Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? (1 Mark)
(a) Oxygen diffuses too slowly
(b) Only lungs can diffuse oxygen
(c) All cells are not in direct contact with the environment
(d) Cells do not require oxygen
Answer: C
In multicellular organisms, the inner cells are far from the surface and not in direct contact with the environment, so diffusion alone cannot meet oxygen requirements.
Q2. Which enzyme in saliva helps in the digestion of starch? (1 Mark)
(a) Pepsin
(b) Lipase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Answer: C
Saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase which breaks down starch (a complex carbohydrate) into simpler sugars like maltose.
Q3. The energy currency of a cell is: (1 Mark)
(a) DNA
(b) Glucose
(c) ATP
(d) Protein
Answer: C
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) stores and provides energy required for all cellular processes.
Q4. The site of gaseous exchange in human lungs is: (1 Mark)
(a) Bronchioles
(b) Alveoli
(c) Trachea
(d) Diaphragm
Answer: B
Alveoli are tiny balloon-like structures in the lungs with a rich blood supply that allows exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Q5. Which of the following statements is true about autotrophic nutrition? (1 Mark)
(a) Organisms depend on others for food
(b) Organisms digest food externally
(c) Organisms prepare food from CO₂ and water using sunlight
(d) Organisms consume complex organic matter only
Answer: C
In autotrophic nutrition, green plants and some bacteria prepare their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
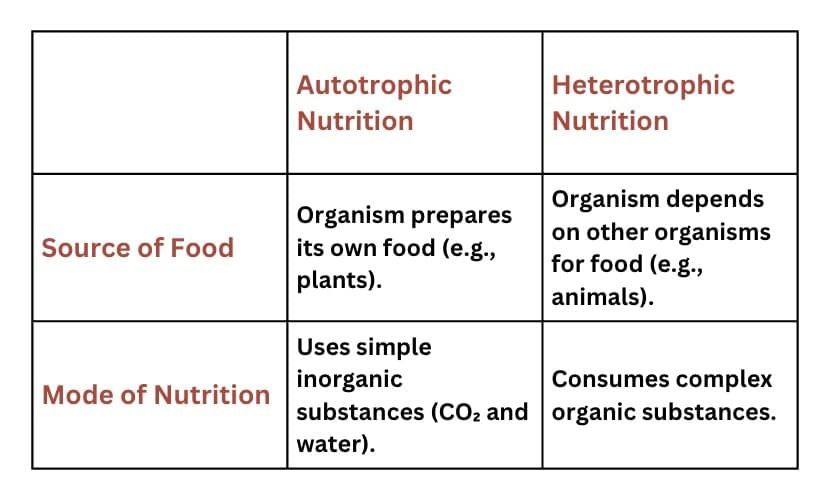
Q6. State two differences between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition. (2 Marks)
Answer: Differences are:
Q7. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food efficiently? (2 Marks)
Answer:
The inner lining of the small intestine has finger-like projections called villi that increase the surface area for absorption.
These villi have a rich network of blood capillaries to transport absorbed nutrients to all body cells.
Q8. What is the role of hydrochloric acid in the stomach? (2 Marks)
Answer:
It creates an acidic environment necessary for the action of pepsin, a protein-digesting enzyme.
It also kills harmful microbes present in the food, aiding digestion and protection.
Q9. Describe the three main steps involved in the process of photosynthesis. (3 Marks)
Answer: Three main steps involved in the process of photosynthesis are:
Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll present in chloroplasts.
Conversion of light energy to chemical energy, followed by splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
Reduction of carbon dioxide using hydrogen to form carbohydrates like glucose.
These steps may not always occur simultaneously (e.g., in desert plants CO₂ is fixed at night and used during the day).
Q10. What are the different products formed during aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Give examples. (3 Marks)
Answer:
Aerobic respiration (in presence of oxygen):
Glucose → CO₂ + H₂O + Energy (e.g., in humans and animals)Anaerobic respiration (in yeast):
Glucose → Ethanol + CO₂ + EnergyAnaerobic respiration (in human muscles):
Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy
The amount of energy released is more in aerobic respiration than in anaerobic.Flowchart of different types of respiration
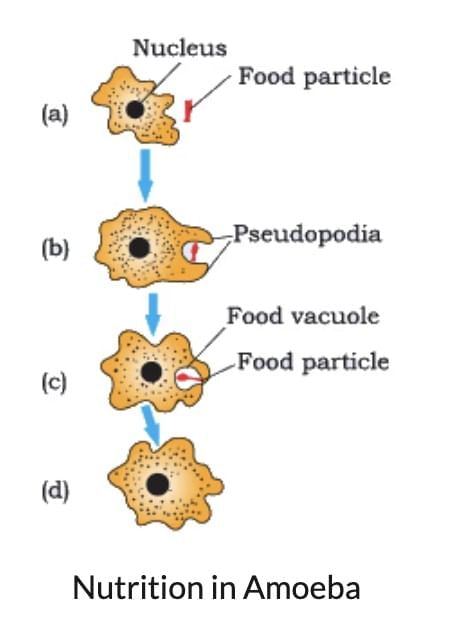
Q11. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba. (3 Marks)
Answer:
Amoeba captures food using finger-like projections called pseudopodia, forming a food vacuole.
Inside the vacuole, food is digested by enzymes into simpler substances.
The nutrients diffuse into the cytoplasm and the undigested food is egested outside the cell.
Q12. Describe the human digestive system and explain how digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. (5 Marks)
Ans: The human digestive system consists of the alimentary canal (from mouth to anus) and digestive glands (salivary glands, liver, and pancreas).
Human Digestive System
1. Mouth
Food is chewed by teeth and mixed with saliva.
Saliva contains the enzyme amylase, which begins the digestion of starch into sugars.
2. Oesophagus (Food Pipe)
A muscular tube that transports food to the stomach using rhythmic contractions called peristalsis.
3. Stomach
Contains gastric glands that secrete:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) – kills germs and activates pepsin.
Pepsin – an enzyme that begins protein digestion.
Mucus – protects the stomach lining from acid.
4. Small Intestine
The longest part of the digestive system. Receives:
Bile from the liver, which emulsifies fats (breaks them into tiny droplets).
Pancreatic juice from the pancreas, containing enzymes to digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Intestinal juice completes the digestion:
Carbohydrates → Glucose
Proteins → Amino acids
Fats → Fatty acids and glycerolInner walls have tiny finger-like projections called villi, which absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
5. Large Intestine
Absorbs excess water from undigested food.
The remaining waste is formed into faeces and eliminated through the anus.
Q13. Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: (5 Marks)
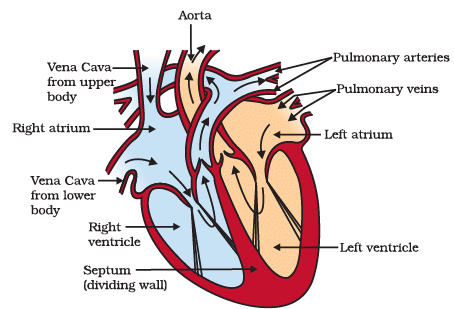 Human Heart
Human Heart
(i) Label the four chambers of the heart in the diagram.
(ii) What is the function of the valves shown in the heart diagram?
(iii) Which side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body, and which side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
(iv) Describe the pathway of blood through the heart starting from the right atrium.
(v) Why does the left ventricle have a thicker muscular wall compared to the right ventricle?
Ans: (i) The four chambers of the heart are labeled as follows:
- Right Atrium
- Right Ventricle
- Left Atrium
- Left Ventricle
(ii) The valves in the heart, such as the tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves, ensure that blood flows in one direction, preventing backward flow. They help maintain the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart.
(iii) The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body, while the right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
(iv) Blood flows into the right atrium from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava. From the right atrium, it passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. When the right ventricle contracts, it pumps blood into the pulmonary artery, which carries it to the lungs for oxygenation.
(v) The left ventricle has a thicker muscular wall because it needs to pump oxygenated blood to the entire body, which requires more force. In contrast, the right ventricle only pumps blood to the nearby lungs, so it has a thinner muscular wall as it doesn't require as much force to do so.
|
80 videos|661 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main life processes essential for sustaining life in organisms? |  |
| 2. How do plants and animals differ in the way they obtain nutrition? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of respiration in living organisms? |  |
| 4. Why is excretion considered a crucial life process? |  |
| 5. What role does reproduction play in the continuity of life? |  |