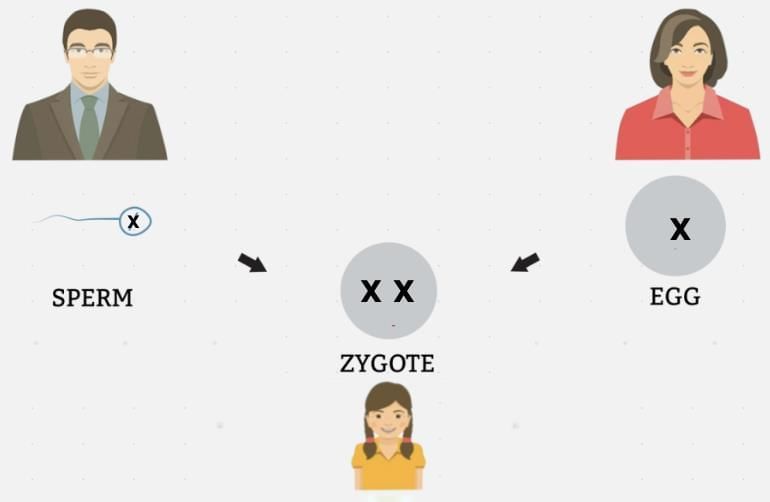
Q1: A zygote which has an X chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a:
(a) boy
(b) girl
(c) X chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
(d) either boy or girl
Ans: (b)
A zygote inherits one X chromosome from the mother. If the father also contributes an X chromosome, the zygote will have an XX combination, which determines that the child will be a girl.
Q2: In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is
(a) 1:3
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:1
(d) 2:1
Ans: (c)
In the F2 generation of a cross between two F1 tall plants (Tt × Tt), the ratio of pure tall plants (TT) to short plants (tt) is 1:1.
Q3: Assertion (A): Human female has a perfect pair of sex chromosomes.
Reason (R): Sex chromosome contributed by the human male in the zygote decides the sex of a child.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Ans: (b)
The answer is (b) because both the assertion and reason are true, but they explain different things. The human female has two X chromosomes (a perfect pair), and while it's true that the male's sperm decides the sex of the child, this fact is not directly explaining the assertion about the female's sex chromosomes.
Q4: A trait in an organism is influenced by
(a) paternal DNA only
(b) maternal DNA only
(c) both maternal and paternal DNA
(d) neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA
Ans: (c)
A trait in an organism is determined by genes, which are segments of DNA. An organism inherits half of its DNA from the mother (maternal DNA) and half from the father (paternal DNA). Both sets of DNA contribute to the genetic makeup of the organism, influencing its traits.
Q5: Assertion (A): Human population shows a great deal of variations in traits.
Reason (R): All variations in a species have equal; chances of surviving in the environment in which they live. (1 Mark)
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but; Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is False.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
Ans: (c)
Sol: Variations get accumulated or discarded as combined effect of environmental factors and reproduction process.
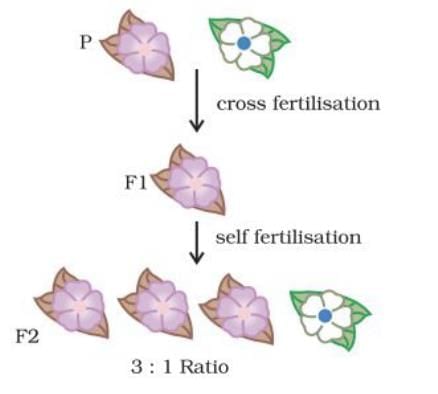
Q6: A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny? (2 Marks)
Ans: According to the Mendelian experiment, violet coloqr (VV) is a dominant trait while white colour (ww) is a recessive trait. Hence, the colour of the flower in F1 progeny will be violet (Vw).
Q7: What is the difference between Recessive and Dominant Traits? (2 Marks)
Ans:
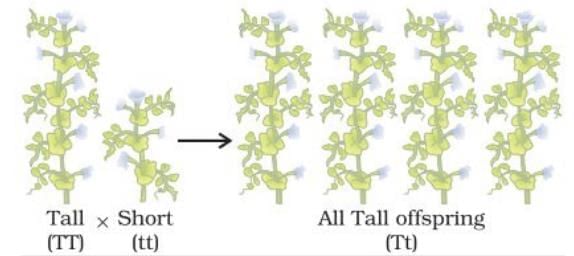
Q8: Why is the progeny always tall when a tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant? (2 Marks)
Ans: When a tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant, the resultant progeny is always tall because tall is dominant trait and short is recessive trait. Therefore, dominant trait expresses itself in the progeny.
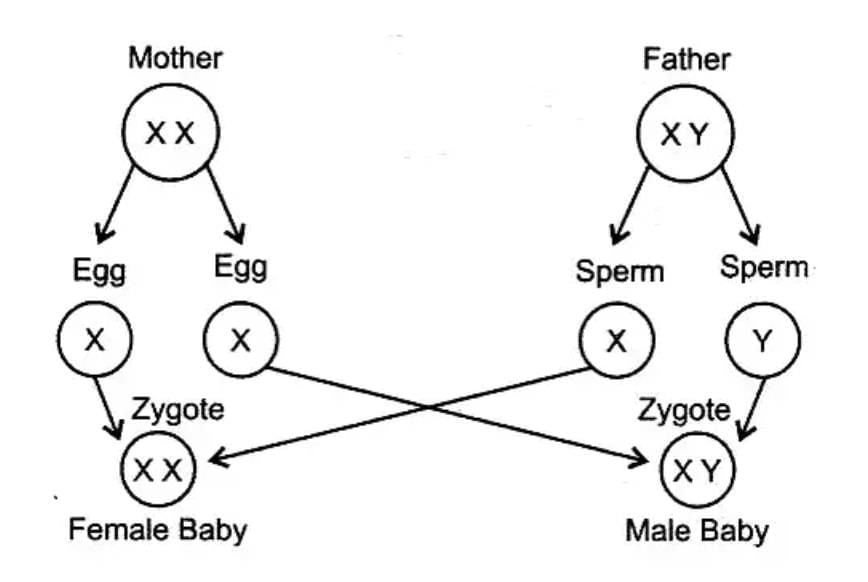
Q9: Explain how the sex of the child is determined at the time of conception in human beings. (3 Marks)
Ans: Male human beings have XY sex-chromosomes and female human beings have XX sex-chromosomes. During reproduction, the mother always contributes one X chromosome to the child.
If a sperm carrying x-chromosome fertilizes with the ovum, then sex of the baby will be female. If a sperm carrying y-chromosome fuses with the ovum, the sex of the baby will be male.
Q10: The survival of a species is promoted through the creation of variations. Illustrate with an example. (3 Marks)
Ans: An original organism produces two slightly different offspring. Each of them again gives rise to two more, leading to four individuals, all different. Some differences are inherited, while others are new. This process creates diversity over generations.
For example: A population of bacteria living in temperate waters that can withstand heat due to the rise in temperature due to global warming will survive better in a heat wave than the non-variant bacteria having no capacity to tolerate heat wave. Thus, suitable variations promote survival.
Q11: Why did Mendel choose a pea plant for his experimentation? (3 Marks)
Ans: Mendel chose the garden pea for his experiment for the following reasons:
Because this plant has a short life cycle, the results may be gathered and evaluated more quickly.
The garden pea possesses a number of features that are diametrically opposed to one another.
This plant is also tiny, easy to grow, and produces a big number of offspring.
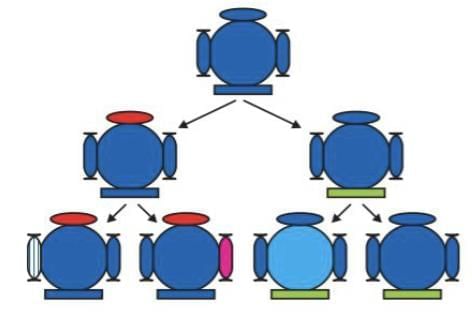
Q12: Explain Mendel’s experiment with peas on inheritance of characters considering only one visible contrasting character. ( 5 Marks)
Ans: Mendel crossed a pure tall pea plant with pure dwarf pea plant. All the plants obtained in F1 generation were tall. When Mendel selfed plants from F1 generation then he obtained both tall and dwarf plants in F2 generation in the ratio of 3:1.
This can be illustrated as follows:This explains that for each pair of contrasting characters there are two alleles. The trait which is expressed in F1 is dominant trait and is controlled by dominant allele and the trait which remains unexpressed in F1 is the recessive trait and is controlled by recessive gene. When both the contrasting alleles are present together in F1 individuals, no mixing of alleles occurs and they again segregate at the time of gamete formation Therefore, when the recessive alleles come together they result in reappearance of recessive trait in F2 generation.
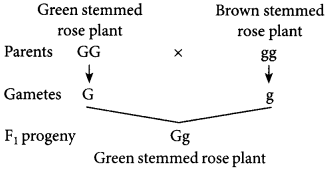
Q13: A green stemmed rose plant denoted by GG and a brown stemmed rose plant denoted by gg are allowed to undergo a cross with each other. (5 Marks)
(a) List your observations regarding:
(i) Colour of stem in their F1 progeny
(ii) Percentage of brown stemmed plants in F2 progeny if plants are self pollinated.
(iii) Ratio of GG and Gg in the F2 progeny.
(b) Based on the findings of this cross, what conclusion can be drawn?
Ans:
(a) (i) Colour of stem in F1 progeny:
The colour in the F1 progeny is green stemmed as green stem colour is dominant.(ii) F1 progeny on self pollination:
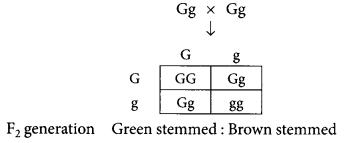
F2 generation Green stemmed: Brown stemmed
1/4 or 25% of F2 progeny are brown stemmed rose plant.(iii) Ratio of GG and Gg in F2 progeny:
Genotype of F2 progeny – GG : Gg 1 :2(b) This is a monohybrid cross. This shows that out of two contrasting traits only one dominant trait appears in F1 generation and the trait which does not express is recessive. On selfing the F1 plants, both the traits appear in next generation but in a definite proportion.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Heredity - Science Class 10
| 1. What is heredity and why is it important in genetics? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of inheritance patterns? |  |
| 3. How did Gregor Mendel contribute to our understanding of heredity? |  |
| 4. What role do genes play in heredity? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of studying heredity in modern science? |  |